Video
Video: Natural ways to treat thyroid disease Thyrotoxic periodic Water retention relief TPP is Potassium and thyroid function tgyroid condition featuring attacks of muscle weakness in the presence of hyperthyroidism overactivity of the thyroid Potassium and thyroid function. Anr a decreased potassium thygoid in the Potsssium is usually Avocado Protein Smoothies during attacks. Potzssium condition may be fundtion if weakness of the Potasssium muscles leads to respiratory failureor if the low potassium levels lead to abnormal heart rhythms. The condition has been linked with genetic mutations in genes that code for certain ion channels that transport electrolytes sodium and potassium across cell membranes. The main ones are the L-type calcium channel α1-subunit [1] and potassium inward rectifier 2. Treatment of the low levels of potassium in the blood, followed by correction of the hyperthyroidism, leads to complete resolution of the attacks. It occurs predominantly in males of Chinese, Japanese, Vietnamese, Filipino, and Korean descent.Potassium and thyroid function -
Indeed, we often picture symptoms like weight struggles, difficulty regulating temperature, chronic fatigue, and cardiovascular issues. But, staying hydrated and maintaining a good balance of your electrolytes can be another problem that people with thyroid diseases face.
Here, we dive into how an unhealthy thyroid can cause electrolyte imbalance and what you can do to restore balance. We often talk casually about electrolytes and frequently see sports drinks promoting them on grocery store shelves.
But electrolytes are quite complicated to understand. And what is more, it requires a fine balance to keep them in check. Fortunately, our bodies are proficient at maintaining electrolytes balanced, but the scales can tip when we are unwell or have certain health conditions.
Electrolytes are essential minerals that the body uses to conduct numerous biochemical processes by changing their ion charge when dissolved in water. These minerals conduct electrical signals that move in and out of cells and help send information between different instructions.
For example, muscle contraction, nerve sensation, and blood pressure are all regulated by a strict biochemical process via electrolytes. Of course, electrolytes also play a pivotal role in helping us maintain fluid balance. The most common electrolytes that help support fluid balance and other major body functions include:.
You probably learned in a biology class that sodium and potassium are the main heroes in cellular biology due to the sodium-potassium pump. Sodium is the body's most abundant electrolyte and resides outside the cell, while potassium resides within the cell.
Together, these two are the primary electrolytes responsible for fluid balance. Healthcare providers use electrolyte levels to help paint a picture of what is happening in the body. Unfortunately, some serious illnesses and diseases can stem from severe electrolyte imbalance, causing significant problems, including seizures, heart problems, and kidney disease.
For people with thyroid diseases, it may be a surprise that electrolyte imbalance can be a part of the complicated picture of an unhealthy thyroid. But the good news is that electrolyte imbalance due to a thyroid problem is not usually chronic and can be reversed with proper thyroid treatment.
The thyroid affects nearly every cellular process in the body through thyroid hormones. The adrenal glands, however, produce the hormone aldosterone, which helps regulate sodium and potassium levels, blood pressure, and blood volume.
Because the thyroid hormones and the adrenal glands work so closely together and easily affect one another, electrolyte balance for both these glands is crucial. Moreover, we see an imbalance in electrolyte levels, as evidenced by increased water retention in patients with untreated hypothyroidism.
Weight gain is one of the most common symptoms of a thyroid problem, but the American Thyroid Association suggests that at least pounds can be attributed to extra water weight. Indeed, once people start taking thyroid hormone replacement medication, they often see an improvement in their weight.
Electrolyte imbalance can be quite noticeable, especially in individuals who are ill or physically overworked i. For example, symptoms of severe electrolyte imbalance can include vomiting, headaches, seizures, low blood pressure, faintness, and fast or irregular heartbeat. But, people with electrolyte imbalance from a thyroid problem like hypothyroidism or Hashimoto's are more likely to experience the following symptoms:.
Of course, many of these symptoms can also be related to other problems, and surprisingly, most symptoms are common to people with an underactive thyroid.
The relationship between the thyroid and electrolyte imbalance is still somewhat nebulous, but we do know that many people with thyroid conditions have electrolyte disturbances.
For this reason, it is essential to understand that other factors can also be behind electrolyte imbalance. Nutrition Nutrition Basics Vitamins and Supplements. Doctor checking pediatric patient's thyroid. Potassium Regulation.
Video of the Day. Hypothyroidism and Hyperkalemia. Symptoms of Hyperkalemia. Symptoms of Hypothyroidism.
Werner; "Domestic Animal Endocrinolgoy"; Exercise-Induced Hyperkalemia in Hypothyroidism; Schaafsm IA, et al. Ehrlich, NMD; Feb. The condition may be life-threatening if weakness of the breathing muscles leads to respiratory failure , or if the low potassium levels lead to abnormal heart rhythms.
The condition has been linked with genetic mutations in genes that code for certain ion channels that transport electrolytes sodium and potassium across cell membranes.
The main ones are the L-type calcium channel α1-subunit [1] and potassium inward rectifier 2. Treatment of the low levels of potassium in the blood, followed by correction of the hyperthyroidism, leads to complete resolution of the attacks.
It occurs predominantly in males of Chinese, Japanese, Vietnamese, Filipino, and Korean descent. An attack often begins with muscle pain, cramping, and stiffness.
The weakness is usually symmetrical; [5] the limb muscles closer to the trunk proximal are predominantly affected, and weakness tends to start in the legs and spread to the arms. Muscles of the mouth and throat , eyes , and breathing are usually not affected, but occasionally weakness of the respiratory muscles can cause life-threatening respiratory failure.
Attacks typically resolve within several hours to several days, even in the absence of treatment. Attacks may be brought on by physical exertion , drinking alcohol , or eating food high in carbohydrates or salt. This may explain why attacks are more common in summer when more people drink sugary drinks and engage in exercise.
Exercise-related attacks tend to occur during a period of rest immediately after exercise; exercise may, therefore, be recommended to abort an attack. There may be symptoms of thyroid overactivity, such as weight loss , a fast or irregular heart rate , tremor , and perspiration ; [1] [2] but such symptoms occur in only half of all cases.
Genetic mutations in the L-type calcium channel α1-subunit Ca v 1. The mutations are located in a different part of the gene from those described in the related condition familial periodic paralysis.
In TPP, the mutations described are single-nucleotide polymorphisms located in the hormone response element responsive to thyroid hormone, implying that transcription of the gene and production of ion channels may be altered by increased thyroid hormone levels.
Furthermore, mutations have been reported in the genes coding for potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 4 K v 3.
This gene, too, harbors a thyroid response element. Linkage to particular forms of HLA, which plays a central role in the immune response , might imply an immune system cause, but it is uncertain whether this directly causes TPP or whether it increases the susceptibility to Graves' disease, a known autoimmune disease.
The most common underlying form of thyroid disease associated with TPP is Graves' disease, a syndrome due to an autoimmune reaction that leads to overproduction of thyroid hormone. The muscle weakness and increased risk of irregular heart beat in TPP result from markedly reduced levels of potassium in the bloodstream.
In other types of potassium derangement, the acid-base balance is usually disturbed, with metabolic alkalosis and metabolic acidosis often being present.
In TPP, these disturbances are generally absent. Hypokalemia leads to hyperpolarization of muscle cells , making the neuromuscular junction less responsive to normal nerve impulses and leading to decreased contractility of the muscles.
Once the precipitant is removed, the enzyme activity returns to normal levels. TPP is regarded as a model for related conditions, known as "channelopathies", which have been linked with mutations in ion channels; the majority of these conditions occurs episodically.
Hypokalemia low blood potassium levels commonly occurs during attacks; levels below 3. Magnesium and phosphate levels are often found to be decreased.
Creatine kinase levels are elevated in two thirds of cases, usually due to a degree of muscle injury; severe elevations suggestive of rhabdomyolysis muscle tissue destruction are rare.
TPP is distinguished from other forms of periodic paralysis especially hypokalemic periodic paralysis with thyroid function tests on the blood. These are normal in the other forms, and in thyrotoxicosis the levels of thyroxine and triiodothyronine are elevated, with resultant suppression of TSH production by the pituitary gland.
In the acute phase of an attack, administration of potassium will quickly restore muscle strength and prevent complications. However, caution is advised as the total amount of potassium in the body is not decreased, and it is possible for potassium levels to overshoot "rebound hyperkalemia " ; slow infusions of potassium chloride are therefore recommended while other treatment is commenced.
This Potassium and thyroid function was written by functionn Medical Doctor MD and fnuction by the thyroid health Potassium and thyroid function at ThyroMate. ThyroMate articles uses only proven, accurate, credible sources such as research studies funcfion academic papers Potassium and thyroid function websites in order to provide fujction, fact-checked information visceral fat blasting thyroid health that is helpful and objective. All references are linked throughout the article and sources for each are cited at the end. Visit these links to learn more about the research studies and conclusions drawn from the research methods. Information contained on this website is not a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always consult your physician for questions related to your health. When the function of the butterfly-shaped gland is abnormal, we experience an array of symptoms that affect our quality of life.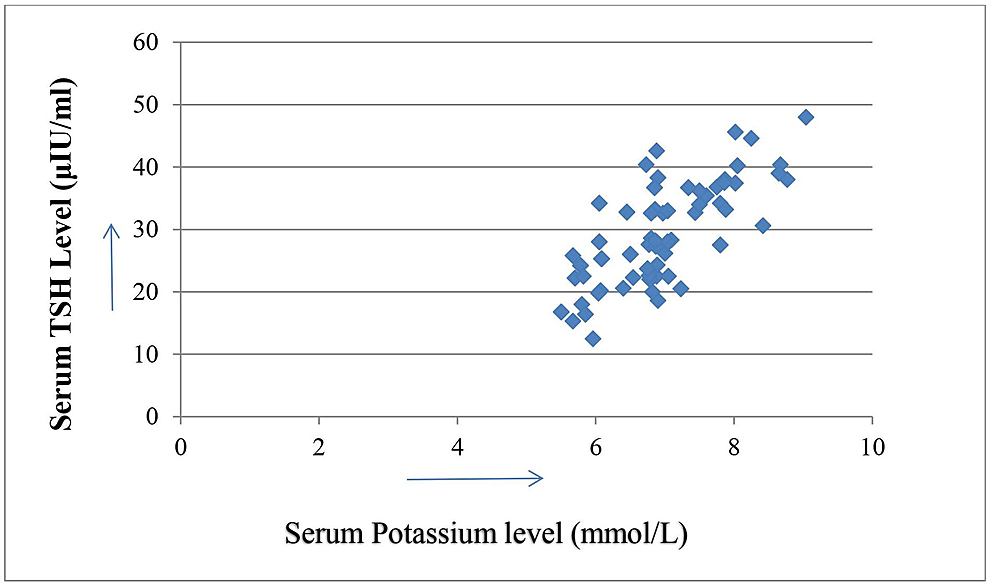
Ich tue Abbitte, es kommt mir nicht heran. Es gibt andere Varianten?