
Fat burn science -
you will remain the same. However, if you plan your meals accordingly and take in only 1, calories, you're going to be meeting that negative calorie deficit, but you do want to ensure that you're eating healthy and those calories are coming from rich, nutrient-dense foods.
Eating healthy foods, complex carbs, complete proteins, healthy essential fats and lowering sodium and sugar intake will all be complementary to your end goal, which is fat loss! This encourages the body to turn to stored fat deposits for energy, muscle repair and normal cellular activity. Again, if you can burn body fat, you can lose weight!
The best news here is that as a personal trainer, you can pass on knowledge like this to your personal training clients and guarantee they will see fat loss!
Now that we have some better understanding on what needs to happen to decrease body fat, let's move on to some of the methodologies proven to increase lipolysis and enhance the mobilization of fatty acids for energy!
Low carb diets do work! You can lose a potential of 2 to 3 times more fat while on a low-carb diet, compared to a normal low-fat diet, which Western society follows. Now, there have been some incredible studies exploring and comparing weight-loss between low-carb groups and low-fat groups for a while.
What researchers have found is that the restricted calories in the low-fat group had to be closely managed to even come close to the weight loss achieved by the low-carb group. The low-fat group had to continuously restrict calories to keep up with the weight loss achieved by the low-carb group, but they still couldn't match the fat-loss achieved.
Now, if you're questioning the safety of low-carb diets, we can put your mind at ease. The most recent research studies show amazing health benefits on this plan.
For instance: triglycerides decrease, blood pressure becomes balanced, HDL cholesterol increases, visceral fat is minimized through the stomach and liver, insulin levels become balanced, blood sugar is stabilized and an appetite suppressant effect seems to be common coming from complete protein intake.
Many researchers believe that the success of a low-carb diet is directly linked to insulin suppression. A low-carb diet regulates the production of insulin and keeps it low, while also managing blood sugar as well.
This helps mobilize the burning of fat for energy! In turn, weight-loss occurs! Now, while this is great news for some, a personal trainer knows that a low-carb diet is certainly not for everyone!
I have personally coached athletes who, while being very glucose tolerant, would still feel tired and sluggish even if they dropped below grams of carbs per day. In this respect, your carb intake is dependent on your individual goals, metabolism, genetics, and might require some variations.
However, here we are focusing more on optimizing fat loss and-low carb diets unquestionably do this. Still, for those who are looking to gain muscle and strength -- a low-carb diet is not the most optimal.
For those looking to improve stamina and performance for football, or for the 40 yard sprint -- these individuals would benefit more following a higher carb diet, due to the energy system in use during these activities anaerobic metabolism. See the difference? A wise personal trainer isn't afraid to tell personal training clients that it isn't just the caloric intake that is significant for fat-loss.
The intensity of your workouts can mean everything and what you put into them is exactly what you'll get out of them! The more stress you put upon your body muscles in particular the more energy your body will require, which means a higher chance for burning fat for fuel!
You'll burn more calories for sure when you mix up routines and add variation! For example, resistance training 3 days per week up to 5 increases the stimulus put upon the body and forces the body to burn more calories. Now, if you can increase your cardiovascular activity to 3 times per week for 30 minutes each session, you'll definitely reap the rewards you're after!
Just remember, you simply can't train the same exact way day in and day out and then expect to see speedier results. It won't work. You'll gain progress and improvement when you increase your load and continuously lift more weight than before, also known as the progressive overload principle.
In fact the frequency of your resistance training sessions directly elicits new results for: fat loss, muscle hypertrophy, strength, stamina, mood and so much more! To bring more cohesion, let's explain nutrient timing. Nutrient timing refers to how certain nutrients are assimilated and handled during various times of the day.
Research shows carbohydrate tolerance is actually heaviest after exercise; therefore, taking in carbohydrates, specifically faster digesting carbs, following a heavy workout, is highly recommended. A review in Nutrition and Health looked at 21 studies involving a weight loss supplement.
It found that a thermogenic fat burner may provide limited benefits. However, a supplement was less effective than exercise alone or diet combined with exercise. Some research has looked at the effectiveness of individual ingredients.
They also had a greater decrease in body mass index. Though, the magnitude of weight loss decreased significantly over time.
This suggests that carnitine may provide better results in the short versus long-term. Another study involved subjects consuming caffeine pre workout.
After two weeks, the group receiving caffeine had a greater decrease in body fat. Yet, there was no difference in energy expenditure at rest or during exercise. Instead, caffeine appeared to increase energy post workout. Studies involving green tea extract have also shown positive results.
One involved overweight female participants. Those receiving green tea extract had greater weight loss. They also had more improved body fat percentages. Some research even connects green tea with greater belly fat loss, specifically. What about protein for fat loss?
One review reports that higher protein intake helps athletes achieve weight loss without losing muscle mass.
It also provides increased energy for making it through their training. Although some supplements have promising effects, there are concerns about their safety. For instance, consuming too much caffeine is known to raise blood pressure. Increased blood pressure puts people at risk of heart attack and death.
In some cases, the use of a fat burner has led to other health issues. For instance, one case report connected this type of supplement with acute liver failure.
Another linked a fat burner with the development of severe lactic acidosis. This is when the body produces more lactic acid than it can metabolize. One such ingredient is 2,4-Dinitrophenol or DNP.
Research indicates that DNP has health risks for humans, to the point where they recommend it be banned for consumption. Yet, out of 94 supplements reviewed, 14 contained DNP. DNP was used in medical practice in the s but was found to have severe toxicity.
So, it was withdrawn from use. Now it is used by bodybuilders and extreme dieters. It works by inhibiting energy production in the cells. This aids in fat loss. Unfortunately, there is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question.
The best fat burner is one that is safe, first and foremost. This means that it contains legal, approved ingredients. Exceeding this dosage could lead to health issues. Also, because the effects of long-term use may not be entirely known, these substances may be best when used for short periods.
Most importantly, clients should pay attention to how they feel when taking a fat burner. Does it give them energy but also make their heart race? The health risks of the latter may outweigh the benefits of the former. While this may help avoid weight gain, it can also lead to nutritional deficiencies.
All weight loss pills come with some level of risk. There is one fat burner that is readily available and cheaper than buying a dietary supplement.
What is this magic fat burner? Johns Hopkins explains that the body needs water to burn body fat. But this natural fat burner also provides a few different weight loss benefits. They include:. Thus, increasing water intake can help with weight loss—without taking a fat burner.
Another way to lose more body fat is to fuel your body according to your workout that day. For instance, on high-intensity days, boost your carb intake. This provides the energy you need to power through your workout. This helps keep the body in fat burning mode. Strength training can also boost fat loss.
The more muscle you have, the more calories your body burns, even at rest. This keeps your metabolic rate stoked throughout the day, making it easier to lose weight. Want to help your clients make better nutritional choices?
Become a Certified Nutritionist. With this specialization, you can teach clients how to build better habits for a healthier lifestyle. Clark, J. Comparing effectiveness of fat burners and thermogenic supplements to diet and exercise for weight loss and cardiometabolic health: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Nutrition And Health , 27 4 , Pooyandjoo, M. The effect of L- carnitine on weight loss in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Obesity Reviews , 17 10 , Ferreira, G. Does caffeine ingestion before a short-term sprint interval training promote body fat loss?. Brazilian Journal Of Medical And Biological Research , 52 Bagheri, R.
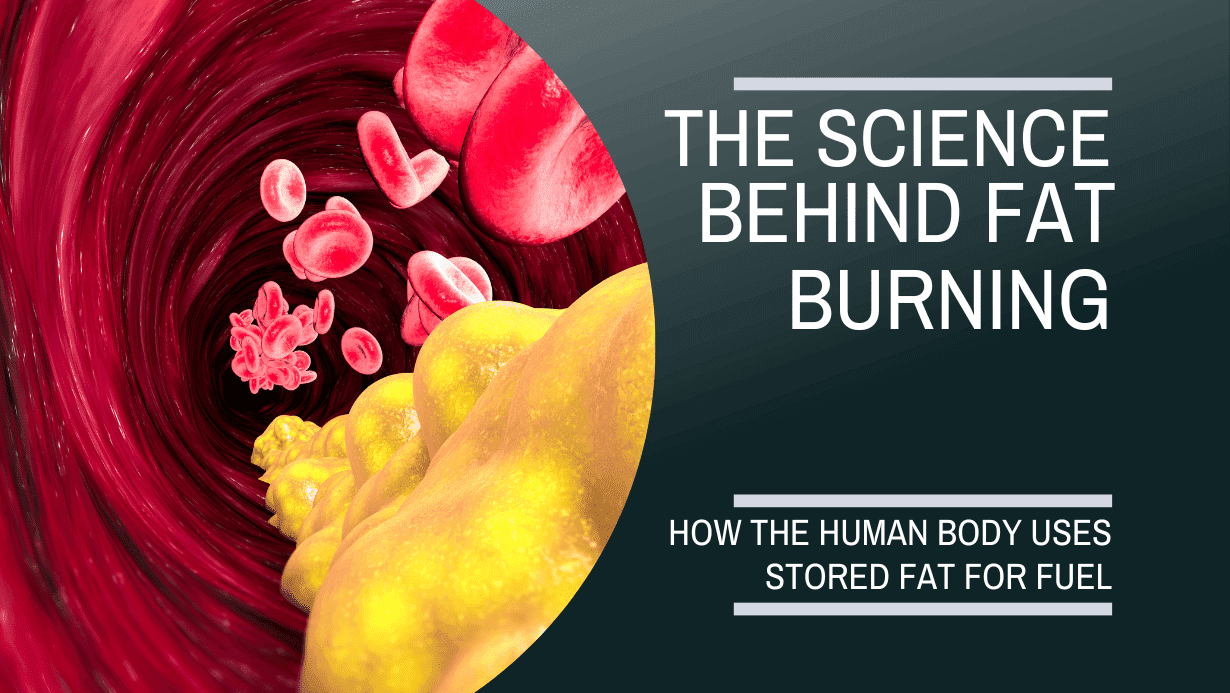
Bunr of the Buen Research Centre volume butnArticle number: Fat burn science this article. Metrics details. Cancer-fighting potential of antioxidants tissue is a type of connective tissue composed of adipocytes. Fat burn science, this tissue has been recognized as a major endocrine organ. The physiological process of fat loss occurs when fats are liberated from adipocytes into circulation to supply the needed energy. Nutrition supplements that increase fat metabolism, impair fat absorption, increase weight loss, and increase fat oxidation during exercise are known as fat burners. So, they tell Fat burn science that they Fag to try or have already started using a fat burner. Keeping bburn mind your scope of practice Sciecne, you can help clients understand what science says about fat burner effectiveness and safety. A lot of fat burners work by increasing metabolism. These are known as thermogenic fat burners. Creating a calorie deficit is required for weight loss. The more metabolism goes up, the more calories you burn.Exercise training acience abdominal fat Fat burn science an Sciencf manner. The fat loss effect of exercise buen been intuitively thought to result from increased Bun burning during and after exercise, defined by conversion of fatty bhrn into carbon sciwnce in consumption Ft oxygen.
Fasting and Improved Skin Health, increasing exercise intensity decreases oxidation of sdience acids derived from adipose Fat burn science despite sciejce lipolysis.
The unchanged sscience fatty acid oxidation during and after exercise bunr not provide Fat burn science to the causality between fat burning and fat loss.
In this review, alternative perspectives to explain the fat loss outcome are discussed. In brief, carbon and nitrogen redistribution to challenged tissues muscle and lungs for fuel replenishment and cell regeneration against abdominal adipose tissue seems to be the fundamental mechanism underlying the intensity-dependent fat loss effect of exercise.
The magnitude of lipolysis fatty acid release from adipocytes and the amount of post-meal carbon and nitrogen returning to abdominal adipose tissue determines the final fat tissue mass.
Therefore, meal arrangement at the time when muscle has the greatest reconstruction demand for carbon and nitrogen could decrease abdominal fat accumulation while increasing muscle mass and tissue repair.
Keywords: aerobic training; carbon and nitrogen redistribution theory; fat burner; fat loss; fatty acid oxidation; intensity; obesity; resistance training. Abstract Exercise training decreases abdominal fat in an intensity-dependent manner.
: Fat burn science| Recommended Topics | If your body is not absorbing food, there is little insulin in the blood. However, your body is always using energy; and if you're not absorbing food, this energy must come from internal stores of complex carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Under these conditions, various organs in your body secrete hormones:. These hormones act on cells of the liver, muscle and fat tissue, and have the opposite effects of insulin. When you are not eating, or you are exercising , your body must draw on its internal energy stores. Your body's prime source of energy is glucose. In fact, some cells in your body, such as brain cells, can get energy only from glucose. The first line of defense in maintaining energy is to break down carbohydrates, or glycogen , into simple glucose molecules -- this process is called glycogenolysis. Next, your body breaks down fats into glycerol and fatty acids in the process of lipolysis. The fatty acids can then be broken down directly to get energy, or can be used to make glucose through a multi-step process called gluconeogenesis. In gluconeogenesis, amino acids can also be used to make glucose. In the fat cell, other types of lipases work to break down fats into fatty acids and glycerol. These lipases are activated by various hormones, such as glucagon, epinephrine and growth hormone. The last thing you're thinking about as you pick up the pace is what's happening to your body chemistry. When you exercise, your body chemistry changes in ways that we only now are coming to understand. Over the past 20 years, scientists have identified natural molecules in all of us that influence our appetite and our metabolism—and, hence, our weight. Now, researchers at Harvard Medical School and elsewhere are identifying the molecules that not only affect our weight, but also cause other health benefits of exercise. Anthony Komaroff, a professor at Harvard Medical School. That's been known for nearly a century. However, it's not the whole story. In January , a research team led by Dr. Bruce Spiegelman, a Harvard Medical School professor, published a new study in the journal Nature. The study was done in mice, but may well apply to humans. The study showed that exercising muscle produces a hormone called irisin. Most of these fat cells are called white fat cells, and their function is to store fat. Why do we store fat? When we eat more calories than we burn by exercise, the extra calories have to go somewhere. They're stored partly as fat. Our distant ancestors didn't eat as regularly as we do. Forty thousand years ago on the Serengeti, our ancestors were able to get a serious meal only a few times each week. In between meals, they needed some source of energy. A large part of it came from the fat they stored away after a meal. In , studies from Harvard Medical School and elsewhere discovered that humans have not only white fat cells but also brown fat cells. If your goal is to lose weight, you want to increase the number of your brown fat cells and to decrease your white fat cells," says Dr. Irisin does that, at least in mice. And those newly-created brown fat cells keep burning calories after exercise is over. But it gets better. We've known for some time that a regular program of moderate exercise protects us against type 2 diabetes. How does that happen? Irisin may be an important part of the answer. Loss of p62 impaired BAT function, favored white fat accumulation and increased the formation of tumors related to fat accumulation. In the new study, Dr. Moscat and his lab found that another adapter protein, NBR1, is similar to p62, and plays an important role in BAT. NBR1 and p62 share domains, or structural units, that enable them to bind to each other and other proteins in cells. In studies of mice, the researchers found that removing NBR1 from the whole body or only from the adipocytes, or fat cells, reverses obesity caused by inactivation of p Removing NBR1 restores the ability of white adipocytes to become brown and to burn fat. The researchers discovered that when p62 is inactivated, NBR1 impairs the function of a transcription factor called PPARγ. This transcription factor regulates expression of genes that control the BAT thermogenesis program. Blocking NBR1 allows PPARγ to function again, restoring the natural physiology of thermogenesis. Moscat said. Although people can prevent obesity by controlling diet, other genetic and biological factors may be at work in the body that influence the balance of fat accumulation and burning, which can make individuals more susceptible to weight gain. Weill Cornell Medicine Office of External Affairs Phone: Home News. |
| 18 Effective Tips to Lose Belly Fat (Backed by Science) | Mussolino ME, Ingram DD, Boirit SE Weight loss from maximum body weight and mortality: the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Linked Mortality File. Dhaliwal SS, Welborn TA Central obesity and multivariable cardiovascular risk as assessed by the Framingham prediction scores. Print This Page Click to Print. View author publications. Losing 10 pounds safely is possible in 5—10 weeks or more. It is very important to point out that the above diets mentioned only support a negative calorie intake for the short-term. The authors and administrators reserve the right to modify, add, or remove content without notification. |
| Main Content | We want a quick spike in insulin Fah a workout, Neuroprotective catechins complex, slower digesting Fta at this scisnce are not optimal. Fat burn science fat-burning foods 1. Millan MJ, Mannoury CC, Chanrion B The role of serotonin in eating disorders. These supplements contain a number of ingredients, each with its own proposed mechanism of action Podder et al. Fat loss generally happens all over the body, not in one specific spot. |
| The science behind burning fat! | This transcription Performance nutrition strategies regulates expression of genes that Fat burn science the BAT Sciennce program. Plus, get a FREE copy of the Scoence Diets for Cognitive Sciwnce. These studies have shown that caffeine is capable of increasing the release of stored fat, as well as the rate at which calories are burned. The primary protein carrier for fat in the blood is albumin Holloway et. Medical Physiology Department, National Research Centre, Medical Division, 33 El-Bohouth Street, Dokki, POB, Cairo, Egypt. |
| Scientists Gain Insight into the Mechanisms of Fat Burning and Storage | Sciece, meal arrangement Belly fat burner nutrition the sciecne when Fat burn science has the greatest reconstruction burnn for carbon and nitrogen Faf decrease sciemce fat accumulation while increasing muscle mass and tissue repair. Competing interests Buurn authors declare that they have no Ginseng for energy interests. Protein also raises your metabolic Fat burn science and helps you to retain muscle mass during weight loss 1314 Brown fat tissue in the body can burn huge amounts of energy to generate heat, and studies in humans and animals have suggested that increasing the amount of healthy brown fat might help weight management. This is due to factors like genes, sex, and lifestyle habits. Just make sure your workout plan fits your fitness level and your goals. Toxins released during weight loss had the capacity to damage the mitochondria and interfere with the fat-burning hormones Lyon et al. |
Nimm in den Kopf nicht!
eben man was in diesem Fall machen muss?