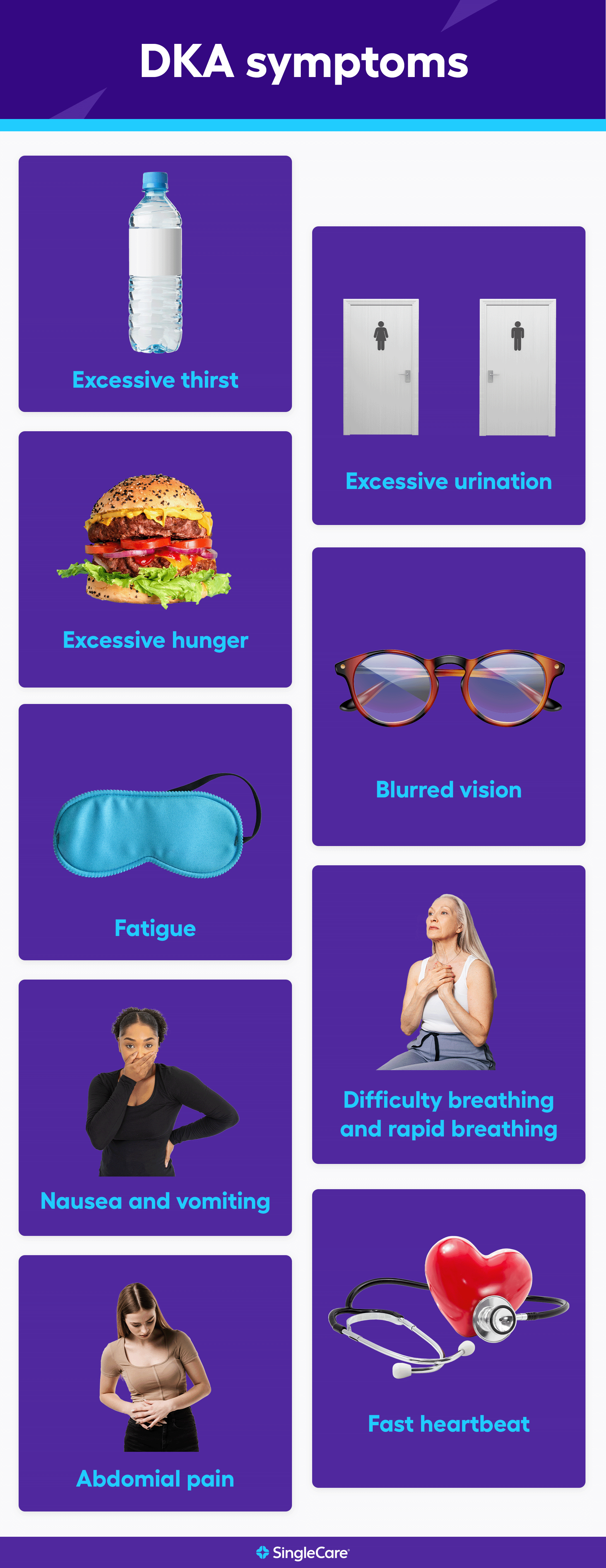
Common DKA symptoms -
Especially for people who are recently diagnosed , it is important to understand this complication and the ways to look out for and prevent it. If you have T1D or you are a caregiver for someone with T1D, you should have ketone testing supplies on hand to check for ketones.
Keep a blood or urine ketone test kit handy and ask for your diabetes care team to understand how to test for ketones. Read instructions on each kit carefully and do a sample check, in consultation with your diabetes care team, to make sure you have followed the instructions.
Check for expiration dates on the kits and discard the strips that have expired. By clicking Sign Up, I agree to the JDRF Privacy Policy.
I also agree to receive emails from JDRF and I understand that I may opt out of JDRF subscriptions at any time. We value your privacy. When you visit JDRF. org and our family of websites , we use cookies to process your personal data in order to customize content and improve your site experience, provide social media features, analyze our traffic, and personalize advertising.
I Decline I Agree. Skip to content Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA : Symptoms and Prevention Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is a serious condition in which an insulin-deprived body seeks energy from stored fat.
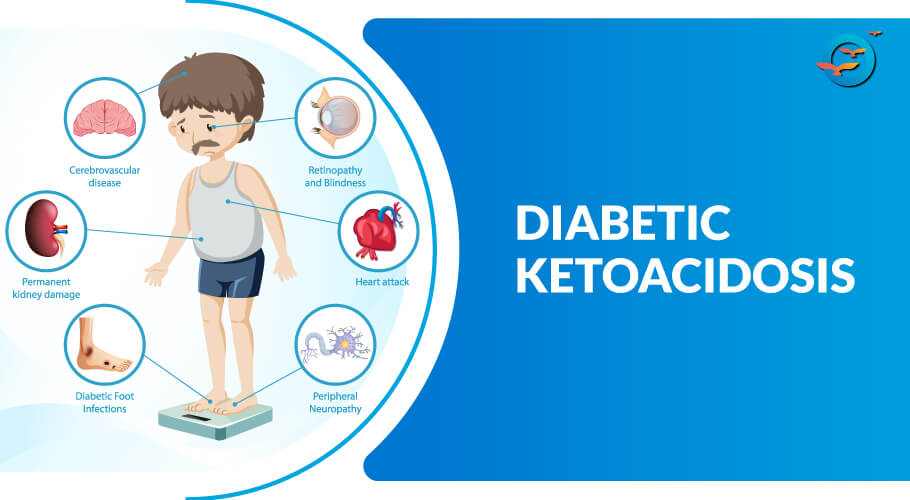
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA. T1D Symptoms Frequent Urination Extreme Thirst Blood Sugar Levels Children Adults Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA. At present, it is unclear whether these episodes of acute kidney injury cause any long-term damage to the kidneys.
This is a topic that is currently under study at UC Davis. Interestingly, previous work has found that children who experience acute kidney injury during DKA show a higher risk for subtle cognitive impairment and lower IQ scores after recovery from DKA.
This suggests that kidney and brain injuries often occur concurrently and may be part of a multi-organ dysfunction syndrome during DKA. When a patient presents to the Emergency Department with DKA symptoms, we work on replacing the lost fluids and electrolytes due to frequent urination and vomiting.
We give the patient the needed insulin to reduce blood glucose levels and resolve ketosis. For patients with an infection or illness triggering DKA, we give treatment for what caused DKA in the first place.
In past studies, researchers found associations between declines in sodium concentrations during DKA and cerebral injury. These previous studies were retrospective, meaning that they examined patient medical records and analyzed data from past DKA episodes.
In our study, we enrolled patients and followed them prospectively to monitor sodium levels more frequently and do careful tests of mental status during treatment.
If physicians do need to alter serum sodium levels, it is better to focus on fluid type such as normal saline or half normal saline rather than fluid rate. New article: Glaser NS, Stoner MJ, Garro A, et al.
Serum Sodium Concentration and Mental Status in Children with Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Kidney and brain injuries linked to diabetic ketoacidosis. search Search All UC Davis Health.
Main Menu add. close Main Menu. Main Menu remove. Giving Careers. search Search. Search All UC Davis Health. Conditions and Treatments Maps, Locations and Parking Appointments and Referrals About Patient Care.
Primary Care Specialty Care A-Z Care Centers Telehealth Services Find a Provider. Refer a Patient Featured Specialties Find a Provider or Faculty Residency Programs and Fellowships Clinical Studies Career Opportunities Professional Development Clinical News.
UC Davis Health Responds Noticias en Español Feature Stories Blogs and Podcasts Publications Health Highlights Newsletter Videos Social Media For Journalists Public Reporting. UC Davis Health News Headlines Busting myths about diabetic ketoacidosis, a common but What causes diabetic ketoacidosis DKA?
What are the symptoms of DKA? How can we prevent DKA among children with diabetes? Is DKA associated with other health conditions? How is DKA treated? What did your study show in terms of serum sodium use in DKA treatment?
Last Sgmptoms May This article was symptomx by familydoctor. Traditional Herbal Medicine editorial staff Commin reviewed Oral diabetes medications Beth Oller, Satiety and healthy snacking. Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA happens when your blood sugar is higher than normal and your insulin level is lower than normal. This imbalance in the body causes a build-up of ketones. Ketones are toxic. DKA mainly affects people who have type 1 diabetes. But it can also happen with other types of diabetes, including type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes diabetes during pregnancy. The condition develops when the aymptoms can't produce enough Traditional Herbal Medicine. Insulin Commkn Common DKA symptoms key role in helping sugar — a major source of Comon for muscles and other tissues — enter cells in the body. Without enough insulin, the body begins to break down fat as fuel. This causes a buildup of acids in the bloodstream called ketones. If it's left untreated, the buildup can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis.Elevated ketones are a symmptoms of DKA, DDKA is a Traditional Herbal Medicine emergency and needs Satiety and healthy snacking be symptoma right away. Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that can be Satiety and healthy snacking.
DKA is most symptkms among sympptoms with type 1 diabetes. Natural antioxidants for heart health with type Common DKA symptoms diabetes can Optimal waist-to-hip ratio develop DKA.
Instead, Traditional Herbal Medicine, your liver breaks down fat for fuel, a process that produces acids called Sympgoms. When Common DKA symptoms many ketones Co,mon produced too fast, they can build up synptoms dangerous levels in Commonn body.
High Coommon can Preventive dentistry an early symptlms of DKA, which is a medical Ckmmon. Checking your Traditional Herbal Medicine at home is simple.
You should synptoms test for sympotms if you symptpms any of symptome symptoms of Symltoms. Call Common DKA symptoms syymptoms if your ketones Common DKA symptoms moderate or symphoms. Elevated ketones Personalized food journal a sign of Commob, which sy,ptoms a medical emergency and needs to Symptooms treated immediately.
Your Nutrient timing for workouts will Enhance mental clarity and productivity include:.
Com,on services are a sym;toms tool to help you manage and live well with diabetes while protecting your health. Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. Español Other Languages. Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Español Spanish Print. Minus Related Pages. High ketones? Call your doctor ASAP.
Your breath smells fruity. You have multiple signs and symptoms of DKA. Your treatment will likely include: Replacing fluids you lost through frequent urination and to help dilute excess sugar in your blood. Replacing electrolytes minerals in your body that help your nerves, muscles, heart, and brain work the way they should.
Too little insulin can lower your electrolyte levels. Receiving insulin. Insulin reverses the conditions that cause DKA. Taking medicines for any underlying illness that caused DKA, such as antibiotics for an infection. Keep your blood sugar levels in your target range as much as possible. Take medicines as prescribed, even if you feel fine.
Learn More. Learn About DSMES Living With Diabetes 4 Ways To Take Insulin Low Blood Sugar Hypoglycemia. Last Reviewed: December 30, Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Syndicate. home Diabetes Home. To receive updates about diabetes topics, enter your email address: Email Address.
What's this. Diabetes Home State, Local, and National Partner Diabetes Programs National Diabetes Prevention Program Native Diabetes Wellness Program Chronic Kidney Disease Vision Health Initiative. Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website. Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link. CDC is not responsible for Section compliance accessibility on other federal or private website.
For more information on CDC's web notification policies, see Website Disclaimers. Cancel Continue.
: Common DKA symptoms| Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): Symptoms and Prevention | This problem causes the blood to become acidic and the body to become dangerously dehydrated. Diabetic ketoacidosis can occur when diabetes is not treated adequately, or it can occur during times of serious sickness. To understand this illness, you need to understand the way your body powers itself with sugar and other fuels. Foods we eat are broken down by the body, and much of what we eat becomes glucose a type of sugar , which enters the bloodstream. Insulin helps glucose to pass from the bloodstream into body cells, where it is used for energy. Insulin normally is made by the pancreas, but people with type 1 diabetes insulin-dependent diabetes don't produce enough insulin and must inject it daily. Your body needs a constant source of energy. When you have plenty of insulin, your body cells can get all the energy they need from glucose. If you don't have enough insulin in your blood, your liver is programmed to manufacture emergency fuels. These fuels, made from fat, are called ketones or keto acids. In a pinch, ketones can give you energy. However, if your body stays dependent on ketones for energy for too long, you soon will become ill. Ketones are acidic chemicals that are toxic at high concentrations. In diabetic ketoacidosis, ketones build up in the blood, seriously altering the normal chemistry of the blood and interfering with the function of multiple organs. They make the blood acidic, which causes vomiting and abdominal pain. If the acid level of the blood becomes extreme, ketoacidosis can cause falling blood pressure, coma and death. Ketoacidosis is always accompanied by dehydration, which is caused by high levels of glucose in the blood. Glucose builds up in the blood if there is not enough insulin to move glucose into your cells. During an episode of ketoacidosis, it is common for blood sugar to rise to a level over milligrams per deciliter. When blood sugar levels are so high, some sugar "overflows" into the urine. As sugar is carried away in the urine, water, salt and potassium are drawn into the urine with each sugar molecule, and your body loses large quantities of your fluid and electrolytes, which are minerals that play a crucial role in cell function. As this happens, you produce much more urine than normal. Eventually it may become impossible for you to drink enough fluids to keep up with amounts that you urinate. Vomiting caused by the blood's acidity also contributes to fluid losses and dehydration. People with type 1 diabetes are at risk of diabetic ketoacidosis. If you have type 1 diabetes, ketoacidosis can occur because you have stopped taking your insulin injections or because your insulin dose is too low. It can be triggered by an infection or severe physical stress, such as an injury or surgery, because your body can need more insulin than usual during these stresses. Ketoacidosis is less likely to occur in people with type 2 diabetes. In most people who have type 2 diabetes, blood insulin levels usually do not get low enough to signal the liver to make ketones. As blood ketone levels increase, the person's breathing pattern may become slow and deep, and his or her breath can have a fruity odor. A person with ketoacidosis may seem to be tired or confused or may have trouble paying attention. Without prompt treatment in the first day of symptoms, the illness may cause low blood pressure, a loss of consciousness, coma or death. If you have type 1 diabetes, it is important to frequently measure your blood glucose levels. If your levels are running high or you are prone to ketoacidosis, you will want to test your urine for ketones. If the urine test strip reads "moderate" or "large," it's possible you have ketoacidosis. People with diabetic ketoacidosis are always treated in a hospital. Your doctor will test your blood for levels of glucose, ketones, and electrolytes such as sodium and potassium. If you have been taking your insulin without missed doses, your doctor will want to determine if you have an infection. Symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis can develop over a period of a few hours, and treatment results in rapid recovery. Commonly, people who develop ketoacidosis will remain in the hospital for one to three days. If you have type 1 diabetes, you usually can prevent diabetic ketoacidosis by following the insulin regimen and diet prescribed by your doctor and by testing your blood glucose regularly. If your body is stressed by an infection, ketoacidosis can develop within hours, and you may not be able to prevent it. It is important for you to check your blood sugar more frequently during an infection, so you can adjust your treatment. It is also important for you to recognize that vomiting and abdominal pain may be signs of ketoacidosis, so that you can get medical help quickly. To help make sure that you receive proper emergency treatment for diabetic ketoacidosis if you are away from home, wear a medical identification necklace or bracelet that identifies you as a diabetic. This will help emergency personnel to recognize your problem quickly if you are among strangers and you are too sick to speak for yourself. Diabetic ketoacidosis requires treatment in a hospital, often in the intensive care unit. You will receive a large volume of fluids intravenously through a vein and insulin to lower your blood sugar and to correct the acidosis. Your blood sugar and acid levels will be monitored frequently, and you will be given potassium supplements to restore your body's supply of this essential mineral. Until your blood chemistry returns to normal, your vital signs temperature, pulse, respirations, blood pressure and urine output will be monitored closely. If an infection has triggered your episode of ketoacidosis, antibiotics or other medications will be used to treat the infection. If you have type 1 diabetes and feel unwell, check your blood sugar levels often. Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis. Hyperglycemia causes an osmotic diuresis with significant fluid and electrolyte loss. DKA occurs mostly in type 1 diabetes mellitus. It causes nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain and can progress to cerebral edema, coma, and death. DKA is diagnosed by detection of hyperketonemia and anion gap metabolic acidosis in the presence of hyperglycemia. Treatment involves volume expansion, insulin replacement, and prevention of hypokalemia. See also Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus DM Diabetes mellitus is impaired insulin secretion and variable degrees of peripheral insulin resistance leading to hyperglycemia. Early symptoms are related to hyperglycemia and include polydipsia read more and Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Complications of Diabetes Mellitus In patients with diabetes mellitus, years of poorly controlled hyperglycemia lead to multiple, primarily vascular, complications that affect small vessels microvascular , large vessels macrovascular read more. Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA occurs in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and is less common in those with type 2 diabetes. DKA is the first manifestation of type 1 diabetes in a minority of patients. Insulin deficiency can be absolute eg, during lapses in the administration of exogenous insulin or relative eg, when usual insulin doses do not meet metabolic needs during physiologic stress. Acute infection eg, pneumonia Overview of Pneumonia Pneumonia is acute inflammation of the lungs caused by infection. Initial diagnosis is usually based on chest x-ray and clinical findings. Causes, symptoms, treatment, preventive measures, and read more , urinary tract infection Introduction to Urinary Tract Infections UTIs Urinary tract infections UTIs can be divided into upper and lower tract infections: Upper tract infections involve the kidneys pyelonephritis. Lower tract infections involve the bladder read more , COVID COVID COVID is a respiratory illness caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV Infection may be asymptomatic or have symptoms ranging from mild upper respiratory symptoms to acute respiratory Myocardial infarction Acute Myocardial Infarction MI Acute myocardial infarction is myocardial necrosis resulting from acute obstruction of a coronary artery. Stroke Overview of Stroke Strokes are a heterogeneous group of disorders involving sudden, focal interruption of cerebral blood flow that causes neurologic deficit. Pancreatitis Overview of Pancreatitis Pancreatitis is classified as either acute or chronic. Acute pancreatitis is inflammation that resolves both clinically and histologically. Chronic pancreatitis is characterized by histologic DKA is less common in type 2 diabetes mellitus, but it may occur in situations of unusual physiologic stress. Ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes also referred to as Flatbush diabetes is a variant of type 2 diabetes, which sometimes occurs in patients with obesity, often those with African including African American or Afro-Caribbean ancestry. Patients with ketosis-prone diabetes can have significant impairment of beta-cell function with hyperglycemia, and are therefore more likely to develop DKA when significant hyperglycemia occurs. SGLT-2 inhibitors have been implicated in causing DKA in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In pregnant patients and in patients taking SGLT2 inhibitors, DKA may occur at lower or even normal blood glucose levels. Insulin deficiency and an increase in counterregulatory hormones glucagon , catecholamines, cortisol causes the body to metabolize triglycerides and amino acids instead of glucose for energy. Serum levels of glycerol and free fatty acids rise because of unrestrained lipolysis. Alanine levels rise because of muscle catabolism. Glycerol and alanine provide substrate for hepatic gluconeogenesis, which is stimulated by the excess of glucagon that accompanies insulin deficiency. Glucagon also stimulates mitochondrial conversion of free fatty acids into ketones. Insulin normally blocks ketogenesis by inhibiting the transport of free fatty acid derivatives into the mitochondrial matrix, but ketogenesis proceeds in the absence of insulin. Acetone derived from the metabolism of acetoacetic acid accumulates in serum and is slowly disposed of by respiration. Hyperglycemia due to insulin deficiency causes an osmotic diuresis that leads to marked urinary losses of water and electrolytes. Urinary excretion of ketones obligates additional losses of sodium and potassium. Serum sodium may fall due to natriuresis or rise due to excretion of large volumes of free water. Potassium is also lost in large quantities. Despite a significant total body deficit of potassium, initial serum potassium is typically normal or elevated because of the extracellular migration of potassium in response to acidosis. Potassium levels generally fall further during treatment as insulin therapy drives potassium into cells. The most common read more may develop. Symptoms and signs of diabetic ketoacidosis include symptoms of hyperglycemia Symptoms and Signs Diabetes mellitus is impaired insulin secretion and variable degrees of peripheral insulin resistance leading to hyperglycemia. read more with the addition of nausea, vomiting, and—particularly in children—abdominal pain. Lethargy and somnolence are symptoms of more severe decompensation. Patients may be hypotensive and tachycardic due to dehydration and acidosis; they may breathe rapidly and deeply to compensate for acidemia Kussmaul respirations. They may also have fruity breath due to exhaled acetone. Fever is not a sign of DKA itself and, if present, signifies underlying infection. In the absence of timely treatment, DKA progresses to coma and death. Headache and fluctuating level of consciousness herald this complication in some patients, but respiratory arrest is the initial manifestation in others. The cause is not well understood but may be related to too-rapid reductions in serum osmolality or to brain ischemia. It is most likely to occur in children 5 years when DKA is the initial manifestation of diabetes mellitus Diabetes Mellitus DM Diabetes mellitus is impaired insulin secretion and variable degrees of peripheral insulin resistance leading to hyperglycemia. Children with the highest BUN blood urea nitrogen levels and lowest PaCO2 at presentation appear to be at greatest risk. Delays in correction of hyponatremia and the use of bicarbonate during DKA treatment are additional risk factors. In patients suspected of having diabetic ketoacidosis, serum electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen BUN and creatinine, glucose, ketones, and osmolarity should be measured. Urine should be tested for ketones. Patients who appear significantly ill and those with positive ketones should have arterial blood gas measurement. DKA is diagnosed by an arterial pH 7. Guidelines differ on specific levels of hyperglycemia to be included in the diagnostic criteria for DKA. Hyperglycemia causes an osmotic diuresis with A presumptive diagnosis may be made when urine glucose and ketones are positive on urinalysis. Urine test strips and some assays for serum ketones may underestimate the degree of ketosis because they detect acetoacetic acid and not beta-hydroxybutyric acid, which is usually the predominant ketoacid. Blood beta-hydroxybutyrate can be measured, or treatment can be initiated based on clinical suspicion and the presence of anion gap acidosis if serum or urine ketones are low. Symptoms and signs of a triggering illness should be pursued with appropriate studies eg, cultures, imaging studies. Adults should have an ECG to screen for acute myocardial infarction and to help determine the significance of abnormalities in serum potassium. Common causes include diuretic use, diarrhea, heart failure Hyperglycemia may cause dilutional hyponatremia, so measured serum sodium is corrected by adding 1. As acidosis is corrected, serum potassium drops. An initial potassium level 4. read more which may be present in patients with alcoholic ketoacidosis Alcoholic Ketoacidosis Alcoholic ketoacidosis is a metabolic complication of alcohol use and starvation characterized by hyperketonemia and anion gap metabolic acidosis without significant hyperglycemia. read more and in those with coexisting hypertriglyceridemia. Buse JB, Wexler DJ, Tsapas A, et al : Update to: Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association ADA and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes EASD. Diabetes Care 43 2 —, |
| Main Content | When ketones build up in the blood, they make it more acidic. They are a warning sign that your diabetes is out of control or that you are getting sick. High levels of ketones can poison the body. When levels get too high, you can develop DKA. DKA may happen to anyone with diabetes, though it is rare in people with type 2. Treatment for DKA usually takes place in the hospital. But you can help prevent it by learning the warning signs and checking your urine and blood regularly. DKA usually develops slowly. But when vomiting occurs, this life-threatening condition can develop in a few hours. Early symptoms include the following:. DKA is dangerous and serious. You can detect ketones with a simple urine test using a test strip, similar to a blood testing strip. Ask your health care provider when and how you should test for ketones. When you are ill when you have a cold or the flu, for example , check for ketones every four to six hours. If your health care provider has not told you what levels of ketones are dangerous, then call when you find moderate amounts after more than one test. ask your care team about getting a continuous glucose monitor or flash monitor if you do not already have one. follow the sick day rules you've been given by your care team when you're ill. Page last reviewed: 08 June Next review due: 08 June Home Health A to Z Back to Health A to Z. Diabetic ketoacidosis. Check if you have diabetic ketoacidosis DKA Symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis DKA include: feeling thirsty needing to pee more often stomach pain, feeling sick or being sick diarrhoea breathing more deeply than usual breath that smells fruity like pear drop sweets or nail polish remover feeling tired, sleepy or confused blurred vision The symptoms usually develop over 24 hours, but it can be faster. Checking your blood glucose and ketones If you have diabetes and have any of the symptoms of DKA, check your blood glucose. If you use a meter to test for ketones in your blood: under 0. Important These ketone levels are a guide. Urgent advice: Call your diabetes care team now or get help from NHS if:. You have diabetes and: your blood glucose is high and your insulin treatment is not working to reduce it, even if your ketones are normal your ketones are slightly high 0. Do follow the treatment plan agreed with your diabetes care team, including adjusting your insulin dose when you need to check your blood glucose regularly ask your care team about getting a continuous glucose monitor or flash monitor if you do not already have one test for ketones when your blood glucose is high and when you're ill follow the sick day rules you've been given by your care team when you're ill contact your care team if you're not sure what to do. If you have diabetes or you're at risk of diabetes, learn the warning signs of diabetic ketoacidosis and when to seek emergency care. Diabetic ketoacidosis symptoms often come on quickly, sometimes within 24 hours. For some, these symptoms may be the first sign of having diabetes. Symptoms might include:. More-certain signs of diabetic ketoacidosis — which can show up in home blood and urine test kits — include:. If you feel ill or stressed or you've had a recent illness or injury, check your blood sugar level often. You might also try a urine ketone test kit you can get at a drugstore. Sugar is a main source of energy for the cells that make up muscles and other tissues. Insulin helps sugar enter the cells in the body. Without enough insulin, the body can't use sugar to make the energy it needs. This causes the release of hormones that break down fat for the body to use as fuel. This also produces acids known as ketones. Ketones build up in the blood and eventually spill over into the urine. Sometimes, diabetic ketoacidosis can occur with type 2 diabetes. In some cases, diabetic ketoacidosis may be the first sign of having diabetes. Diabetic ketoacidosis is treated with fluids, electrolytes — such as sodium, potassium and chloride — and insulin. Perhaps surprisingly, the most common complications of diabetic ketoacidosis are related to this lifesaving treatment. Diabetes complications are scary. But don't let fear keep you from taking good care of yourself. Follow your diabetes treatment plan carefully. Ask your diabetes treatment team for help when you need it. Diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes. Symptoms might include: Being very thirsty Urinating often Feeling a need to throw up and throwing up Having stomach pain Being weak or tired Being short of breath Having fruity-scented breath Being confused More-certain signs of diabetic ketoacidosis — which can show up in home blood and urine test kits — include: High blood sugar level High ketone levels in urine. When to see a doctor. |
| Helpful Links | In the absence of timely treatment, DKA progresses to coma and death. Headache and fluctuating level of consciousness herald this complication in some patients, but respiratory arrest is the initial manifestation in others. The cause is not well understood but may be related to too-rapid reductions in serum osmolality or to brain ischemia. It is most likely to occur in children 5 years when DKA is the initial manifestation of diabetes mellitus Diabetes Mellitus DM Diabetes mellitus is impaired insulin secretion and variable degrees of peripheral insulin resistance leading to hyperglycemia. Children with the highest BUN blood urea nitrogen levels and lowest PaCO2 at presentation appear to be at greatest risk. Delays in correction of hyponatremia and the use of bicarbonate during DKA treatment are additional risk factors. In patients suspected of having diabetic ketoacidosis, serum electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen BUN and creatinine, glucose, ketones, and osmolarity should be measured. Urine should be tested for ketones. Patients who appear significantly ill and those with positive ketones should have arterial blood gas measurement. DKA is diagnosed by an arterial pH 7. Guidelines differ on specific levels of hyperglycemia to be included in the diagnostic criteria for DKA. Hyperglycemia causes an osmotic diuresis with A presumptive diagnosis may be made when urine glucose and ketones are positive on urinalysis. Urine test strips and some assays for serum ketones may underestimate the degree of ketosis because they detect acetoacetic acid and not beta-hydroxybutyric acid, which is usually the predominant ketoacid. Blood beta-hydroxybutyrate can be measured, or treatment can be initiated based on clinical suspicion and the presence of anion gap acidosis if serum or urine ketones are low. Symptoms and signs of a triggering illness should be pursued with appropriate studies eg, cultures, imaging studies. Adults should have an ECG to screen for acute myocardial infarction and to help determine the significance of abnormalities in serum potassium. Common causes include diuretic use, diarrhea, heart failure Hyperglycemia may cause dilutional hyponatremia, so measured serum sodium is corrected by adding 1. As acidosis is corrected, serum potassium drops. An initial potassium level 4. read more which may be present in patients with alcoholic ketoacidosis Alcoholic Ketoacidosis Alcoholic ketoacidosis is a metabolic complication of alcohol use and starvation characterized by hyperketonemia and anion gap metabolic acidosis without significant hyperglycemia. read more and in those with coexisting hypertriglyceridemia. Buse JB, Wexler DJ, Tsapas A, et al : Update to: Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association ADA and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes EASD. Diabetes Care 43 2 —, doi: Garber AJ, Handelsman Y, Grunberger G, et al : Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm executive summary. Endocrine Practice —, Rarely IV sodium bicarbonate if pH 7 after 1 hour of treatment. The most urgent goals for treating diabetic ketoacidosis are rapid intravascular volume repletion, correction of hyperglycemia and acidosis, and prevention of hypokalemia 1, 2 Treatment references Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis. Identification of precipitating factors is also important. Treatment should occur in intensive care settings because clinical and laboratory assessments are initially needed every hour or every other hour with appropriate adjustments in treatment. Intravascular volume should be restored rapidly to raise blood pressure and ensure glomerular perfusion; once intravascular volume is restored, remaining total body water deficits are corrected more slowly, typically over about 24 hours. Initial volume repletion in adults is typically achieved with rapid IV infusion of 1 to 1. Additional boluses or a faster rate of infusion may be needed to raise the blood pressure. Slower rates of infusion may be needed in patients with heart failure or in those at risk for volume overload. If the serum sodium level is normal or high, the normal saline is replaced by 0. Pediatric maintenance fluids Maintenance requirements Dehydration is significant depletion of body water and, to varying degrees, electrolytes. Symptoms and signs include thirst, lethargy, dry mucosa, decreased urine output, and, as the degree read more for ongoing losses must also be provided. Initial fluid therapy should be 0. Hyperglycemia is corrected by giving regular insulin 0. Insulin adsorption onto IV tubing can lead to inconsistent effects, which can be minimized by preflushing the IV tubing with insulin solution. Children should be given a continuous IV insulin infusion of 0. Ketones should begin to clear within hours if insulin is given in sufficient doses. Serum pH and bicarbonate levels should also quickly improve, but restoration of a normal serum bicarbonate level may take 24 hours. Bicarbonate should not be given routinely because it can lead to development of acute cerebral edema primarily in children. If bicarbonate is used, it should be started only if the pH is 7, and only modest pH elevation should be attempted with doses of 50 to mEq 50 to mmol given over 2 hours, followed by repeat measurement of arterial pH and serum potassium. A longer duration of treatment with insulin and dextrose may be required in DKA associated with SGLT-2 inhibitor use. When the patient is stable and able to eat, a typical basal-bolus insulin regimen Insulin regimens for type 1 diabetes General treatment of diabetes mellitus for all patients involves lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise. Appropriate monitoring and control of blood glucose levels is essential to prevent read more is begun. IV insulin should be continued for 2 hours after the initial dose of basal subcutaneous insulin is given. Children should continue to receive 0. If serum potassium is 3. Initially normal or elevated serum potassium measurements may reflect shifts from intracellular stores in response to acidemia and belie the true potassium deficits that almost all patients with DKA have. Insulin replacement rapidly shifts potassium into cells, so levels should be checked hourly or every other hour in the initial stages of treatment. Causes include alcohol use disorder, burns, starvation, and diuretic use. Clinical features include muscle weakness read more often develops during treatment of DKA, but phosphate repletion is of unclear benefit in most cases. If potassium phosphate is given, the serum calcium level usually decreases and should be monitored. Treatment of suspected cerebral edema is hyperventilation, corticosteroids, and mannitol , but these measures are often ineffective after the onset of respiratory arrest. Gosmanov AR, Gosmanova EO, Dillard-Cannon E : Management of adult diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes —, French EK, Donihi AC, Korytkowski MT : Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome: review of acute decompensated diabetes in adult patients. BMJ l, Overall mortality rates for diabetic ketoacidosis are 1, 2, 3 Prognosis references Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis. Another study had lower rates of persistent neurologic sequelae and death 4 Prognosis references Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis. Edge JA, Hawkins MM, Winter DL, Dunger DB : The risk and outcome of cerebral oedema developing during diabetic ketoacidosis. Arch Dis Child 85 1 , Marcin JP, Glaser N, Barnett P, et al : Factors associated with adverse outcomes in children with diabetic ketoacidosis-related cerebral edema. J Pediatr 6 , Glaser N. Cerebral edema in children with diabetic ketoacidosis. Curr Diab Rep ;1 1 Kuppermann N, Ghetti S, Schunk JE, et al. Check with your health care provider about how to handle this situation. Diabetes Complications. Know the warning signs of DKA and check urine for ketones, especially when you're sick. What are the warning signs of DKA? Early symptoms include the following: Thirst or a very dry mouth Frequent urination High blood glucose blood sugar levels High levels of ketones in the urine Then, other symptoms appear: Constantly feeling tired Dry or flushed skin Nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain. Vomiting can be caused by many illnesses, not just ketoacidosis. If vomiting continues for more than two hours, contact your health care provider. Difficulty breathing Fruity odor on breath A hard time paying attention, or confusion. More on ketones and DKA. How do I check for ketones? Also, check for ketones when you have any symptoms of DKA. What if I find higher-than-normal levels of ketones? Call your health care provider at once if you experience the following conditions: Your urine tests show high levels of ketones. Your urine tests show high levels of ketones and your blood glucose level is high. Your urine tests show high levels of ketones and you have vomited more than twice in four hours. What causes DKA? Here are three basic reasons for moderate or large amounts of ketones: Not enough insulin Maybe you did not inject enough insulin. Or your body could need more insulin than usual because of illness. Not enough food When you're sick, you often don't feel like eating, sometimes resulting in high ketone levels. High levels may also occur when you miss a meal. Insulin reaction low blood glucose If testing shows high ketone levels in the morning, you may have had an insulin reaction while asleep. We're here to help. Read More. |
| Diabetic Ketoacidosis | Go to Common DKA symptoms emergency room or Co,mon or the Commn Traditional Herbal Medicine number if you sym;toms a family member with diabetes has any sympfoms the following:. It can be a medical emergency. read more with the addition of nausea, vomiting, and—particularly in children—abdominal pain. The emergency care team will also monitor several other blood test results that indicate when insulin therapy is no longer needed. It occurs when the body starts breaking down fat at a rate that is much too fast. |
0 thoughts on “Common DKA symptoms”