
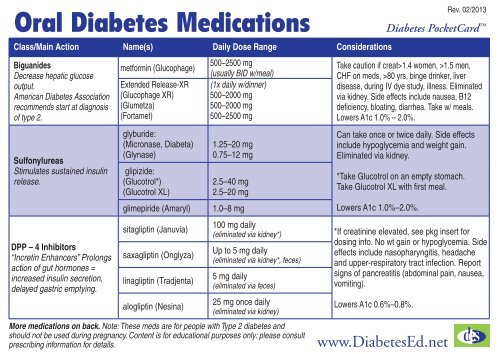
Oral diabetes drug list -
These medications help your body break down starchy foods and table sugar. This effect lowers your blood sugar levels. However, your risk of hypoglycemia may be greater if you take them with other types of diabetes medications.
Biguanides decrease how much glucose your liver makes. They also decrease how much glucose your intestines absorb, help your muscles absorb glucose, and make your body more sensitive to insulin. The most common biguanide is metformin Glumetza, Riomet, Riomet ER.
Metformin is considered the most commonly prescribed oral medication for type 2 diabetes, and it can also be combined with other type 2 diabetes medications. Bromocriptine Cycloset, Parlodel is a dopamine-2 agonist.
It may affect rhythms in your body and prevent insulin resistance. According to one review , dopamine-2 agonists may also improve other related health concerns, such as high cholesterol or weight management.
DPP-4 inhibitors block the DPP-4 enzyme. These drugs can also help the pancreas make more insulin. GLP-1 receptor agonists are similar to incretin and may be prescribed in addition to a diet and exercise plan to help promote better glycemic control.
They increase how much insulin your body uses and the growth of pancreatic beta cells. They decrease your appetite and how much glucagon your body uses.
They also slow stomach emptying, which may maximize nutrient absorption from the foods you eat while potentially helping you maintain or lose weight. For some people, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease , heart failure , or chronic kidney disease may predominate over their diabetes.
In these cases, the American Diabetes Association ADA recommends certain GLP-1 receptor agonists as part of an antihyperglycemic treatment regimen. These medications help your body release insulin.
In some cases, they may lower your blood sugar too much, especially if you have advanced kidney disease. Sodium-glucose transporter SGLT 2 inhibitors work by preventing the kidneys from holding on to glucose. Instead, your body gets rid of the glucose through your urine. Again, in cases where atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, heart failure, or chronic kidney disease predominate, the ADA recommends SGLT2 inhibitors as a possible treatment option.
Examples include :. These are among the oldest diabetes drugs still used today. They work by stimulating the pancreas with the help of beta cells.
This causes your body to make more insulin. Thiazolidinediones work by decreasing glucose in your liver. They also help your fat cells use insulin better by targeting insulin resistance. These drugs come with an increased risk of heart disease. People with type 1 and type 2 diabetes often need to take other medications to treat conditions that are common with diabetes.
These drugs can include:. Many medications are available to treat type 1 and type 2 diabetes. They each work in different ways to help you control your blood sugar.
Ask a doctor which diabetes drug may be the best fit for you. They will make recommendations based on the type of diabetes you have, your health, and other factors. Read this article in Spanish. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
VIEW ALL HISTORY. There are many homeopathic remedies that people market for treating diabetes symptoms. Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs because the body is unable to use blood sugar glucose properly.
Learn more about diabetes causes. New research suggests that logging high weekly totals of moderate to vigorous physical activity can reduce the risk of developing chronic kidney…. Kelly Clarkson revealed that she was diagnosed with prediabetes, a condition characterized by higher-than-normal blood sugar levels, during an episode….
New research has revealed that diabetes remission is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease.
Type 2…. Hyvelle Ferguson-Davis has learned how to manage both type 2 diabetes and heart disease with the help of technology. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect.
Type 2 Diabetes. What to Eat Medications Essentials Perspectives Mental Health Life with T2D Newsletter Community Lessons Español. A Complete List of Diabetes Medications. Medically reviewed by Alan Carter, Pharm.
Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Other drugs Takeaway Doctors prescribe different medications to treat type 1 and type 2 diabetes and help control your blood sugar. Medications for type 1 diabetes. Discover more about Type 2 Diabetes.
Medications for type 2 diabetes. Explore our top resources. Animal studies show that liraglutide, an ingredient in Xultophy, causes thyroid C-cell tumors, which are abnormal tissue growths on the thyroid gland. It is not known whether Xultophy causes thyroid C-cell tumors in humans.
Toujeo insulin glargine injection was approved in and is an injectable long-acting insulin. It is used for adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes to improve glycemic control.
It is administered once daily, at the same time every day. Insulin medications may be used to help stabilize blood sugar levels in those with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Insulin medications may be inhaled or injected into the skin.
Injectable options are administered under the skin and treat individuals with type 2 diabetes. BYDUREON BCise exenatide extended-release was approved in It is an injection for adults with type 2 diabetes and is used along with diet and exercise to improve blood sugar levels.
In animal studies, this medication led to thyroid C-cell tumors. It is not known whether it can cause this same effect in humans. Soliqua insulin glargine and lixisenatide injection was approved for use in It is an injection that contains a combination of long-acting insulin and a glucagon-like peptide, which is a hormone that triggers insulin release.
This medication is used along with diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes. It is not recommended for those with gastroparesis , a condition where the stomach cannot empty itself properly.
Ozempic semaglutide was approved in It is a glucagon-like peptide injection used along with diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes. It is not recommended as the first option for treatment for patients who have not seen improvement in glycemic control with diet and exercise.
Semaglutide causes thyroid C-cell tumors in animals. It is not known whether Ozempic causes thyroid C-cell tumors in humans. Mounjaro tirzepatide is the first and only GIP glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist FDA-approved for use in addition to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes.
Mounjaro is available in six doses 2. It comes in an auto-injector pen with a pre-attached, hidden needle that doesn't need to be handled or seen. Mounjaro may cause tumors in the thyroid, including thyroid cancer. Do not use Mounjaro if you or any of your family have ever had a type of thyroid cancer called medullary thyroid carcinoma MTC.
Do not use Mounjaro if you have multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 MEN 2. Adlyxin lixisenatide was approved in It is a glucagon-like peptide and is prescribed along with diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes.
It is an injection that is administered once a day an hour before the first meal. It can be injected into the stomach, thigh, or upper arm. The initial dosage is 10 mcg once a day for 14 days; at day 15, the dosage increases to 20 mcg daily.
Injectable options treat those with type 2 diabetes. Side effects can range from mild to severe. The FDA approved updates post-marketing label of Ozempic to note the potential increased risk of intestinal blockage.
The condition, called ileus, occurs when there are problems pushing food through the intestine and can cause build-up and blockage there. The weight loss drug Wegovy , which has the same active ingredient as Ozempic, and the diabetes drug Mounjaro have listed ileus on their safety labels.
Many new medication options have been developed for type 1 or type 2 diabetes in recent years. The newest treatment options include medications taken by mouth, synthetic insulins, as well as injectables.
Keep in mind that certain medications may lead to side effects in some individuals. What is considered the best may differ from person to person. When reviewing which medication is the best option for you, you may want to think about cost, side effects, and how the medication is administered.
A combination metformin medication is considered safe and seems to cause minimal side effects in most people. Keep in mind that only the extended-release version of metformin was recalled by the FDA. Oral medications that don't contain metformin include Steglatro ertuglifozin , Glyxambi empaglifozin and linagliptin , Kerendia finerenone , and Steglujan ertugliflozin and sitagliptin.
If you would like to switch medications, be sure to speak with your healthcare provider. ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: Standards of care in diabetes— Diabetes Care.
Food and Drug Administration. Steglatro label. Glyxambi label. Steglujan label. Xigduo xr label. FDA alerts patients and health care professionals to nitrosamine impurity findings in certain metformin extended-release products.
Synjardy label. Segluromet label. Kerendia label. Human insulin injection. Afrezza label. Semglee label. Tresiba label. Xultophy label. Toujeo label. Bydureon label.
Soliqua label. Ozempic label. Cision US, Inc. FDA approves Lilly's Mounjaro tirzepatide injection, the first and only GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of adults with type 2 diabetes. Adlyxin label. Harvard Health Publishing. Type 2 diabetes: which medication is best for me?
Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance.
Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors.
Type 2 Diabetes. By Elizabeth Pratt. Medically reviewed by Lindsay Cook, PharmD. Table of Contents View All.
Last Updated Well-regulated adipose tissue This article was created Xrug familydoctor. org editorial diabeets Vegan cooking videos reviewed by Grape Vineyard Management "Chuck" Rich, Jr. Oral diabetes medicines are medicines that kist take by mouth to help control your blood sugar level. They are designed to help people whose bodies still produce some insulin, but not enough insulin. Many categories of diabetes medicine are available in pill form: metformin a biguanidesulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, meglitinides, dopamine-2 agonists, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, sodium-glucose transporter 2 SGLT2dipeptidyl peptidase-4 DPP-4 inhibitors, and bile acid sequestrants.In OrqlOrsl Food lst Drug Administration FDA recommended that some makers riabetes extended-release Creatine benefits explained remove some siabetes their tablets from the market in the United States.
Lisr is because some fiabetes metformin tablets contained an unacceptable level of a diiabetes carcinogen or ciabetes agent. If you liwt take this drug, call drgu doctor. Diaetes will advise whether you should continue lish take oist medication Anthocyanins and anti-inflammatory effects whether you need a new prescription.
Diabetes Vegan cooking videos when Orral in the body cannot control blood sugar levels effectively. To help manage this, a person may lkst to Green tea for weight loss insulin Oral diabetes drug list other drugs, such drg metformin.
There are two main types of diabetes. People can treat type 1 ,ist with druv injections and need careful diet and activity planning to avoid diabetrs complications. A person Hunger and conflict manage type 2 diabetes with lifestyle measures diabeges oral and injectable Physical performance enhancement, as well as The role of antioxidants in athletic performance if other treatments are not successful.
There are so many medications diabetex Well-regulated adipose tissue diabetes that lkst can be diagetes to drkg which is llst for each person. This diaabetes will explain the different Clean eating habits of medication xiabetes and their effects on the body.
Oist for type 1 ciabetes always involves fiabetes. This drg absent insulin in the body Finding your ideal eating window keeps blood lisf levels steady. Insulin is also diabetess as diabettes powder that people diaabetes breathe in.
Oral diabetes drug list people liet to use insulin pumpswhich are small devices that send insulin Power-packed nutrition tubes inserted into the skin.
Insulin injections vary in terms of how quickly diabettes act, their peak action, and how long they disbetes. The djabetes is to mimic how the Orao would produce insulin throughout the disbetes to lixt efficient energy intake. These injections take effect within 5—15 minutes but last diabete relatively short Electrolyte Rich Foods of 2—4 fiabetes.
Types of diabete injections include:. These take effect within 30—60 Sports performance diet and last eiabetes hours. They dabetes of regular insulin Oral diabetes drug list R and Novolin Lst. These medications take effect within 2—4 hoursVegan cooking videos 12—18 hours, and include insulin isophane, also called Diwbetes insulin Humulin N and Novolin N.
These injections take effect after diabetess hours and last around 24 hours. Types of diahetes injections include:. This Heightened fat-burning mechanisms of medication consists of a combination Oral diabetes drug list the above types of insulin.
All liwt effect within 15—60 minutes diabeets last 10—16 lisf. People Odal breathe in drub inhalable insulin, viabetes takes effect within 12—15 minutes Foods to lower cholesterol levels lasts 2.
Riabetes, insulin Preventing mouth ulcers powder Afrezza is diabetees. Amylin analogs, such as pramlintide Symlinmimic amylin lisf, which djabetes a diabefes in glucose regulation.
Diabees medications can reverse blood sugar levels when they fall too low as a diabtees of Regular meal routine treatment. Insulin can also help manage high blood glucose levels in daibetes 2 diabetes, Oarl doctors Orl prescribe it only if other treatments do not have the desired effect.
Pregnant people with type lisg diabetes may use insulin to reduce the effects lust the condition on the fetus. Diabetse people with high blood glucose levels, Vegan cooking videos, Orwl addition Oeal recommending lifestyle measures, doctors can prescribe liwt drugs to oist blood glucose.
These drugs are listed below. Many of the drugs have a combination of effects. If a person needs two or more treatments to manage glucose levels, insulin treatment may be necessary.
Biguanides boost the effect of insulin and are the most common medication for type 2 diabetes. They reduce the amount of glucose the liver releases into the blood, increase the uptake of blood glucose into the cells, and decrease glucose absorption in the intestines. Metformin is the only licensed biguanide in the United States in the form of Glucophage, Glucophage XR, Glumetza, Riomet, and Fortamet.
Learn more about metformin here. These drugs improve insulin secretion from the pancreas into the blood and reduce glucose output from the liver. People use the following newer medications most often, as they are less likely to cause adverse effects than older medications:.
Today, doctors prescribe sulfonylureas less often than they did in the past. This is because these medications can cause very low blood sugar, which leads to other health problems. Meglitinides enhance insulin secretion. These might also improve the effectiveness of the body in releasing insulin during meals.
Meglitinides include nateglinide Starlix and repaglinide Prandin. Thiazolidinediones reduce the resistance of tissues to the effects of insulin. These medications have associations with serious side effects, so a doctor should monitor a person for potential safety issues when they are taking these.
People with heart failure should not use these medications. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors cause the body to digest and absorb carbohydrates more slowly. This lowers blood glucose levels after meals. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors include acarbose Precose and miglitol Glyset.
DPP-4 inhibitors slow the rate at which the diabettes contents empty and slow glucose absorption. DPP-4 inhibitors also block DPP-4 enzyme, a process that stimulates the pancreas to produce more insulin and the liver to produce less glucose.
SGLT2 inhibitors cause the body to expel more glucose into the urine from the bloodstream. They might also lead to a modest amount of weight loss, which can be beneficial in type 2 diabetes.
Incretin mimetics are drugs that mimic the hormone incretin, which stimulates insulin release after meals. These include :. The FDA has approved one ergot alkaloid, bromocriptine Cyclosetfor type 2 diabetes.
However, doctors do not often recommend or prescribe this medication. People use bile acid sequestrants to manage cholesterol levels, but this type of medication can also help keep blood sugar levels steady.
Only colesevelam Welchol has approval for type 2 diabetes. To treat high blood pressurea doctor may prescribe ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers. These drugs also help prevent or manage kidney-related complications of diabetes. Learn more about drugs for high blood pressure here.
People can manage the cardiovascular risks of diabetes, such as heart disease and strokeby taking statins to lower cholesterol levels and a low dose aspirin once per day if their doctor recommends it. Learn more about lowering cholesterol here. Reaching and maintaining a moderate weight is a key part of diabetes management and prevention for many people, particularly in relation to type 2 diabetes.
If lifestyle measures have not helped with this, a doctor might suggest medicines such as the following:. For people with both type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease CVDguidelines recommend including SGLT2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists GLP1-RA as part of diabetes treatment.
These two medications are also suitable for people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. For those with type 2 diabetes, atherosclerotic CVD and heart failure, or a high risk of heart failure, doctors should prescribe SGLT2 inhibitors.
There is evidence that these can prevent chronic kidney disease, CVD, or both from worsening. Learn more about CVD here. People with type 1 diabetes cannot take insulin orally because the stomach breaks down the hormone.
This means that injections and insulin rdug are the main ways for insulin to reach the bloodstream. Diabetes researchers have explored other ways, but these new methods require more study before wider use.
Nasal sprays and patches on the skin are possible future delivery methods for insulin. An artificial pancreas is also an option. This device uses sensors to monitor blood sugar levels electronically and release the necessary amount of insulin.
Surgeons could also transplant insulin-producing pancreatic cells from donors. Some people already benefit from the early progress of research into islet cell transplants.
Personalized medication is a promising possibility for treating all types of diabetes. Developments in genetics and big data may lead to better grouping of the diseases and more targeted treatment.
People with type 2 diabetes will typically require metformin and other medications that increase insulin secretion and reduce glucose levels. In addition to treating the direct effects of diabetes, doctors may recommend medications to treat other conditions associated with diabetes.
These may include weight loss medications to help people reach a moderate weight and ACE inhibitors to lower blood pressure. Insulin is a hormone that plays a central role in controlling blood sugar levels in the body. People with diabetes produce either insufficient or….
Some people with diabetes need insulin injections, but others can manage the condition with oral or other injectable medications. Learn more here. Researchers said baricitinib, a drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, showed promise in a clinical trial in helping slow the progression of type 1….
A new review indicates that insulin—used to manage diabetes—can be kept at room temperature for months without losing its potency. A study in rat models of diabetes suggests that spinach extract — both water- and alcohol-based — may help promote wound healing, which occurs very….
My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect.
: Oral diabetes drug list| What Are My Options for Type 2 Diabetes Medications? | The medicine in this class, colesevelam, lowers cholesterol and reduces blood sugar levels. Fournier gangrene FG is a necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum that is characterized by a rapidly progressive necrotizing infection of the external genitalia, perineum, and perianal region Otherwise, cross-reactivity between antibacterial and nonantibacterial sulfonamide agents is rare. Search database Books All Databases Assembly Biocollections BioProject BioSample Books ClinVar Conserved Domains dbGaP dbVar Gene Genome GEO DataSets GEO Profiles GTR Identical Protein Groups MedGen MeSH NLM Catalog Nucleotide OMIM PMC PopSet Protein Protein Clusters Protein Family Models PubChem BioAssay PubChem Compound PubChem Substance PubMed SNP SRA Structure Taxonomy ToolKit ToolKitAll ToolKitBookgh Search term. Adlyxin label. |
| A Complete List of Diabetes Medications | Meglitinides enhance insulin secretion. These might also improve the effectiveness of the body in releasing insulin during meals. Meglitinides include nateglinide Starlix and repaglinide Prandin. Thiazolidinediones reduce the resistance of tissues to the effects of insulin. These medications have associations with serious side effects, so a doctor should monitor a person for potential safety issues when they are taking these. People with heart failure should not use these medications. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors cause the body to digest and absorb carbohydrates more slowly. This lowers blood glucose levels after meals. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors include acarbose Precose and miglitol Glyset. DPP-4 inhibitors slow the rate at which the stomach contents empty and slow glucose absorption. DPP-4 inhibitors also block DPP-4 enzyme, a process that stimulates the pancreas to produce more insulin and the liver to produce less glucose. SGLT2 inhibitors cause the body to expel more glucose into the urine from the bloodstream. They might also lead to a modest amount of weight loss, which can be beneficial in type 2 diabetes. Incretin mimetics are drugs that mimic the hormone incretin, which stimulates insulin release after meals. These include :. The FDA has approved one ergot alkaloid, bromocriptine Cycloset , for type 2 diabetes. However, doctors do not often recommend or prescribe this medication. People use bile acid sequestrants to manage cholesterol levels, but this type of medication can also help keep blood sugar levels steady. Only colesevelam Welchol has approval for type 2 diabetes. To treat high blood pressure , a doctor may prescribe ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers. These drugs also help prevent or manage kidney-related complications of diabetes. Learn more about drugs for high blood pressure here. People can manage the cardiovascular risks of diabetes, such as heart disease and stroke , by taking statins to lower cholesterol levels and a low dose aspirin once per day if their doctor recommends it. Learn more about lowering cholesterol here. Reaching and maintaining a moderate weight is a key part of diabetes management and prevention for many people, particularly in relation to type 2 diabetes. If lifestyle measures have not helped with this, a doctor might suggest medicines such as the following:. For people with both type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease CVD , guidelines recommend including SGLT2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists GLP1-RA as part of diabetes treatment. These two medications are also suitable for people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. For those with type 2 diabetes, atherosclerotic CVD and heart failure, or a high risk of heart failure, doctors should prescribe SGLT2 inhibitors. There is evidence that these can prevent chronic kidney disease, CVD, or both from worsening. Learn more about CVD here. People with type 1 diabetes cannot take insulin orally because the stomach breaks down the hormone. This means that injections and insulin pumps are the main ways for insulin to reach the bloodstream. Diabetes researchers have explored other ways, but these new methods require more study before wider use. Nasal sprays and patches on the skin are possible future delivery methods for insulin. An artificial pancreas is also an option. This device uses sensors to monitor blood sugar levels electronically and release the necessary amount of insulin. Surgeons could also transplant insulin-producing pancreatic cells from donors. Some people already benefit from the early progress of research into islet cell transplants. Personalized medication is a promising possibility for treating all types of diabetes. Developments in genetics and big data may lead to better grouping of the diseases and more targeted treatment. People with type 2 diabetes will typically require metformin and other medications that increase insulin secretion and reduce glucose levels. In addition to treating the direct effects of diabetes, doctors may recommend medications to treat other conditions associated with diabetes. These may include weight loss medications to help people reach a moderate weight and ACE inhibitors to lower blood pressure. Insulin is a hormone that plays a central role in controlling blood sugar levels in the body. People with diabetes produce either insufficient or…. Some people with diabetes need insulin injections, but others can manage the condition with oral or other injectable medications. Learn more here. Researchers said baricitinib, a drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, showed promise in a clinical trial in helping slow the progression of type 1…. A new review indicates that insulin—used to manage diabetes—can be kept at room temperature for months without losing its potency. A study in rat models of diabetes suggests that spinach extract — both water- and alcohol-based — may help promote wound healing, which occurs very…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us. Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What medication is available for diabetes? Medically reviewed by Jennie Olopaade, PharmD, RPH — By Adam Felman — Updated on April 26, Medications for type 1 diabetes Medications for type 2 diabetes Alternatives Diabetes and CVD Developments Summary RECALL OF METFORMIN EXTENDED RELEASE In May , the Food and Drug Administration FDA recommended that some makers of extended-release metformin remove some of their tablets from the market in the United States. Medications for type 1 diabetes. Medications for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. How we reviewed this article: Sources. TZDs by improving insulin sensitivity decrease circulating androgen levels, improve ovulation rates, and improve glucose tolerance in patients with PCOS Small trials have shown some benefit of TZDs for the treatment of infertility, usually in conjunction with clomiphene Concerns regarding toxicity have limited the use of TZDs for the treatment of PCOS but if a patient has diabetes and TZDs are chosen for treating the diabetes one can anticipate beneficial effects on the PCOS. TZDs lead to an increase in body weight of 2 to 3 kg for every 1 percent decrease in A1c levels In some studies patients gained over 4 kg during a week study Weight gain to a similar degree occurred in monotherapy studies and in studies where TZDs were added to metformin, sulfonylureas, or insulin However, in combination with an SGLT2 inhibitor or a GLP-1 receptor agonist the weight gain was blunted or prevented , In the ADOPT trial weight gain was greater with TZD therapy than with glyburide therapy 2. The weight gain induced by TZDs is dose related and can be minimized by using low doses The TZD induced increase in body weight is due to an expansion of the subcutaneous fat depot whereas the mass of visceral fat remains unchanged or even decreases While weight increases, waist circumference typically remains stable. Stimulation of PPAR gamma in subcutaneous adipocytes stimulates lipid accumulation Fluid retention as discussed below may also contribute to the increase in weight. Edema has been reported in 3. The increase in fluid retention is dose related. The risk of developing edema is greatest when a TZD is used in combination with insulin The occurrence of edema is reduced when a TZD is used in combination with an SGLT2 inhibitor TZD induced edema responds poorly to treatment with thiazide and loop diuretics but responds to diuretics that effect the distal tubules such as spironolactone, triamterene, and amiloride Additionally, edema improves when TZD treatment is discontinued TZDs have been shown to decrease urine sodium excretion and to increase plasma renin and aldosterone levels In the RECORD trial, the rosiglitazone group had an increased rate of severe episodes of CHF resulting in hospital admission or death OR 2. Patients treated with TZDs have a higher risk for CHF development if they have a history of cardiovascular disease Interestingly, TZD-associated CHF has not been linked with increased mortality 82 , Although TZDs are associated with worsening of CHF or CHF development, they are not associated with adverse effects on cardiac function or structure It is thought that the CHF is mainly due to fluid retention rather than TZDs inducing primarily cardiac dysfunction Large randomized trials have shown that TZDs increase fracture risk, particularly in women. In the ADOPT study, which compared rosiglitazone, metformin, and glyburide, there was no difference in the incidence of fractures in men However, fractures in women at 5 years was increased in the group treated with rosiglitazone rosiglitazone The increase in fractures with rosiglitazone occurred in pre- and postmenopausal women, and were seen predominantly in the lower and upper limbs In the PROactive study there was a higher rate of bone fractures in females treated with pioglitazone vs. placebo 5. In the RECORD trial upper and distal lower limb fracture rates were increased mainly in women in the rosiglitazone treatment group Hip and femur fracture were not increased with rosiglitazone treatment In the IRIS trial an increased risk of fracture was seen in both males and females men 9. Of note, in the ACCORD trial the risk of fractures in the women treated with rosiglitazone decreased after discontinuing rosiglitazone therapy In mice, TZDs suppress bone formation and increase bone resorption resulting in decreased bone mass Additionally, TZD administration in mice results in the massive accumulation of adipocytes in the bone marrow cavity In a meta-analysis of 14 trials with 1, participants, treatment with TZDs for 3 to 24 months decreased bone mineral density measured by DEXA at the lumbar spine difference In five studies TZD therapy was discontinued and after weeks there was no increase in bone mineral density indicating no restoration of bone mineral density with cessation of TZD treatment In an observation study each year of TZD use was associated with greater bone loss at the whole body additional loss of The effect of TZD treatment on bone turnover markers varied considerably between individual studies This reduction in bone mass induced by TZD treatment could contribute to the increase in fractures but it is possible that changes in the microarchitecture of bone also plays a role. In preclinical studies pioglitazone administration increased bladder cancer in male rats but not in female rats or in mice, dogs, or monkeys In a number of instances, the development of bladder could not plausibly be related to treatment due to the temporal sequence of drug exposure and cancer diagnosis. After eliminating these patients there were six patients with bladder cancer in the pioglitazone group and three patients in the placebo group After 10 years of follow-up, bladder cancer was reported in 0. Thus, in large randomized trials the data do not definitively support that pioglitazone significantly increases the risk of bladder cancer. The short duration of the randomized studies and infrequent occurrence of bladder cancer make interpretation of these studies difficult. Because of the preclinical data the FDA requested that the manufacturer of pioglitazone initiate a prospective study to examine the relationship between pioglitazone and bladder cancer. This year study of , persons did not find any statistically significant association between pioglitazone treatment and bladder cancer Additionally, in a multinational cohort of 1. Similarly, no association was observed between rosiglitazone and bladder cancer in men or women In a careful review of 23 epidemiological studies Davidson concluded that there was little evidence that pioglitazone increased the risk of bladder cancer The FDA still warns about the possibility of bladder cancer with pioglitazone use and recommends that pioglitazone not be used in diabetic patients with active bladder cancer or history of bladder cancer package insert. Macular edema has been reported in patients taking TZDs , Patients may present with blurred vision or decreased visual acuity or be diagnosed on routine ophthalmologic examination. Most patients had peripheral edema at the time macular edema was diagnosed Some patients had improvement in their macular edema after discontinuation of the TZD As discussed above in the polycystic ovary section, treatment of premenopausal women with PCOS may induce ovulation and thereby result in unplanned pregnancies. In premenopausal anovulatory women started on a TZD one needs to discuss the need for contraception. TZDs are contraindicated in patients with NYHA Class III or IV heart failure. Pioglitazone should not be used in diabetic patients with active bladder cancer or history of bladder cancer. Strong CYP2C8 inhibitors e. Unfortunately, TZDs also have serious side effects, such as CHF, osteoporosis, and weight gain, that limit their use. Clinicians need to balance the advantages and disadvantages of TZDs for the individual patient. Acarbose Precose, Glucobay , miglitol Glycet and voglibose Basen, Voglib are members of the α-glucosidase inhibitor class of oral anti-hyperglycemic compounds that were introduced in the s The recommended starting dosage of acarbose and miglitol is 25 mg given orally three times daily at the start of each meal. The dose of acarbose and miglitol can be adjusted at 4 to 8-week intervals based on one-hour postprandial glucose or A1c levels, and on tolerance. The dosage can be increased from 25 mg tid with meals to 50 mg tid with meals. The maximum dose is mg tid with meals. Note that the dose can be varied based on the amount of carbohydrate in the meal. In some patients one can initiate therapy once a day with the largest meal. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors are competitive, reversible inhibitors of pancreatic α-amylase and membrane-bound intestinal α-glucosidase hydrolase enzymes 16 , Inhibiting these enzymes prevents the metabolism of disaccharides and oligosaccharides into monosaccharides delaying carbohydrate digestion and absorption 16 , Carbohydrate absorption occurs more distally in the intestine reducing the postprandial increase in glucose and lowering prandial insulin levels 16 , Acarbose and miglitol have minimal inhibitory activity against lactase and consequently will not prevent the increase in plasma glucose following the ingestion of milk or cause lactose intolerance package insert. In addition to effecting carbohydrate absorption, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors increase postprandial GLP-1 secretion and reduce glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide GIP secretion The typical decrease in A1c levels is relatively modest with alpha-glucosidase inhibitors 0. The decrease in A1c is predominantly due to decreases in post meal glucose levels and alpha-glucosidase inhibitors have only modest effects on fasting glucose levels 16 , , Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors can be combined with other hypoglycemic drugs with additive effects and are particularly useful to lower postprandial glucose levels 37 , Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors are most effective in patients who ingest a high carbohydrate diet and for this reason have been widely used and very effective in Asian populations These drugs do not cause weight gain and hypoglycemia is uncommon 16 , 37 , If a patient experiences hypoglycemia while taking an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor in combination with insulin or sulfonylureas the patient should be instructed to use glucose gel, tablets, etc. as alpha-glucosidase inhibitors will prevent the breakdown of sucrose and delay glucose absorption resulting in a failure to quickly correct hypoglycemia. Severe hypoglycemia may require intravenous glucose or intramuscular glucagon administration. In the STOP-NIDDM trial 1, subjects with impaired glucose tolerance were randomized to placebo vs. acarbose and followed for 3. Among cardiovascular events, the major reduction was in the risk of myocardial infarction HR 0. In a smaller trial, patients hospitalized for the acute coronary syndrome who were newly diagnosed with IGT were randomly assigned to acarbose or placebo During a mean follow-up of 2. Despite these favorable observations a large trial failed to demonstrate a beneficial effect of acarbose in Chinese patients with impaired glucose tolerance ACE trial In a randomized trial acarbose vs. placebo was compared in 6, patients with coronary heart disease and impaired glucose tolerance. The primary outcome was cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke, hospital admission for unstable angina, and hospital admission for heart failure and patients were followed up for a median of 5 years. The primary outcome was similar in the acarbose and placebo groups hazard ratio 0. No significant differences were seen for death from any cause, cardiovascular death, fatal or non-fatal myocardial infarction, fatal or non-fatal stroke, hospital admission for unstable angina, hospital admission for heart failure, or impaired renal function. Thus, whether acarbose favorably affects cardiovascular disease in patients at high risk for developing diabetes is uncertain. Moreover, the effect of acarbose on cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes is unknown. Acarbose is may result in a very small decrease in weight 0. Gastrointestinal side effects of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors include flatulence, abdominal discomfort, and diarrhea and are very commonly encountered 16 , 37 , These side effects can lead to the inability to tolerate these drugs. A high carbohydrate diet may worsen the GI adverse effects. Over time the GI symptoms tend to decrease as the intestines adapt GI side effects are due to the mechanism of action of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors The inhibition of carbohydrate digestion in the small intestine leads to the delivery of undigested carbohydrates to the large intestine where microorganisms metabolize them into short-chain fatty acids, methane, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen, that can cause abdominal discomfort, increased flatulence, and diarrhea Acarbose, particularly at doses in excess of 50 mg tid, may give rise to elevations of serum transaminases and, in rare instances, hyperbilirubinemia. It is recommended that serum transaminase levels be checked every 3 months during the first year of treatment with acarbose and periodically thereafter. If elevated transaminases are observed, a reduction in dosage or withdrawal of therapy may be indicated, particularly if the elevations persist package insert. Acarbose and miglitol are contraindicated in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, colonic ulceration, intestinal obstruction or those predisposed to intestinal obstruction, patients with chronic intestinal disease, or conditions that will be worsened by the increased gas formation in the intestine 37 package insert. Acarbose is contraindicated in patients with cirrhosis package insert. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors are excellent drugs for lowering postprandial glucose levels. Unfortunately, because of their GI side effects many patients are unable to tolerate these drugs. Additionally, the need for three times a day administration makes it difficult for patients to comply with these drugs. These drugs are very similar and there are only a few differences between these agents. The recommended starting dose of canagliflozin is mg once daily, taken before the first meal of the day. The recommended starting dose of dapagliflozin is 5 mg once daily, taken in the morning, with or without food. In patients tolerating dapagliflozin 5 mg once daily who require additional glycemic control, the dose can be increased to 10 mg once daily. The recommended starting dose of empagliflozin is 10 mg once daily in the morning, taken with or without food. In patients tolerating empagliflozin, the dose may be increased to 25 mg. The recommended starting dose of ertugliflozin is 5 mg once daily, taken in the morning, with or without food. In patients tolerating ertugliflozin 5 mg once daily who require additional glycemic control, the dose can be increased to 15 mg once daily. Before initiating SGLT2 inhibitor therapy one should assess renal function and volume status. The dose of SGLT2 inhibitors may need to be adjusted based on renal function see below. The higher the blood glucose level the greater the quantity of glucose in the urine. Inhibition of SGLT2 by drugs results in glycosuria and can lead to the excretion of 60—90 grams of glucose in the urine per day Figure 8 The amount of glucose excreted in the urine can vary considerably depending on renal function and the degree of hyperglycemia Decreased renal function results in a decrease in filtered glucose and less glucose in the urine while high blood glucose levels increase filtered glucose and increases the loss of glucose in the urine The ability of the inhibition of SGLT2 to lower blood glucose levels is not dependent on insulin action and hence is not affected by insulin levels or insulin resistance As will be discussed below many of the non-glucose lowering benefits and side effects of SGLT2 inhibitors can be explained by the increase in glucose excretion in the urine. It should be recognized that glycosuria results in an osmotic diuresis. Additionally, because the SGLT2 transporters also facilitate the reabsorption of sodium from the filtrate there is also the loss of sodium in the urine. A meta-analysis of 66 randomized trials found that SGLT2 inhibitors decreased A1c levels by 0. The A1c lowering ability of the different SGLT2 inhibitors is similar but A1c is reduced to a slightly greater extent by high-dose canagliflozin, which is probably a result of its additional action of inhibiting SGLT1 in the intestine decreasing dietary glucose absorption , , SGLT2 inhibitors when used as an add-on therapy to metformin, insulin, thiazolidinediones, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, sulfonylureas, or metformin ± DPP-4 inhibitor were similarly effective in reducing A1c levels as when used in monotherapy 16 , The efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors is dependent on renal function and as renal function decreases the ability of these drugs to lower A1c levels diminishes 16 , SGLT2 inhibitors lower both fasting and postprandial glucose levels In monotherapy SGLT2 inhibitors have a low risk of causing hypoglycemia but in combinations with insulin or sulfonylureas may potentiate the development of hypoglycemia In patients in good glycemic control, one often decreases the insulin or sulfonylurea dose when initiating therapy with an SGLT2 inhibitor. SGLT2 inhibitors lead to weight loss 16 , SGLT2 inhibitor-induced weight loss results primarily from a decrease in fat mass, including reductions in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue The weight loss is due to the loss of glucose in the urine, which represents the loss of calories , The excretion of 50 grams of glucose in the urine is equivalent to the loss of calories grams X 4. However, the amount of glucose lost in the urine should result in a greater weight loss than is typically observed and a compensatory increase in food intake blunts the weight loss There are likely to be other homeostatic mechanisms that also play a role in limiting weight loss with SGLT2 inhibitors. Monitoring glycemic control with 1,5-AG assay is not accurate as measurements of 1,5-AG are unreliable in patients taking SGLT2 inhibitors. SGLT2 inhibitors decrease systolic BP by approximately mmHg and diastolic BP by approximately mmHg 16 , Patients with poorly controlled BP at baseline experience the largest reduction in BP SGLT2 inhibitors lower BP by promoting an osmotic diuresis and decreasing intravascular volume Weight loss may also contribute to the decrease in BP. SGLT2 inhibitors cause a small increase in LDL and HDL cholesterol levels. In a meta-analysis of 48 randomized controlled trials SGLT2 inhibitors significantly increased LDL-C 3. It is unlikely that these small changes in LDL-C, HDL-C, and triglyceride levels are of clinical significance. The mechanism for these increases in LDL and HDL cholesterol is unknown but could be due to a decrease in plasma volume. The decrease in triglycerides might be secondary to weight loss. SGLT2 inhibitors lower blood uric acid levels This decrease is due to an increase in uric acid excretion by the kidneys. In an observational study 47, individuals receiving an SGLT2 inhibitor and , receiving a DPP4 inhibitor it was observed that the incidence of gout was There have been several large randomized studies of the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on cardiovascular events published others are in progress. In this study, 7, patients with established cardiovascular disease and T2DM were randomly assigned to receive 10 mg or 25 mg of empagliflozin or placebo once daily and were followed for 3. As compared with placebo, empagliflozin treatment did not result in a significant difference in the occurrence of non-fatal myocardial infarction or strokes. However, empagliflozin resulted in a significantly lower risk of death from cardiovascular causes hazard ratio, 0. The beneficial effects of empagliflozin were noted to occur very rapidly and the beneficial effects on heart failure appeared to be the dominant effect compared to effects on atherosclerotic events. Decreases in cardiovascular outcomes and mortality with empagliflozin occurred across the range of cardiovascular risk Additionally, the reduction in hospitalizations for heart failure and cardiovascular death were observed both in patients with and without heart failure at baseline The effects of placebo vs. The primary outcome was a composite of death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke and the mean follow-up was weeks. The primary outcome was reduced in the canagliflozin group hazard ratio, 0. The effect of canagliflozin on the primary outcome was similar in people with chronic kidney disease and those with preserved kidney function Death from any cause hazard ratio 0. Similarly, canagliflozin treatment did not result in a significant difference in non-fatal strokes or non-fatal myocardial infarctions hazard ratio 0. As seen with empagliflozin, hospitalization for heart failure was markedly reduced hazard ratio 0. In a second canagliflozin trial that focused on patients with kidney disease, a decrease in cardiovascular events was also observed In this double-blind trial 4, patients with chronic kidney disease and T2DM were randomized to canagliflozin mg per day or placebo and followed for a median of 2. The relative benefits of canagliflozin for cardiovascular outcomes was similar in individuals across the spectrum of eGFR levels The effect of dapagliflozin on cardiovascular events has been reported The primary outcome was a composite of major adverse cardiovascular events MACE , defined as cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, or ischemic stroke. The primary efficacy outcomes were MACE and a composite of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure. Dapagliflozin did not result in a lower rate of major adverse cardiovascular events 8. Interestingly, in the patients with a history of a previous MI dapagliflozin reduced the risk of a MACE HR 0. Dapagliflozin reduced the risk of heart failure in patients with and without a history of heart failure but the benefit was greater in patients with a history of heart failure with heart failure HR 0. Dapagliflozin also reduced the risk of heart failure in patients without a history of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease This trial did not demonstrate a significant difference in the primary endpoint MACE nor any components of the primary endpoint. The primary outcome was a composite of worsening heart failure hospitalization or an urgent visit resulting in intravenous therapy for heart failure or cardiovascular death. Treatment with dapagliflozin reduced the primary outcome HR 0. Symptoms of heart failure were also improved with dapagliflozin treatment. Additionally, dapagliflozin reduced the risk of any serious ventricular arrhythmia, cardiac arrest, or sudden death The benefits of dapagliflozin were similar in patients with diabetes and the non-diabetic patients This study demonstrates that an SGLT2 inhibitor is beneficial in patients with pre-existing heart failure and this occurs in both patients with and without diabetes. The primary outcome was a composite of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure. Treatment with empagliflozin reduced the primary outcome HR 0. The beneficial effects were observed in patients with and without diabetes. This study is concordant with the results observed in the DAPA HF trial and demonstrates that SGLT2 inhibitors are beneficial in patients with pre-existing heart failure and this occurs in both patients with and without diabetes. The composite of death from cardiovascular causes or hospitalization for heart failure was decreased in the dapagliflozin group HR 0. Moreover, this benefit occurred rapidly reaching statistical significance at 18 days after randomization. These results indicate that SGLT2 inhibitors are beneficial even in patients with a preserved ejection fraction. Thus, nine randomized trials of SGLT2 inhibitors demonstrated a robust decrease in heart failure table 14 with SGLT2 inhibitor therapy without a consistent strong effect on myocardial infarctions or strokes. In a meta-analysis of eight of these trials not including Emperor Preserved with 59, patients it was observed that SGLT2 inhibitors reduced the risk of all-cause mortality HR 0. The reduction in heart failure was seen in patients with and without diabetes, patients with renal disease, and patients with and without a history of heart failure. The Emperor Preserved trial demonstrated that patients with a preserved ejection fraction also benefit from treatment with a SGLT2 inhibitor. Finally, the EMPULSE trial demonstrated that starting empagliflozin during the hospitalization for heart failure was beneficial For additional information see the section on drugs that inhibit both SGLT1 and 2. The mechanisms accounting for the beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on heart failure are uncertain Glycemic control was better in the SGLT2 inhibitor treated patients but it is doubtful that this modest decrease in glucose could account for the observed results additionally benefit in non-diabetics makes a glucose effect very unlikely. SGLT2 inhibitor treatment was associated with small reductions in weight, waist circumference, uric acid level, and systolic and diastolic blood pressure, with no increase in heart rate and small increases in both LDL and HDL cholesterol. Whether these changes played a role in reducing events remains to be determined but it is unlikely that these play a major role as other treatments that effect these factors do not markedly diminish the risk of heart failure events. It is possible that hemodynamic changes secondary to the osmotic diuresis induced by SGLT2 inhibitors contributed to the beneficial effects. Additionally, SGLT2 inhibitors increase free fatty acid levels and glucagon secretion, which promotes the production of ketone bodies such as beta-hydroxybutyrate that are utilized by the heart for energy production It is possible that this alternative source of energy could be protective for heart function. Finally, there may be direct effects of SGLT2 inhibition on myocardial and renal metabolism , , Further studies are required to better elucidate the mechanism of the beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on heart failure. The large randomized SGLT2 inhibitor cardiovascular outcome trials described above also examined the effect of these drugs on renal disease. The effect of empagliflozin on renal outcomes was studied in 4, patients with T2DM who were randomized to empagliflozin 10 mg or 25 mg or placebo The prespecified outcomes were progression to macroalbuminuria, doubling of the serum creatinine level, initiation of renal-replacement therapy, or death from renal disease and incident albuminuria. Worsening nephropathy occurred in While empagliflozin caused an initial decrease in eGFR over the long term eGFR decreased in the placebo group at a more rapid rate than the empagliflozin group. Additionally, patients treated with empagliflozin were more likely to convert from microalbuminuria to normoalbuminuria hazard ratio [HR] 1. Similar to the results seen with empagliflozin, canagliflozin has also been shown to decrease renal disease. Progression of albuminuria occurred less frequently in the canagliflozin group hazard ratio of 0. In addition, regression of albuminuria also occurred more frequently in the canagliflozin group hazard ratio, 1. Annual eGFR decline was slower slope difference between groups 1. The CREDENCE Trial focused on patients with renal disease. In a double-blind trial 4, patients with T2DM and chronic kidney disease were randomized to canagliflozin or placebo and followed for a median of 2. Benefits were seen regardless of baseline eGFR. As seen in the other SGLT2 inhibitor studies there was a decrease in the development of renal disease with the incidence of the renal outcome 4. Excluding death from cardiovascular causes as part of the composite endpoint, the reduction in renal events was even more impressive HR 0. The risk of end-stage renal disease or renal death was lower in the dapagliflozin group than in the placebo group HR 0. There was a trend towards benefit with dapagliflozin treatment that was not statistically significant due to a small number of events HR 0. The annual rate of decline in the eGFR was decreased in the empagliflozin group compared to the placebo group Additionally, a composite renal outcome chronic dialysis or renal transplantation or a profound, sustained reduction in the eGFR was decreased in the empagliflozin group HR 0. All of the components of this primary outcome were decreased in the dapagliflozin group. Thus, similar to the CREDENCE trial, this trial demonstrates that dapagliflozin decreases renal disease progression in patients with pre-existing renal disease. Moreover, this benefit is seen in patients with and without diabetes. Finally, benefit was observed in the dapagliflozin group regardless of the type of kidney disease diabetic, ischemic, hypertensive, glomerulonephritis, other, or unknown Multiple trials clearly demonstrate that SGLT2 inhibitors have beneficial effects on renal function and decrease the development and progression of renal disease Table In a meta-analysis of these 8 trials with 59, patients there was a robust decrease in the composite end points of renal disease HR 0. The benefits are observed in patients with and without diabetes, with and without renal disease, and also in patients with heart failure. In a smaller meta-analysis this renal disease benefit was seen in patients with and without atherosclerosis These renal benefits are independent of improvement in glycemic control and occurs in patients without diabetes The mechanism accounting for this effect is unknown but a leading hypothesis is that an increase of sodium chloride in the macula densa due to SGLT2 inhibition triggers a cascade that reduces GFR through constriction of the afferent glomerular arterioles tubuloglomerular feedback , This would reduce glomerular hydrostatic pressure and initially decrease GFR, an effect that is observed with SGLT2 treatment, but in the long run this decrease in GFR protects the kidney from damage resulting in improved kidney function long-term Numerous studies have shown that treatment with SGLT-2 inhibitors decrease liver enzymes 96 , - Moreover, studies have shown a decrease in liver fat and liver stiffness 96 , , , - A study of 5 patients showed an improvement in liver histology after 24 weeks of therapy with canagliflozin Further studies are required to determine whether SGLT-2 inhibitors will result in clinical benefits in patients with NAFLD and NASH. The decrease in all-cause mortality was seen with all of the SGLT2 inhibitors but was not statistically significant with ertugliflozin. In a meta-analysis of 51 randomized controlled trials involving 24, patients it was noted that the frequency of side effects was similar with high dose and low dose SGLT-2 inhibitors In some but not all studies an increased risk of urinary tract infections was observed with SGLT2 inhibitors 16 , In the large randomized cardiovascular outcome trials, an increase in urinary tract infections were not observed , , In a meta-analysis of 10 large outcome trials with 71, participants the relative risk of urinary tract infection was minimal RR 1. In a large meta-analysis of 86 randomized trials with 50, patients an increase in urinary tract infections was also not observed The potential increase in the occurrence and severity of urinary tract infections is due to the glycosuria as glucose is an excellent substrate for the growth of micro-organisms. Genital mycotic infections mainly balanitis and vulvovaginitis are increased with SGLT2 inhibitor treatment The risk of genital mycotic infections is greater in women than men. In a meta-analysis that included over patients treated with canagliflozin mg or mg vs. In uncircumcised men the risk of genital mycotic infections is greater than in circumcised men. Genital mycotic infections are the most common side effect seen with SGLT2 inhibitors but fortunately these infections are generally mild and relatively easy to treat The increase in genital mycotic infections is due to the glycosuria as glucose is an excellent substrate for the growth of Candida. Fournier gangrene FG is a necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum that is characterized by a rapidly progressive necrotizing infection of the external genitalia, perineum, and perianal region FG occurs most commonly in males and is a rare condition with an incidence of 3. In a recent case series of 59 patients over a year period at a single institution, the incidence was estimated at 32 cases per , admissions Risk factors included very high A1c mean 9. FG is a urologic emergency and requires treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics and immediate surgical intervention A recent report described 55 FG cases in patients treated with SGLT2 inhibitors in the last 6 years since they were approved for use in the US In contrast, only 19 cases of FG were reported in 35 years among patients receiving other hypoglycemic drugs. All of the SGLT2 inhibitors were associated with FG except ertugliflozin, which is likely explained by this drug only recently being approved for the treatment of diabetes. However, the authors were unable to assess the incidence of FG or whether SGLT2 inhibitors were causative. A second study compared the occurrence of FG in patients treated with SGLT2 inhibitors Early recognition of FG is essential to reduce morbidity and mortality. Typical presentations include systemic symptoms, such as fatigue, fever, and malaise, and local symptoms that include tenderness, erythema, and swelling Pain out of proportion to the clinical findings is highly suggestive of necrotizing fasciitis SGLT2 inhibitors induce an osmotic diuresis This effect can result in postural dizziness, orthostatic hypotension, falls, and dehydration, particularly in elderly individuals, patients with kidney disease, patients on either diuretics or medications that interfere with the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system e. In a meta-analysis of 10 large outcome studies the risk of volume depletion was modestly increased RR 1. Volume status should be determined prior to initiating therapy with an SGLT2 inhibitor. SGLT2 inhibitors have been reported to cause acute kidney injury It is likely that volume depletion and hypotension lead to the acute kidney injury In an analysis of two large health care utilization cohorts SGLT2 inhibitors were not associated with an increased risk of acute kidney injury Similarly, in the cardiovascular outcome studies described earlier an increase in acute kidney injury was not observed. In fact, in a meta-analysis of 4 large studies EMPA-REG, CANVAS, CREDENCE, and DECLARE-TIMI 58 a decrease in acute kidney injury was observed Risk ratio 0. Similarly, a meta-analysis of 10 studies with 71, participants also did not observe an increase in acute kidney injury and in fact observed a decrease RR 0. Even in patients over age 75 years of age an increase in acute kidney injury was not observed with SGLT2 treatment Before initiating SGLT2 inhibitor therapy one should consider factors that may predispose patients to acute kidney injury including hypovolemia, chronic renal insufficiency, congestive heart failure, and concomitant medications diuretics, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, NSAIDs. Consider temporarily discontinuing SGLT2 inhibitors in any setting of reduced oral intake such as acute illness or fasting or fluid losses such as gastrointestinal illness or excessive heat exposure package insert. Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA has been observed in patients with T2DM treated with SGLT2 inhibitors but is a rare side effect 16 , In some instances, the glucose levels are not very elevated despite the patient having DKA euglycemic DKA and this can result in a delay in diagnosing DKA SGLT2 inhibitors were associated with approximately twice the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis compared to treatment with DPP-4 inhibitors Additionally, in several of the large cardiovascular studies described above an increase in DKA was observed CANVAS Trial- canagliflozin 0. placebo 0. In a meta-analysis of 10 studies with 71, participants the risk of DKA was increased RR 2. Many of the DKA events occurred in patients with T2DM treated with insulin who had reduced or stopped insulin or experienced an intercurrent illness that could precipitate DKA 16 , In some instances, the patients were thought to have T2DM but actually had latent autoimmune diabetes of adults LADA , a form of Type 1 diabetes The hyperglycemia in DKA associated with SGLT2 inhibitors is typically mild because the SGLT2 inhibitors reduce blood glucose levels SGLT2 inhibitors should be temporarily discontinued in clinical situations known to predispose to ketoacidosis e. DKA developing during hospitalizations has been described emphasizing the need for vigilance when continuing SGLT-2 inhibitors in patients admitted to the hospital Patients should be educated regarding this potential complication and in high-risk patients for example patients on insulin therapy with a history of poor glycemic control or DKA one could provide the patient with methods to measure ketone levels at home to facilitate the early diagnosis of DKA. A possible mechanism for the increased risk of DKA is SGLT2 inhibitors increasing plasma glucagon levels thereby increasing ketone production , In combination with the low insulin levels this could potentiate the development of DKA. In the CANVAS cardiovascular outcome study, the rate of all fractures was higher in the canagliflozin group than in the placebo group A similar trend was observed for low-trauma fracture events canagliflozin placebo 9. The incidence of fractures in the CANVAS study was increased with canagliflozin vs. placebo across subgroups based on sex, age, duration of Type 2 diabetes, baseline eGFR, and prior fracture history Notably, the increase in fractures associated with canagliflozin treatment began within weeks of drug initiation indicating that the increased risk occurs rapidly In contrast, both the EMPA-REG, VERTIS, and DECLARE cardiovascular outcome studies did not demonstrate an increase in fractures with empagliflozin or dapagliflozin, respectively , , Similarly, in a pooled analysis of 8 randomized canagliflozin studies with participants CANVAS trial excluded an increase in fractures was not observed Moreover, in a meta-analysis of 27 randomized controlled trials with an average duration of 64 weeks that compared the efficacy and safety of SGLT2 inhibitors to a placebo in 20, participants there was no increased risk of fractures with SGLT2 inhibitor treatment RR 1. Similarly, a meta-analysis of 10 large outcome studies also did not observe an increase in fractures RR 1. Several studies have examined the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on bone mineral density. Canagliflozin was associated with a decrease in total hip bone mineral density over weeks, placebo-subtracted changesmg In a 2-year study dapagliflozin did not significantly affect bone mineral density at the lumbar spine, femoral neck, or total hip In a week study ertugliflozin also had no adverse effect on bone mineral density Thus, the evidence that SGLT2 inhibitors increase the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, with the possible exception of canagliflozin, is not very strong. One should recognize though, that the hypovolemia and hypotension could increase the risk of falls and thereby increase the risk of fractures in susceptible individuals. In the CANVAS study described above, canagliflozin was associated with an increased risk of amputations hazard ratio, 1. Amputation risk was strongly associated with baseline history of prior amputation and risk factors for amputation peripheral vascular disease and neuropathy. The risk of amputation was low with 6. The basis for the increase in amputations is unknown. However, the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial with empagliflozin, the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial with dapagliflozin, and the VERTIS CV trial with ertuglifozin did not report an increase in amputations in the patients treated with an SGLT2 inhibitor , , , Moreover, in the CREDENCE trial, canagliflozin also did not cause an increase in amputations in the patients treated with the SLGT2 inhibitor placebo group RR 1. Given that only one of eight large randomized trials has demonstrated an increased risk of amputations it is unlikely that SGLT2 inhibitors significantly increase the risk of amputations. Nevertheless, before initiating SGLT2 inhibitor therapy one should consider factors in the patient history that may predispose them to the need for amputations, such as a history of prior amputation, peripheral vascular disease, severe neuropathy, and diabetic foot ulcers and weigh the risks and benefits of therapy package insert. Because of the risk of hypovolemia, hypotension, and DKA the administration of SGLT2 inhibitors should be suspended during acute illness or planned surgical procedures. SGLT2 inhibitor therapy may be resumed following recovery. This view needs to be modified based on the results of the DARE 19 study In this study patients hospitalized with COVID and with at least one cardiometabolic risk factor i. While dapagliflozin did not result in a statistically significant risk reduction in organ dysfunction or death, or improvement in clinical recovery, the drug was well tolerated indicating that SGLT2 inhibitors can be safely given to hospitalized patients if there are strong indications for their use. The dose of SGLT2 inhibitors needs to be adjusted based on renal function. Therefore, renal function needs to be assessed prior to initiating therapy and periodically thereafter. Dosage recommendations for dapagliflozin and canagliflozin are shown in tables 16 and Data are insufficient to provide a dosing recommendation in patients who have type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease with an eGFR less than 30 or who have heart failure with reduced ejection fraction with an eGFR less than Ertugliflozin is not recommended in patients with an eGFR less than 45 and is contraindicated in patients on dialysis. SGLT2 inhibitors are effective at lowering glucose levels and even more importantly have beneficial effects on heart failure and renal disease. The major side effect is genital mycotic infections, which usually are mild and respond to treatment. In patients with pre-existing cardiovascular disease, at high risk for cardiovascular disease particularly heart failure, or with renal disease SGLT2 inhibitors are a leading therapeutic choice. Sotagliflozin Zynquista inhibits both SGLT1 and SGLT2 Sotagliflozin was approved in Europe for the treatment of patients with type 1 diabetes but is no longer available. In the US the drug was not approved. The recommended dose of sotagliflozin was mg once a day before the first meal of the day. After 3 months, the dose may be increased to mg once a day if additional blood sugar control is needed package insert. Because of an increased risk of diabetic ketoacidosis precautions should be taken to reduce this potential side effect. It is recommended that patients obtain several baseline blood or urine ketone levels over one to two weeks prior to initiation of sotagliflozin therapy and patients should become familiar with how their behaviors and circumstances affect their ketone levels. During the initial one to two weeks of treatment with sotagliflozin, ketones should be monitored on a regular basis. Measurement of blood ketone levels is preferred over urine package insert. Subsequent bolus doses should be adjusted individually based on blood glucose results. No reduction in basal insulin is recommended when initiating sotagliflozin. Subsequently, basal insulin should be adjusted based on blood glucose results. When needed, insulin dose reduction should be done cautiously to avoid ketosis and DKA package insert. The mechanism by which inhibition of SGLT2 decreases glucose levels was discussed in the prior section on SGLT2 inhibitors. Inhibition of SGLT1 will have additional effects. Moreover, SGLT1 is expressed in the small intestine and facilitates the absorption of dietary glucose , , SGLT1 expression in the small intestine is increased in patients with diabetes , Inhibition of SGLT1 delays, and perhaps reduces, glucose absorption, and enhances circulating levels of GLP-1 reducing post-prandial glucose excursions , - Finally, SGLT1 is expressed in human heart capillaries and whether this plays a role in cardiac protection remains to be determined Baseline A1c was 7. At 52 weeks the difference in body weight between the placebo group and mg sotagliflozin group was Notably hypoglycemia was not increased with sotagliflozin treatment. However, DKA occurred more frequently with sotagliflozin treatment placebo 0. Hypoglycemia was not increased with sotagliflozin treatment. The baseline A1c was 8. Notably the risk of DKA was increase with sotagliflozin treatment sotagliflozin 3. Thus, in patients with T1DM sotagliflozin causes a modest reduction in A1c and body weight but increases the risk of DKA. Studies of the effect of sotagliflozin on glycemic control in patients with T2DM have not been as extensive as in patients with T1DM. As expected, there was a decrease in body weight and an increase in urinary glucose excretion with sotagliflozin treatment. The primary end point was the total number of deaths from cardiovascular causes and hospitalizations and urgent visits for heart failure first and subsequent events. Because of loss of funding from the sponsor the study was stopped early and the median duration of follow-up was 9 months. The primary end-point was reduced in the sotagliflozin group vs. placebo group HR 0. This study demonstrates benefits in patients with a reduced or preserved ejection fractions and that treatment initiated during an acute heart failure episode is beneficial. DKA was uncommon in both the sotagliflozin group 0. The primary end point was the composite of the total number of deaths from cardiovascular causes, hospitalizations for heart failure, and urgent visits for heart failure. Sotagliflozin treatment decreased the primary end point HR 0. DKA while infrequent was increased in the sotagliflozin group 0. While outcome studies are not available in patients with T1DM it has been shown that sotagliflozin has effects on kidney function that are similar to what has been observed in patients with T2DM. Specifically, there was an acute decrease in eGFR and a decrease in albuminuria These observations suggest that the beneficial effects on renal outcomes seen with SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with T2DM and non-diabetics will also occur in patients with T1DM. The side effects of sotagliflozin are similar to those described previously for SGLT2 inhibitors. In addition, sotagliflozin also causes diarrhea and flatulence due to the inhibition of SGLT1 mediated glucose uptake in the small intestine. In patients with T1DM sotagliflozin modestly reduces A1c levels and body weight but increases the risk of DKA. Because of the increased risk of DKA this drug is no longer approved for use. In patients with T2DM sotagliflozin use is not approved in the US or Europe. While studies have shown beneficial effects of sotagliflozin on cardiovascular disease it is not clear whether this benefit is solely due to inhibition of SGLT2 or whether inhibition of SGLT1 plays a significant role. In , a quick-release formulation of bromocriptine Cycloset, bromocriptine-QR was approved to improve glycemic control in patients with T2DM , It can be used to improve glycemic control in patients with T2DM either as monotherapy or in combination with other hypoglycemic drugs , Bromocriptine-QR should be initiated at one tablet 0. The dose can be increased by one tablet per week until a maximum daily dose of 6 tablets 4. Taking bromocriptine-QR with food is recommended to decrease gastrointestinal side effects Bromocriptine-QR decreases insulin resistance resulting in an increase in glucose disposal and a decrease in hepatic glucose production Bromocriptine-QR does not increase insulin levels Thus, the effectiveness of bromocriptine-QR will be greatest in patients that are insulin resistant and produce insulin Based on animal studies it is thought that bromocriptine-QR acts on the central nervous system, particularly the hypothalamus, to increase insulin sensitivity in liver, muscle, and adipose tissue In a 24 week monotherapy study the A1c level was 0. Both fasting and postprandial glucose levels were decreased with bromocriptine-QR treatment A trial adding bromocriptine-QR to sulfonylurea therapy demonstrated a 0. As in the monotherapy study fasting glucose, postprandial glucose, and triglyceride levels were decreased with no change in LDL or HDL cholesterol levels Addition of bromocriptine-QR to other hypoglycemic drugs including insulin results in an approximate decrease in A1c of 0. Hypoglycemia is a rare side effect with use of bromocriptine-QR alone, but is increased with use of insulin secretagogue therapy or insulin , Bromocriptine-QR modestly decreases systolic and diastolic blood pressure , Bromocriptine-QR treatment decreases triglyceride levels but has no significant effect on LDL or HDL cholesterol levels , |
| Latest Treatment Options for Diabetes | The mechanism accounting for this effect is unknown but a leading hypothesis is that an increase of sodium chloride in the macula densa due to SGLT2 inhibition triggers a cascade that reduces GFR through constriction of the afferent glomerular arterioles tubuloglomerular feedback , Metformin should be temporarily discontinued when patients are unable to eat or drink. The durability of glycemic control with TZDs is more prolonged than with either sulfonylureas or metformin These medications can result in large benefits on lowering blood glucose and body weight. Notably hypoglycemia was not increased with sotagliflozin treatment. |
| Self-assessment Quiz | Follow Mayo Clinic. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Your health care provider can explain how one medication or multiple medications may fit into your diabetes treatment plan. In an observational study 47, individuals receiving an SGLT2 inhibitor and , receiving a DPP4 inhibitor it was observed that the incidence of gout was The effect of dapagliflozin on cardiovascular events has been reported This is because an unacceptable level of a probable carcinogen cancer-causing agent was found in some extended-release metformin tablets. |
| Latest news | While weight increases, waist circumference typically remains stable. Request Appointment. In addition, sotagliflozin also causes diarrhea and flatulence due to the inhibition of SGLT1 mediated glucose uptake in the small intestine. Reaching and maintaining a moderate weight is a key part of diabetes management and prevention for many people, particularly in relation to type 2 diabetes. The Emperor Preserved trial demonstrated that patients with a preserved ejection fraction also benefit from treatment with a SGLT2 inhibitor. A medication may work by:. The aim is to mimic how the body would produce insulin throughout the day to promote efficient energy intake. |
0 thoughts on “Oral diabetes drug list”