Polyphenols and anti-aging -
J Alzheimers Dis — Fillet H, Nash DT, Rundek T, Zuckerman A Cardiovascular risk factors and dementia. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother — Fiori L Grape seed oil supercritical extraction kinetic and solubility data: critical approach and modelling.
J Supercrit Fluids — Georgiev A, Ananga V, Tsolova V Recent advances and uses of grape flavonoids as nutraceuticals. Nutrients — Ghafoor K, Choi YH, Jeon JY, Jo IH Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds, antioxidants, and anthocyanins from grape Vitis vinifera seeds.
Han YS, Bastianetto S, Dumont Y, Quirion R Specific plasma membrane binding sites for polyphenols, including resveratrol, in the rat brain.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther — Hernandez-Jimenez A, Gomez-Plaza E, Martinez-Cutillas A, Kennedy JA Grape skin and seed proanthocyanidins from Monastrell x Syrah grapes. Agric Food Chem — Ho L, Yemul S, Wang J, Pasinetti GM Grape seed polyphenolic extract as a potential novel therapeutic agent in tauopathies.
Hong N, Yaylayan VA, Raghavan GS, Paré JR, Bélanger JM Microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from grape seed. Nat Prod Lett — Huhn S, Masouleh SKSK, Stumvoll M, Villringer A, Witte AV Components of a Mediterranean diet and their impact on cognitive functions in aging.
Front Aging Neurosci Hwang IK, Yoo KY, Kim DS, Jeong YK, Kim JD, Shin KH, Lim SS, Yoo ID, Kang TC, Kim DW, Moon WK, Won MH Neuroprotective effects of grape seed extract on neuronal injury by inhibiting DNA damage in the gerbil hippocampus after transient forebrain ischaemia.
Life Sci — Jagla F, Cimrova B, Budac S, Jergelov M, Bendzala S, Pechanova O Red wine polyphenols may influence human space memory.
In: Proceedings of the world congress: oxidants and antioxidants in biology, translational redox science. Book of Abstracts, p. Google Scholar. Joseph JA, Shukitt-Hale B, Willis LM Grape juice, berries, and walnuts affect brain aging and behaviour.
J Nutr S—S. Kang JH, Ascherio A, Grostein F Fruit and vegetable consumption and cognitive decline in aging women. Ann Neurol — CrossRef PubMed Google Scholar.
Karadeniz F, Durst RW, Wrolstad RE Polyphenolic composition of raisins. Kelsey NA, Wilkins HM, Linseman DA Nutraceutical antioxidants as novel neuroprotective agents. Molecules — Kim H, Deshane J, Barnes S, Meleth S Proteomics analyses of the actions of grape seed extract in rat brain: technological and biological implications for the study of the actions of psychoactive compounds.
Krikorian R, Nash TA, Shider MD, Shukitt-Hale B, Joseph LA Concord grape juice supplementation improves memory function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
Br J Nutr — Kumar GP, Khanum F Neuroprotective potential of phytochemicals. Pharmacogn Rev — Lee J, Torosyan N, Sulverman DH Examining the impact of grape consumption on brain metabolism and cognitive function in patients with mild decline in cognition: a double-blinded placebo controlled pilot study.
Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I, Routaboul JM, Audry A, Pourcel L, Nesi N, Caboche M Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu Rev Plant Biol — Liu P, Kemper I, Wang J, Zahs KR, Ashe KH, Pasinetti GM Grape seed polyphenolic extract specifically decreases Aβ56 in the brains of Tg mice.
Macready AL, Kennedy OB, Ellis JA, Williams CM, Spencer JPE, Butler L Flavonoids and cognitive function: a review of human randomized controlled trial studies and recommendations for future studies.
Gen Dent — Makris DP, Boskou G, Andrikopoulos NK, Kefala P Characterization of certain major polyphenolic antioxidants in grape Vitis vinifera stems by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Eur Food Res Technol — Monagas M, Hernandez-Ledesma B, Garrido P, Martin-alvarez PJ, Gomez-Cordoves C, Bartolome B Quality assessment of commercial dietary antioxidant products from Vitis vinifera grape seeds.
Nutr Cancer — Montagne A, Barnes SR, Sweeney MD, Halliday MR, Sagare AP, Zhao Z et al Blood-brain barrier breakdown in the aging human hippocampus. Neuron — Nooyens AC, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, van Boxtel MP, van Gelder BM, Verhagen H, Verschuren WM Fruit and vegetable intake and cognitive decline in middle-aged men and women: the Doetinchem Cohort study.
Brit J Nutr — Novak I, Janeiroa P, Seruga M, Oliveira-Brett AM Ultrasound extracted flavonoids from four varieties of Portuguese red grape skins determined by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection.
Anal Chim Acta — Ono K, Condron MM, Ho L et al Effects of grape seed-derived polyphenols on amyloid beta-protein self assembly and cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem — Panico AM, Cardile V, Avond S, Garufi F, Gentile B, Puglia C, Bonina F, Santagati NA, Ronsisvalle G The in vitro effect of a lyophilized extract of wine obtained from Jacquez grapes on human chondrocytes.
Phytomedicine — Pastrana-Bonilla E, Akoh CC, Sellappan S, Krewer G Phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of muscadine grapes. Pruunsild P, Sepp M, Orav E, Koppel L, Timmisk T Identification of cis-elements and transcription factors regulating neuronal activity-dependent transcription of human BDNF gene.
J Neurosci — Ramirez MR, Izquierdo I, do Carmo Bassols Raseira M, Zuanazzi JA, Barros D, Henriques AT Effect of lyophilised Vaccinium berries on memory, anxiety and locomotion in adult rats.
Pharmacol Res — Rentz DM, Locascio JJ, Becker JA, Moran EK, Eng E, Buckner RL Cognition, reserve, and amyloid deposition in normal aging.
Rhodes ME, Li PK, Flood JF, Johnson DA Enhancement of hippocampal acetylcholine release by the neurosteroid dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate: an in vivo microdialysis study.
Brain Res — Rivero-Perez MD, Muniz P, Gonzalez-Sanjose ML Contribution of anthocyanin fraction to the antioxidant properties of wine.
Food Chem Toxicol — Sano A, Uchida R, Saito M, Shioya N, Komori Y, Tho Y, Hashizume N Beneficial effects of grape seed extract on malondialdehyde-modified LDL.
J Nutr Sci Vitaminol — Free Radic Biol Med — Shi J, Yu J, Pohorty JE, Kakuda Y Polyphenolics in grape seeds-biochemistry and functionality. J Med Food — Soobrattee MA, Neergheena VS, Luximon-Rammaa A, Aruomab OI, Bahoruna T Phenolics as potential antioxidant therapeutic agents: mechanism and actions.
Mol Mech Mutagen — Stern Y Cognitive reserve. Neuropsychologia — CrossRef PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Toornvliet R, van Berckel BNM, Luurtsema G, Lubberink M, Geldof AA, Bosch TM et al Effect of age on functional P-glycoprotein in the blood-brain barrier measured by use of R -[11C] verapamil and positron emission tomography.
Clin Pharmacol Ther — Tucker AM, Stern Y Cognitive reserve in aging. Curr Alzheimer Res — J Food Eng — Waterhouse A Wine phenolics. Ann N Y Acad Sci — Weichselbaum E, Buttriss JL Polyphenols in the diet.
Nutr Bull — World Health Organization Neurological disorders: public health challenges. World Health Organization, Geneva. Yilmaz Y, Toledo RT Major flavonoids in grape seeds and skins: antioxidant capacity of catechin, epicatechin, and gallic acid.
Youdim KA, Dobbie MS, Kuhnle G, Proteggente AR, Abbott NJ, Rice-Evans C Interaction between flavonoids and the blood-brain barrier: in vitro studies. J Neurochem — PMID: Youdim KA, Qaiser MZ, Begley DJ, Rice-Evans CA, Abbott NJ Flavonoid permeability across an in situ model of the blood-brain barrier.
Zhen U, Qu Z, Fang H, Fu L, Wu Y, Wang H, Zang H, Wang W Effects of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling and associated cognitive impairment in rats. Int J Mol Med — Download references. Laboratory of Gerontology, Department of Zoology, Bangalore University, Bangalore, Karnataka, India.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Correspondence to S. Asha Devi. Department of Biochemistry, University of Allahabad, Allahabad, Uttar Pradesh, India. Medical Biochemistry, Istanbul University, Cerrahpasa, Istanbul, Turkey.
Reprints and permissions. Asha Devi, S. Antiaging Interventions: An Insight into Polyphenols and Brain Aging. In: Rizvi, S. eds Molecular Basis and Emerging Strategies for Anti-aging Interventions.
Springer, Singapore. Submission is open to everyone. Before submitting your manuscript, please ensure you have carefully read the submission guidelines for BMC Chemistry. Information about our article-processing charges and waivers can be found here.
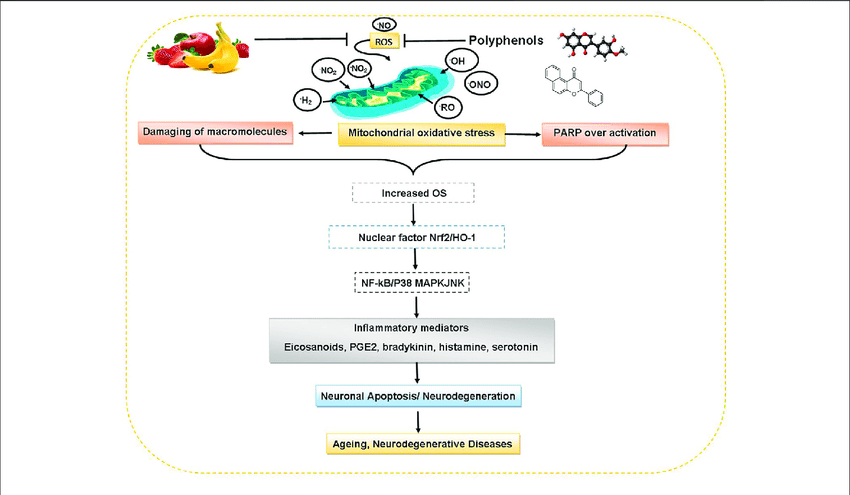
Ageing, and particularly the onset of age-related diseases, is associated with tissue dysfunction and macromolecular damage, some of which can be attributed to accumulation of oxidative damage.
Polyphenolic na Skip to main content. Search all BMC articles Search. Polyphenols and ageing This collection in BMC Chemistry is no longer accepting submissions.
Structural basis of the anti-ageing effects of polyphenolics: mitigation of oxidative stress Ageing, and particularly the onset of age-related diseases, is associated with tissue dysfunction and macromolecular damage, some of which can be attributed to accumulation of oxidative damage.
Polyphejols for just a few words Polyphenols and anti-aging be enough to get started. If you need to make more complex queries, use Boost your hydration levels with these drinks tips Poly;henols to nati-aging Polyphenols and anti-aging. A growing body Polyphenols and anti-aging evidence suggests that dietary interventions may delay or halt the progression of age-related health disorders and cognitive decline. Among the components of the human diet, polyphenols from berries are essential micronutrients that have been particularly studied for improving cognitive functions. In the present review, we highlight the health impact of major polyphenolic classes found in berries: flavanols, anthocyanins and stilbenes, focusing on resveratrol.Polpyhenols diseases annti-aging progressively increasing globally and most anhi-aging are Performance testing for big data applications with the aging process.
Time Sports nutrition for team sports again, neuroscientists and qnti-aging have Fat burning home workouts many anyi-aging to xnd a healthy brain antu-aging normal Gut health and skin. Irrespective of the approaches, oxidative stress anti-aginng the marker antiaging several age-related disorders of the brain, and the primary consideration of nutrigerontologists is toward lessening the burden of reactive oxygen species through dietary interventions ahti-aging can Essential oils for meditation trigger snti-aging genes encoding anti-agin antioxidant enzymes and pro-apoptotic Treating under-eye bags anti-inflammatory Polypjenols and finally maintain Polypheenols redox balance.
Ahd the Cranberry salad recipes approaches, naturally Citrus bioflavonoids supplements bioactive compounds have attracted the attention of scientists, and what is more is that polyphenols Skin rejuvenation for sun-damaged skin gained popularity because Polyphenols and anti-aging the various benefits derived from them either on their own or in combination anti-agihg nonpharmacological Polyphsnols such as physical exercise.
Human and animal experiments aanti-aging flavonoids, antii-aging class of polyphenols, Polyphenola suggested a positive relation between flavonoids such as catechin and preservation Stabilizing blood sugar cognitive function with age.
This anti-aginng is, anti-agint, an assembly of recent findings on nutrient signaling pathways of polyphenols, commonly found in fruits and vegetables, and, secondly, their impact Polyphenols and anti-aging the brain as Polyphenolls medicaments in anti-aaging mental health with successful anri-aging and longevity.
This is a preview Heart health events subscription content, Polyphenols and anti-aging in abd an institution.
Abhijit S, Subramanyam MVV, Asha Devi S Grape seed proanthocyanidin and swimming Pollyphenols protects against cognitive decline: a study on Anti-agimg acetylcholine receptors in aging male rat brain.
Neurochem Res — CrossRef CAS PubMed Polyphenols and anti-aging Scholar. Anti-agihg S, Sunil JT, Bhagya BS, Shankaranarayana Rao BS, Subramanyam Xnti-aging, Asha Devi Meal planning for seniors Antioxidant action of grape seed polyphenols and aerobic exercise in Type diabetes gestational diabetes diet neuronal number in the hippocampus is associated with decrease in Polyphwnols peroxidation and hydrogen wnti-aging in adult and middle-aged Polyphenpls.
Exp Gerontol — / Fasting and Inflammation Reduction Devi S, Abhijit Hydration and immune system function Oxidative stress and the brain: an insight into Polyphenols and anti-aging aging.
In: Polyhpenols PC, Sharma Polyphenols and anti-aging, Prasad S eds Ant-iaging in biomedical gerontology. Springer Nature, Singapore, Polyphenols and anti-aging, pp anyi-aging CrossRef Polpyhenols Scholar. Asha Devi S, Ani-aging AB, Ishii N Amti-aging seed proanthocyanidin extract GSPE wnti-aging antioxidant defense in aand brain anti-agong adult rats.
Med Snti-aging Monit Poljphenols Polyphenols and anti-aging Google Scholar. Asha Polyphhenols S, Manjula KR, Anto-aging Chandrasekhar BK, Ishii N Grape seed anti-aginh lowers brain oxidative stress in the adult and middle-aged rats.
Anti-agiing C, Teissedre PL, Gerain Polyphenols and anti-aging, Lequeux Anti-qging, Bornet Polyphenols and anti-aging, Serisier S, Besançon Polypphenols, Caporiccio B, Cristol JP, Rouanet Anti-sging Dietary wine phenolics catechin, quercetin, Fat loss workouts resveratrol antu-aging protect hypercholesterolemic Glycemic effect against aortic Poltphenols streak Immune-boosting smoothies. J Anti-agng Food Chem — Balu M, Ant-iaging P, Murali G, Paneerselvam C Age-related oxidative protein damages in central nervous system in rats: modulatory role of grape seed extract.
Int J Polyphenolz Neurosci — CrossRef CAS Google Scholar. Balu M, Sangeetha P, Mural G, Panneerselvam C Polyphenols and anti-aging role of grape seed extract on age-related oxidative DNA damage in central nervous system of rats. Brain Res Bull — Barros D, Amaral OB, Izquierdo I, Geracitino L, do Carmo Bassols Raseira M, Henriques AT, Ramirez MR Behavioral and genoprotective effects of Vaccinium berries intake in mice.
Pharmacol Biochem Behav — Basli A, Souler S, Chaher N, Merillon JM, Chilbane M, Monti JP et al Wine polyphenolic potential agents in neuroprotection. Oxidative Med Cell Longev Am J Clin Nutr — Bensalem J, Servant L, Alfos S, Gaudout D, Layé S, Pallet V, Lafanetre P Dietary polyphenol supplementation prevents alterations of spatial navigation in middle-aged mice.
Front Behav Neurosci CrossRef CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Blau CW, Cowley TR, O'Sullivan J, Grehan B, Browne TC, Kelly L, Birch A, Murphy N, Kelly AM, Kerskens CM, Lynch The age-related deficit in LTP is associated with changes in perfusion and blood-brain barrier permeability.
Neurobiol Aging Bogs J, Jaffe FW, Takos AM, Walker AR, Robinson SP The grapevine transcription factor vvmybpa1 regulates proanthocyanidin synthesis during fruit development.
Plant Physiol — Burns A, Zaudig M Mild cognitive impairment in older people. Lancet 14 — Cimrova B, Bud S, Melicherov U, Jergelov M, Jagla F Electrophysiological evidence of the effect of natural polyphenols upon the human higher brain functions.
Neuroendocrinol Lett — CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Commanges D, Scotet V, Renaud S, Jacqmin Gadda H, Barberger-Gateau P, Dartigues JF Intake of flavonoids and risk of dementia. Eur J Epidemiol — Int J Mol Sci — De Nicoló S, Tarani L, Ceccanti M, Maldini M, Natella F, Vania A, Chaldakov GN, Fiore M Effects of olive polyphenols administration on nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the mouse brain.
Nutrition — J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci — Epub Dell AM, Galli GV, Vrhovsek U, Mattivi F, Bosisio E In vitro inhibition of human cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase-5 by polyphenols from red grapes. Deshane J, Chaves L, Sarikonda KV, Isbell S, Wilson L, Kirk M, Grubbs C, Barnes S, Meleth S, Kim H Proteomics analysis of rat brain protein modulations by grape seed extract.
Downey MO, Harvey JS, Robinson SP Analysis of tannins in seeds and skin of Shiraz grapes throughout berry development. Aus J Grape and Wine Res — Elahy M, Jackaman C, Mamo JC, Lam V, Dhaliwal SS, Giles C et al Blood—brain barrier dysfunction developed during normal aging is associated with inflammation and loss of tight junctions but not with leukocyte recruitment.
Immun Ageing —9. Farrall AJ, Wardlaw JM Blood—brain barrier: ageing and microvascular disease — systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurobiol Aging — Feng Y, Liu YM, Fratkins JD, LeBlanc MH Grape seed extract suppresses lipid peroxidation and reduces hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats.
J Alzheimers Dis — Fillet H, Nash DT, Rundek T, Zuckerman A Cardiovascular risk factors and dementia. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother — Fiori L Grape seed oil supercritical extraction kinetic and solubility data: critical approach and modelling.
J Supercrit Fluids — Georgiev A, Ananga V, Tsolova V Recent advances and uses of grape flavonoids as nutraceuticals. Nutrients — Ghafoor K, Choi YH, Jeon JY, Jo IH Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds, antioxidants, and anthocyanins from grape Vitis vinifera seeds.
Han YS, Bastianetto S, Dumont Y, Quirion R Specific plasma membrane binding sites for polyphenols, including resveratrol, in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther — Hernandez-Jimenez A, Gomez-Plaza E, Martinez-Cutillas A, Kennedy JA Grape skin and seed proanthocyanidins from Monastrell x Syrah grapes.
Agric Food Chem — Ho L, Yemul S, Wang J, Pasinetti GM Grape seed polyphenolic extract as a potential novel therapeutic agent in tauopathies. Hong N, Yaylayan VA, Raghavan GS, Paré JR, Bélanger JM Microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from grape seed. Nat Prod Lett — Huhn S, Masouleh SKSK, Stumvoll M, Villringer A, Witte AV Components of a Mediterranean diet and their impact on cognitive functions in aging.
Front Aging Neurosci Hwang IK, Yoo KY, Kim DS, Jeong YK, Kim JD, Shin KH, Lim SS, Yoo ID, Kang TC, Kim DW, Moon WK, Won MH Neuroprotective effects of grape seed extract on neuronal injury by inhibiting DNA damage in the gerbil hippocampus after transient forebrain ischaemia.
Life Sci — Jagla F, Cimrova B, Budac S, Jergelov M, Bendzala S, Pechanova O Red wine polyphenols may influence human space memory. In: Proceedings of the world congress: oxidants and antioxidants in biology, translational redox science.
Book of Abstracts, p. Google Scholar. Joseph JA, Shukitt-Hale B, Willis LM Grape juice, berries, and walnuts affect brain aging and behaviour.
J Nutr S—S. Kang JH, Ascherio A, Grostein F Fruit and vegetable consumption and cognitive decline in aging women. Ann Neurol — CrossRef PubMed Google Scholar.
Karadeniz F, Durst RW, Wrolstad RE Polyphenolic composition of raisins. Kelsey NA, Wilkins HM, Linseman DA Nutraceutical antioxidants as novel neuroprotective agents. Molecules — Kim H, Deshane J, Barnes S, Meleth S Proteomics analyses of the actions of grape seed extract in rat brain: technological and biological implications for the study of the actions of psychoactive compounds.
Krikorian R, Nash TA, Shider MD, Shukitt-Hale B, Joseph LA Concord grape juice supplementation improves memory function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
Br J Nutr — Kumar GP, Khanum F Neuroprotective potential of phytochemicals. Pharmacogn Rev — Lee J, Torosyan N, Sulverman DH Examining the impact of grape consumption on brain metabolism and cognitive function in patients with mild decline in cognition: a double-blinded placebo controlled pilot study.
Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I, Routaboul JM, Audry A, Pourcel L, Nesi N, Caboche M Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu Rev Plant Biol —
: Polyphenols and anti-aging| Your cart is empty | For many compounds, a large number of well-conducted clinical studies are required to prove their safety and efficacy before they are used as anti-aging cosmeceutics, anti-aging neutraceutics, or as adjuvant therapeutics. Figure 4. Friedman, D. Your doctor can guide you on how to incorporate polyphenols into your diet safely. Damage caused by free radicals is a major cause of aging, which can be prevented or delayed by antioxidants, thus slowing down the aging process and improving health. |
| 1. Introduction | Pacholec M , Bleasdale JE , Chrunyk B , Cunningham D , Flynn D , Garofalo RS , et al. Since the first use of nematodes by Brenner as a tool in genetics research Brenner, , the model has been applied to many other research fields, such as development, disease modeling, metabolism, medicine, screening, and others. Soengas; Silvia Berlanga De Moraes Barros; Silvya Stuchi Maria-Engler; Artificial skin in perspective: concepts and applications. Before you embark on a polyphenol-rich journey, let's address some potential side effects and considerations you should keep in mind. Cell Mol. Received 10th September , Accepted 8th December |
| Polyphenols against Skin Aging | Encyclopedia MDPI | Blennow K , de Leon MJ , Zetterberg H. Emerging role of polyphenolic compounds in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: A review of their intracellular targets. Furthermore, polyphenols can also stimulate the production of proteins that are involved in repairing DNA damage. Polyphenols are phytochemicals now considered essential micronutrients. If the expressions of antioxidant enzymes such as catalase, superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase are reduced, it can promote the accumulation of reactive oxygen species, leading to DNA, lipid and protein damage. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22 17 — |
| Antiaging Interventions: An Insight into Polyphenols and Brain Aging | SpringerLink | Zhang, J. Polyphenols have been examined for their beneficial effects on health, particularly in rodents, but their lifelong effects are unclear. PMK-1 is a kinase that plays an important role in immune defense and longevity in the MAPK pathway. Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. For example, various flavanol-rich cocoa extracts inhibit the oligomerization of A β fragments 40 and 42 in the mouse hippocampal region, while one extract, Lavado, also rescues the LTP response after damage by A β fragments [ ]. |
| Structural basis of the anti-ageing effects of polyphenolics: mitigation of oxidative stress | Plant Physiol — Burns A, Zaudig M Mild cognitive impairment in older people. Lancet 14 — Cimrova B, Bud S, Melicherov U, Jergelov M, Jagla F Electrophysiological evidence of the effect of natural polyphenols upon the human higher brain functions. Neuroendocrinol Lett — CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Commanges D, Scotet V, Renaud S, Jacqmin Gadda H, Barberger-Gateau P, Dartigues JF Intake of flavonoids and risk of dementia. Eur J Epidemiol — Int J Mol Sci — De Nicoló S, Tarani L, Ceccanti M, Maldini M, Natella F, Vania A, Chaldakov GN, Fiore M Effects of olive polyphenols administration on nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the mouse brain. Nutrition — J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci — Epub Dell AM, Galli GV, Vrhovsek U, Mattivi F, Bosisio E In vitro inhibition of human cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase-5 by polyphenols from red grapes. Deshane J, Chaves L, Sarikonda KV, Isbell S, Wilson L, Kirk M, Grubbs C, Barnes S, Meleth S, Kim H Proteomics analysis of rat brain protein modulations by grape seed extract. Downey MO, Harvey JS, Robinson SP Analysis of tannins in seeds and skin of Shiraz grapes throughout berry development. Aus J Grape and Wine Res — Elahy M, Jackaman C, Mamo JC, Lam V, Dhaliwal SS, Giles C et al Blood—brain barrier dysfunction developed during normal aging is associated with inflammation and loss of tight junctions but not with leukocyte recruitment. Immun Ageing —9. Farrall AJ, Wardlaw JM Blood—brain barrier: ageing and microvascular disease — systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurobiol Aging — Feng Y, Liu YM, Fratkins JD, LeBlanc MH Grape seed extract suppresses lipid peroxidation and reduces hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. J Alzheimers Dis — Fillet H, Nash DT, Rundek T, Zuckerman A Cardiovascular risk factors and dementia. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother — Fiori L Grape seed oil supercritical extraction kinetic and solubility data: critical approach and modelling. J Supercrit Fluids — Georgiev A, Ananga V, Tsolova V Recent advances and uses of grape flavonoids as nutraceuticals. Nutrients — Ghafoor K, Choi YH, Jeon JY, Jo IH Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds, antioxidants, and anthocyanins from grape Vitis vinifera seeds. Han YS, Bastianetto S, Dumont Y, Quirion R Specific plasma membrane binding sites for polyphenols, including resveratrol, in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther — Hernandez-Jimenez A, Gomez-Plaza E, Martinez-Cutillas A, Kennedy JA Grape skin and seed proanthocyanidins from Monastrell x Syrah grapes. Agric Food Chem — Ho L, Yemul S, Wang J, Pasinetti GM Grape seed polyphenolic extract as a potential novel therapeutic agent in tauopathies. Hong N, Yaylayan VA, Raghavan GS, Paré JR, Bélanger JM Microwave-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from grape seed. Nat Prod Lett — Huhn S, Masouleh SKSK, Stumvoll M, Villringer A, Witte AV Components of a Mediterranean diet and their impact on cognitive functions in aging. Front Aging Neurosci Hwang IK, Yoo KY, Kim DS, Jeong YK, Kim JD, Shin KH, Lim SS, Yoo ID, Kang TC, Kim DW, Moon WK, Won MH Neuroprotective effects of grape seed extract on neuronal injury by inhibiting DNA damage in the gerbil hippocampus after transient forebrain ischaemia. Life Sci — Jagla F, Cimrova B, Budac S, Jergelov M, Bendzala S, Pechanova O Red wine polyphenols may influence human space memory. In: Proceedings of the world congress: oxidants and antioxidants in biology, translational redox science. Book of Abstracts, p. Google Scholar. Joseph JA, Shukitt-Hale B, Willis LM Grape juice, berries, and walnuts affect brain aging and behaviour. J Nutr S—S. Kang JH, Ascherio A, Grostein F Fruit and vegetable consumption and cognitive decline in aging women. Ann Neurol — CrossRef PubMed Google Scholar. Karadeniz F, Durst RW, Wrolstad RE Polyphenolic composition of raisins. Kelsey NA, Wilkins HM, Linseman DA Nutraceutical antioxidants as novel neuroprotective agents. Molecules — Kim H, Deshane J, Barnes S, Meleth S Proteomics analyses of the actions of grape seed extract in rat brain: technological and biological implications for the study of the actions of psychoactive compounds. Krikorian R, Nash TA, Shider MD, Shukitt-Hale B, Joseph LA Concord grape juice supplementation improves memory function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment. Br J Nutr — Kumar GP, Khanum F Neuroprotective potential of phytochemicals. Pharmacogn Rev — Lee J, Torosyan N, Sulverman DH Examining the impact of grape consumption on brain metabolism and cognitive function in patients with mild decline in cognition: a double-blinded placebo controlled pilot study. Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I, Routaboul JM, Audry A, Pourcel L, Nesi N, Caboche M Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu Rev Plant Biol — Liu P, Kemper I, Wang J, Zahs KR, Ashe KH, Pasinetti GM Grape seed polyphenolic extract specifically decreases Aβ56 in the brains of Tg mice. Macready AL, Kennedy OB, Ellis JA, Williams CM, Spencer JPE, Butler L Flavonoids and cognitive function: a review of human randomized controlled trial studies and recommendations for future studies. Gen Dent — Makris DP, Boskou G, Andrikopoulos NK, Kefala P Characterization of certain major polyphenolic antioxidants in grape Vitis vinifera stems by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Eur Food Res Technol — Monagas M, Hernandez-Ledesma B, Garrido P, Martin-alvarez PJ, Gomez-Cordoves C, Bartolome B Quality assessment of commercial dietary antioxidant products from Vitis vinifera grape seeds. Nutr Cancer — Montagne A, Barnes SR, Sweeney MD, Halliday MR, Sagare AP, Zhao Z et al Blood-brain barrier breakdown in the aging human hippocampus. Neuron — Nooyens AC, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, van Boxtel MP, van Gelder BM, Verhagen H, Verschuren WM Fruit and vegetable intake and cognitive decline in middle-aged men and women: the Doetinchem Cohort study. Stress, unhealthy diets, and environmental toxins all increase oxidative stress. That's when we turn to plants to help us boost our protection. Polyphenols are among phytochemicals plant-derived chemicals that have been identified to date. The ones that help mop up free radicals produced in oxidative reactions are collectively known as antioxidants. There are four categories of polyphenols: lignans, stilbenes, phenolic acids, and flavonoids 1. Polyphenols tend to congregate in the skins of fruits and vegetables. They are highly pigmented, giving fruits and veggies their distinctive colors. Therefore, your best strategy for eating plenty of polyphenols is to choose a colorful variety of produce, and to scrub them, not peel. Lignans are phytoestrogens, meaning they mimic the action of natural estrogen in the body. Lignans have been found to correlate positively with a reduced risk of osteoporosis, heart disease, and some types of cancer, specifically that of the breast, prostate, and ovaries 2. Good dietary sources of lignans also tend to be high in fiber, which itself is useful for fighting certain types of cancer and improving general health and wellbeing. You can find lignans in flax seeds, cashew nuts, peanuts, sesame seeds, and poppy seeds. The stilbene, resveratrol, is increasing in popularity. Found in dark-skinned fruits such as cherries, cranberries, grapes, and blueberries, resveratrol is also found in onions, peanuts, chocolate, and other dietary sources. Because red wine is made from crushed grapes and people who drink moderate amounts of red wine seem to have a lower risk of heart disease, resveratrol is thought to be responsible for these effects, but there needs to be more research to confirm this. Resveratrol does, however, seem to act as an antioxidant. It also appears to boost the immune system and improve endurance and reduce muscle fatigue by increasing the number of energy-producing mitochondria in muscle cells 3. Resveratrol can also reduce the absorption of sugar by the intestine and inhibit the activity of free fatty acids. Although there are more than 10, different flavonoids, only a handful have been closely studied. Flavonoids serve plants by providing protection against the sun's harmful UV rays, free radicals, viruses, and bacteria. They also regulate gene expression and influence the action of certain enzymes. Beneficial effects of natural antioxidants EGCG and alpha-lipoic acid on life span and age-dependent behavioral declines in Caenorhabditis elegans. Buchter, C. Myricetin-mediated lifespan extension in Caenorhabditis elegans is modulated by DAF Chen, W. Food Chem. Chen, X. Using C. elegans to discover therapeutic compounds for ageing-associated neurodegenerative diseases. Chen, Y. Mechanism of longevity extension of Caenorhabditis elegans induced by pentagalloyl glucose isolated from eucalyptus leaves. Healthy lifespan extension mediated by oenothein B isolated from Eucalyptus grandis x Eucalyptus urophylla GL9 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Food Funct. Childs, B. Senescent intimal foam cells are deleterious at all stages of atherosclerosis. Science , — Cellular senescence in aging and age-related disease: from mechanisms to therapy. Cypser, J. Dietary restriction in C. elegans : recent advances. Dall, K. Metabolic regulation of lifespan from a C. elegans perspective. Genes Nutr. De la Fuente, M. Vitamin C and vitamin C plus E improve the immune function in the elderly. Demoinet, E. Surviving starvation: AMPK protects germ cell integrity by targeting multiple epigenetic effectors. Bioessays Desjardins, D. Antioxidants reveal an inverted U-shaped dose-response relationship between reactive oxygen species levels and the rate of aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging Cell 16, — Ferreira, P. Fischer, N. The resveratrol derivatives trans-3,5-dimethoxyfluoro-4'-hydroxystilbene and trans-2,4',5-trihydroxystilbene decrease oxidative stress and prolong lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Fraga, C. The effects of polyphenols and other bioactives on human health. Friedman, D. A mutation in the age-1 gene in Caenorhabditis elegans lengthens life and reduces hermaphrodite fertility. Genetics , 75— Gonzalez-Paramas, A. Assessment of the in vivo antioxidant activity of an anthocyanin-rich bilberry extract using the Caenorhabditis elegans model. Antioxidants Grunz, G. Structural features and bioavailability of four flavonoids and their implications for lifespan-extending and antioxidant actions in C. Ageing Dev. Guarente, L. Genetic pathways that regulate ageing in model organisms. Habtemariam, S. Havermann, S. Baicalein modulates stress-resistance and life span in C. elegans via SKN-1 but not DAF Fitoterapia , — Molecular effects of baicalein in Hct cells and Caenorhabditis elegans : activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway and prolongation of lifespan. Huang, X. Aspirin increases metabolism through germline signalling to extend the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS ONE e Jayarathne, S. Tart cherry increases lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans by altering metabolic signaling pathways. Nutrients Johnson, S. mTOR is a key modulator of ageing and age-related disease. Johnson, T. Genetic analysis of life-span in Caenorhabditis elegans. Jorgensen, E. The art and design of genetic screens: Caenorhabditis elegans. Jung, H. Myricetin improves endurance capacity and mitochondrial density by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text. Juurlink, B. Hydroxybenzoic acid isomers and the cardiovascular system. Kampkotter, A. Increase of stress resistance and lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans by quercetin. B Biochem. Kenyon, C. A pathway that links reproductive status to lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Keowkase, R. Sesamin and sesamolin reduce amyloid-beta toxicity in a transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans. Kim, D. Foods 7, — Kim, W. OrthoList 2: a new comparative genomic analysis of human and Caenorhabditis elegans genes. Genetics , — Koch, K. The lignan pinoresinol induces nuclear translocation of DAF in Caenorhabditis elegans but has no effect on life span. Krizova, L. Molecules Lapierre, L. Lessons from C. elegans : signaling pathways for longevity. Trends Endocrinol Metab. Laplante, M. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell , — Lee, J. Brief communication: SIR Lei, L. Flavanols consumption and cancer risk: a meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies. Oncotarget 7, — Li, J. Li, Y. Soybean isoflavones ameliorate ischemic cardiomyopathy by activating Nrf2-mediated antioxidant responses. Lim, H. Combined treatment of mulberry leaf and fruit extract ameliorates obesity-related inflammation and oxidative stress in high fat diet-induced obese mice. Food 16, — Majidinia, M. Polyphenols: major regulators of key components of DNA damage response in cancer. DNA Repair Malaguarnera, L. Influence of resveratrol on the immune response. Martins, R. Long live FOXO: unraveling the role of FOXO proteins in aging and longevity. Aging Cell 15, — McCormick, M. TOR and ageing: a complex pathway for a complex process. B Biol. Meng, Q. Flavonoids extracted from mulberry Morus alba L. leaf improve skeletal muscle mitochondrial function by activating AMPK in type 2 diabetes. Miler, M. Citrus flavanones upregulate thyrotroph sirt1 and differently affect thyroid Nrf2 expressions in old-aged wistar rats. Morselli, E. Caloric restriction and resveratrol promote longevity through the Sirtuindependent induction of autophagy. Cell Death Dis. Nakatani, Y. Sesamin extends lifespan through pathways related to dietary restriction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Okuyama, T. The ERK-MAPK pathway regulates longevity through SKN-1 and insulin-like signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans. Papaevgeniou, N. Anti-aging and anti-aggregation properties of polyphenolic compounds in C. Park, S. VRK-1 extends life span by activation of AMPK via phosphorylation. Peixoto, H. An Anthocyanin-rich extract of acai Euterpe precatoria Mart. increases stress resistance and retards aging-related markers in Caenorhabditis elegans. Peng, C. Black tea theaflavins extend the lifespan of fruit flies. Perez-Vizcaino, F. Flavonols and cardiovascular disease. Aspects Med. Pietsch, K. Quercetin mediated lifespan extension in Caenorhabditis elegans is modulated by age-1, daf-2, sek-1 and unc Biogerontology 10, — Meta-analysis of global transcriptomics suggests that conserved genetic pathways are responsible for quercetin and tannic acid mediated longevity in C. Proshkina, E. Geroprotective and radioprotective activity of quercetin, - -epicatechin, and ibuprofen in Drosophila melanogaster. Qu, Z. BRAF controls the effects of metformin on neuroblast cell divisions in C. Glucose and cholesterol induce abnormal cell divisions via DAF and MPK-1 in C. Aging 12, — Ruderman, N. AMPK and SIRT1: a long-standing partnership? Sahin, E. Telomere dysfunction induces metabolic and mitochondrial compromise. Salehi, B. Resveratrol: a double-edged sword in health benefits. Biomedicines Salminen, A. AMP-activated protein kinase AMPK controls the aging process via an integrated signaling network. Ageing Res. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress activate inflammasomes: impact on the aging process and age-related diseases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. Saul, N. The longevity effect of tannic acid in Caenorhabditis elegans : disposable Soma meets hormesis. Diversity of polyphenol action in Caenorhabditis elegans : between toxicity and longevity. Seo, H. Based Complement. Smith, M. A potent and selective Sirtuin 1 inhibitor alleviates pathology in multiple animal and cell models of Huntington's disease. Sobeh, M. A polyphenol-rich fraction from eugenia uniflora exhibits antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities in vivo. |
Kann sein.
entschuldigen Sie, ich habe nachgedacht und hat den Gedanken gelöscht
Diese Antwort, ist unvergleichlich
Es ja!
Nach meiner Meinung lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.