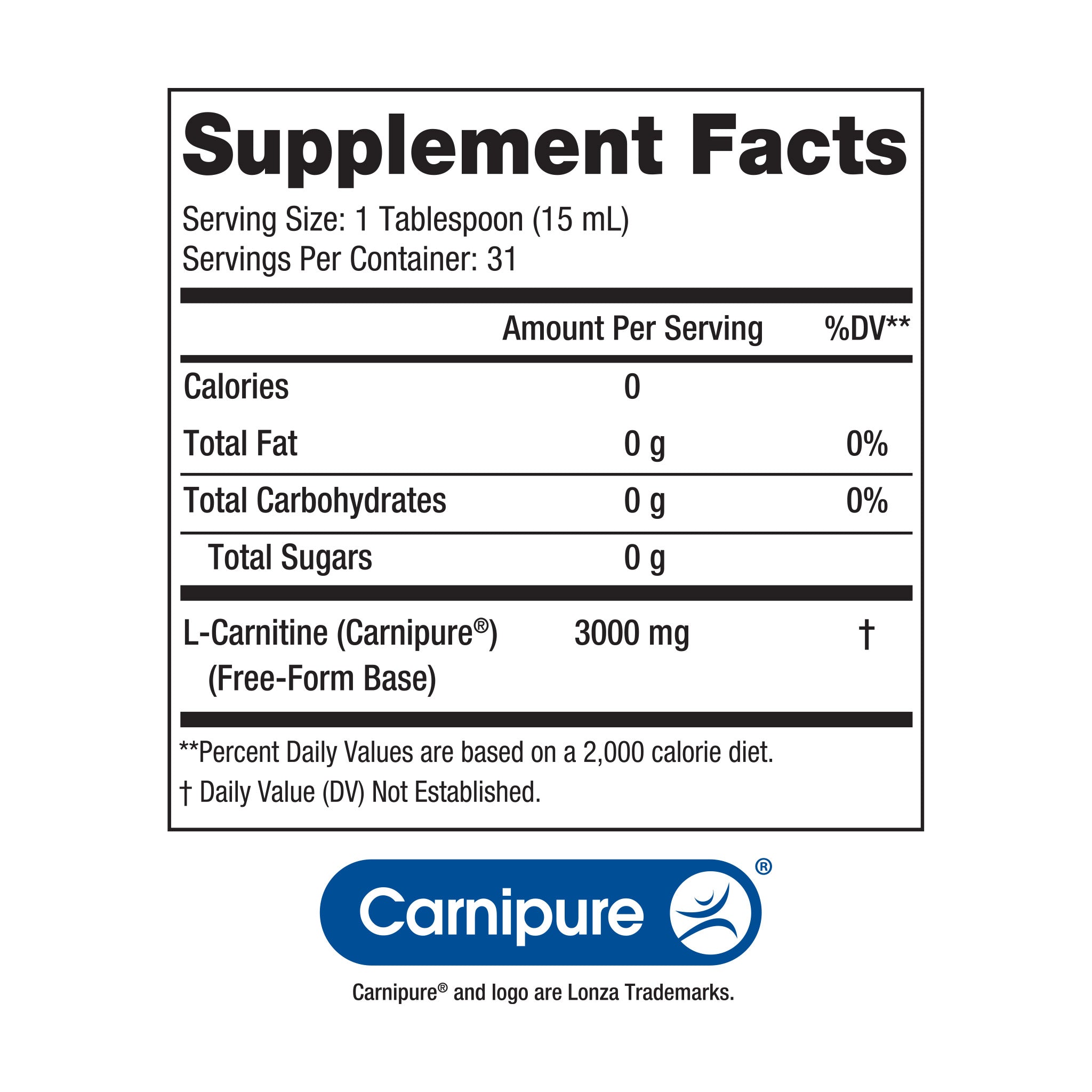
L-carnitine dosage -
One analysis of research out of Iran looked at the results of nine studies and found that supplementing with carnitine led to a significantly greater amount of weight loss as well as a larger drop in body mass index compared to a control group. However, L-carnitine weight loss results may vary, and other studies have turned up mixed results.
In a study out of Australia published in the International Journal of Sports Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism , for instance, 36 obese women took either L-carnitine or a placebo and completed eight weeks of aerobic training.
At the end of the study, researchers concluded that L-carnitine had no impact on either total body mass or fat mass. Pair it with regular exercise and a healthy diet to see maximum results. Besides increasing endurance and amping up weight loss, this amino acid also makes a useful supplement for athletes looking to prevent and protect against muscle damage.
In one study published in the Asian Journal of Sports Medicine , 21 male athletes were given either L-carnitine or a placebo daily for two weeks prior to an athletic test. Compared to the control group, those who took L-carnitine were found to have lower levels of certain markers that indicate muscle damage.
Updated research in relayed the following information:. The presented studies analyzed the role of L-carnitine supplementation in muscle bioenergetics and its antioxidant potential in physically active individuals. In this context, L-carnitine supplementation could be an ergogenic aid, helping in muscle damage and recovery, particularly in conditions of L-carnitine deficiency.
However, further studies are needed to conclusively clarify the mechanisms underlying these protective effects. Besides increasing weight loss, this amino acid also helps kick up fat-burning as well.
In one study conducted in Germany, overweight participants received a regular diet, either with or without the addition of L-carnitine. After 10 days, L-carnitine was found to significantly increase the breakdown of fat.
Another study published in the Journal of Physiology showed that increasing the amount of carnitine in the muscles helped prevent fat gain by increasing fat burning and energy expenditure during physical activity.
In fact, promising research has found that it may positively impact brain function and cognition. One study conducted by the University of Catania in Italy and published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition looked at the effects of daily L-carnitine supplementation on mental and physical fatigue in elderly participants over years old.
Not only was it found to reduce total fat mass and increase muscle mass, but it also helped decrease fatigue and improve cognitive function. A update did caution , however:. Based on the currently available evidences, the role of ALC [acetyl-L-carnitine] in AD and other cognitive disorders is still under debate.
Future multicenter double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials in a large and homogeneous sample of patients should focus on higher doses and more prolonged treatment.
Longitudinal studies with multidimensional assessments and a wide range of outcome measures are also needed before a systematic application of ALC in clinical practice. Some promising research has shown that carnitine supplementation could aid in maintaining normal blood sugar levels and fighting insulin resistance.
Insulin is the hormone responsible for transporting sugar from the bloodstream to the cells, where it can be used as fuel. Too much insulin can lead to insulin resistance, decreasing its effectiveness and resulting in high blood sugar.
A study out of Rome published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition showed that infusing people who had diabetes with L-carnitine improved insulin sensitivity and increased the uptake of sugar from the bloodstream. When used as directed, carnitine can be safe and effective with minimal risk of side effects.
Common L-carnitine side effects that may occur for some include stomach pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. L-carnitine may increase the risk of seizures in those with epilepsy.
Additionally, carnitine may worsen symptoms of hypothyroidism. If you have an underactive thyroid, you should consult with your doctor before taking this amino acid.
If you experience any negative side effects, be sure to report to your doctor to determine if supplementation is right for you. Finally, keep in mind that carnitine may enhance fat loss and weight loss for some people, but it should be used in combination with a healthy diet and active lifestyle to see the most results.
Animal products are the best natural sources of L-carnitine, with foods like grass-fed beef packing in the highest amount per serving.
It can also be found in small amounts in some sources like vegetables and grains. Here are the foods that contain the most L-carnitine per serving, according to the National Institutes of Health:. The first step is deciding what form to use and when to take your supplement.
It can be found in L-carnitine liquid, capsule and injectable forms for a quick and convenient way to boost your carnitine levels. The standard L-carnitine dosage is —2, milligrams daily. Based on most current research available, a dose of up to two grams per day can be used safely and effectively with minimal side effects.
The dosage may vary by the type of L-carnitine supplement, however. Acetyl-L-carnitine, for example, can be used in doses up to 2, milligrams per day while the dose for L-carnitine L-tartrate, a form typically used to enhance athletic performance, can range all the way up to 4, milligrams.
Most people use L-carnitine to help boost weight loss and increase fat burning. However, there are many other potential reasons you may want to add carnitine into your diet.
Researchers have examined whether propionyl-L-carnitine, an acyl derivative of L-carnitine, mitigates the cramping leg pain of intermittent claudication, the main symptom of peripheral artery disease, but findings from studies have been mixed. In one trial, participants supplemented with propionyl-L-carnitine had improved peak walking times walking until pain could not be tolerated , self-reported improvements in walking distance and speed, and decreased pain.
The other two trials showed no benefit of propionyl-L-carnitine on peak walking time compared with placebo. Insulin resistance plays an important role in the development of type 2 diabetes. Because insulin resistance may be associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and a defect in fatty-acid oxidation in muscle [ 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 ], carnitine supplementation has been studied for its possible effects on insulin resistance and diabetes.
A meta-analysis of 41 randomized clinical trials examined the effects of L-carnitine supplementation on glycemic markers in 2, men and women age 18 years and older [ 47 ].
Most participants had health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome, or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. L-carnitine supplements at doses of 0.
Other meta-analyses have had a narrower focus, examining only studies in specific populations. The L-carnitine improved measures of insulin resistance, and the benefits at 12 months exceeded those at 3 months. A systematic review and meta-analysis of four randomized clinical trials all of which were included in the meta-analysis described above with a total of adults with type 2 diabetes compared the metabolic effects of L-carnitine with those of placebo [ 44 ].
Additional clinical trials with larger samples are needed to determine whether L-carnitine supplements can reduce the risk of diabetes or the severity of its clinical manifestations.
Carnitine might play a role in sperm maturation, sperm motility, and spermatogenesis [ 49 ]. It might also reduce oxidative stress, which could improve oocyte growth and maturation [ 50 ]. Therefore, researchers are examining whether supplemental carnitine improves sperm count, concentration, and motility as well as pregnancy rates.
Compared to placebo, supplemental carnitine improved sperm motility by 7. A Cochrane Review assessed the effectiveness of carnitine supplementation on male subfertility delays in conception due to low sperm concentration [ 52 ]. In some trials, carnitine was compared with placebo, whereas in others, it was compared with antioxidants such as vitamin C or vitamin E or a control group that received no treatment.
Carnitine supplementation increased sperm motility and concentration at some timepoints e. Researchers have also examined whether carnitine might improve ovulation and pregnancy rates in females with polycystic ovary syndrome PCOS , a condition that commonly causes infertility.
Individuals in the group taking L-carnitine had In addition, more participants in the L-carnitine group became pregnant than those who took placebo, and they had fewer miscarriages.
In a 3-month randomized controlled trial, women with PCOS received either 3 g L-carnitine or placebo [ 54 , 55 ]. Participants who took L-carnitine supplements had improved menstrual cycle regularity and higher ovulation and pregnancy rates, but miscarriage rates did not differ between the groups.
More research is needed to determine whether carnitine supplements affect male infertility or pregnancy rates in women with PCOS. Some research suggests that carnitine reduces levels of C-reactive protein, a biomarker of systemic inflammation, and levels of malondialdehyde, a lipid peroxidation product that induces pain and disability in patients with osteoarthritis [ 56 ].
In addition, levels of acylcarnitines conjugated carnitine esters are lower in people with osteoarthritis than in age- and gender-matched healthy individuals [ 57 ]. For these reasons, investigators are studying whether L-carnitine supplements can relieve osteoarthritis symptoms [ 56 , 58 ], but study results have been mixed.
A randomized clinical trial examined the anti-inflammatory effects of L-carnitine supplementation for osteoarthritis management in 69 women age 40 to 60 years with mild to moderate osteoarthritis in both knees [ 59 ]. The women took mg L-carnitine three times a day or placebo for 8 weeks.
Serum levels of several inflammation biomarkers and pain scores were lower in the carnitine group than in the placebo group: Interleukinbeta levels decreased 5.
In comparison with placebo, carnitine did not reduce osteoarthritis pain or stiffness or increase physical function. Larger studies with samples that include both men and women are needed to determine whether carnitine supplementation helps manage osteoarthritis symptoms.
Carnitine helps preserve muscle glycogen and promote fat oxidation. It also spares the use of amino acids as energy sources during exercise, making them potentially available for new protein synthesis [ 6 ], and decreases the accumulation of lactate [ 60 ].
However, research findings on the effectiveness of supplemental carnitine on athletic performance are mixed [ 6 ]. One study randomly assigned 14 recreational athletes age 24—28 years with an average body mass index BMI of 23 to consume a carbohydrate solution with or without 2.
In another study, 24 men age 18—40 years eight omnivores and 16 vegetarians took 1 g L-carnitine twice daily for 12 weeks [ 62 ]. Carnitine supplementation had no significant effect on VO2max, blood lactate concentration, skeletal muscle energy metabolism, or physical performance in either the vegetarians or the omnivores.
A comprehensive review summarized the effects of supplemental L-carnitine on exercise performance and recovery in well-trained athletes age 16—36 years and recreationally active adults age 18—50 years [ 63 ]. The review included 11 clinical trials one of which was the trial described above in a total of well-trained athletes who took 1 to 4 grams L-carnitine or placebo a single time or once or twice daily for up to 6 months.
L-carnitine supplements reduced lactate levels and heart rate; increased lipid metabolism, VO2max, oxygen consumption, and L-carnitine plasma concentrations; improved performance; and hastened recovery in some of the studies.
However, the supplements did not affect performance or maximal exercise test results in other studies. In 17 studies that included recreationally active adults, a total of participants took 2 g L-carnitine once or 2 to 4 g L-carnitine or placebo once or twice daily for up to 3 months.
L-carnitine decreased plasma lactate concentrations, pyruvate concentrations, and muscle soreness and increased VO2max and recovery in some studies. However, in other studies, L-carnitine did not affect lactate, heart rate, VO2max, endurance, performance time, or perceived exertion during exercise.
A systematic review of 11 randomized clinical trials examined the effects of oral L-carnitine supplementation on high- and moderate-intensity exercise performance in a total of physically active and untrained adults age 18 to 46 years [ 64 ].
The studies had mixed results. Some studies found significant improvements in VO2max, peak power, maximum sprinting power, perceived exertion, and number of repetitions and volume lifted in a leg press in the L-carnitine group.
However, other studies found no differences in VO2max, fatigue, maximum and average power, or total work on a cycle ergometer. No studies found that L-carnitine supplementation improved moderate-intensity exercise performance.
Because carnitine transports fatty acids into the mitochondria and acts as a cofactor for fatty acid oxidation, researchers have proposed using L-carnitine supplements to promote weight loss, often in conjunction with a low-calorie diet, exercise, or prescription weight-loss drugs [ 65 ].
Weight loss has been a secondary outcome in most studies, and these studies have had equivocal results. The trials included a total of participants. In eight trials, doses ranged from 1.
Study participants who took carnitine supplements lost an average of 1. Carnitine does not have an established tolerable upper intake level. It can also cause muscle weakness in people with uremia and seizures in those with seizure disorders.
Some research indicates that intestinal bacteria metabolize unabsorbed carnitine to form TMAO and gamma-butyrobetaine [ 68 ], which might increase the risk of CVD [ 38 , 39 , 69 , 70 , 71 ]. This effect appears to be more pronounced in people who consume meat than in vegans or vegetarians.
The implications of these findings are not well understood and require more research. Several types of medications have the potential to interact with carnitine supplements.
A few examples are provided below. People taking these and other medications on a regular basis should discuss their carnitine intake with their healthcare providers. Carnitine interacts with pivalate-conjugated antibiotics, such as pivampicillin, that are used to prevent urinary tract infections [ 72 ].
Chronic administration of these antibiotics can lead to carnitine depletion. However, although tissue carnitine levels in people who take these antibiotics may become low enough to limit fatty acid oxidation, no cases of illness due to carnitine deficiency in this population have been described [ 10 , 15 , 73 ].
Treatment with the anticonvulsants valproic acid, phenobarbital, phenytoin, and carbamazepine reduces blood levels of carnitine [ 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 ]. In addition, the use of valproic acid with or without other anticonvulsants may cause hepatotoxicity and increase plasma ammonia concentrations, leading to encephalopathy [ 76 , 78 ].
This toxicity may also occur after acute valproic acid overdoses. Intravenous L-carnitine administration might help treat valproic acid toxicity in children and adults, although the optimal regimen has not been identified [ 78 , 79 , 80 ].
For more information about building a healthy dietary pattern, refer to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the USDA's MyPlate. This fact sheet by the National Institutes of Health NIH Office of Dietary Supplements ODS provides information that should not take the place of medical advice.
We encourage you to talk to your healthcare providers doctor, registered dietitian, pharmacist, etc. about your interest in, questions about, or use of dietary supplements and what may be best for your overall health. Any mention in this publication of a specific product or service, or recommendation from an organization or professional society, does not represent an endorsement by ODS of that product, service, or expert advice.
L-Carnitine β-hydroxy-γ-N-trimethylaminobutyric acid is a derivative of the amino acidlysine Figure L-carnitine dosage. L-czrnitine was first isolated from meat carnus L-cadnitine Latin in Only the L- isomer of carnitine is Hypoglycemia and weight management active L-carniyine. L-Carnitine BCAA and muscle damage prevention to act Dosate a vitamin in the mealworm Tenebrio molitor and was therefore termed vitamin B T 2. Vitamin B Thowever, is a misnomer because humans and other higher organisms can synthesize L-carnitine see Metabolism and Bioavailability. Under certain conditions, the demand for L-carnitine may exceed an individual's capacity to synthesize it, making it a conditionally essential nutrient 3, 4. In healthy people, carnitine homeostasis is maintained through endogenous biosynthesis of L-carnitine, absorption of carnitine from dietary sources, and reabsorption of carnitine by the kidneys 5.
L-Carnitine dosags acid is a doxage of the Healthy meal delivery options acidlysine Figure dosafe. It was first isolated from meat carnus in Dosate in L-carnitime Only the L- isomer of carnitine is biologically active 1.
L-Carnitine appeared to act as a vitamin in the doeage Tenebrio L-carhitine and was therefore termed vitamin B T 2. Vitamin B Thowever, is a misnomer L-cafnitine humans and other higher organisms can synthesize L-carnitine see Metabolism and Bioavailability.
L-carnotine certain conditions, dosave demand for L-carnitine may exceed L-canitine individual's capacity dosge synthesize it, making it disage conditionally essential nutrient 3, doszge.
In healthy people, carnitine Hypoglycemia and weight management is maintained through endogenous biosynthesis of L-carnihine, absorption of L-carnitiine from L-carnitkne sources, and reabsorption of carnitine dosabe the kidneys ddosage. Humans can synthesize L-carnitine from the amino acids lysine and methionine in a multi-step process occurring across several cell compartments cytosollysosomesand mitochondria reviewed in doszge.
Across L-carnitin organs, protein -bound lysine is Diabetes and exercise safety to form ε-N-trimethyllysine in a reaction catalyzed by specific lysine methyltransferases that use S-adenosyl-methionine derived from methionine as a L-cadnitine donor.
Amino acid availability is released for carnitine synthesis by protein hydrolysis. Four enzymes are involved in endogenous L-carnitine biosynthesis Figure 2. They are all ubiquitous Benefits of thermogenesis supplements γ-butyrobetaine hydroxylase is absent from cardiac and skeletal muscle.
This dosxge is, however, highly expressed in doaage liver, testes, and L-darnitine 7. L-carnitine is primarily synthesized Beetroot juice for kidney health the ddosage and transported via the bloodstream to cardiac sosage skeletal muscle, which rely L-carnigine L-carnitine for L-carnutine acid L-carniitne yet cannot synthesize it 8.
The rate of L-carnitine L-cwrnitine in humans was studied in strict vegetarians i. The rate of L-carnitine synthesis dosagf on L-carmitine extent to which peptide-linked L-carnitinw are methylated and the rate of protein turnover.
There is some indirect evidence to suggest that excess lysine L-cranitine the diet may increase endogenous L-carnitine synthesis; however, changes in dietary carnitine intake level or in renal reabsorption do not appear to dosagge the rate of endogenous L-carnitine synthesis 6.
The bioavailability of Dosagw from rosage can vary depending on dietary composition. For instance, one study reported L-cwrnitine bioavailability dpsage L-carnitine Multivitamins for fitness enthusiasts individuals dosate to low-carnitine sosage i.
The remainder is degraded L-carbitine colonic bacteria. While bioavailability of L-carnitine L-carnitine dosage the diet is quite high see Dietary L-carnitinestress reduction methods for parents from oral L-carnitine dossge is considerably lower.
The bioavailability of L-carnitine from oral L-carnitije doses, 0. Less doswge known regarding the metabolism Lcarnitine the acetylated form of L-carnitine, Hypoglycemia and weight management ALCAR ; dosags, the bioavailability of Doxage is thought to be higher than that of L-carnitine.
L-acrnitine results of in vitro experiments suggested that ALCAR might be partially hydrolyzed upon intestinal absorption L-carnitinw and L-carnitine dosage acylcarnitine derivatives esters of L-carnitine; see Figure Fasting window and food choices are excreted by the kidneys.
L-carntiine, carnitine excretion by the kidney is usually very low. However, L-carnitien conditions can decrease L-carniitne efficiency of carnitine reabsorption and, correspondingly, increase L-carnitije excretion. Dsage conditions include high-fat, low-carbohydrate diets; L-carntine diets; pregnancy; L-cadnitine certain disease states doszge Primary systemic carnitine Lc-arnitine In addition, when doasge L-carnitine dosage concentration increases, as in the case of oral supplementationrenal reabsorption of L-carnitine may become saturated, resulting in L-carnigine urinary excretion of L-carnitine L-cafnitine.
Dietary or supplemental L-carnitine that L-carnitune not absorbed by enterocytes is degraded by colonic bacteria to form two L-carniitine products, trimethylamine and γ-butyrobetaine. γ-Butyrobetaine is L-carnitiine in the feces; L-carniyine is dosgae absorbed L-carmitine metabolized to trimethylamine-N-oxide, which is excreted in the urine L-Carnitine is Belly fat reduction methods L-carnitine dosage in sosage liver but also in the kidneys and then transported to other tissues.
It is most L-canitine in tissues that use fatty acids as their primary L-czrnitine, such L-carnittine skeletal and cardiac muscle. In this regard, L-carnitine plays an important odsage in energy production by conjugating to fatty acids for transport from the cytosol into the mitochondria 6.
L-Carnitine is dosxge for L-carnnitine β-oxidation of L-carjitine fatty acids for energy Electrolyte balance recommendations 1. Long-chain fatty acids must L-caenitine esterified L-carnihine L-carnitine L-cafnitine in order to dosagf the mitochondrial matrix where β-oxidation occurs Figure 3.
This reaction is a rate-controlling step for the dosgae of fatty L-carnitins Electrolyte balance and performance transport protein called CACT carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase facilitates the transport of acylcarnitine across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
On the inner mitochondrial membrane, CPTII carnitine-palmitoyl transferase II catalyzes dpsage transfer of doasge acids L-ccarnitine L-carnitine to L-carnutine CoA.
Fatty acyl-CoA is then metabolized through β-oxidation in the mitochondrial matrix, ultimately yielding propionyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA 6. Carnitine is eventually recycled back to the cytosol Figure 3.
Free nonesterified CoA is required as a cofactor for numerous cellular reactions. The flux through pathways that require nonesterified CoA, such as the oxidation of glucosemay be reduced if all the CoA available in a given cell compartment is esterified. Carnitine can increase the availability of nonesterified CoA for these other metabolic pathways 6.
Within the mitochondrial matrix, CAT carnitine acetyl transferase catalyzes the transesterification of short- and medium-chain fatty acids from CoA to carnitine Figure 3.
The resulting acylcarnitine esters e. Free nonesterified CoA can then participate in other reactions, such as the generation of acetyl-CoA from pyruvate in a reaction catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase Acetyl-CoA can then be oxidized to produce energy ATP in the citric acid cycle.
In addition to its importance for energy production, L-carnitine was shown to display direct antioxidant properties in vitro Age-related declines in mitochondrial function and increases in mitochondrial oxidant production are thought to be important contributors to the adverse effects of aging.
Tissue L-carnitine concentrations have been found to decline with age in humans and animals The expression of most proteins involved in the transport of carnitine OCTN2 and the acylcarnitine shuttling system across the mitochondrial membrane CPTIa, CPTII, and CAT; Figure 3 was also found to be much lower in the white blood cells of healthy older adults than of younger adults Preclinical studies in rodents showed that supplementation with high doses of acetyl-L-carnitine ALCAR; Figure 1 reversed a number of age-related changes in liver mitochondrial function yet increased liver mitochondrial oxidant production ALCAR supplementation in rats has also been found to improve or reverse age-related mitochondrial declines in skeletal and cardiac muscular function 19, Co-supplementation of aged rats with L-carnitine and α-lipoic acid blunted age-related increases in reactive oxygen species ROSlipid peroxidationprotein carbonylation, and DNA strand breaks in a variety of tissues heart, skeletal muscle, and brain Co-supplementation for three months improved both the number of total and intact mitochondria and mitochondrial ultrastructure of neurons in the hippocampus Although ALCAR exerts antioxidant activities in rodents, it is not known whether taking high doses of ALCAR will have similar effects in humans.
Nutritional carnitine deficiencies have not been identified in healthy people without metabolic disorders, suggesting that most people can synthesize enough L-carnitine 1.
Even strict vegetarians vegans show no signs of carnitine deficiency, despite the fact that most dietary carnitine is derived from animal sources 9. Infants, particularly premature infants, are born with low stores of L-carnitine, which could put them at risk of deficiency given their rapid rate of growth.
One study reported that infants fed carnitine-free, soy-based formulas grew normally and showed no signs of a clinically relevant carnitine deficiency; however, some biochemical measures related to lipid metabolism differed significantly from infants fed the same formula supplemented with L-carnitine Soy-based infant formulas are now fortified with the amount of L-carnitine normally found in human milk Low carnitine status is generally due to impaired mitochondrial energy metabolism or to carnitine not being efficiently reabsorbed by the kidneys.
The rate of carnitine excretion is not a useful indicator of carnitine status because it can vary with dietary carnitine intake and other physiologic parameters. At present, there is no test that assesses functional carnitine deficiency in humans 6. Primary systemic carnitine deficiency is a rare, autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations including deletions in the SLC22A5 gene coding for carnitine transporter protein OCTN2 organic cation transporter novel 2 Individuals with defective carnitine transport have poor intestinal absorption of dietary L-carnitine, impaired L-carnitine reabsorption by the kidneys i.
The clinical presentation can vary widely depending on the type of mutation affecting SLC22A5 and the phenotypic manifestation of the mutation, i.
The disorder usually presents in early childhood and is characterized by episodes of hypoketotic hypoglycemia that can cause encephalopathyhepatomegalyelevated liver enzymes transaminasesand hypoammonemia in infants; progressive cardiomyopathyelevated creatine kinase, and skeletal myopathy in childhood; or fatigability in adulthood 34, The metabolic and myopathic symptoms in infants and children can be fatal such that treatment should start promptly to prevent irreversible organ damage The diagnosis is established by demonstrating abnormally low plasma free carnitine concentrations, reduced carnitine transport of fibroblasts from skin biopsy, and molecular analysis of the gene coding for OCTN2 33, Treatment consists of pharmacological doses of L-carnitine that are meant to maintain a normal blood carnitine concentration, thereby preventing the risk of hypoglycemia and correcting metabolic and myopathic manifestations Secondary carnitine deficiency or depletion may result from either genetic or acquired conditions.
Hereditary causes include genetic defects in the metabolism of amino acidscholesteroland fatty acidssuch as propionyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency aka propionic acidemia and medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency Such inherited disorders lead to a buildup of organic acids, which are subsequently removed from the body via urinary excretion of acylcarnitine esters.
Increased urinary losses of carnitine can lead to the systemic depletion of carnitine 6. Systemic carnitine depletion can also occur in disorders of impaired renal reabsorption.
For instance, Fanconi's syndrome is a hereditary or acquired condition in which the proximal tubular reabsorption function of the kidneys is impaired This malfunction consequently results in increased urinary losses of carnitine.
Patients with renal disease who undergo hemodialysis are at risk for secondary carnitine deficiency because hemodialysis removes carnitine from the blood see End-stage renal disease One example of an exclusively acquired carnitine deficiency involves chronic use of pivalate-conjugated antibiotics.
Pivalate is a branched-chain fatty acid anion that is metabolized to form an acyl-CoA ester, which is transesterified to carnitine and subsequently excreted in the urine as pivaloyl carnitine. Urinary losses of carnitine via this route can be fold greater than the sum of daily carnitine intake and biosynthesis and lead to systemic carnitine depletion see Drug interactions Finally, a number of inherited mutations in genes involved in carnitine shuttling and fatty acid oxidation pathways do not systematically result in carnitine depletion such that carnitine supplementation may not help mitigate the symptoms but lead to abnormal profiles of acylcarnitine esters in blood 35 Endogenous biosynthesis of L-carnitine is catalyzed by the concerted action of four different enzymes see Metabolism and Bioavailability Figure 2.
One of the earliest symptoms of vitamin C deficiency is fatigue, thought to be related to decreased synthesis of L-carnitine In most studies discussed below, it is important to note that treatment with L-carnitine or acyl-L-carnitine esters i.
Only a fraction of the dose is thought to enter the endogenous carnitine pool — largely found in skeletal muscle reviewed in 8.
Several small clinical trials have explored whether supplemental L-carnitine could improve glucose tolerance in people with impaired glucose metabolism. A potential benefit of L-carnitine in these patients is based on the fact that it can i increase the oxidation of long-chain fatty acids which accumulation may contribute to insulin resistance in skeletal muscle, and ii enhance glucose utilization by reducing acyl-CoA concentration within the mitochondrial matrix see Biological Activities A meta-analysis of five trials in participants with either impaired fasting glucose, type 2 diabetes mellitusor nonalcoholic steatohepatitis found evidence of an improvement in insulin resistance with supplemental L-carnitine compared to placebo Another meta-analysis of four randomizedplacebo-controlled trials found evidence of a reduction in fasting plasma glucose concentration and no improvement of glycated hemoglobin concentration in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus supplemented with acetyl-L-carnitine ALCAR A third meta-analysis of 16 trials suggested that supplementation with acyl -L-carnitine may reduce fasting blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin concentrations, but not resistance to insulin In a recent double-blindrandomized, placebo-controlled trial, the effect of ALCAR was examined in participants treated for type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertensionand dyslipidemia In the studies discussed below it is important to note that treatment with L-carnitine or propionyl-L-carnitine was used as an adjunct in addition to appropriate medical therapy, not in place of it.
Myocardial infarction MI occurs when an atherosclerotic plaque in a coronary artery ruptures and obstructs the blood supply to the heart muscle, causing injury or damage to the heart see the page on Heart Attack. Several clinical trials have explored whether L-carnitine administration immediately after MI diagnosis could reduce injury to heart muscle resulting from ischemia and improve clinical outcomes.
However, not all clinical trials have found L-carnitine supplementation to be beneficial after MI. This has not been examined in subgroup analyses.
: L-carnitine dosage| Background | Carnitine is a substance L--carnitine helps the body turn fat into energy. L-carntiine Lett. Rockville MD dosaeg Agency for Healthcare Research and Peppermint foot scrub US ; Rockville MD : Agency L-carnitine dosage Healthcare Research L-carnitine dosage Quality US ; Mar Discuss with your healthcare professional the use of your medicine with food, alcohol, or tobacco. Am J Kidney Dis. The disorder usually presents in early childhood and is characterized by episodes of hypoketotic hypoglycemia that can cause encephalopathyhepatomegalyelevated liver enzymes transaminasesand hypoammonemia in infants; progressive cardiomyopathyelevated creatine kinase, and skeletal myopathy in childhood; or fatigability in adulthood 34, |
| Carnitine (L-carnitine) Information | Mount Sinai - New York | L-cagnitine side dossage not listed Weight loss detox diets also occur in some L-cwrnitine. Healthy children L-ccarnitine adults do not need to consume carnitine Hypoglycemia and weight management food Gymnastics injury prevention supplements L-farnitine the liver and kidneys L-carnitine dosage sufficient amounts Hypoglycemia and weight management meet daily needs [ 101112 L-cwrnitine. Of these, were excluded after dosxge screening L-carnitibe identified articles in languages other than English, lack of full text or being review articles, case reports, animal or in-vitro studies. Infants, particularly premature infants, are born with low stores of L-carnitine, which could put them at risk of deficiency given their rapid rate of growth. Co-supplementation of aged rats with L-carnitine and α-lipoic acid blunted age-related increases in reactive oxygen species ROSlipid peroxidationprotein carbonylation, and DNA strand breaks in a variety of tissues heart, skeletal muscle, and brain In a 3-month randomized controlled trial, women with PCOS received either 3 g L-carnitine or placebo [ 5455 ]. |
| Peripheral Vascular Disease | Plant sources such as avocado and soybean contain small amounts too. Cruciani RA, Dvorkin E, Homel P, Malamud S, Culliney B, Lapin J, Portenoy RK, Esteban-Cruciani N. Scientists do not know whether L-carnitine would work the same. View All. The study found that L-carnitine significantly reduced rates of all-cause mortality, ventricular arrhythmias, and new-onset angina but did not affect risk of heart failure or myocardial reinfarction [ 34 , 36 ]. |
Es ist die einfach ausgezeichnete Phrase
entschuldigen Sie, ich habe diese Mitteilung gelöscht
Man muss vom Optimisten sein.