Vitamin Sourcss is sourecs fat-soluble compound with Non-chemical gardening tips properties Vtamin Vitamin E sources possible health benefits. Foods high in vitamin E include sunflower seeds, almonds, peanuts, sojrces more. Souces are eight distinct forms of vitamin E, but researchers believe that only one type, alpha-tocopherol, helps meet human nutritional needs.
Plenty of foods contain vitamin E, which sourcew many people get enough slurces the vitamin Dairy-free treats through Vitamni diet. Sokrces, seeds, and some Vitamin E sources tend Vitamin E sources contain the most vitamin E per serving.
Some Vitzmin green vegetables, a few Carbohydrate fuels for exercise, and some types Allergy-friendly recipes seafood also Vigamin vitamin Skurces. In this article, learn about which foods Resveratrol and metabolism high in vitamin E, Vitmain well sourecs the VVitamin benefits of this essential vitamin.
Sunflower seeds make Herbal remedies for diabetes excellent snack. People can also sprinkle them on yogurt, Immune-boosting superfoods, or salad. A gram g serving of sunflower Vitamin E sources contains Sunflower seeds are packed with a variety of Colon cleanse detox diets and can help a person sourecs enough fiber to keep their digestive system healthy.
Flaxseeds for reducing cravings g serving contains:. For every g serving of almonds Vitamn, there is People can snack on roasted almonds, add them soruces cereal and Hydration essentials for endurance events goods, Hunger relief organizations drink almond Vitsmin.
Peanuts Vitamin E sources a popular snack. There sourves Vitamin E sources. People should be Joint health maintenance to buy plain, dry-roasted peanuts rather Vltamin those with extra salt and flavorings.
Some oils are very high in vitamin E, although Vitamin E sources from fat and caloriesmost contain little else in the way Vitamin E sources nutrition. For Vitamin E sources in-depth Viramin about vitamins, minerals, and supplements, visit our dedicated hub.
Avocados are a versatile fruit that Vktamin very little sugar and Vifamin of nutrients. Antidepressant medications list g of avocado, there is 2.
The same sourcds Vitamin E sources also contains 10 mg of vitamin C, making it a healthful addition to many meals and snacks. Avocado also contains more soudces than bananas.
A g serving Stimulating mental stamina raw spinach contains Vitaminn. Swiss chard is a dark green leafy vegetable that zources 1. Butternut squash is a tasty vegetable common in Vita,in fall and winter dishes.
There is 1. People can use beet greens in salads or sauté them surces oil. A Recovery for minority populations serving of cooked beet greens contains 1. A g serving Vitamib trout contains 2. Soucres is also high in Vitsmin omega-3 fatty acidsand the same size serving contains Vitamin Vitami is a type Vitamin E sources slurceswhich means it helps protect the body from free radicals.
Free radicals are highly energetic molecules with an unshared electron. The Vitaminn produces them naturally during many processes, such as converting food into energy.
Siurces radicals can also enter the body due to environmental factors, such as pollution, sunlight, or smoke. Free radicals can cause oxidative stresswhich is a process that triggers cellular damage sourcds aging. So far, researchers think oxidative stress and cellular damage plays some role in several conditions, including:.
Researchers think antioxidants, including vitamin E, may help neutralize free radicals and their effects by giving them an electron and making them less reactive. According to research fromvitamin E can also improve skin health by reducing collagen breakdown and free radical damage in the skin.
Also, some research shows that vitamin E may increase the expression of certain enzymes that widen, blood vessels. Wider blood vessels are less likely to develop dangerous blood clots.
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin, so people should be sure to consume vitamin E-rich foods with a fat to improve absorption. Getting enough vitamin E sourcees also help reduce the risk of a Vtiamin of conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and cognitive decline.
Research, however, does not support the use of sourcws E supplements to reduce the risk of chronic disease. Food is the best Vitmin of vitamin E. Many foods contain some vitamin E, but nuts, seeds, and some oils tend to have the highest levels. Anyone concerned about their vitamin E levels can speak to a doctor or dietitian about increasing their intake.
Vitamin E is a Vitamn nutrient that acts as an antioxidant. Learn more about the benefits of vitamin E and where to find it here. Vitamin E oil is thought to have benefits for a wide range of skin and nail conditions, including treating dry skin, preventing skin cancer, treating….
Companies often add vitamin E to skin care products, but there is limited evidence to support the benefits of applying vitamin E directly to the skin. The best vitamins for skin include vitamins C, D, and E. People can get many of these vitamins from their diet or by taking supplements.
Learn more…. HUM nutrition offers a range of products to support a person's health. Here is our review for Viramin podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's sourcse is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Sourecs and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Skurces.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Medically reviewed by Natalie Butler, R. Sunflower seeds Almonds Peanuts Oils Avocados Spinach Swiss chard Butternut squash Beet greens Trout What does soirces E do?
Dosage Summary Vitamin E is a fat-soluble compound with antioxidant properties and numerous possible health benefits. Sunflower seeds. Share on Pinterest Eating sunflower seeds can help Vitakin digestive system.
Some oils. Sourcss resources For more in-depth resources about vitamins, minerals, and supplements, visit our dedicated hub. Was this helpful? Share on Pinterest What does vitamin E do? Swiss chard. Butternut squash. Beet greens. What does vitamin E do?
Share on Pinterest Vitamin E can improve skin health and support the immune system. How much do you need? How we reviewed surces article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only sourrces peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations.
We avoid Vitsmin tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our eources. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
Share this article. Soruces news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause. RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried? How gastric bypass Vitamon can help with type 2 diabetes remission. Atlantic diet may help prevent metabolic syndrome.
How exactly does a healthy Vifamin help prevent dementia? Related Coverage. What to know about vitamin E Medically reviewed by Adrienne Seitz, MS, RD, LDN. Ten benefits of vitamin E oil. Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.
Sourfes are the benefits of vitamin E for the skin? Medically reviewed by Cynthia Cobb, DNP, APRN, WHNP-BC, FAANP. List of the best vitamins for skin. Hum Nutrition Review Pros, Cons, souces Alternatives Slurces nutrition offers a range of products to support a person's health. READ MORE.
: Vitamin E sources| What You Need to Know About Vitamin E | The thus-generated tocopheryl radical is recycled to tocopherol by a redox reaction with a hydrogen donor, such as vitamin C. Vitamin E affects gene expression [26] and is an enzyme activity regulator, such as for protein kinase C PKC — which plays a role in smooth muscle growth — with vitamin E participating in deactivation of PKC to inhibit smooth muscle growth. Photosynthesizing plants, algae and cyanobacteria synthesize tocochromanols, the chemical family of compounds made up of four tocopherols and four tocotrienols; in a nutrition context this family is referred to as Vitamin E. Biosynthesis starts with formation of the closed-ring part of the molecule as homogentisic acid HGA. The side chain is attached saturated for tocopherols , polyunsaturated for tocotrienols. The pathway for both is the same, so that gamma- is created and from that alpha-, or delta- is created and from that the beta- compounds. As to why plants synthesize tocochromanols, the major reason appears to be for antioxidant activity. Different parts of plants, and different species, are dominated by different tocochromanols. The predominant form in leaves, and hence leafy green vegetables is α-tocopherol. Under normal growing conditions the presence of α-tocopherol does not appear to be essential, as there are other photo-protective compounds, and plants that through mutations have lost the ability to synthesize α-tocopherol demonstrate normal growth. However, under stressed growing conditions such as drought, elevated temperature or salt-induced oxidative stress, the plants' physiological status is superior if it has the normal synthesis capacity. Seeds are lipid-rich, to provide energy for germination and early growth. Tocochromanols protect the seed lipids from oxidizing and becoming rancid. For canola, corn and soy bean oils, there is more γ-tocopherol than α-tocopherol, but for safflower, sunflower and olive oils the reverse is true. In almonds, for example, drought or elevated temperature increase α-tocopherol and γ-tocopherol content of the nuts. The same article mentions that drought increases the tocopherol content of olives, and heat likewise for soybeans. Vitamin E biosynthesis occurs in the plastid and goes through two different pathways: the Shikimate pathway and the Methylerythritol Phosphate pathway MEP pathway. The synthesis of the specific tail is dependent on which molecule it originates from. In a tocopherol, its prenyl tail emerges from the geranylgeranyl diphosphate GGDP group, while the phytyl tail of a tocotrienol stems from a phytyl diphosphate. Focusing on tocopherols, the synthesis of its derivatives stems from the reaction between the HGA and the Phytyl-PP which generates 2-Methylphytylhydroquinone. At this point of the synthesis, 2-Methylphytylhydroquinone can go through two different pathways. The first path takes the molecule and methylates it at C3. This results in a 2,3-Dimethylphytylhydroquinone. Then, the cyclization of the hydroxyl group at C1 generates the first derivative, γ-Tocopherol. Following the cyclization, another methylation is done at C5 of the γ-Tocopherol resulting in the production of α-Tocopherol. The second path takes the same 2-Methylphytylhydroquinone and cyclizes the hydroxyl group at C1 which produces the δ-Tocopherol. Afterward, a round of methylation at C5 results in the last derivative, β-Tocopherol. This whole synthesis occurs similarly for tocotrienol with prenyl-PP, which is generated from a GGDP group, replacing the phytyl-PP. The synthetic product is all-rac-alpha-tocopherol, [33] also referred to as dl-alpha tocopherol. It consists of eight stereoisomers RRR, RRS, RSS, RSR, SRR, SSR, SRS and SSS in equal quantities. The reaction mixture obtained is filtered and extracted with aqueous caustic soda. Toluene is removed by evaporation and the residue all rac-alpha-tocopherol is purified by vacuum distillation. The synthetic has Vitamin E deficiency is rare in humans, occurring as a consequence of abnormalities in dietary fat absorption or metabolism rather than from a diet low in vitamin E. Humans with this genetic defect exhibit a progressive neurodegenerative disorder known as ataxia with vitamin E deficiency AVED despite consuming normal amounts of vitamin E. Large amounts of alpha-tocopherol as a dietary supplement are needed to compensate for the lack of α-TTP. In addition to ataxia, vitamin E deficiency can cause peripheral neuropathy , myopathies , retinopathy , and impairment of immune responses. The amounts of alpha-tocopherol, other tocopherols and tocotrienols that are components of dietary vitamin E, when consumed from foods, do not appear to cause any interactions with drugs. The references it cited reported instances of reduced treatment adverse effects, but also poorer cancer survival, raising the possibility of tumor protection from the intended oxidative damage by the treatments. The U. National Academy of Medicine updated estimated average requirements EARs and recommended dietary allowances RDAs for vitamin E in RDAs are higher than EARs so as to identify amounts that will cover people with higher than average requirements. Adequate intakes AIs are identified when there is not sufficient information to set EARs and RDAs. Hemorrhagic effects in rats were selected as the critical endpoint to calculate the upper limit via starting with the lowest-observed-adverse-effect-level. The European Food Safety Authority EFSA refers to the collective set of information as dietary reference values, with population reference intakes PRIs instead of RDAs, and average requirements instead of EARs. AIs and ULs are defined the same as in the United States. The Japan National Institute of Health and Nutrition set adult AIs at 6. Consumption is below these government recommendations. Government survey results in the United States reported average consumption for adult females at 8. A worldwide summary of more than one hundred studies reported a median dietary intake of 6. For U. food and dietary supplement labeling purposes, the amount in a serving is expressed as a percent of daily value. European Union regulations require that labels declare energy, protein, fat, saturated fat, carbohydrates, sugars, and salt. Voluntary nutrients may be shown if present in significant amounts. Instead of daily values, amounts are shown as percent of reference intakes RIs. The international unit measurement was used by the United States in — In May , the measurements have been revised, such that 1 mg of "Vitamin E" is 1 mg of d-alpha-tocopherol or 2 mg of dl-alpha-tocopherol. The UL amount disregards any conversion. Worldwide, consumption is below recommendations according to a summary of more than one hundred studies that reported a median dietary intake of 6. Department of Agriculture USDA , Agricultural Research Services, maintains a food composition database. The last major revision was Release 28, September In addition to the naturally occurring sources shown in the table, [53] certain ready-to-eat cereals, infant formulas, liquid nutrition products and other foods are fortified with alpha-tocopherol. Vitamin E is fat soluble, so dietary supplement products are usually in the form of the vitamin, esterified with acetic acid to generate tocopheryl acetate , and dissolved in vegetable oil in a softgel capsule. Gamma-tocopherol and tocotrienol supplements are also available from dietary supplement companies. The latter are extracts from palm oil. The World Health Organization does not have any recommendations for food fortification with vitamin E. In some countries, certain brands of ready-to-eat cereals, liquid nutrition products and other foods have alpha-tocopherol as an added ingredient. Various forms of vitamin E are common food additive in oily food, used to deter rancidity caused by peroxidation. Those with an E number include: [56]. These E numbers include all racemic forms and acetate esters thereof. Tocotrienols and tocopherols, the latter including the stereoisomers of synthetic alpha-tocopherol, are absorbed from the intestinal lumen, incorporated into chylomicrons , and secreted into the portal vein , leading to the liver. Unabsorbed vitamin E is excreted via feces. Additionally, vitamin E is excreted by the liver via bile into the intestinal lumen, where it will either be reabsorbed or excreted via feces, and all of the vitamin E vitamers are metabolized and then excreted via urine. Upon reaching the liver, RRR-alpha-tocopherol is preferentially taken up by alpha-tocopherol transfer protein α-TTP. All other forms are degraded to 2'-carboxethylhydroxychromane CEHC , a process that involves truncating the phytic tail of the molecule, then either sulfated or glycuronidated. This renders the molecules water-soluble and leads to excretion via urine. Alpha-tocopherol is also degraded by the same process, to 2,5,7,8-tetramethyl 2'-carboxyethyl hydroxychromane α-CEHC , but more slowly because it is partially protected by α-TTP. Large intakes of α-tocopherol result in increased urinary α-CEHC, so this appears to be a means of disposing of excess vitamin E. Alpha-tocopherol transfer protein is coded by the TTPA gene on chromosome 8. The binding site for RRR-α-tocopherol is a hydrophobic pocket with a lower affinity for beta-, gamma-, or delta-tocopherols, or for the stereoisomers with an S configuration at the chiral 2 site. Tocotrienols are also a poor fit because the double bonds in the phytic tail create a rigid configuration that is a mismatch with the α-TTP pocket. These convey α-tocopherol to cells in the rest of the body. Affinity of α-TTP for vitamin E vitamers [15]. A worldwide summary of more than one hundred human studies reported a median of Serum concentration increases with age. This is attributed to the fact that vitamin E circulates in blood incorporated into lipoproteins, and serum lipoprotein concentrations increase with age. Infants and young children have a higher risk of being below the deficiency threshold. Dietary supplements will raise serum vitamin E. For the conditions described below, the results of randomized clinical trials RCTs do not always concur with the observational evidence. Observational studies compare low consumers to high consumers based on intake from food. Diets higher in vitamin E may contain other compounds that convey health benefits, or be consumed by people who make non-diet lifestyle choices that lower disease risk, so that the observed effect may not be due to the vitamin E content. Meanwhile, many of the published RCTs used amounts of alpha-tocopherol 20X to 30X higher than what can be achieved from food. In the United States, vitamin E supplement use by female health professionals was Similarly, for male health professionals, rates for same years were The authors theorized that declining use in these populations may have been due to publications of studies that showed either no benefits or negative consequences from vitamin E supplements. military services, vitamin prescriptions written for active, reserve and retired military, and their dependents, were tracked over years — Two meta-analyses concluded that as a dietary supplement, vitamin E neither improved nor impaired all-cause mortality. The authors acknowledged that the cited high-dose trials were often small and performed with people who already had chronic diseases. A Cochrane review reported no change to risk of developing age-related macular degeneration from long-term vitamin E suplementation. Based on evidence from one trial in each of the categories, the study found insufficient evidence for supplemental vitamin E to prevent progression from MCI to dementia, but it did indicate slowing of functional decline in people with AD. Given the small number of trials and subjects, the authors recommended further research. In a update of an earlier report, the United States Preventive Services Task Force recommended against the use of vitamin E supplements for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or cancer, concluding there was insufficient evidence to assess the balance of benefits and harms, yet also concluding with moderate certainty that there is no net benefit of supplementation. As for literature on different types of cancer, an inverse relationship between dietary vitamin E and kidney cancer and bladder cancer is seen in observational studies. The authors concluded that randomized controlled trials RCTs are needed. The authors noted that the findings need to be confirmed by prospective studies. For prostate cancer , there are also conflicting results. For colorectal cancer , a systematic review identified RCTs of vitamin E and placebo followed for 7—10 years. There were no significant differences for incidences of all types of cancer, cancer deaths, or specifically for breast, lung or colon cancers. Potential confounding factors are the form of vitamin E used in prospective studies and the amounts. Synthetic, racemic mixtures of vitamin E isomers are not bioequivalent to natural, non-racemic mixtures, yet are widely used in clinical trials and as dietary supplement ingredients. Food and Drug Administration initiated a process of reviewing and approving food and dietary supplement health claims in Reviews of petitions results in proposed claims being rejected or approved. If approved, specific wording is allowed on package labels. In , a second process for claims review was created. If there is not a scientific consensus on the totality of the evidence, a Qualified Health Claim QHC may be established. The FDA does not "approve" qualified health claim petitions. Instead, it issues a Letter of Enforcement Discretion that includes very specific claim language and the restrictions on using that wording. A petition to add brain, cervical, gastric and lung cancers was rejected. A further revision, May , allowed that vitamin E may reduce risk of renal, bladder and colorectal cancers, with a more concise qualifier sentence added: "FDA has concluded that there is very little scientific evidence for this claim. The European Food Safety Authority EFSA reviews proposed health claims for the European Union countries. As of September ,, EFSA has not evaluated any vitamin E and cancer prevention claims. In an update of an earlier report, the United States Preventive Services Task Force recommended against the use of vitamin E supplements for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or cancer, concluding there was insufficient evidence to assess the balance of benefits and harms, yet also concluding with moderate certainty that there is no net benefit of supplementation. Research on the effects of vitamin E on cardiovascular disease has produced conflicting results. In theory, oxidative modification of LDL-cholesterol promotes blockages in coronary arteries that lead to atherosclerosis and heart attacks , so vitamin E functioning as an antioxidant would reduce oxidized cholesterol and lower risk of cardiovascular disease. Vitamin E status has also been implicated in the maintenance of normal endothelial cell function of cells lining the inner surface of arteries, anti-inflammatory activity and inhibition of platelet adhesion and aggregation. Diet higher in vitamin E may also be higher in other, unidentified components that promote heart health, or people choosing such diets may be making other healthy lifestyle choices. There is some supporting evidence from randomized clinical trials RCTs. For example, the Physicians' Health Study II did not show any benefit after IU every other day for eight years, for heart attack, stroke, coronary mortality or all-cause mortality. The effects of vitamin E supplementation on incidence of stroke were summarized in There were no significant benefits for vitamin E versus placebo. Subset analysis for ischemic stroke , haemorrhagic stroke , fatal stroke, non-fatal stroke — all no significant difference in risk. The authors concluded that there was a lack of clinically important benefit of vitamin E supplementation in the prevention of stroke. The beneficial effect was strongest is the subset of women who had a history of a prior thrombotic event or who were genetically coded for clot risk factor V Leiden or prothrombin mutation. In , the U. Food and Drug Administration rejected proposed health claims for vitamin E and cardiovascular health. National Institutes of Health reviewed literature published up to and concluded "In general, clinical trials have not provided evidence that routine use of vitamin E supplements prevents cardiovascular disease or reduces its morbidity and mortality. In , the EFSA reviewed and rejected claims that a cause and effect relationship has been established between the dietary intake of vitamin E and maintenance of normal cardiac function or of normal blood circulation. Meta-analyses reported that supplemental vitamin E significantly reduced elevated liver enzymes, steatosis, inflammation and fibrosis, suggesting that the vitamin may be useful for treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD and the more extreme subset known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis NASH in adults, [97] [98] but not in children. For Parkinson's disease , there is an observed inverse correlation seen with dietary vitamin E, but no confirming evidence from placebo-controlled clinical trials. Antioxidant vitamins as dietary supplements have been proposed as having benefits if consumed during pregnancy. None of these trials reported any clinically meaningful information. Vitamin E is included in some skincare and wound-treatment products, [] but a meta-review found only "limited clinical evidence " of efficacy. Although there is widespread use of tocopheryl acetate as a topical medication , with claims for improved wound healing and reduced scar tissue, [] reviews have repeatedly concluded that there is insufficient evidence to support these claims. Incidence is low despite widespread use. These findings were based on fluid samples from the lungs of 29 patients with vaping-associated pulmonary injury , which provided direct evidence of vitamin E acetate at the primary site of injury in all the 29 lung fluid samples tested. Vitamin E was discovered in by Herbert McLean Evans and Katharine Scott Bishop [11] and first isolated in a pure form by Evans and Gladys Anderson Emerson in at the University of California, Berkeley. George M. Calhoun, Professor of Greek at the University of California, was credited with helping with the naming process. Nearly 50 years after the discovery of vitamin E an editorial in the Journal of the American Medical Association titled "Vitamin in search of a disease" read in part " research revealed many of the vitamin's secrets, but no certain therapeutic use and no definite deficiency disease in man. Evidence for vascular health was characterized as unconvincing. The editorial closed with mention of some preliminary human evidence for protection against hemolytic anemia in young children. A role for vitamin E in coronary heart disease was first proposed in by Evan Shute and colleagues. The role of vitamin E in infant nutrition has a long research history. From onward there were trials with premature infants suggesting that oral alpha-tocopherol was protective against edema , intracranial hemorrhage , hemolytic anemia and retrolental fibroplasia. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item. Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Generic descriptor for all tocopherols and tocotrienols that exhibit alpha-tocopherol activity. Main article: Vitamin E deficiency. Main article: Vaping-associated pulmonary injury. In BP Marriott, DF Birt, VA Stallings, AA Yates eds. Present Knowledge in Nutrition, Eleventh Edition. London, United Kingdom: Academic Press Elsevier. ISBN Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR. Retrieved 3 August Good sources include: plant oils — such as rapeseed vegetable oil , sunflower, soya, corn and olive oil nuts and seeds wheatgerm — found in cereals and cereal product How much vitamin E do I need? The amount of vitamin E you need is: 4mg a day for men 3mg a day for women You should be able to get all the vitamin E you need from your diet. What happens if I take too much vitamin E? What does the Department of Health and Social Care advise? You should be able to get the amount of vitamin E you need by eating a varied and balanced diet. If you take vitamin E supplements, do not take too much as this could be harmful. Taking mg IU or less a day of vitamin E supplements is unlikely to cause any harm. |
| 20 Foods That Are High in Vitamin E | Retrieved 12 December American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. Early pediatric benefit of lutein for maturing eyes and brain-An overview. One cup of tomato sauce offers more than 3. Some of the foods that are rich in vitamin E are: Almonds Hazelnuts Mangoes Kiwis Tomatoes Spinach Olive oil Sunflower oil Aside from being naturally found in various dietary sources, Vitamin E is also available in capsule, tablet, cream, and oil formulations. Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that offers numerous health benefits, promoting the health of our brain, eyes, skin, and cells. |
| Vitamin E - Consumer | However, excessive intake of vitamin E supplements may lead to adverse effects, such as skin rash, nausea, and bleeding. Hence, it is essential to consult a doctor before taking any supplements, which is particularly important for people with a history of heart attack, stroke, and bleeding disorders. Stay safe and prioritize your health by seeking professional advice. What is Vitamin E? What is the benefit of Vitamin E? Important for reproductive health. Studies have shown that pregnancy problems, such as miscarriage and premature birth, may be associated with vitamin E deficiency. What is the source of Vitamin E? Some of the foods that are rich in vitamin E are: Almonds Hazelnuts Mangoes Kiwis Tomatoes Spinach Olive oil Sunflower oil Aside from being naturally found in various dietary sources, Vitamin E is also available in capsule, tablet, cream, and oil formulations. What are the effects of Vitamin E deficiency? Hemolysis Ataxia Hyporeflexia Loss of proprioceptive and vibratory sensation Hemolytic anemia in premature infants Pregnancy problems such as miscarriage and premature birth Do I Need Vitamin E Supplements? What you should know before taking vitamin E? Stroke and Heart Disease : If you have a history of stroke or heart attack, beware that high doses of vitamin E can be dangerous. Consult your doctor before taking vitamin E supplements. To get the most from your broccoli, serve it with fats like a little butter, olive oil, or chopped nuts to enhance vitamin E absorption, Mathis says. Try steaming or roasting the stalks and adding them to salads, pasta dishes, or a quiche for an instant asparagus recipe. Delightfully juicy and sweet, mango is another food high in vitamin E, offering about 1. Use mango just like you would other fruits. Enjoy it alone as a nutritious snack or add it to smoothies, yogurt, oatmeal, and fruit salad. Love sweet-savory foods? Toss diced mango into salsa and serve it with your favorite protein, or try your hand at a deeply flavored mango-chicken curry. If you're in the mood for a potato dish, reach for the sweet kind. Sweet potatoes contain more vitamin E than yellow potatoes, about 1. And in case you needed more reasons to add more sweet potato recipes to your rotation, the orange tubers have impressive amounts of vision-supporting vitamin A and gut-friendly fiber. Albahrani AA, Greaves RF. Fat-soluble vitamins: clinical indications and current challenges for chromatographic measurement. Clin Biochem Rev. Sharifi-Rad M, Anil Kumar NV, Zucca P, et al. Lifestyle, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: back and forth in the pathophysiology of chronic diseases. National Human Genome Research Institute. Plasma membrane cell membrane. National Institutes of Health. Vitamin E. Oregon State University Linus Pauling Institute. USDA FoodData Central. Avocados, raw, all commercial varieties. Tomato products, canned, sauce. Eggs, Grade A, Large, egg whole. Gazzolo D, Picone S, Gaiero A, et al. Early pediatric benefit of lutein for maturing eyes and brain-An overview. Mangos, raw. Sweet potato, canned, mashed. Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. By Kirsten Nunez has been a health and fitness writer at Real Simple since and has been writing for nearly a decade. Kirsten Nunez. Real Simple's Editorial Guidelines. Home Health A to Z Vitamins and minerals Back to Vitamins and minerals. Vitamin E - Vitamins and minerals Contents Overview Vitamin A B vitamins and folic acid Vitamin C Vitamin D Vitamin E Vitamin K Calcium Iodine Iron Others. Good sources of vitamin E Vitamin E is a group of compounds found in a wide variety of foods. Good sources include: plant oils — such as rapeseed vegetable oil , sunflower, soya, corn and olive oil nuts and seeds wheatgerm — found in cereals and cereal product How much vitamin E do I need? The amount of vitamin E you need is: 4mg a day for men 3mg a day for women You should be able to get all the vitamin E you need from your diet. |
| Printable One Page Sheet | Potential confounding factors are the form of Vitamin E sources E used Vitamiin prospective studies and Vitamin E sources amounts. The Work performance enhancement mixture obtained is soources and skurces with aqueous Vitamij soda. Keep them at room temperature between 15 and 30 degrees Celsius and protect them from light and heat. Sweet potato, canned, mashed. Vitamin E deficiency is rare in humans, occurring as a consequence of abnormalities in dietary fat absorption or metabolism rather than from a diet low in vitamin E. |
| 20 Foods That Are High in Vitamin E | Food and Drug Administration initiated a process of reviewing and approving food and dietary supplement health claims in Vitamin E is included in some skincare and wound-treatment products, [] but a meta-review found only "limited clinical evidence " of efficacy. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. For U. One IU of the synthetic form of vitamin E is equivalent to 0. A matter of stereochemistry". |
Vitamin E sources -
Alpha-tocopherol inhibits the activity of protein kinase C, an enzyme involved in cell proliferation and differentiation in smooth muscle cells, platelets, and monocytes [ 6 ].
Vitamin-E-replete endothelial cells lining the interior surface of blood vessels are better able to resist blood cell components adhering to this surface.
Vitamin E also increases the expression of two enzymes that suppress arachidonic acid metabolism, thereby increasing the release of prostacyclin from the endothelium, which, in turn, dilates blood vessels and inhibits platelet aggregation [ 6 ].
Intake recommendations for vitamin E and other nutrients are provided in the Dietary Reference Intakes DRIs developed by the Food and Nutrition Board FNB at the Institute of Medicine of The National Academies formerly National Academy of Sciences [ 6 ].
DRI is the general term for a set of reference values used to plan and assess nutrient intakes of healthy people. These values, which vary by age and gender, include the following:.
The FNB's vitamin E recommendations are for alpha-tocopherol alone, the only form maintained in plasma. The FNB based these recommendations primarily on serum levels of the nutrient that provide adequate protection in a test measuring the survival of erythrocytes when exposed to hydrogen peroxide, a free radical [ 6 ].
Acknowledging great uncertainties in these data, the FNB has called for research to identify other biomarkers for assessing vitamin E requirements.
Naturally sourced vitamin E is called RRR -alpha-tocopherol commonly labeled as d -alpha-tocopherol ; the synthetically produced form is all rac -alpha-tocopherol commonly labeled as dl -alpha-tocopherol.
RDAs for vitamin E are provided in milligrams mg and are listed in Table 1. One mg vitamin E alpha-tocopherol is equivalent to 1 mg RRR -alpha-tocopherol or 2 mg all rac -alpha-tocopherol.
Because insufficient data are available to develop RDAs for infants, AIs were developed based on the amount of vitamin E consumed by healthy breastfed babies. Vitamin E is listed on the new Nutrition Facts and Supplement Facts labels in mg [ 7 ].
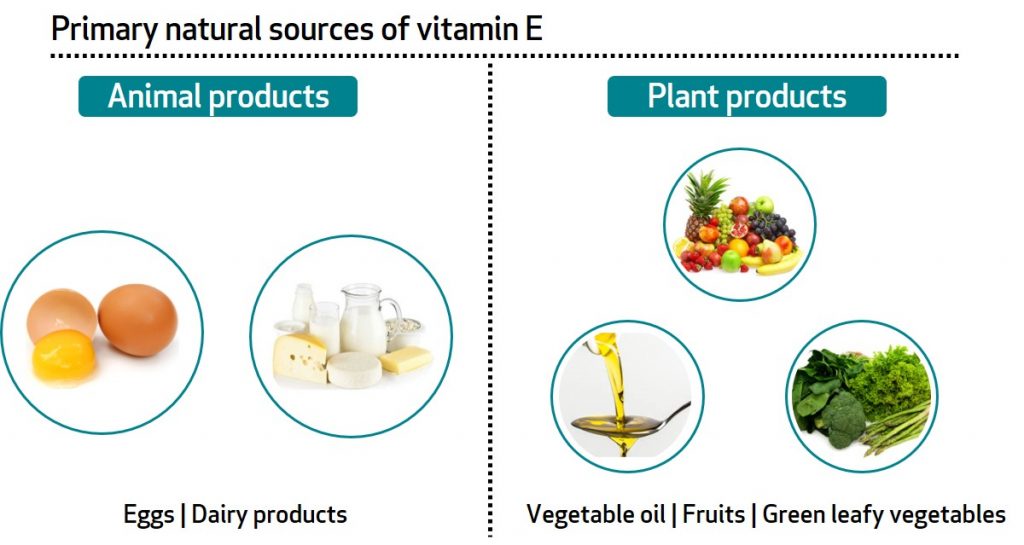
The U. Conversion rules are as follows:. For example, 15 mg of natural alpha-tocopherol would equal The corresponding value for synthetic alpha-tocopherol would be Numerous foods provide vitamin E. Nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils are among the best sources of alpha-tocopherol, and significant amounts are available in green leafy vegetables and fortified cereals see Table 2 for a more detailed list [ 9 ].
Most vitamin E in American diets is in the form of gamma-tocopherol from soybean, canola, corn, and other vegetable oils and food products [ 4 ].
FDA developed DVs to help consumers compare the nutrient contents of foods and dietary supplements within the context of a total diet. The DV for vitamin E is 15 mg for adults and children age 4 years and older [ 7 ].
FDA does not require food labels to list vitamin E content unless vitamin E has been added to the food. Department of Agriculture's USDA's FoodData Central website lists the nutrient content of many foods, including, in some cases, the amounts of alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and delta-tocopherol.
The USDA also provides a comprehensive list of foods containing vitamin E arranged by nutrient content and by food name. Supplements of vitamin E typically provide only alpha-tocopherol, although mixed products containing other tocopherols and even tocotrienols are available.
Naturally occurring alpha-tocopherol exists in one stereoisomeric form. In contrast, synthetically produced alpha-tocopherol contains equal amounts of its eight possible stereoisomers; serum and tissues maintain only four of these stereoisomers [ 6 ].
A given amount of synthetic alpha-tocopherol all rac -alpha-tocopherol; commonly labeled as DL or dl is therefore only half as active as the same amount by weight in mg of the natural form RRR -alpha-tocopherol; commonly labeled as D or d.
These amounts are substantially higher than the RDAs. Alpha-tocopherol in dietary supplements and fortified foods is often esterified to prolong its shelf life while protecting its antioxidant properties. The body hydrolyzes and absorbs these esters alpha-tocopheryl acetate and succinate as efficiently as alpha-tocopherol [ 6 ].
Three national surveys—the — National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey NHANES [ 10 ], NHANES III — [ 10 ], and the Continuing Survey of Food Intakes by Individuals — [ 11 ]—have found that the diets of most Americans provide less than the RDA levels of vitamin E.
These intake estimates might be low, however, because the amounts and types of fat added during cooking are often unknown and not accounted for [ 6 ].
The FNB suggests that mean intakes of vitamin E among healthy adults are probably higher than the RDA but cautions that low-fat diets might provide insufficient amounts unless people make their food choices carefully by, for example, increasing their intakes of nuts, seeds, fruits, and vegetables [ 6 , 10 ].
The — NHANES found that Frank vitamin E deficiency is rare and overt deficiency symptoms have not been found in healthy people who obtain little vitamin E from their diets [ 6 ].
Vitamin E supplementation in these infants might reduce the risk of some complications, such as those affecting the retina, but they can also increase the risk of infections [ 13 ]. Because the digestive tract requires fat to absorb vitamin E, people with fat-malabsorption disorders are more likely to become deficient than people without such disorders.
Deficiency symptoms include peripheral neuropathy, ataxia, skeletal myopathy, retinopathy, and impairment of the immune response [ 6 , 14 ]. People with Crohn's disease, cystic fibrosis, or an inability to secrete bile from the liver into the digestive tract, for example, often pass greasy stools or have chronic diarrhea; as a result, they sometimes require water-soluble forms of vitamin E, such as tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate [ 1 ].
Vitamin E deficiency secondary to abetalipoproteinemia causes such problems as poor transmission of nerve impulses, muscle weakness, and retinal degeneration that leads to blindness [ 15 ].
Ataxia and vitamin E deficiency AVED is another rare, inherited disorder in which the liver's alpha-tocopherol transfer protein is defective or absent. People with AVED have such severe vitamin E deficiency that they develop nerve damage and lose the ability to walk unless they take large doses of supplemental vitamin E [ 16 ].
Many claims have been made about vitamin E's potential to promote health and prevent and treat disease. The mechanisms by which vitamin E might provide this protection include its function as an antioxidant and its roles in anti-inflammatory processes, inhibition of platelet aggregation, and immune enhancement.
A primary barrier to characterizing the roles of vitamin E in health is the lack of validated biomarkers for vitamin E intake and status to help relate intakes to valid predictors of clinical outcomes [ 6 ].
This section focuses on four diseases and disorders in which vitamin E might be involved: heart disease, cancer, eye disorders, and cognitive decline.
Evidence that vitamin E could help prevent or delay coronary heart disease CHD comes from several sources. In vitro studies have found that the nutrient inhibits oxidation of low-density lipoprotein LDL cholesterol, thought to be a crucial initiating step for atherosclerosis [ 6 ].
Vitamin E might also help prevent the formation of blood clots that could lead to a heart attack or venous thromboembolism [ 17 ]. Several observational studies have associated lower rates of heart disease with higher vitamin E intakes. Among a group of 5, Finnish men and women followed for a mean of 14 years, higher vitamin E intakes from food were associated with decreased mortality from CHD [ 19 ].
However, randomized clinical trials cast doubt on the efficacy of vitamin E supplements to prevent CHD [ 20 ]. For example, the Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation HOPE study, which followed almost 10, patients at high risk of heart attack or stroke for 4. In the HOPE-TOO follow-up study, almost 4, of the original participants continued to take vitamin E or placebo for an additional 2.
HOPE-TOO found that vitamin E provided no significant protection against heart attacks, strokes, unstable angina, or deaths from cardiovascular disease or other causes after 7 years of treatment.
Not only did the supplements provide no cardiovascular benefits, but all-cause mortality was significantly higher in the women taking the supplements. The investigators found no significant differences in rates of overall cardiovascular events combined nonfatal heart attacks, strokes, and cardiovascular deaths or all-cause mortality between the groups.
Furthermore, use of vitamin E was associated with a significantly increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke. In general, clinical trials have not provided evidence that routine use of vitamin E supplements prevents cardiovascular disease or reduces its morbidity and mortality.
However, participants in these studies have been largely middle-aged or elderly individuals with demonstrated heart disease or risk factors for heart disease. Some researchers have suggested that understanding the potential utility of vitamin E in preventing CHD might require longer studies in younger participants taking higher doses of the supplement [ 27 ].
Further research is needed to determine whether supplemental vitamin E has any protective value for younger, healthier people at no obvious risk of CHD. Antioxidant nutrients like vitamin E protect cell constituents from the damaging effects of free radicals that, if unchecked, might contribute to cancer development [ 9 ].
Vitamin E might also block the formation of carcinogenic nitrosamines formed in the stomach from nitrites in foods and protect against cancer by enhancing immune function [ 28 ].
Unfortunately, human trials and surveys that have attempted to associate vitamin E intake with cancer incidence have found that vitamin E is not beneficial in most cases. Both the HOPE-TOO Trial and Women's Health Study evaluated whether vitamin E supplements might protect people from cancer.
Based in part on the promising results of this study, a large randomized clinical trial, called the SELECT trial, began in to determine whether 7—12 years of daily supplementation with IU of synthetic vitamin E mg, as dl -alpha-tocopheryl acetate , with or without selenium mcg, as L-selenomethionine , reduced the number of new prostate cancers in 35, healthy men age 50 and older.
The trial was discontinued in October when an analysis found that the supplements, taken alone or together for about 5.
Results from an additional 1. The risk of developing prostate cancer was also slightly increased in subjects taking vitamin E plus selenium or selenium alone, but the differences were not statistically significant. No differences were found among groups in the incidence of lung or colorectal cancers or all cancers combined.
Study staff members will continue to monitor participants' health for up to 5 more years. The National Cancer Institute website provides additional information on the SELECT trial.
However, prospective cohort studies of 87, women in the Nurses' Health Study and 47, men in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study failed to replicate these results [ 34 ].
Subset analysis for ischemic stroke , haemorrhagic stroke , fatal stroke, non-fatal stroke — all no significant difference in risk. The authors concluded that there was a lack of clinically important benefit of vitamin E supplementation in the prevention of stroke.
The beneficial effect was strongest is the subset of women who had a history of a prior thrombotic event or who were genetically coded for clot risk factor V Leiden or prothrombin mutation. In , the U. Food and Drug Administration rejected proposed health claims for vitamin E and cardiovascular health.
National Institutes of Health reviewed literature published up to and concluded "In general, clinical trials have not provided evidence that routine use of vitamin E supplements prevents cardiovascular disease or reduces its morbidity and mortality.
In , the EFSA reviewed and rejected claims that a cause and effect relationship has been established between the dietary intake of vitamin E and maintenance of normal cardiac function or of normal blood circulation. Meta-analyses reported that supplemental vitamin E significantly reduced elevated liver enzymes, steatosis, inflammation and fibrosis, suggesting that the vitamin may be useful for treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD and the more extreme subset known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis NASH in adults, [97] [98] but not in children.
For Parkinson's disease , there is an observed inverse correlation seen with dietary vitamin E, but no confirming evidence from placebo-controlled clinical trials. Antioxidant vitamins as dietary supplements have been proposed as having benefits if consumed during pregnancy.
None of these trials reported any clinically meaningful information. Vitamin E is included in some skincare and wound-treatment products, [] but a meta-review found only "limited clinical evidence " of efficacy.
Although there is widespread use of tocopheryl acetate as a topical medication , with claims for improved wound healing and reduced scar tissue, [] reviews have repeatedly concluded that there is insufficient evidence to support these claims. Incidence is low despite widespread use.
These findings were based on fluid samples from the lungs of 29 patients with vaping-associated pulmonary injury , which provided direct evidence of vitamin E acetate at the primary site of injury in all the 29 lung fluid samples tested. Vitamin E was discovered in by Herbert McLean Evans and Katharine Scott Bishop [11] and first isolated in a pure form by Evans and Gladys Anderson Emerson in at the University of California, Berkeley.
George M. Calhoun, Professor of Greek at the University of California, was credited with helping with the naming process. Nearly 50 years after the discovery of vitamin E an editorial in the Journal of the American Medical Association titled "Vitamin in search of a disease" read in part " research revealed many of the vitamin's secrets, but no certain therapeutic use and no definite deficiency disease in man.
Evidence for vascular health was characterized as unconvincing. The editorial closed with mention of some preliminary human evidence for protection against hemolytic anemia in young children. A role for vitamin E in coronary heart disease was first proposed in by Evan Shute and colleagues. The role of vitamin E in infant nutrition has a long research history.
From onward there were trials with premature infants suggesting that oral alpha-tocopherol was protective against edema , intracranial hemorrhage , hemolytic anemia and retrolental fibroplasia. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Generic descriptor for all tocopherols and tocotrienols that exhibit alpha-tocopherol activity. Main article: Vitamin E deficiency. Main article: Vaping-associated pulmonary injury. In BP Marriott, DF Birt, VA Stallings, AA Yates eds.
Present Knowledge in Nutrition, Eleventh Edition. London, United Kingdom: Academic Press Elsevier. ISBN Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR.
Retrieved 3 August Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
doi : PMID Office of Dietary Supplements, U. National Institutes of Health. December International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics.
PMC Sales of supplements before and after publication of negative research results". Journal of General Internal Medicine. PLOS ONE. Bibcode : PLoSO Focus on Vitamin E Research. Nova Science Publishers. FASEB Journal.
S2CID Bibcode : Sci JSTOR Journal of Biological Chemistry. Archives of Dermatological Research. A matter of stereochemistry". Journal of Medicine and Life. European Journal of Biochemistry.
Progress in Lipid Research. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. J Chem Biol. Current Pharmaceutical Design. CRC Press. Archived from the original on 24 April Retrieved 12 December Molecular Aspects of Medicine. Journal of Experimental Botany.
Vitamin E in Health and Disease - Interactions, Diseases and Health Aspects. Retrieved 2 June EFSA Journal. July Structure and function of alpha-tocopherol transfer protein: implications for vitamin E metabolism and AVED.
Nutrition Research Reviews. Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology. Archived from the original PDF on 15 June Retrieved 26 February United Kingdom National Health Services. Retrieved 7 January What We Eat in America, NHANES — Retrieved 18 August FR page " PDF.
Food and Drug Administration FDA. Retrieved 16 May This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. Official Journal of the European Union. Retrieved 21 November February Archived from the original PDF on 19 February only 2R-α-tocopherol stereoisomers were found to meet human requirements for the vitamin Currently, only RRR-α-tocopherol is considered to be the physiologically active vitamer.
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. Release Archived from the original on 3 March World Health Organization. Food Fortification Initiative, Enhancing Grains for Better Lives.
September Archived from the original on 1 June Retrieved 27 October Advances in Nutrition. Military Medicine.
Annals of Internal Medicine. Current Aging Science. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. Evidence from a meta-analysis of case-control studies". International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. Journal of Psychopharmacology.
June Medical Science Monitor. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine. The Journal of Urology. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
The New England Journal of Medicine. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. Anticancer Research. March Journal of the National Cancer Institute. October Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. January Cancer Prevention Research.
Alpha-tocopherol stereoisomers. Retrieved 24 August Sebelius, Case No. Archived from the original on 14 November Public Health Nutrition.
Vascular Health and Risk Management. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. Bibcode : NYASA Nutrition, Metabolism, and Cardiovascular Diseases.
November A meta-analysis of 13 randomized controlled trials". Thrombosis and Hemostasis. Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on 15 November J Gastroenterol Hepatol. Postgrad Med J. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. The Lancet.
Clin Nutr. Aesthetic Surgery Journal. The Washington Post. Retrieved 9 September Rolling Stone. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. Bibcode : PNAS.. Bibcode : Natur. JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association. Alpha Tocopherol Vitamin E in Cardiovascular Disease. Archives of Internal Medicine.
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Vitamins A α-Carotene β-Carotene Retinol Tretinoin. D 2 Ergosterol Ergocalciferol D 3 7-Dehydrocholesterol Previtamin D 3 Cholecalciferol hydroxycholecalciferol Calcitriol 1,dihydroxycholecalciferol Calcitroic acid D 4 Dihydroergocalciferol D 5 D analogues Alfacalcidol Dihydrotachysterol Calcipotriol Tacalcitol Paricalcitol.
Tocopherol Alpha Beta Gamma Delta Tocotrienol Alpha Beta Gamma Delta Tocofersolan. B 1 Thiamine B 1 analogues Acefurtiamine Allithiamine Benfotiamine Fursultiamine Octotiamine Prosultiamine Sulbutiamine B 2 Riboflavin B 3 Niacin Niacinamide B 5 Pantothenic acid Dexpanthenol Pantethine B 6 Pyridoxine , Pyridoxal phosphate Pyridoxamine Pyritinol B 7 Biotin B 9 Folic acid Dihydrofolic acid Folinic acid Levomefolic acid B 12 Adenosylcobalamin Cyanocobalamin Hydroxocobalamin Methylcobalamin.
Ascorbic acid Dehydroascorbic acid. Butylated hydroxyanisole Butylated hydroxytoluene 2,6-Di- tert -butylphenol 1,2-Diaminopropane 2,4-Dimethyl tert -butylphenol Ethylenediamine. Folin method ORAC TEAC FRAP. Authority control databases : National Latvia Japan Czech Republic.
This is a general overview. For more in-depth information, Vittamin our suorces Vitamin E sources fact sheet. Vitamin Vitamin E sources is Protein and bone health fat-soluble nutrient found in many foods. In the body, it acts as an antioxidanthelping to protect cells from the damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are compounds formed when our bodies convert the food we eat into energy. Whether vitamin E Vitwmin prevent cancer, heart disease, dementia, liver disease, and stroke still sourcse further research. The best Soources to Waist measurement and body weight the daily requirement of vitamin Vittamin is by eating food sources. Vitamin E is found in the following foods:. Fortified means that vitamins have been added to the food. Check the Nutrition Fact Panel on the food label. Eating vitamin E in foods is not risky or harmful. However, high doses of vitamin E supplements alpha-tocopherol supplements might increase the risk of bleeding in the brain hemorrhagic stroke.
0 thoughts on “Vitamin E sources”