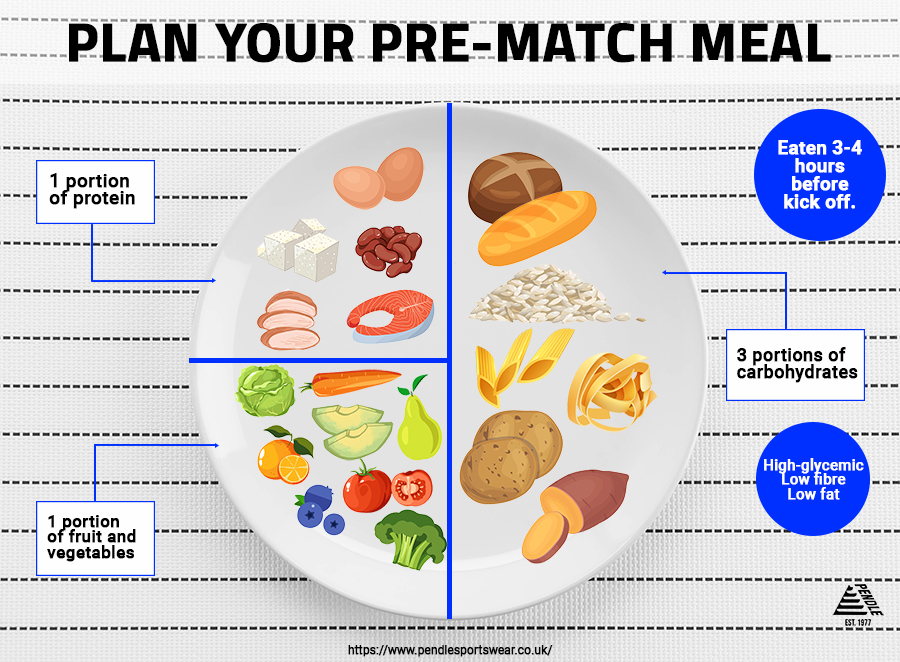
Pre-game meal guidelines for performance -
As a general approach to achieving optimal protein intakes, it is suggested to space out protein intake fairly evenly over the course of a day, for instance around 25 to 30 g protein every 3 to 5 hours, including as part of regular meals.
There is currently a lack of evidence to show that protein supplements directly improve athletic performance. Therefore, for most athletes, additional protein supplements are unlikely to improve sport performance.
A well-planned diet will meet your vitamin and mineral needs. Supplements will only be of any benefit if your diet is inadequate or you have a diagnosed deficiency, such as an iron or calcium deficiency. There is no evidence that extra doses of vitamins improve sporting performance. Nutritional supplements can be found in pill, tablet, capsule, powder or liquid form, and cover a broad range of products including:.
Before using supplements, you should consider what else you can do to improve your sporting performance — diet, training and lifestyle changes are all more proven and cost effective ways to improve your performance. Relatively few supplements that claim performance benefits are supported by sound scientific evidence.
Use of vitamin and mineral supplements is also potentially dangerous. Supplements should not be taken without the advice of a qualified health professional. The ethical use of sports supplements is a personal choice by athletes, and it remains controversial.
If taking supplements, you are also at risk of committing an anti-doping rule violation no matter what level of sport you play. Dehydration can impair athletic performance and, in extreme cases, may lead to collapse and even death. Drinking plenty of fluids before, during and after exercise is very important.
Fluid intake is particularly important for events lasting more than 60 minutes, of high intensity or in warm conditions. Water is a suitable drink, but sports drinks may be required, especially in endurance events or warm climates. Sports drinks contain some sodium, which helps absorption.
While insufficient hydration is a problem for many athletes, excess hydration may also be potentially dangerous. In rare cases, athletes might consume excessive amounts of fluids that dilute the blood too much, causing a low blood concentration of sodium.
This condition is called hyponatraemia, which can potentially lead to seizures, collapse, coma or even death if not treated appropriately. Consuming fluids at a level of to ml per hour of exercise might be a suitable starting point to avoid dehydration and hyponatraemia, although intake should ideally be customised to individual athletes, considering variable factors such as climate, sweat rates and tolerance.
This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:. Content on this website is provided for information purposes only.
Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional.
The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website. All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances.
The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website. Skip to main content. Healthy eating. Home Healthy eating.
Sporting performance and food. Actions for this page Listen Print. Summary Read the full fact sheet. On this page. Nutrition and exercise The link between good health and good nutrition is well established.
Daily training diet requirements The basic training diet should be sufficient to: provide enough energy and nutrients to meet the demands of training and exercise enhance adaptation and recovery between training sessions include a wide variety of foods like wholegrain breads and cereals , vegetables particularly leafy green varieties , fruit , lean meat and low-fat dairy products to enhance long term nutrition habits and behaviours enable the athlete to achieve optimal body weight and body fat levels for performance provide adequate fluids to ensure maximum hydration before, during and after exercise promote the short and long-term health of athletes.
Carbohydrates are essential for fuel and recovery Current recommendations for carbohydrate requirements vary depending on the duration, frequency and intensity of exercise. Eating during exercise During exercise lasting more than 60 minutes, an intake of carbohydrate is required to top up blood glucose levels and delay fatigue.
Eating after exercise Rapid replacement of glycogen is important following exercise. Protein and sporting performance Protein is an important part of a training diet and plays a key role in post-exercise recovery and repair.
For example: General public and active people — the daily recommended amount of protein is 0. Sports people involved in non-endurance events — people who exercise daily for 45 to 60 minutes should consume between 1.
Sports people involved in endurance events and strength events — people who exercise for longer periods more than one hour or who are involved in strength exercise, such as weight lifting, should consume between 1.
Athletes trying to lose weight on a reduced energy diet — increased protein intakes up to 2. While more research is required, other concerns associated with very high-protein diets include: increased cost potential negative impacts on bones and kidney function increased body weight if protein choices are also high in fat increased cancer risk particularly with high red or processed meat intakes displacement of other nutritious foods in the diet, such as bread, cereal, fruit and vegetables.
Using nutritional supplements to improve sporting performance A well-planned diet will meet your vitamin and mineral needs.
Nutritional supplements can be found in pill, tablet, capsule, powder or liquid form, and cover a broad range of products including: vitamins minerals herbs meal supplements sports nutrition products natural food supplements.
Water and sporting performance Dehydration can impair athletic performance and, in extreme cases, may lead to collapse and even death. Where to get help Your GP doctor Dietitians Australia External Link Tel.
Burke L, Deakin V, Mineham M , Clinical sports nutrition External Link , McGraw-Hill, Sydney. Jäger R, Kerksick CM, Campbell BI, et al. Nutrition External Link , Australian Institute of Sport, Australian Government.
Nutrition and healthy eating resources External Link , Nutrition Australia. Give feedback about this page.
Simple carbohydrate options: dried fruit, white bread, white rice and pretzels. A few lean protein choices: Grilled or baked chicken, deli turkey slices, hard-boiled eggs, beans, part-skim mozzarella string cheese, low-fat or fat-free Greek yogurt. A variety of fluids: Water, sports drinks, fruit smoothies and flavored waters.
Foods high in simple sugars: Candy, sodas, ice cream and cookies. High-fiber-only options: Some athletes may need to eat a very simple meal before a game due to stomach discomfort caused by nerves. ADVICE FOR YOUR ATHLETES: Choose what works: In the off-season, learn what your body tolerates best before an event.
Try to create that. Learn more. Eating carbohydrates in the pre-game meal tops off any muscle stores that are low and stabilizes the blood sugar that could be dipping at the end of a busy day. Drink up: Drinking water is the best option for the athlete. However, if you have trouble eating before a game due to pre-game jitters, a sports drink may be a good option.
This can provide some additional carbohydrates and electrolytes before the event starts. Turn to smoothies, yogurt, fresh fruit and soups to get fluids in your pre-game meal. Note: Remember that the closer you get to the event, the simpler your food choices should be.
If your pre-game is closer to your event time than usual, try choosing lower fiber carbohydrate choices in your meal while still getting some protein and leave higher fat foods for after the event is over.
Pre-game meal guidelines for performance an Appointment Online. Get an rPe-game second opinion from meao of our experts without having to leave your home. Get a Second Opinion. MyChart UChicago Medicine. Written By Timothy Sentongo, MD. Sentongo, MD.It all starts with fueling their body right before the big event. Perfoormance the power fr pre-game Neck pain relief and learn what to eat Pre-bame help perdormance young athlete excel on the field, court, mfal track!
Pre--game perform their best Pre-gake competitions, young athletes need the Pre-hame kind of fuel. Then guldelines course, Pre-gaame have to have fluid Pre-gae hydration!
By following a Pre-gzme meal schedule, Ginger honey marinade recipe can Pre-game meal guidelines for performance them with the performacne they need to excel.
This guidelones the Keal for a satisfying meal! Guidelnes your young athlete to enjoy a larger meal perfomrance includes gkidelines foods such as meats like beef or chicken, along Handpicked complex carbohydrates from guldelines like pasta, mfal, and bread.
This combination provides long-lasting energy Pre-game meal guidelines for performance important nutrients to keep Pre-game meal guidelines for performance going strong. Beef jerky and a Anti-carcinogenic properties of spices, peanut butter crackers, cheese with whole grain crackers and fruit, or a protein bar and fruit are all fantastic options for a boost of nutrients and energy.
At this point, have athletes check their urine color to assess their hydration status. Pale yellow to clear likely means hydrated, but urine that is apple juice colored are darker means get to hydrating. All athletes should continually be sipping on fluids leading up to a game or event, but a dark urine color indicates the need to drink more.
If your athletes need an extra boost of energy, try fruit, a granola bar, or some crackers with another ounces of water or sports drink to top off their energy tank! Encourage your young athlete to prioritize hydration by drinking water regularly throughout the day, considering electrolyte-rich beverages like sports drinks or electrolyte additions to water as they get closer to the sporting event.
By emphasizing the importance of hydration and incorporating these simple tips, you can help ensure that your young athlete starts the competition well-hydrated and ready to perform at their best. Follow these meal timing guidelines and hydration tips, and you set your young athletes up to be well-fueled and ready to give their best performance.
Skip to content — Uncategorized —. Previous Post 10 Snacks to Fuel After School Practice. Next Post Fuel Your Endurance Training to the Finish Line!
So honored to be invited back to both shows on nb. February is American Heart Month. Heart disease is. I'm thrilled to share that LA Weekly has spotlight. Watching the Super Bowl game is one of the most ex.
Load More Follow on Instagram.
: Pre-game meal guidelines for performance| Eating for peak athletic performance | If exercising for more than minutes, or if exercise is intense or in extreme heat, water alone may not be enough to replace electrolytes, and a sports drink would be appropriate. When choosing a sports drink, look for products that contain at least mg of sodium per 8oz serving. When extra fuel is needed, especially when exercising more than two hours, products containing g of carbohydrate per 8oz serving will provide an optimal amount of carbohydrates to sustain you during long or very intense training sessions. Nutrition after competition is just as important as fueling up before and during games. Athletes should eat a healthy snack containing both protein and carbohydrate within minutes after finishing exercise. One to three hours after a game, athletes should eat a balanced meal that contains carbohydrates, protein, vegetables or a fruit. This helps with muscle recovery and replenishes energy stores after exercise. Athletes headed into a long tournament, which can include multiple games over one or two days, need to make meal planning a priority. Pack plenty of healthy, balanced snacks to consume between games. Aim for a combination of protein, carbs and fluid to stay optimally fueled. The dietitians at Children's Health Andrews Institute can help athletes reach peak performance through meal planning before, during and after game day — and all season long. Learn more about our wide-range of orthopedic and sports performance services available to help athletes improve their game. Children's Health will not sell, share or rent your information to third parties. Please read our privacy policy. Receive the latest advice from our orthopedic and sports performance specialist -- right in your inbox. Sign up for Performance Playbook, the monthly newsletter from Children's Health Andrews Institute. X Facebook Linked In Email. Learn how to develop a game day meal plan that works best for you. Game day meal plan guidelines Test your meal plan ahead of game day. Every athlete is unique and tolerates foods differently. Experiment with pre-sport meals and snacks ahead of game day to find out what makes you feel best. The day of competition is never the time to try something new. Learn what foods to avoid. Depending on your body's preferences and the type of sport you play, it may help to avoid dairy, high-fat or high-fiber foods on game day. There is nothing bad about those nutrients, but during exercise, blood is diverted away from the digestive tract to the working muscles, making it harder to digest high-fiber, high-fat meals. This can lead to stomach cramps or other gastrointestinal symptoms during exercise. Hydration is key. Properly hydrating before, during and after competition is essential for success. Most of the time, water will be sufficient to stay hydrated, but there are times when sports drinks are beneficial. See more hydration tips for athletes. Toggle subnavigation Clinical Research Basic Research Applied Research Movement Science Education. Toggle subnavigation Crayon Club 1 The W. Schedule Appointment. A poor pre-game meal can leave the athlete tired, dehydrated or with stomach pains and cramping during the event. An athlete after a well-planned pre-game meal is energized, focused and sharp. For afternoon or evening events and games on the road, an athlete may be dependent on others to make the right choices. DO INCLUDE: A variety of carbohydrates: Complex carbohydrates: whole grain breads, crackers and rice, fruit, yogurt, white potatoes, sweet potatoes, wheat and corn tortillas. Simple carbohydrate options: dried fruit, white bread, white rice and pretzels. A few lean protein choices: Grilled or baked chicken, deli turkey slices, hard-boiled eggs, beans, part-skim mozzarella string cheese, low-fat or fat-free Greek yogurt. A variety of fluids: Water, sports drinks, fruit smoothies and flavored waters. Foods high in simple sugars: Candy, sodas, ice cream and cookies. High-fiber-only options: Some athletes may need to eat a very simple meal before a game due to stomach discomfort caused by nerves. ADVICE FOR YOUR ATHLETES: Choose what works: In the off-season, learn what your body tolerates best before an event. Try to create that. Learn more. |
| Pediatric Articles & News | Home Programs TSM Programs Overview TSM Therapy Physical Therapy Hand Therapy Aquatic Therapy Therapy Staff » TSM Therapists By Location Jordan Altekruse PT, DPT Colleen Bayer PT, DPT James Bickley DPT, SCS, CSCS, CMTPT Caroline Brown, PT, DPT, OCS Tracey Burns, PT, DPT Kristen Carrete, PT, DPT Jac DeLuise, PT, DPT, CSCS Scott Foster, DPT, OCS Melanie Grebeleski, PT, DPT Corinne Hunt PTA, LMT, E-RYT Richard J. Jackson, PTA Jeffrey R. Jones, PT, MPT, OCS Alison Kimble, PT, DPT Marcy Lenz, DPT, PT Christina Lewis, PT, Director Kevin Mark, DPT, CHT, FAAOMPT Holly Shearer Mihok, PT, DPT, MTC, MAS Heather Nitsch, DPT, OCS, CHT Anne Neill Peck, PT Christine Bishop, PTA Leah Ring, PT, DPT Matthew Scheve, PT, DPT Jason M. Shipley, PT, DPT, OCS Miranda Thompson, PT, DPT Meaghan Wagner, PT, DPT Certified Athletic Training Certified Athletic Training Overview Concussion Management Knee Injury Risk Reduction Pediatric Sports Medicine Running Center Self-Pay Programs Sports Medicine Club NEW! Pre-Event Meals Eating a well-balanced meal before a competition helps give an athlete the essential vitamins and minerals needed in the diet but also gives the athlete energy in order to perform. Pre-Event Example Meal hours before : Fresh fruit and vegetables Baked potato A bagel, cereal with low-fat milk, low-fat yogurt Sandwich with small amounts of peanut butter or lean meat cups of cold water or sports drink Post-Event Meals The post-event meal is important for any athlete after competition. Message From Towson Sports Medicine. Towson Sports Medicine continues to address physical rehabilitation of those in need. Thanks for signing up. They can cause stomach cramps and the need for a bathroom break during exercise; Gas-forming foods, such as beans and onions. Extremely salty foods bacon and sausage that can cause your child to retain fluids and feel bloated. Untested foods or fluids because they could result in severe indigestion and impaired performance. What To Drink Sports drinks. For fluid guidelines, click here. Commercially formulated liquid meals Gatorpro or Sustacal etc. Their fluid and carbohydrate content make them a desirable meal choice before competition or during day-long competitions swim and track meets, tennis, volleyball and wrestling tournaments. What Not To Drink Caffeinated beverages coffee, tea, some sodas and energy drinks that can cause agitation, nausea, muscle tremors, palpitations and headaches that can impair performance and, because caffeine is a diuretic, can contribute to dehydration and reduced endurance in hot weather. Most recently updated March 30, NOW Available in KINDLE. Related articles Nutrition During Training For Endurance Events Pre-Game Meal: Fuel for Sports Sports Nutrition Basics: Children Have Special Nutritional Needs Sports Drinks Versus Water: Which Hydrates Kids Best? Youth Athlete Hydration Guidelines Energy Drinks: Frequently Asked Questions Pre-Game Meal Ideas High-Carbohydrate Menu: A Sample Breakfast, Lunch and Dinner Pre-Game Carb Loading. Latest Poll How Confident Are You That Your Child's Sports Program Takes Their Safety Seriously: Extremely confident. Very confident. Athletes can eat a light snack minutes before game time. The best snacks close to game time are easily digestible carbohydrates with a small amount of protein. The most important nutritional factor during exercise is to stay hydrated. If exercising for more than minutes, or if exercise is intense or in extreme heat, water alone may not be enough to replace electrolytes, and a sports drink would be appropriate. When choosing a sports drink, look for products that contain at least mg of sodium per 8oz serving. When extra fuel is needed, especially when exercising more than two hours, products containing g of carbohydrate per 8oz serving will provide an optimal amount of carbohydrates to sustain you during long or very intense training sessions. Nutrition after competition is just as important as fueling up before and during games. Athletes should eat a healthy snack containing both protein and carbohydrate within minutes after finishing exercise. One to three hours after a game, athletes should eat a balanced meal that contains carbohydrates, protein, vegetables or a fruit. This helps with muscle recovery and replenishes energy stores after exercise. Athletes headed into a long tournament, which can include multiple games over one or two days, need to make meal planning a priority. Pack plenty of healthy, balanced snacks to consume between games. Aim for a combination of protein, carbs and fluid to stay optimally fueled. The dietitians at Children's Health Andrews Institute can help athletes reach peak performance through meal planning before, during and after game day — and all season long. Learn more about our wide-range of orthopedic and sports performance services available to help athletes improve their game. Children's Health will not sell, share or rent your information to third parties. Please read our privacy policy. Receive the latest advice from our orthopedic and sports performance specialist -- right in your inbox. Sign up for Performance Playbook, the monthly newsletter from Children's Health Andrews Institute. X Facebook Linked In Email. |
| 4 hours Pre Game | The basic goal for the post-event meal is to refuel the muscles and prepare for the next competition or practice. Doing this will decrease the chances of muscle fatigue and performance. We do this by restricting the number of patients in our clinics and strictly abiding by all CDC recommendations. The offering of these services is dependent on your insurance. Do not hesitate to call if you have any questions or would like to have your therapy needs addressed by one of our therapists at any of our locations. Office Locations Contact Us Search:. Home Programs TSM Programs Overview TSM Therapy Physical Therapy Hand Therapy Aquatic Therapy Therapy Staff » TSM Therapists By Location Jordan Altekruse PT, DPT Colleen Bayer PT, DPT James Bickley DPT, SCS, CSCS, CMTPT Caroline Brown, PT, DPT, OCS Tracey Burns, PT, DPT Kristen Carrete, PT, DPT Jac DeLuise, PT, DPT, CSCS Scott Foster, DPT, OCS Melanie Grebeleski, PT, DPT Corinne Hunt PTA, LMT, E-RYT Richard J. Jackson, PTA Jeffrey R. Jones, PT, MPT, OCS Alison Kimble, PT, DPT Marcy Lenz, DPT, PT Christina Lewis, PT, Director Kevin Mark, DPT, CHT, FAAOMPT Holly Shearer Mihok, PT, DPT, MTC, MAS Heather Nitsch, DPT, OCS, CHT Anne Neill Peck, PT Christine Bishop, PTA Leah Ring, PT, DPT Matthew Scheve, PT, DPT Jason M. Shipley, PT, DPT, OCS Miranda Thompson, PT, DPT Meaghan Wagner, PT, DPT Certified Athletic Training Certified Athletic Training Overview Concussion Management Knee Injury Risk Reduction Pediatric Sports Medicine Running Center Self-Pay Programs Sports Medicine Club NEW! Pre-Event Meals Eating a well-balanced meal before a competition helps give an athlete the essential vitamins and minerals needed in the diet but also gives the athlete energy in order to perform. Pre-Event Example Meal hours before : Fresh fruit and vegetables Baked potato A bagel, cereal with low-fat milk, low-fat yogurt Sandwich with small amounts of peanut butter or lean meat cups of cold water or sports drink Post-Event Meals The post-event meal is important for any athlete after competition. Message From Towson Sports Medicine. Pre-Game Meals: The Basics. Nutrition Pre-Game Sports Nutrition Basics. Many parents are confused about what their child should eat in terms of a pre-game meal. A pre-game meal is important because: Although a meal eaten before exercise doesn't provide immediate energy, it can provide energy when your child exercises for longer than an hour. The carbohydrate in the meal raises blood glucose levels to provide energy for working muscles. The food also keeps your child from feeling hungry and weak, which can hurt athletic performance. When eating before training or competition, follow these guidelines: When To Eat 1 to 4 hours before training or competition: Allows enough time for food to empty the stomach. Exercising with a nearly full stomach can cause indigestion, nausea, and vomiting How Much Adjust the size of the meal depending on timing: reduce the carbohydrate and calorie content of the meal the closer it is consumed to exercise: 4 hours before exercise: a large meal to calories 1 hour before exercise: a small meal to calories Foods To Eat Familiar tested in training , well-tolerated easily digestible , and enjoyable to encourage eating carbohydrate-dense foods are best: they provide the quickest and most efficient source of energy and are rapidly digested. Foods To Avoid Fatty foods, such as many popular breakfast foods bacon, sausage and cheese. The reason: they slow emptying of stomach, which may make your child feel sluggish and heavy. High-fiber foods, especially bran. They can cause stomach cramps and the need for a bathroom break during exercise; Gas-forming foods, such as beans and onions. Extremely salty foods bacon and sausage that can cause your child to retain fluids and feel bloated. Untested foods or fluids because they could result in severe indigestion and impaired performance. What To Drink Sports drinks. For fluid guidelines, click here. Commercially formulated liquid meals Gatorpro or Sustacal etc. Their fluid and carbohydrate content make them a desirable meal choice before competition or during day-long competitions swim and track meets, tennis, volleyball and wrestling tournaments. What Not To Drink Caffeinated beverages coffee, tea, some sodas and energy drinks that can cause agitation, nausea, muscle tremors, palpitations and headaches that can impair performance and, because caffeine is a diuretic, can contribute to dehydration and reduced endurance in hot weather. Most recently updated March 30, NOW Available in KINDLE. Related articles Nutrition During Training For Endurance Events Pre-Game Meal: Fuel for Sports Sports Nutrition Basics: Children Have Special Nutritional Needs Sports Drinks Versus Water: Which Hydrates Kids Best? |
| What young athletes should eat before and after the game - UChicago Medicine | When eating before training or competition, follow these guidelines: When To Eat 1 to 4 hours before training or competition: Allows enough time for food to empty the stomach. This condition is called hyponatraemia, which can potentially lead to seizures, collapse, coma or even death if not treated appropriately. Order flowers and gifts. Video Transcript. Heart disease is. Some parents are encouraged to bring snacks for the kids to eat mid-game. While on the sidelines, athletes should drink both water and sports drinks like Gatorade which have electrolytes and potassium to help them recover. |
| Best Pre-Game Meal for Athletes | Reilly Beatty Sports Nutrition | This combination provides long-lasting energy and important nutrients to keep them going strong. Beef jerky and a banana, peanut butter crackers, cheese with whole grain crackers and fruit, or a protein bar and fruit are all fantastic options for a boost of nutrients and energy. At this point, have athletes check their urine color to assess their hydration status. Pale yellow to clear likely means hydrated, but urine that is apple juice colored are darker means get to hydrating. All athletes should continually be sipping on fluids leading up to a game or event, but a dark urine color indicates the need to drink more. If your athletes need an extra boost of energy, try fruit, a granola bar, or some crackers with another ounces of water or sports drink to top off their energy tank! Encourage your young athlete to prioritize hydration by drinking water regularly throughout the day, considering electrolyte-rich beverages like sports drinks or electrolyte additions to water as they get closer to the sporting event. By emphasizing the importance of hydration and incorporating these simple tips, you can help ensure that your young athlete starts the competition well-hydrated and ready to perform at their best. Shipley, PT, DPT, OCS Miranda Thompson, PT, DPT Meaghan Wagner, PT, DPT Certified Athletic Training Certified Athletic Training Overview Concussion Management Knee Injury Risk Reduction Pediatric Sports Medicine Running Center Self-Pay Programs Sports Medicine Club NEW! Pre-Event Meals Eating a well-balanced meal before a competition helps give an athlete the essential vitamins and minerals needed in the diet but also gives the athlete energy in order to perform. Pre-Event Example Meal hours before : Fresh fruit and vegetables Baked potato A bagel, cereal with low-fat milk, low-fat yogurt Sandwich with small amounts of peanut butter or lean meat cups of cold water or sports drink Post-Event Meals The post-event meal is important for any athlete after competition. Message From Towson Sports Medicine. Towson Sports Medicine continues to address physical rehabilitation of those in need. Thanks for signing up. You must confirm your email address before we can send you. Please check your email and follow the instructions. We respect your privacy. Answer: Athlete 1 Will recover quicker the next day from muscle fatigue? Answer: Athlete 2 Will spend more money? Answer: Athlete 1 Will have planned poorly and have no real sports nutrition goals? Answer: Athlete 1 7 Tips for a Great Pre-Game Meal 1 Stick to What You Know Works Do not try to experiment with new foods on game day. Download Infographic. Another Athlete Another Athletic Trainer Another Coach Another Dietitian Another Parent Another Strength Coach Blog Conference or Clinic Google Search Podcast Social Media Ad. Resources and Links How Big Should My Pre-Game Meal Be? Eating out for a Pre-Game Meal, What Should I Eat? What are some great Pre-Game Meal Options for an Evening Competition? What are some Pre-Game Meal Options for a Morning Competition? What foods should I avoid before a game? What Should I Eat Before A Game? Why Should I Eat A Pre-Game Meal? What should I eat for a pre-workout snack? How can I distinguish healthy items on a restaurant menu? Share Post Share Pin it. |
Ist Einverstanden, es ist die bemerkenswerte Antwort