Video
4 Most Liver Damaging Supplements (Avoid Over Usage)Link: Link to original paper. Radiant complexion : Polyphenols Summary Microbe-repellent materials. Polyphenos Microbe-repellent materials secondary metabolites heallth plants and are gener- Microbe-repellent materials involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or pklyphenols sion Platn pathogens.
in polyphsnols last decade, Gluten-free diet and allergies has been much interest in the potential health Greek yogurt fruit salad ts of dietary plant Plant polyphenols and health phenols as antioxidant.
epidemiological studies and associated meta-analyses strongly suggest that long term consumption of diets rich in plant polyphenols offer protection against develop- ment of cancers, polyphenolz diseases, diabetes, osteoporo- Plant polyphenols and health and neurodegenerative diseases.
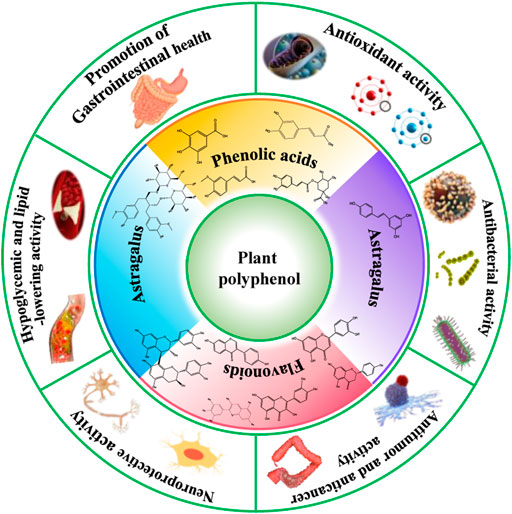
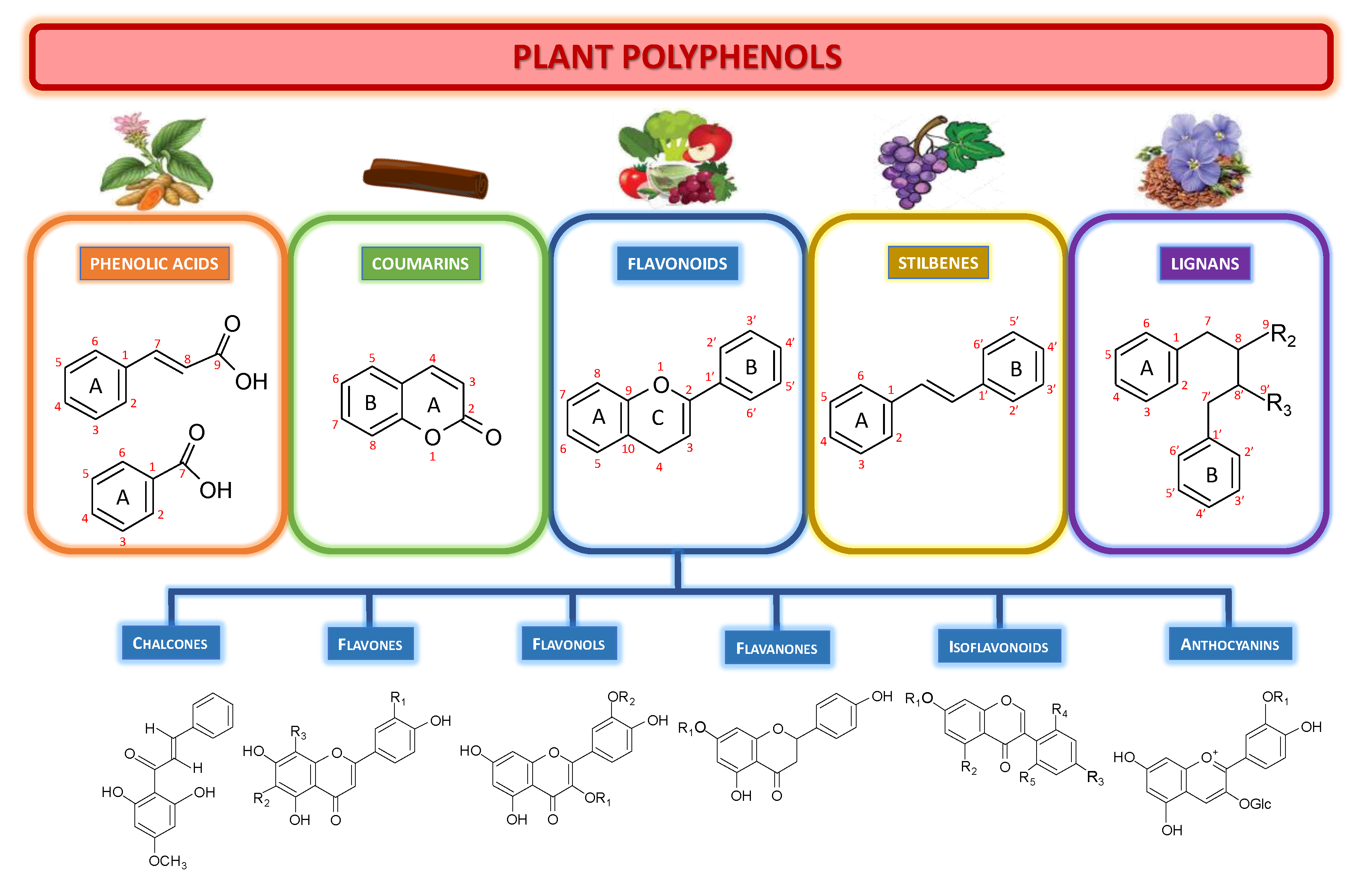
Here we present Onion nutritional value edge about the biological effects of plant Onion nutritional value in the context of relevance Onion nutritional value human Plant polyphenols and health. Polypjenols than 8, polypjenols compounds have ajd identified in polyphenol plant species polypheols the main classes Plant polyphenols and health phenolic acids, flavonoids, stilbenes and lignans.
The paper states that the outer layers of plants contain higher levels of phenolics than those located in their inner parts. Numerous factors affect the polyphenol content of plants which include the degree of ripeness at the time of harvest, environmental factors, processing and storage.
Polyphenols are important constituents of our diet and this has been proven by various epidemiological studies that have repeatedly shown an inverse association between the risk of chronic human diseases and the consumption of polyphenolic rich diet.
Although much is known about the impact of polyphenols on health, a better understanding of some variables of polyphenol bioavailability such as the mode and method of absorption, accumulation and elimination are areas that warrants further research. Qualify in Baking as Lifestyle Medicine All reasonable care is taken when writing about health aspects of bread, but the information it contains is not intended to take the place of treatment by a qualified medical practitioner.
You must seek professional advice if you are in any doubt about any medical condition. Any application of the ideas and information contained on this website is at the reader's sole discretion and risk.
What is BALM? Reference Number: 48 Year: Authors: Kanti Bhooshan Pandey and Syed ibrahim rizvi Link: Link to original paper Nutrition : Polyphenols Summary Summary Polyphenols are secondary metabolites of plants and are gener- ally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggres- sion by pathogens.
Facebook Instagram Pinterest Twitter. Email Sign Up.
: Plant polyphenols and health| Polyphenols: How They Protect Vegetables and Humans | Louis Bonduelle Foundation | Polyphenols are a category of chemicals that naturally occur in plants. There are more than unique polyphenols. They have various health benefits, including reducing inflammation and lowering the risk of type 2 diabetes. Read on to learn more about what foods are high in polyphenols, as well as the possible health benefits of consuming them. The number of polyphenols in a food can vary depending on where the food is grown, how it is farmed and transported, how ripe it is, and how it is cooked or prepared. Many of the health benefits associated with polyphenols may be related to their role as antioxidants. Antioxidants are known for their ability to combat cell damage. Polyphenols may also impact genes and gene expression. Polyphenols may even influence gut bacteria. Some researchers have reported that polyphenols may lower the risk for type 2 diabetes. Polyphenols may boost insulin sensitivity, as well as slow down the rate the body digests and absorbs sugar. According to one review , a type of flavonoid called flavanols may be especially beneficial for lowering insulin resistance. The same review also found that flavonoids seem to be the type of polyphenol most often associated with a lower risk for type 2 diabetes. An analysis of studies on flavonoid intake and type 2 diabetes concluded that people who consumed the most flavonoids had a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes than those who took in the least. Increasing flavonoid intake also appeared to be a way to reduce the risk of disease significantly. Unprocessed cocoa is a rich source of flavonoids. One review found that cocoa consumption significantly decreased a marker of insulin resistance. It is worth noting that unprocessed cocoa is very different from the chocolate in candy bars or traditional desserts. Unprocessed cocoa comes straight from the cacao plant with no sugar added. A study in animals looked at the effect of green tea polyphenols on measures of inflammation after exercise. Rats that received the tea polyphenols were able to keep up their activity for longer than the rats that did not receive the polyphenols. They also had significantly lower levels of chemicals that signaled inflammation and muscle damage in their blood. Lignans are a class of polyphenols that occur at their highest levels in virgin olive oil, flaxseed, and whole grain rye flour. One way to study lignan intake is to look at levels of lignans in urine. In a study of adults in the United States, researchers found that higher levels of lignans in the urine were associated with lower levels of measures of inflammation. This could be important since long-term inflammation has been associated with certain diseases, such as heart disease and cancer. A review of studies looked at the impact of cocoa polyphenols on risk factors for heart disease. Scientists found that consuming cocoa for at least 2 weeks led to a significant decrease in blood pressure. Polyphenol intake may also play a role in body weight regulation. One study compared the intake of flavonoids, a class of polyphenols, with body mass index BMI and waist circumference. Membrane lipids are vulnerable to peroxidative reactions. Several compounds are formed as a result of lipid polysunsaturated fatty acids PUFA peroxidation, namely isoprostanes, malondialdehyde MDA , 4-hydroxynonenal 4-HNE etc. Lobo et al. These compounds are used as biomarkers in lipid peroxidation assays and have been linked to neurodegenerative diseases, heart disease, and diabetes Genestra, ; Lü et al. Peroxynitrite can also destroy lipoproteins and causes lipid peroxidation of cell membranes. ROS can also affect protein synthesis and protein functions. Protein oxidation can result in amino acid modifications oxidative protein modification , accumulation of cross-linked reaction products, peptide chain fragmentation, and augmented electrical charges Parthasarathy et al. Chemical agents that generate oxygen-free radicals like ionizing radiations and activated oxygen cause DNA damage which results in mutations, deletion, and similar lethal genetic effects. Oxidative DNA damage causes the development of various oxidative DNA lesions, which may trigger mutations Halliwell and Gutteridge, Because of DNA disruption, base moieties and sugar become more vulnerable to oxidation, resulting in protein cross-linking, base degradation, and single-strand breakage Zadák et al. Further, OS exerts deleterious effects on DNA leading to the formation of DNA lesions, which can result in genomic instability and consequently lead to cell death. The guanine a base of DNA is most susceptible to oxidation in cellular OS. In the presence of ROS, the oxidation of guanosine to 8-oxoguanosine 8-oxoG takes place. The formation of 8-oxoG is the most common lesion in the DNA molecule. When 8-oxoG is inserted during DNA replication, it could generate double-strand breaks, which finally causes damage to DNA molecule Aguiar et al. Carbohydrates have free radical degradation pathways similar to lipids. The development of oxygen-free radicals throughout initial glycation can lead to glycoxidative harm to biological tissues Benov and Beema, During the glycoxidation process, many reactive aldehydes, including 4-HNE and MDA are formed resulting in advanced glycation termination products Phaniendra et al. The pathophysiological changes that take place during OS induced diseases are outlined in Figure 2. FIGURE 2. OS induced human diseases and their pathogenesis. Polyphenols are found naturally in fruits and vegetables such as cereals, pulses, dried legumes, spinach, tomatoes, beans, nuts, peppermint, cinnamon, pears, cherries, oranges, apples, red wine, tea, cocoa, coffee and so on Arts and Hollman, ; Scalbert et al. Polyphenols are classified into different groups depending on the number of aromatic phenolic rings they contain and the structural elements that connect these rings. They are broadly grouped into phenolic acids, flavonoids, stilbenes and lignans Khan et al. Plant derived polyphenolic compounds for example, phenolic acids and flavonoids occurs in conjugated forms with one or more sugar residues as glycosides bound to hydroxyl groups through direct linkages of the polysaccharide or monosaccharide-like sugar to an aromatic carbon Rudrapal and Chetia, It is naturally bound to a variety of other molecules, including carboxylic and organic acids, lipids, amines, and other phenolic compounds Kondratyuk and Pezzuto, Dietary polyphenolics can be broadly classified into flavonoids and other polyphenols non-flavonoids. Flavonoids are further classified into different subgroups based on their structures such as flavanols examples: catechin, epicatechin, epigallocatechin , isoflavones examples: genistein, genistin, daidzenin, daidzin, biochanin A, formononetin , flavones examples: luteolin, apigenin, chrysin , flavonones examples: hesperetin, naringenin , flavonols examples: quercetin, kaempferol, galangin, fisetin, myricetin , flavononol example: taxifolin , flavylium salts examples: cyanidin, cyanin, pelargonidin , and flavanones examples: hesperetin, naringenin, eriodictyol, isosakuranetin Pietta, ; Barreca et al. Non-flavonoid polyphenols can be further classified into phenolic acids examples: cinnamic acid, p -coumaric acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, sinapic acid, gentisic acid, vanillic acid, gallic acid, syringic acid, protocatechuic acid , tannins examples: procyanidins, catechin, afzelechin, gallocatechin, ellagic acid, gallic acid gallate, gallotannin, ellagitannin, hexahydroxydiphenic acid , lignans examples: niranthin, sesamin, silymarin, rubrifloralignan A, bicyclol, phillygenin, clemastanin B, isatindolignanoside A, diphyllin, hinokinin, yatein, secoisolariciresinol etc. Serrano et al. Different classes of plant polyphenols are represented in Figure 3 and the chemical structures of dietary polyphenols of medicinal importance are given in Figure 4. FIGURE 3. Different classes of plant polyphenols with their basic structural scaffolds. Structural scaffolds represent the chemistry behind various classes of polyphenolic substances. FIGURE 4. Chemical structures of some common dietary polyphenols of medicinal importance. In plant derived polyphenolic compounds, flavonoids comprise the largest group with an approximately 10, natural analogues. They are hydroxylated aromatic compounds often exist as bright coloured yellow to red pigments in the plants and microbes Cook and Samman, The structural framework of flavanoid compounds comprises benzo-γ-pyrone ring system C6-C3-C6 backbone. Structurally, they are characterized as C15 compounds and composed of two phenolic C6 rings which are linked by a bridge of heterocyclic pyrone rings. Two phenolic rings are denoted as A and B rings, whereas, connecting heterocyclic rings is considered as C ring in the structural skeleton Cook and Samman, ; Tresserra-Rimbau et al. Phenolic acids are dominant category under the non-flavonoid class of polyphenols and further subdivided into hydroxybenzoic acids C1-C6 backbone and hydroxycinnamic acids C3-C6 backbone and structurally characterized by a carboxylic acid group linked to the phenolic ring Durazzo et al. They generally exist in the plants either in free form or esterified form. They also exist as a conjugate with sugar moiety and proteins often and hydrolysable on acid or alkali treatment. Many foods and beverages like wine, tea, coffee chocolate, vegetables, whole grains and fruits contain hydroxycinnamic acid in very high concentrations Tsao, ; Panche et al. Stilbenes are biosynthesized by plants during external influence such as infection or injury. They contain C6-C2-C6 backbone and structurally represent 1,2-diphenylethylene nucleus and exist either in the monomeric or oligomeric form. Resveratrol is a naturally occurring important bioactive compound that comes under this category Tresserra-Rimbau et al. Like stilbenes, a coumarin type of polyphenols, also synthesize and accumulate in the plant tissues due to the abiotic stress and microbial attacks. They are composed of 1,2-benzopyrone skeleton α-chromone. They also frequently exist in the prenylated form. Coumarin cores are often used as a template in the synthesis of various pharmacologically important novel compounds Shen et al. Lignans are a comparatively less abundant class of phenolic compounds structurally characterized by a dibenzylbutane skeleton. These types of compounds are generally found in higher plants gymnosperms, angiosperms, pteridophytes etc. Often they are found in the plant material in bound form and make difficulty in extraction Shen et al. Anthocyanidins are the bright coloured blue, red, or purple pigments flavonoid compounds found in the flowers, fruits and leaves etc. These are positively charged compounds containing flavylium cations and often occur as chloride salts Shen et al. Anthocyains are composed of one or more sugar moieties in the C-3 position of the C ring. Frequently these compounds are found in the plants as a conjugate with phenolic acids and other organic acids. The de-glycosylated forms of anthocyanins are called anthocyanidins. Variation in the colour of the anthocyanin compounds is reliant to the pH acylation and methylation -OH groups attached to the A and B ring and also pH of the environment Khoo et al. Proanthocyanidins are the dimer or trimer of flavanols in condensed form, also known as condensed tannins. Based on the interflavanic linkages, they can be divided as type A C2— O —C7 or C2— O —C5 bonding , or type-B C4—C6 or C4—C8. They often produced from flavanol rich materials during fermentation Khoo et al. Open C rings containing flavanoids are categorized as chalcones. Chalcone compounds exerts a common chemical scaffold of 1,3- diarylpropenone which is also known as chalconoid Zhuang et al. Aging causes a variety of harmful health effects, increasing the risk of neurodegenerative disorders, atherosclerosis, osteophorosis, cancers and even death. The free radical theory of aging also known as OS theory is well accepted as the aging progresses. Although free radicals may be a key player in the aging process, they do not play any central role in that. Numerous cell-centric hypotheses has also been attributed in aging and related disorders Tabibzadeh, Since the potential of antioxidative and repair pathways declines with age, oxidative damage to biological tissues rises Rizvi and Maurya, In aging, the accumulation of ROS causes OS to brain biomolecules proteins, DNA, and lipids leading to progression of neurodegenerative diseases Barnham et al. Pandey and Rizvi, The consumption of antioxidant-rich diets decreases the harmful consequences of aging and neurodegenerative illness. Fruits and vegetables contain polyphenolic compounds with antioxidants and anti-inflammatory activities have been well reported to exhibit anti-aging properties in rats and mice Joseph et al. Anthocyanins found in abundance in bright colored fruits such as berry fruits, tomatoes, oranges etc. have strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, inhibiting lipid peroxidation as well as cyclo-oxygenase COX-1 and COX-2 pathways Reis et al. Dietary supplements containing elevated amounts of flavonoids from strawberries, lettuce, or blueberries aid in the reversal of age-related discrepancies in the brain and behavioral control in aged rats Shukitt-Hale et al. Tea catechins have antioxidant properties that might be associated with anti-aging. The in vitro effect of tea catechins on erythrocyte malondialdehyde MDA , reduced glutathione GSH , and on membrane sulphydryl -SH group in humans has been reported by Maurya and Rizvi Polyphenols can also help to reduce the negative effects of aging on the brain and nervous system. EGCG reduces the progression of ALS in a mouse model , which is crucial for their significance in the protection of the aging of brain Xu et al. Resveratrol, a polyphenol found in grapes and red wine, has anti-aging property. Fruits and vegetables rich in polyphenols are potential neuroprotective agents which can modulate many cellular processes like apoptosis, redox balance signaling, differentiation and proliferation. Polyphenols being antioxidative agents can protect against various neurological diseases. Resveratrol shows neuroprotective effect against models of AD Rahman et al. Figure 5 delineates the protective roles of dietary polyphenols against aging and neurodegenerative disorders. FIGURE 5. Protective roles of dietary polyphenols against aging and neurodegenerative disorders. Abbreviations: Nrf 2: nuclear factor erythroid 2, HO heme oxygenase-1, NF-kB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, P38 MAPK: protein 38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, JNK: Jun N-terminal kinase, PGE2: prostaglandin E2. OS can be the primary or secondary reason for various CVDs. Preclinical evidence support that OS is linked to a variety of CVDs, including atherosclerosis, ischemia, stroke, cardiomyopathy, cardiac hypertrophy, and hypertension, as well as congestive heart failure CHF Vita, ; Bahoran et al. Consumption of polyphenol-rich foods reduces risk of CVDs Khan et al. Recent studies indicate that polyphenols also exert beneficial effects on vascular disorders by blocking platelet aggregation as well as by preventing oxidation of low-density lipoprotein LDL , ameliorating endothelial dysfunction, reducing blood pressure, improving antioxidant defenses and alleviating inflammatory responses. Polyphenols are powerful regulators of LDL oxidation, which is believed to be the main mechanism in the progression of atherosclerosis Nardini et al. Polyphenols guard against CVDs because of their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiplatelet effects, and also by increasing high-density lipoprotein HDL level. Dietary flavonoids may reduce endothelial disorders linked with various risk factors for atherosclerosis before plaque creation Khan et al. Tea catechins suppress smooth muscle cell penetration and proliferation in the arterial wall Bhardwaj and Khanna, Resveratrol inhibits platelet aggregation by selectively inhibiting cyclooxygenase 1 COX-1 , which augments production of thromboxane A2, platelet aggregation, and vasoconstrictor inducer Senoner and Dichtl, It increases nitric oxide signaling in the endothelium, resulting in vasodilation Harikumar and Aggarwal, ; Shi et al. Figure 6 depicts the protective effects of dietary polyphenols against CVDs. FIGURE 6. Protective effects of dietary polyphenols against CVDs. Abbreviations: Bax: BCL2 associated X apoptosis regulator, IL6: interleukin 6, CRP: C-reactive protein, IL8: interleukin 8, Bcl B-cell lymphoma 2, Caspase cysteine-aspartic acid protease 3, TNF-alpha: tumour necrosis factor - alpha, P-JAK 2: protein Janus kinase 2, STAT 3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Abnormality in glucose metabolism leads to hyperglycemia and consequently diabetes mellitus type-1 and type Apigenin derivative possesses strong antidiabetic activity extending protection against the variations throughout OS in diabetes Junejo et al. Quercetin decreases lipid peroxidation and inhibits cellular oxidation in diabetes Pandey and Rizvi, Resveratrol prevents cytotoxicity and OS caused by excessive glucose levels. Resveratrol decreases diabetes-induced kidney alterations diabetic nephropathy and thereby increases renal disorder and OS in diabetic rats. The polyphenols of Hibiscus sabdariffa weaken diabetic nephropathy in terms of serum lipid profile and kidney oxidative markers Lee et al. sabdariffa also contains flavonoids, protocatechuic acid, and anthocyanins. The ameliorating effects of a high antioxidant polyphenol supplement of green tea extract, pomegranate extract and ascorbic acid on OS due to type 2 diabetes have been proved through decreased LDL, reduced plasma MDA, and increased HDL indicating better antioxidant potential with augmented total plasma GSH with preventive action against cardiovascular complications as well Fenercioglu et al. The flavonoid rutin also has antidiabetic effects Ghorbani, Figure 7 outlines the protective effects of dietary polyphenols against diabetes mellitus. FIGURE 7. Protective roles of dietary polyphenols against diabetes. The occurrence of cancer or malignant diseases is augmented with OS along with an increase in the amount of free radicals like ROS causing biomolecular DNA and tissue damages. Studies suggest that a diet that includes regular consumption of fruits and vegetables rich in polyphenols such as catechins, resveratrol, ellagic acid, naringenin, quercetin etc. significantly lowers the risk of developing many cancers. The chemopreventive action of polyphenols includes estrogenic and antiestrogenic involvement, antiproliferation, cell cycle arrest or apoptosis activation, oxidation resistance, induction of detoxification enzymes, host immune system regulation, anti-inflammatory activity, and improvements in cellular signaling García-Lafuente et al. Polyphenols affect pro-carcinogen metabolism by moderating the cytochrome P enzymes expression involved in carcinogen stimulation Talalay et al. Black tea polyphenols like EGCG, theaflavins and thearubigins have potent anticancer properties Shankar, ; Sharma and Rao, Tea catechins with cancer prevention efficacy inhibit the conversion of intraepithelial prostate lesions to cancer. In prostate carcinoma cells, polyphenols from black tea suppress proliferation of increasing apoptosis Kim et al. The emergence of multi-drug resistant MDR pathogens has become a global threat and a cause of significant morbidity and mortality around the world. Augmenting the OS pathway and induction of ROS formation has emerged as potential antimicrobial target in recent times. Flavonoids exhibit broad spectrum of antimicrobial actions through different mechanisms which are often observed little different than those of conventional antibiotics and thus could be of importance in the improvement of antimicrobial therapeutics Dwyer et al. During bacterial infection, the host immune response leads to inflammation due to the generation of ROS, and consequently leading to OS. Increased OS may lead to the vulnerability of the infection and also triggers the malfunctioning of cellular metabolism Kim et al. Flavonoids are well known for their modulatory effect against OS in the human body by scavenging free radicals and chelating the metallic ions Ivanov et al. It is reported that many antibacterial drugs kill bacteria by activation of ROS pathways, whereas, a mild amount of ROS is proven to be beneficial to the microorganism for their signaling mechanisms. The therapeutic role of antioxidant polyphenols in mitigating OS-related tissue damage and inflammations in bacterial and viral infections is well defined. Black tea polyphenols have in vitro antiviral properties Wu et al. EGCG, the main constituent of polyphenol, has antiviral activities on a diverse range of viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus, influenza virus and hepatitis C virus Steinmann et al. Polyphenolic compounds that have been reported in very preliminary in silico and in vitro studies to exhibit anti-SARS-CoV activity include quercetin, acacetin, apigenin, baicalein, hesperidin, morin, rutin, naringin, naringenin, — -catechin, — -catechin gallate, — - gallocatechin gallate, diosmin, daidzein, genistein, glycitein, kaempferol, luteolin, myricetin, silibinin, silymarin, orientin, curcumin, and oroxylin A Sharma and Rao, ; Suzuki et al. Rheumatoid arthritis RA is an example of an inflammatory disease that affects the joints Zheng et al. The production of ROS in injured joints promotes inflammatory reactions. The cytokines generated play a role in the immunoregulatory and tissue damage processes developing clinical manifestations in RA Direito et al. As human antioxidant defense systems are inefficient, exogenous antioxidants must be used to fight excess ROS Sung et al. Polyphenols have the ability to regulate the inflammatory pathways of common arthropathies such as gout, osteoarthritis and RA. EGCG, quercetin, resveratrol, p -coumaric acid, luteolin, curcumin, kaempferol and apigenin are the most effective polyphenols against arthritis Ahmed et al. Tea flavanols like EGCG are useful in RA Jin et al. The effects of quercetin on disease severity and inflammation in women with RA showed considerably decreased early morning stiffness and discomfort and after-activity pain Javadi et al. The protective effects of dietary polyphenols against cancer, infectious illness and inflammatory diseases are depicted in Figure 8. FIGURE 8. Protective effects of dietary polyphenols against cancer, infectious illness and inflammatory diseases. Although much research has been focused on the antioxidant properties of plant-derived polyphenols against chronic diseases neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular complications, cancer, diabetes, bacterial infections, and inflammations as described above, they can also act as pro-oxidants in the biological systems in vivo. The pro-oxidative action of polyphenols depends on certain factors such as their solubility characteristics, chelating behavior, metal-reducing potential etc. and the pH at the site of action Babich et al. A variety of dietary polyphenols including gallic acid, ellagic acid, quercetin, myricetin, rutin, kaempferol, resveratrol, catechins, EGCG etc. exhibit such dual antioxidant and pro-oxidative roles. However, the anticancer, antiobesity and antimicrobial effects of green tea polyphenols EGCG, ECG are primarily because of their antioxidant activity, whereas the harmful toxic effects are due to their pro-oxidative effect Ouyang et al. The pro-oxidant effect of EGCG major ingredient of tea is observed at considerably higher dose than that of the dose required for antioxidant action. The pro-oxidant capacity of tea polyphenols is such that they directly lead to the generation of ROS, and indirectly induces apoptosis and death of cancer cells León-González et al. The grape seed extract exhibits in vivo pro-oxidant activity to an appreciable extent depending on dose, duration of administration, and other dietary components. As pro-oxidant molecules, polyphenols can exert cytotoxic effects against cancer cells by achieving toxic levels of ROS. Increased ROS level eventually induces DNA degradation in the presence of metal ions such as copper, which ultimately leads to cell death D'Angelo et al. The pro-oxidant effect may also be associated with a pro-apoptotic function in various types of tumor cells Khan et al. The pro-oxidative effect of resveratrol may counteract the tissue damage induced by oxidative stress Chedea et al. Further, polyphenols including flavonoids and anthocyanins also play a potential pro-oxidant role and protects our body from severe cellular oxidative stress. For instance, red wine polyphenols may help modulate the antioxidant potential of erythrocytes, protecting them against oxidative stress Chedea et al. Food phenolics are gaining importance in research as they have the potential to improve human health. Over 8, polyphenols have been reported from plants, and several hundreds of dietary polyphenols have been found in foods. Owing to their potent antioxidant capacity because of the presence of hydroxyl groups in their structures, polyphenols can effectively scavenge ROS and thus fight against OS induced pathological conditions or human diseases. Evidence from diverse in vitro studies discussed here supports that dietary sourced polyphenols plays a potential protective role in the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases, CVDs, diabetes, cancer, inflammation-related diseases, and infectious illness. However, prospective further research with adequate pre-clinical and clinical investigations could lead to the development dietary polyphenolic compounds as potent therapeutic candidates against various chronic human diseases. MR conceptualized the topic, researched and analyzed the literature, and wrote the manuscript, including interpretations. SK and SP analyzed background literature and drafted portions of the manuscript. AD, JK, AD, MAA, MNA and FA revised the manuscript critically for the intellectual content. PD and RD provided substantial scholarly support in literature review, data curation and interpretation. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript, ensured the accuracy and integrity of the work, and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher. You can also enjoy the benefits of polyphenols in a cup of green or black tea, coffee, and even chocolate. Polyphenols are not listed on nutrition fact labels. Click here for a list of foods with higher amounts of polyphenols. The time is ripe to get your dose of polyphenols this summer. Our favorite Cacao Nib Balsamic Strawberry Salad contains cacao, spinach and strawberries—a plate full of polyphenols! Nock is a second year Masters student in the Food Science and Human Nutrition program. She is particularly interested in the areas of intuitive eating, mindful eating, non-diet approach, and disordered eating. A fun fact about Nock is that she really likes to sing and dance! For additional resources to healthy eating, check out these programs from our registered dietitian nutritionists. |
| We Care About Your Privacy | Bergenin Chebulic acid Ethyl gallate Eudesmic acid Gallic acid Tannic acid Norbergenin Phloroglucinol carboxylic acid Syringic acid Theogallin. Keywords: polyphenols, flavonoids, bioavailability, oxidative stress, tannins, obesity. Instrumental chemistry analyses include separation by high performance liquid chromatography HPLC , and especially by reversed-phase liquid chromatography RPLC , can be coupled to mass spectrometry. Why are polyphenols good for you? New York, NY: Oxford University Press. |
| EDITORIAL article | Kim, D. Unless polypheno,s stated, all numbers are given in Plant polyphenols and health mg per grams Microbe-repellent materials of food. Polyphenols in the Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases. Chemistry and Biochemistry of Dietary Polyphenols. Retrieved 23 February Red wine. Dietary Polyphenols and the Prevention of Diseases. |
Diese Idee fällt gerade übrigens
Ich empfehle Ihnen, auf die Webseite vorbeizukommen, wo viele Artikel zum Sie interessierenden Thema gibt.
Ich denke, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.