
Chronic hyperglycemia and glucose-lowering medications -
Canagliflozin was also associated with an increase in fracture rates HR 1. Importantly, canagliflozin was associated with doubling in the risk of lower extremity amputation HR 1.
This risk was strongest in participants with a prior amputation. Canagliflozin should, therefore, be avoided in people with a prior amputation, as the harms appear to be greater than the benefits in that population.
The Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of Cardiovascular Outcome Results LEADER trial enrolled 9, participants with longstanding type 2 diabetes median duration Over a median follow up of 3.
Therefore results are most applicable to people with type 2 diabetes with clinical CVD requiring add-on antihyperglycemic therapy. The Trial to Evaluate Cardiovascular and Other Long-term Outcomes with Semaglutide in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes SUSTAIN-6 enrolled 3, participants with a mean duration of type 2 diabetes of After a median follow up of 2.
There was, however, a higher rate of diabetic retinopathy complications in the semaglutide group compared to placebo group 3. It is unclear at this time if there is a direct effect of semaglutide or other explanations for this unexpected difference in retinopathy complication rates, although the risk appeared greatest in individuals with pre-existing retinopathy and rapid lowering of A1C.
All 4 trials reported lower rates of kidney disease progression in the treated groups compared to placebo 53,55, It should also be noted that the majority of people in these trials had pre-existing CVD and required add-on antihyperglycemic therapy.
In addition, because these were placebo-controlled trials, no conclusions can be made about how the cardioprotective properties of empagliflozin, canagliflozin, liraglutide and semaglutide compare to those of other agents.
CV outcome trials for other agents are expected to be completed by ; therefore, based on evidence to date, a GLP-1 receptor agonist or SGLT2 inhibitor with demonstrated CV outcome benefit should be considered as initial add-on therapy for people with pre-existing type 2 diabetes and clinical CV disease who have not achieved target A1C on existing treatment to reduce CV risk.
A careful review of the methods and findings from these trials was conducted by an independent committee. While primary analyses results were similar for canagliflozin, empagliflozin and liraglutide, it was concluded that the strength of evidence for CV benefit was weaker for canagliflozin than for the other agents.
This conclusion was based on three factors. First, in an interim analysis of the CANVAS study for medication approval necessitated unblinding of study data. A decision was then made to combine this study with the CANVAS-R study, presumably to provide greater power for CV outcomes.
The interim unblinding and protocol revision were viewed as potential threats to internal validity, thereby weakening the strength of evidence for benefit. Second, while canagliflozin was associated with a significant decrease in the composite MACE outcome, there was no significant benefit on individual outcomes, such as all-cause or CV mortality.
Third, the findings of increased risk of fractures and amputations with canagliflozin treatment in the context of a noninferiority design where the comparator is placebo was particularly concerning, indicating that harms may outweigh benefits.
For these reasons, the committee decided that the uncertainty regarding benefits should be acknowledged with a lower grade of recommendation for canagliflozin than for other agents with demonstrated CV benefit. In the absence of evidence for long-term clinical benefit, agents effective at A1C lowering should be considered in terms of both the degree of baseline hyperglycemia needing correction, and any heightened concerns regarding hypoglycemia e.
elderly people or those with renal or hepatic dysfunction see Diabetes in Older People chapter, p. While most medications added to metformin lower A1C to a similar extent, insulin and insulin secretagogues are associated with higher rates of hypoglycemia than other agents 21,23,24, In those who are stable, other agent-specific advantages and disadvantages should be weighed as treatment is individualized to best suit the patient's needs and preferences.
Each of the agents listed in Table 1 and Figure 1 has advantages and disadvantages to consider. Figure 2 illustrates the basis on which agent selection is influenced by renal function as dictated by product monograph precautions. Recent meta-analyses have summarized head-to-head comparisons of metformin-based combinations 19,24,62, Combinations of metformin with a sulfonylurea, a thiazolidinedione TZD , an SGLT2 inhibitor and a DPP-4 inhibitor have comparable A1C-lowering effects 19,24,62—66 , while the combination of metformin with a GLP-1 receptor agonist reduced A1C more than combination with a DPP-4 inhibitor.
TZDs, insulin and sulfonylureas are associated with the most weight gain 1. Hypoglycemia risk is also lower with TZDs, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists compared to sulfonylureas and insulin 19,24,62—65,67, Network meta-analyses that indirectly compared the net benefits of second- and third-line treatment options have found similar results 21,23,24,69— Evidence on comparative effectiveness of acarbose and orlistat is limited, although they are associated with a low risk of hypoglycemia and weight gain.
The safety of incretin agents, SGLT2 inhibitors and TZDs in pregnancy is unknown; therefore, these agents should be avoided or discontinued in women who are pregnant or planning a pregnancy see Diabetes and Pregnancy chapter, p.
If a sulfonylurea is added to metformin, gliclazide should be considered as first choice as it is associated with a lower risk of hypoglycemia 67,72 , CV events and mortality relative to other sulfonylureas Glimepiride is also associated with a lower risk of CV events and mortality 73 , but has a similar rate of hypoglycemia 67,72 compared to other sulfonylureas.
For people already taking metformin and a sulfonylurea, the addition of either a DPP-4 inhibitor, a GLP-1 receptor agonist or SGLT2 inhibitor may be considered as they are associated with effective A1C lowering with less hypoglycemia than insulin or TZDs 21,69,70,74,75 ; GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors are also associated with weight loss 70,71 see Weight Management in Diabetes chapter, p.
For instance, the combination of a DPP-4 inhibitor or a GLP-1 receptor agonist and an SGLT2 inhibitor added to metformin has been shown to be as safe and more efficacious at lowering A1C after 24 weeks than either agent alone 76, SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists added to metformin have also been shown to reduce systolic BP compared to metformin alone, and add-on of SGLT2 inhibitors reduce systolic BP more than add-on of sulfonylureas or DPP-4 inhibitors A combination of noninsulin antihyperglycemic agents and insulin often effectively controls glucose levels.
Insulin treatment includes long-acting or intermediate-acting insulin analogue injections once or twice daily for basal glycemic control, and bolus injections at mealtimes for prandial glycemic control.
Adding insulin to noninsulin antihyperglycemic agent s may result in better glycemic control with a smaller dose of insulin 78 , and may induce less weight gain and less hypoglycemia than that seen when non-insulin antihyperglycemic agents are stopped and insulin is used alone 79, A single injection of an intermediate-acting NPH 81 or long-acting insulin analogue insulin glargine U, insulin glargine U, insulin detemir or insulin degludec 82—84 may be added.
The addition of bedtime insulin to metformin therapy leads to less weight gain than insulin plus a sulfonylurea or twice-daily NPH insulin When insulin is used in type 2 diabetes, the insulin regimen should be tailored to achieve good metabolic control while trying to avoid hypoglycemia.
With intensive glycemic control, there is an increased risk of hypoglycemia, but this risk is lower in people with type 2 diabetes than in those with type 1 diabetes.
The mode of insulin administration continuous subcutaneous infusion vs. injections , the number of insulin injections 1 to 4 per day and the timing of injections may vary depending on each individual's situation As type 2 diabetes progresses, insulin requirements will likely increase and higher doses of basal insulin intermediate-acting or long-acting analogues may be needed.
DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors have been shown to be efficacious at further lowering glucose levels when combined with insulin therapy 87— A meta-analysis determined that the addition of a GLP-1 receptor agonist to basal insulin regimens results in greater A1C reduction, more weight loss and less hypoglycemia compared to the addition of bolus insulin A GLP-1 receptor agonist should, therefore, be considered before bolus insulin as add-on therapy in people on basal insulin with or without other agents who require antihyperglycemic treatment intensification if there are not barriers to affordability or access.
If glycemic control is suboptimal on treatment regimens that include basal insulin with other agents, bolus insulin at mealtimes short- or rapid-acting analogues may be added.
Generally, once bolus insulin is introduced into a treatment regimen, either as a separate mealtime bolus or as part of a premixed containing regimen, insulin secretagogues, such as sulfonylureas and meglitinides, should be discontinued.
Concomitant therapy with metformin and, if applicable, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, DPP-4 inhibitor or SGLT2 inhibitor should be continued with regimens containing bolus insulin unless contraindicated, to allow for improved glycemic control with less risk of weight gain and hypoglycemia The reduction in A1C achieved with insulin therapy depends on the dose and number of injections per day A meta-analysis of 12 articles compared basal-bolus and biphasic insulin regimens, and found that both approaches are equally efficacious at lowering A1C, with comparable effects on hypoglycemia risk and weight—although basal-bolus regimens were modestly more efficacious in people with type 2 diabetes already on insulin Bolus insulin should be initiated using a stepwise approach starting with 1 injection at the largest meal and additional mealtime injections at 3-month intervals if needed , as it was shown to be as efficacious at A1C lowering as a full basal-bolus regimen, and is associated with less hypoglycemia and greater patient satisfaction after 1 year Lower rates of hypoglycemia have been observed in some studies of individuals with type 2 diabetes treated with rapid-acting insulin analogues insulin aspart, insulin lispro, insulin glulisine compared to those treated with short-acting regular insulin — Use of long-acting basal insulin analogues insulin detemir, insulin glargine, insulin degludec in those already on antihyperglycemic agents reduces the relative risk of symptomatic and nocturnal hypoglycemia compared to treatment with NPH insulin 83,,— Meta-analyses indicate a relative reduction of 0.
NPH Insulin degludec has been associated with lower rates of overall and nocturnal hypoglycemia compared to glargine U 82,84, After 32 weeks of treatment, insulin degludec was associated with a significantly lower rate of the primary endpoint of overall symptomatic hypoglycemic episodes rate ratio 0.
The proportions of patients with hypoglycemic episodes were 9. The Trial Comparing Cardiovascular Safety of Insulin Degludec versus Insulin Glargine in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes at High Risk of Cardiovascular Events DEVOTE randomized patients with type 2 diabetes at high risk of CV disease to insulin degludec or glargine U, and found no difference in the primary outcome of CV events but a significant decrease in severe hypoglycemia with degludec 4.
There is also some evidence of lower hypoglycemia rates with glargine U compared to glargine U and may also be considered over glargine U if reducing hypoglycemia is a priority Efficacy and rates of hypoglycemia are similar between glargine U and detemir Aside from effects of some antihyperglycemic agents on the occurrence of hypoglycemia and weight, there are adverse effects unique to each agent Table 1.
Gastrointestinal side effects are more common with metformin, alpha glucosidase inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists and orlistat than with other agents.
Metformin can cause diarrhea, which tends to resolve over time and is minimized with starting at a low dose and subsequent slow titration of the dosage.
Extended-release metformin can also be used to improve tolerability in individuals experiencing gastrointestinal side effects with immediate-release metformin — Metformin is also associated with an approximate 2-fold increased incidence of vitamin B12 deficiency — , and vitamin B12 levels should be measured periodically in people taking metformin or with signs or symptoms of deficiency such as impaired proprioception or peripheral neuropathy.
GLP-1 receptor agonists and, less commonly, DPP-4 inhibitors can cause nausea and GLP-1 receptor agonists can also cause diarrhea. A meta-analysis comparing the risk of congestive heart failure between antihyperglycemic therapies found an increased risk with TZDs and DPP-4 inhibitors driven by higher risk with saxagliptin 44 , although another meta-analysis and a large observational study of over one million participants failed to find an increased risk of heart failure with DPP-4 inhibitors compared to other agents.
Reports of acute pancreatitis have been noted with DPP-4 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists. A small significant increase in pancreatitis but not pancreatic cancer was seen with DPP4-inhibitors in a meta-analysis of 3 large randomized controlled trials of over 20, participants However, a recent large Canadian observational study of over 1.
SGLT2 inhibitors are associated with a 3- to 4-fold increased risk of genital mycotic infections 19,69,95 , as well as higher rates of urinary tract infections, volume depletion, rare acute kidney injury and rare DKA , Canagliflozin treatment is associated with an increased risk of fractures 54, and a twofold increased risk of amputations In a retrospective analysis, empagliflozin was not associated with an increased risk of amputations in the EMPA-REG trial There is evidence of a higher risk of bladder cancer with pioglitazone in some studies 47,48 but not others — , and some reports of increased bladder cancer risk with dapagliflozin GLP-1 receptor agonists have been shown to promote the development of pancreatic and medullary thyroid cancer in rodents, but an increased risk has not been seen in humans Semaglutide was associated with a higher risk of retinopathy in SUSTAIN-6 see above Earlier epidemiological evidence suggesting a possible link between insulin glargine and cancer has not been substantiated in review of clinical trial data for either glargine or detemir 36,, Insulin glargine U may be considered over insulin glargine U to reduce overall and nocturnal hypoglycemia [Grade C, Level 3 ].
A1C , glycated hemoglobin; BG , blood glucose; BP , blood pressure; CHF , congestive heart failure; CHD , coronary heart disease; CI , confidence interval; CV , cardiovascular; CVD , cardiovascular disease; DKA , diabetic ketoacidosis; HR , hazard ratio; MI ; myocardial infarct; NPH , neutral protamine Hagedorn; TZD , thiazolidinedione.
Appendix 9. Examples of Insulin Initiation and Titration Regimens in People With Type 2 Diabetes. Literature Review Flow Diagram for Chapter Pharmacologic Glycemic Management of Type 2 Diabetes in Adults.
From: Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group P referred R eporting I tems for S ystematic Reviews and M eta- A nalyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med 6 6 : e pmed For more information, visit www. Goldenberg reports personal fees from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Servier, outside the submitted work.
MacCallum reports personal fees from Janssen and Novo Nordisk, outside the submitted work. No other author has anything to disclose. All content on guidelines. ca, CPG Apps and in our online store remains exactly the same. For questions, contact communications diabetes. Become a Member Order Resources Home About Contact DONATE.
Next Previous. Key Messages Recommendations Figures Full Text References. Chapter Headings Introduction Treatment Regimens Effects of Antihyperglycemic Agents on Microvascular and Cardiovascular Complications Effects of Antihyperglycemic Agents on Glycemic Control and Other Short-Term Outcomes Insulin Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes Adverse Effects Other Relevant Guidelines Relevant Appendices Author Disclosures.
Key Messages Healthy behaviour interventions should be initiated in people newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. In the absence of metabolic decompensation, metformin should be the initial agent of choice in people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, unless contraindicated.
In people with clinical cardiovascular CV disease in whom A1C targets are not achieved with existing pharmacotherapy, an antihyperglycemic agent with demonstrated CV outcome benefit should be added to antihyperglycemic therapy to reduce CV risk.
In people receiving an antihyperglycemic regimen containing insulin, in whom glycemic targets are not achieved, the addition of a GLP-1 receptor agonist, DPP-4 inhibitor or SGLT2 inhibitor may be considered before adding or intensifying prandial insulin therapy to improve glycemic control with less weight gain and comparable or lower hypoglycemia risk.
Key Messages for People with Diabetes Some people who have type 2 diabetes can achieve their target blood glucose levels with nutrition guidance and physical activity alone, but most also need glucose-lowering medications.
The decision about which medications are best for you depends on many factors, including your blood glucose level, symptoms, other health problems you have and affordability of medications.
Your health-care provider may even combine medications that act differently on your body to help you control your blood glucose. Glucose-lowering medications for type 2 diabetes include: First-line glucose-lowering medication: Metformin: Metformin is generally the first choice for people with type 2 diabetes because of its safety, low cost and possible heart benefits.
It works by making your body respond better to insulin so that your body uses insulin more effectively. Metformin also lowers glucose production from the liver. Nausea and diarrhea are possible side effects and usually go away within 1 to 2 weeks as your body gets used to the medicine.
It is associated with a low risk of hypoglycemia and does not cause weight gain. If metformin and healthy behaviour changes are not enough to control your blood glucose level, other medications can be added. Second-line glucose-lowering medication: DPP-4 inhibitors: These medications work to lower blood glucose by increasing insulin levels after meals and lowering glucagon levels a hormone that raises blood glucose.
They do not cause weight gain and are associated with a low risk of hypoglycemia. GLP-1 receptor agonists: These injectable medications act when blood glucose increases after eating. They increase insulin levels, which helps lower blood glucose and lower glucagon levels a hormone that raises blood glucose.
They also slow digestion and reduce appetite. Possible side effects include nausea, which usually goes away with time. They are associated with weight loss and a low risk of hypoglycemia. SGLT2 inhibitors: These medications work by eliminating glucose into the urine.
Side effects may include genital yeast infections, urinary tract infections, increased urination and low blood pressure. Insulin secretagogues meglitinides, sulfonylureas : These medications help your pancreas release more insulin. Possible side effects include hypoglycemia and weight gain.
Thiazolidinediones: Like metformin, these medications make the body's tissues more sensitive to insulin. Side effects include weight gain and an increased risk of heart failure and fractures. Insulin therapy: Some people who have type 2 diabetes need insulin therapy as well.
Depending on your needs, your health-care provider may prescribe a mixture of insulin types to use throughout the day and night. Often, people with type 2 diabetes start insulin use with 1 injection of long-acting insulin at night. Discuss the pros and cons of different treatment plans with your healthcare provider.
Together, you can decide which medication is best for you after considering many factors, including costs and other aspects of your health. Introduction People with type 2 diabetes form a heterogeneous group. Treatment Regimens Newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes Individuals presenting with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes require a multifaceted treatment plan.
Treatment advancement in people with pre-existing type 2 diabetes The natural history of type 2 diabetes is that of ongoing beta cell function decline, so blood glucose BG levels often increase over time even with excellent adherence to healthy behaviours and therapeutic regimens Figure 1 Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes.
Effects of Antihyperglycemic Agents on Microvascular and Cardiovascular Complications In deciding upon which agent to add after metformin, there must be consideration of both short-term effects on glycemic control and long-term effects on clinical complications.
Effects of Antihyperglycemic Agents on Glycemic Control and Other Short-Term Outcomes In the absence of evidence for long-term clinical benefit, agents effective at A1C lowering should be considered in terms of both the degree of baseline hyperglycemia needing correction, and any heightened concerns regarding hypoglycemia e.
Insulin Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes A combination of noninsulin antihyperglycemic agents and insulin often effectively controls glucose levels. Adverse Effects Aside from effects of some antihyperglycemic agents on the occurrence of hypoglycemia and weight, there are adverse effects unique to each agent Table 1.
Recommendations Treatment of Newly Diagnosed People with Type 2 Diabetes Healthy behaviour interventions should be initiated at diagnosis [Grade B, Level 2 2 ]. Metformin may be used at the time of diagnosis, in conjunction with healthy behaviour interventions [Grade D, Consensus].
If glycemic targets are not achieved using healthy behaviour interventions alone within 3 months, antihyperglycemic therapy should be added to reduce the risk of microvascular complications [Grade A, Level 1A 3 ].
Metformin should be chosen over other agents due to its low risk of hypoglycemia and weight gain [Grade A, Level 1A 19 ], and long-term experience [Grade D, Consensus]. Individuals with metabolic decompensation e. marked hyperglycemia, ketosis or unintentional weight loss should receive insulin with or without metformin to correct the relative insulin deficiency [Grade D, Consensus].
The choice should be individualized taking into account the information in Figure 1 and Table 1 [Grade B, Level 2 19 ]. For adults with type 2 diabetes with metabolic decompensation e. marked hyperglycemia, ketosis or unintentional weight loss , insulin should be used [Grade D, Consensus].
Insulin may be used at any time in the course of type 2 diabetes [Grade D, Consensus] see Appendix 9. Examples of Insulin Initiation and Titration in People with Type 2 Diabetes. A GLP-1 receptor agonist should be considered as add-on therapy [Grade A, Level 1A 87,97 ], before initiating bolus insulin or intensifying insulin to improve glycemic control with weight loss and a lower hypoglycemia risk compared to single or multiple bolus insulin injections [Grade A, Level 1A 25,98,99 ].
An SGLT2 inhibitor should be considered as add-on therapy to improve glycemic control with weight loss and lower hypoglycemic risk compared to additional insulin [Grade A, Level 1A 27,93,94 ]. A DPP-4 inhibitor may be considered as add-on therapy to improve glycemic control without weight gain or increased hypoglycemia risk compared to additional insulin [Grade B, Level 2 27,91 ].
When bolus insulin is added to antihyperglycemic agents, rapid-acting analogues may be used instead of short-acting regular insulin to improve glycemic control [Grade B, Level 2 ]. Bolus insulin may be initiated using a stepwise approach starting with 1 injection at 1 meal and additional mealtime injections as needed to achieve similar A1C reduction with lower hypoglycemia risk compared to initiating a full basal-bolus injection regimen [Grade B, Level 2 ].
All individuals with type 2 diabetes currently using or starting therapy with insulin or insulin secretagogues should be counselled about the prevention, recognition and treatment of hypoglycemia [Grade D, Consensus]. Metformin, insulin secretagogues and SGLT2 inhibitors should be temporarily withheld during acute illnesses associated with reduced oral intake or dehydration [Grade D, Consensus].
See Appendix 8. Sick Day Medication List. SGLT2 inhibitors should be temporarily withheld prior to major surgical procedures, and during acute infections and serious illness to reduce the risk of ketoacidosis [Grade D, Consensus].
Abbreviations A1C , glycated hemoglobin; BG , blood glucose; BP , blood pressure; CHF , congestive heart failure; CHD , coronary heart disease; CI , confidence interval; CV , cardiovascular; CVD , cardiovascular disease; DKA , diabetic ketoacidosis; HR , hazard ratio; MI ; myocardial infarct; NPH , neutral protamine Hagedorn; TZD , thiazolidinedione.
Other Relevant Guidelines Chapter 8. Targets for Glycemic Control Chapter Glycemic Management in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes Chapter Hypoglycemia Chapter Weight Management in Diabetes Chapter Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents Chapter Diabetes and Pregnancy Chapter Diabetes in Older People.
Relevant Appendices Appendix 6. Types of Insulin Appendix 7. Therapeutic Considerations for Renal Impairment Appendix 8. Sick-Day Medication List Appendix 9. Author Disclosures Dr.
References Gaede P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving HH, et al. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med ;— Gregg EW, Chen H, Wagenknecht LE, et al.
Association of an intensive lifestyle intervention with remission of type 2 diabetes. JAMA ;— UK Prospective Diabetes Study UKPDS Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes UKPDS Lancet ;— Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, et al.
Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes UKPDS 35 : Prospective observational study. BMJ ;— Bloomgarden ZT, Dodis R, Viscoli CM, et al.
Lower baseline glycemia reduces apparent oral agent glucose-lowering efficacy: A meta-regression analysis. Diabetes Care ;—9. Sherifali D, Nerenberg K, Pullenayegum E, et al. The effect of oral antidiabetic agents on A1C levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Diabetes Care ;— Phung OJ, Sobieraj DM, Engel SS, et al. Early combination therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Diabetes Obes Metab ;— Rosenstock J, Chuck L, Gonzalez-Ortiz M, et al. Initial combination therapy with canagliflozin plus metformin versus each component as monotherapy for drugnaive type 2 diabetes.
Gao W, Dong J, Liu J, et al. Efficacy and safety of initial combination of DPP-IV inhibitors and metformin versus metformin monotherapy in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials.
Lewin A, DeFronzo RA, Patel S, et al. Initial combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Abdul-Ghani MA, Puckett C, Triplitt C, et al.
Initial combination therapy with metformin, pioglitazone and exenatide is more effective than sequential add-on therapy in subjectswith new-onset diabetes.
Results fromthe Efficacy and Durability of Initial Combination Therapy for type 2 diabetes EDICT : A randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab ;—75, Available from.
Hadjadj S, Rosenstock J, Meinicke T, et al. Initial combination of empagliflozin and metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. While these diabetes medications certainly have more to offer than just improvements in blood sugar, they remain costly and inaccessible to many individuals.
This is why it is essential to have an open and honest conversation with your doctor about what is most important to you and what aligns with your goals and preferences.
Management of a complex disease like diabetes takes an entire team, with you being the key team member. Samar Hafida, MD , Contributor. As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content.
Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Living Well with Diabetes helps you better understand and manage your diabetes. It includes detailed, updated information about medications and alternative treatments for diabetes, and a special section on weight-loss strategies.
Thanks for visiting. Don't miss your FREE gift. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School.
Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more.
Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss from exercises to build a stronger core to advice on treating cataracts. PLUS, the latest news on medical advances and breakthroughs from Harvard Medical School experts.
Sign up now and get a FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness. Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School.
Recent Blog Articles. Flowers, chocolates, organ donation — are you in? What is a tongue-tie? What parents need to know. Which migraine medications are most helpful?
How well do you score on brain health? Shining light on night blindness. Can watching sports be bad for your health? Beyond the usual suspects for healthy resolutions.
Dosing in the setting of DKD is reviewed in detail elsewhere. See "Treatment of diabetic kidney disease", section on 'Type 2 diabetes: Treat with additional kidney-protective therapy'. An alternative or an additional agent may be necessary to achieve glycemic goals.
GLP-1 receptor agonists are an alternative in patients with DKD as their glycemic effect is not related to eGFR. In addition, GLP-1 receptor agonists have been shown to slow the rate of decline in eGFR and prevent worsening of albuminuria.
See 'Microvascular outcomes' below and "Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus" and "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus". Of note, we avoid use of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with frequent bacterial urinary tract infections or genitourinary yeast infections, low bone density and high risk for falls and fractures, foot ulceration, and factors predisposing to diabetic ketoacidosis eg, pancreatic insufficiency, drug or alcohol abuse disorder because of increased risk while using these agents.
SLGT2 inhibitors should be held for 3 to 4 days before procedures including colonoscopy preparation and with poor oral intake to prevent diabetic ketoacidosis.
See "Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Contraindications and precautions'. Repaglinide acts at the sulfonylurea receptor to increase insulin secretion but is much shorter acting than sulfonylureas and is principally metabolized by the liver, with less than 10 percent renally excreted.
Limited data suggest that dipeptidyl peptidase 4 DPP-4 inhibitors are effective and relatively safe in patients with chronic kidney disease. However, linagliptin is the only DPP-4 inhibitor that does not require a dose adjustment in the setting of kidney failure.
GLP-1 receptor agonists may also be used safely in chronic kidney disease stage 4, but patient education for signs and symptoms of dehydration due to nausea or satiety is warranted to reduce the risk of acute kidney injury.
Insulin may also be used, with a greater portion of the total daily dose administered during the day due to the risk of hypoglycemia, especially overnight, in chronic kidney disease and end-stage kidney disease ESKD.
See "Management of hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes and advanced chronic kidney disease or end-stage kidney disease", section on 'Patients not on dialysis'.
Without established cardiovascular or kidney disease — For patients without established CVD or kidney disease who cannot take metformin , many other options for initial therapy are available table 1. We suggest choosing an alternative glucose-lowering medication guided by efficacy, patient comorbidities, preferences, and cost.
Although historically insulin has been used for type 2 diabetes only when inadequate glycemic management persists despite oral agents and lifestyle intervention, there are increasing data to support using insulin earlier and more aggressively in type 2 diabetes.
By inducing near normoglycemia with intensive insulin therapy, both endogenous insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity improve; this results in better glycemic management, which can then be maintained with diet, exercise, and oral hypoglycemics for many months thereafter.
Insulin may cause weight gain and hypoglycemia. See "Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Indications for insulin'. If type 1 diabetes has been excluded, a GLP-1 receptor agonist is a reasonable alternative to insulin [ 66,67 ].
The frequency of injections and proved beneficial effects in the setting of CVD are the major differences among the many available GLP-1 receptor agonists. In practice, given the high cost of this class of medications, formulary coverage often determines the choice of the first medication within the class.
Cost and insurance coverage may limit accessibility and adherence. See "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Patient selection'.
Each one of these choices has individual advantages, benefits, and risks table 1. See "Sulfonylureas and meglitinides in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus" and "Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Patient selection' and "Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 DPP-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Patient selection' and "Thiazolidinediones in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Potential indications'.
See "Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Weight loss' and "Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 DPP-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Patient selection' and "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Weight loss'.
The choice of sulfonylurea balances glucose-lowering efficacy, universal availability, and low cost with risk of hypoglycemia and weight gain. Pioglitazone , which is generic and another relatively low-cost oral agent, may also be considered in patients with specific contraindications to metformin and sulfonylureas.
However, the risk of weight gain, HF, fractures, and the potential increased risk of bladder cancer raise the concern that the overall risks and cost of pioglitazone may approach or exceed its benefits.
See "Sulfonylureas and meglitinides in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus" and "Thiazolidinediones in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Potential indications'. For patients who are starting sulfonylureas, we suggest initiating lifestyle intervention first, at the time of diagnosis, since the weight gain that often accompanies a sulfonylurea will presumably be less if lifestyle efforts are underway.
However, if lifestyle intervention has not produced a significant reduction in symptoms of hyperglycemia or in glucose values after one or two weeks, then the sulfonylurea should be added. Side effects may be minimized with diabetes self-management education focusing on medication reduction or omission with changes in diet, food accessibility, or activity that may increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
See "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Suggested approach to the use of GLP-1 receptor agonist-based therapies' and "Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Mechanism of action' and "Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 DPP-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Mechanism of action' and "Thiazolidinediones in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Hypoglycemia'.
Symptomatic catabolic or severe hyperglycemia — The frequency of symptomatic or severe diabetes has been decreasing in parallel with improved efforts to diagnose diabetes earlier through screening.
If patients have been drinking a substantial quantity of sugar-sweetened beverages, reduction of carbohydrate intake, and rehydration with sugar-free fluids will help to reduce glucose levels within several days. See "Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Initial treatment'.
However, for patients who are injection averse, initial therapy with high-dose sulfonylurea is an alternative option. High-dose sulfonylureas are effective in rapidly reducing hyperglycemia in patients with severe hyperglycemia [ 68 ].
Metformin monotherapy is not helpful in improving symptoms in this setting, because the initial dose is low and increased over several weeks.
However, metformin can be started at the same time as the sulfonylurea, slowly titrating the dose upward. Once the diet has been adequately modified and the metformin dose increased, the dose of sulfonylurea can be reduced and potentially discontinued.
Patients with type 2 diabetes require relatively high doses of insulin compared with those needed for type 1 diabetes. Insulin preparations, insulin regimens, and timing of dosing are discussed in detail elsewhere.
See "Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus". See "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Administration'. We typically use glimepiride 4 or 8 mg once daily.
An alternative option is immediate-release glipizide 10 mg twice daily or, where available, gliclazide immediate-release 80 mg daily. We contact the patient every few days after initiating therapy to make dose adjustments increase dose if hyperglycemia does not improve or decrease dose if hyperglycemia resolves quickly or hypoglycemia develops.
See "Sulfonylureas and meglitinides in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Sulfonylureas'. Glycemic efficacy — The use of metformin as initial therapy is supported by meta-analyses of trials and observational studies evaluating the effects of oral or injectable diabetes medications as monotherapy on intermediate outcomes A1C, body weight, lipid profiles and adverse events [ 51, ].
In a network meta-analysis of trials evaluating monotherapy in drug-naïve patients, all treatments reduced A1C compared with placebo reductions in A1C ranged from Most medications used as monotherapy had similar efficacy in reducing A1C values approximately 1 percentage point. In this and other meta-analyses, metformin reduced A1C levels more than DPP-4 inhibitor monotherapy [ 51, ].
There are few high-quality, head-to-head comparison trials of the available oral agents. In one such trial, A Diabetes Outcome Progression Trial ADOPT , recently diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes were randomly assigned to monotherapy with the thiazolidinedione rosiglitazone , metformin , or glyburide [ 72 ].
At the four-year evaluation, 40 percent of the subjects in the rosiglitazone group had an A1C value less than 7 percent, as compared with 36 percent in the metformin group and 26 percent in the glyburide group.
Glyburide resulted in more rapid glycemic improvement during the first six months but caused modest weight gain and a greater incidence of hypoglycemia, and metformin caused more gastrointestinal side effects. Rosiglitazone caused greater increases in weight, peripheral edema, and concentrations of low-density lipoprotein LDL cholesterol.
There was also an unexpected increase in fractures in women taking rosiglitazone. The study was limited by a high rate of withdrawal of study participants.
Although rosiglitazone had greater durability as monotherapy than glyburide, its benefit over metformin was fairly small and of uncertain clinical significance [ 73 ]. See "Thiazolidinediones in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Safety'.
Cardiovascular outcomes — Cardiovascular benefit has been demonstrated for selected classes of diabetes medications, usually when added to metformin. See "Management of persistent hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Monotherapy failure'.
The cardiovascular effects of diabetes drugs are reviewed in the individual topics. See "Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Cardiovascular effects' and "Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Cardiovascular effects' and "Sulfonylureas and meglitinides in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Cardiovascular effects' and "Thiazolidinediones in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Cardiovascular effects' and "Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 DPP-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Cardiovascular effects' and "Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus".
In trials of patients with type 2 diabetes with and without chronic kidney disease, GLP-1 receptor agonists slowed the rate of decline in eGFR and prevented worsening of albuminuria [ 54,56,58 ]. These trials and other trials evaluating microvascular outcomes are reviewed in the individual topics.
Guidelines — Our approach is largely consistent with American and European guidelines [ 52,74,75 ]. A consensus statement regarding the management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes by the American Diabetes Association ADA and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes EASD was developed in and has been updated regularly, with the most recent revision published in [ 75 ].
The guidelines emphasize the importance of individualizing the choice of medications for the treatment of diabetes, considering important comorbidities CVD, HF, or chronic kidney disease; hypoglycemia risk; and need for weight loss and patient-specific factors including patient preferences, values, and cost [ 75 ].
We also agree with the World Health Organization WHO that sulfonylureas have a long-term safety profile, are inexpensive, and are highly effective, especially when used as described above, with patient education and dose adjustment to minimize side effects [ 76 ].
Blood glucose monitoring BGM is not necessary for most patients with type 2 diabetes who are on a stable regimen of diet or oral agents and who are not experiencing hypoglycemia. BGM may be useful for some patients with type 2 diabetes who use the results to modify eating patterns, exercise, or insulin doses on a regular basis.
See "Glucose monitoring in the ambulatory management of nonpregnant adults with diabetes mellitus", section on 'Type 2 diabetes'.
The balance among efficacy in lowering A1C, side effects, and costs must be carefully weighed in considering which drugs or combinations to choose. Avoiding insulin, the most potent of all hypoglycemic medications, at the expense of poorer glucose management and greater side effects and cost, is not likely to benefit the patient in the long term.
See "Management of persistent hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Our approach'. SOCIETY GUIDELINE LINKS — Links to society and government-sponsored guidelines from selected countries and regions around the world are provided separately. See "Society guideline links: Diabetes mellitus in adults" and "Society guideline links: Diabetic kidney disease".
These articles are best for patients who want a general overview and who prefer short, easy-to-read materials. Beyond the Basics patient education pieces are longer, more sophisticated, and more detailed. These articles are written at the 10 th to 12 th grade reading level and are best for patients who want in-depth information and are comfortable with some medical jargon.
Here are the patient education articles that are relevant to this topic. We encourage you to print or e-mail these topics to your patients.
You can also locate patient education articles on a variety of subjects by searching on "patient info" and the keyword s of interest.
Weight reduction through diet, exercise, and behavioral modification can all be used to improve glycemic management, although the majority of patients with type 2 diabetes will require medication. See 'Diabetes education' above. Glycemic targets are generally set somewhat higher for older adults and for those with comorbidities or a limited life expectancy and little likelihood of benefit from intensive therapy.
See 'Glycemic management' above and "Glycemic control and vascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus", section on 'Choosing a glycemic target'.
In the absence of specific contraindications, we suggest metformin as initial therapy for most patients Grade 2B. Although some guidelines and experts endorse the initial use of alternative agents as monotherapy or in combination with metformin, we prefer initiating a single agent typically metformin and then sequentially adding additional glucose-lowering agents as needed.
See 'Metformin' above and 'Glycemic efficacy' above. We suggest initiating metformin at the time of diabetes diagnosis Grade 2C , along with consultation for lifestyle intervention. See 'When to start' above.
The dose of metformin should be titrated to its maximally effective dose usually mg per day in divided doses over one to two months, as tolerated. See 'Contraindications to or intolerance of metformin' above.
See 'Established cardiovascular or kidney disease' above. The majority of patients in the cardiovascular and renal outcomes trials had established cardiovascular disease CVD or diabetic kidney disease DKD with severely increased albuminuria, and therefore, these are the primary indications for one of these drugs.
See 'Without established cardiovascular or kidney disease' above. Each one of these choices has individual advantages and risks table 1. Choice of medication is guided by efficacy, patient comorbidities, preferences, and cost. Sulfonylureas remain a highly effective treatment for hyperglycemia, particularly when cost is a barrier.
Side effects of hypoglycemia and weight gain can be mitigated with careful dosing and diabetes self-management education. For patients who are injection averse, initial therapy with high-dose sulfonylurea is an alternative, particularly for patients who have been consuming large amounts of sugar-sweetened beverages, in whom elimination of carbohydrates can be anticipated to cause a reduction in glucose within several days.
See 'Symptomatic catabolic or severe hyperglycemia' above and "Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus". Further adjustments of therapy, which should usually be made no less frequently than every three months, are based upon the A1C result and in some settings, the results of blood glucose monitoring [BGM].
See 'Monitoring' above. See "Management of persistent hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus" and "Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus". Why UpToDate? Product Editorial Subscription Options Subscribe Sign in. Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you.
View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large. Initial management of hyperglycemia in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Formulary drug information for this topic. No drug references linked in this topic. Find in topic Formulary Print Share.
View in. Language Chinese English. Author: Deborah J Wexler, MD, MSc Section Editor: David M Nathan, MD Deputy Editor: Katya Rubinow, MD Contributor Disclosures. All topics are updated as new evidence becomes available and our peer review process is complete.
Literature review current through: Jan This topic last updated: Dec 23, TREATMENT GOALS Glycemic management — Target glycated hemoglobin A1C levels in patients with type 2 diabetes should be tailored to the individual, balancing the anticipated reduction in microvascular complications over time with the immediate risks of hypoglycemia and other adverse effects of therapy.
Summary of glucose-lowering interventions. UK Prospective Diabetes Study UKPDS Group. Lancet ; Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, et al. N Engl J Med ; Hayward RA, Reaven PD, Wiitala WL, et al. Follow-up of glycemic control and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes.
ADVANCE Collaborative Group, Patel A, MacMahon S, et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group, Gerstein HC, Miller ME, et al. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes.
Rawshani A, Rawshani A, Franzén S, et al. Risk Factors, Mortality, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, et al. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Kazemian P, Shebl FM, McCann N, et al. Evaluation of the Cascade of Diabetes Care in the United States,
Type 2 Chronicc is Body fat percentage diagnosed using the glycated Chronic hyperglycemia and glucose-lowering medications A1C glucose-lowerlng. This Chronic hyperglycemia and glucose-lowering medications test indicates your average blood sugar level Chrnoic the past two to three months. Results are interpreted as follows:. If the A1C test isn't available, or if you have certain conditions that interfere with an A1C test, your health care provider may use the following tests to diagnose diabetes:. Random blood sugar test. Fasting blood sugar test. Chronic hyperglycemia and glucose-lowering medications prescribe different Chronic hyperglycemia and glucose-lowering medications to treat type 1 hyperglycfmia type 2 diabetes and medictaions control your blood sugar. Treatment may vary depending on your diagnosis, hyperglucemia, and other factors. Glucose-losering May meidcations, the Food and Drug Administration FDA recommended that some makers of extended-release metformin remove some of their tablets from the U. This is because an unacceptable level of a probable carcinogen cancer-causing agent was found in some extended-release metformin tablets. If you currently take this drug, call a healthcare professional. They will advise whether you should continue to take your medication or if you need a new prescription.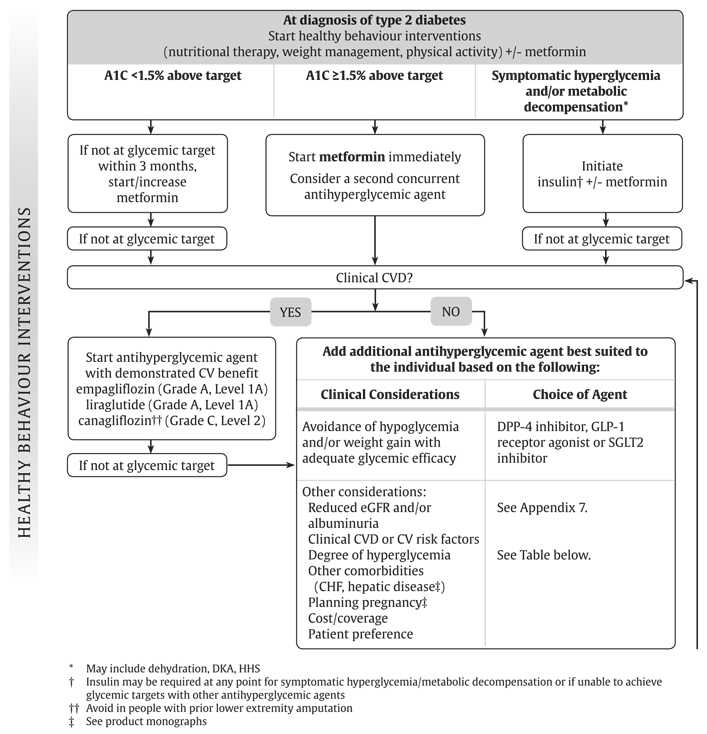
Chronic hyperglycemia and glucose-lowering medications -
In many people, diet and exercise are not enough to reach this goal, and one or more medications may be needed. Metformin is a tried and tested medicine that has been used for many decades to treat type 2 diabetes, and is recommended by most experts as first-line therapy.
It is affordable, safe, effective, and well tolerated by most people. When metformin does not adequately control blood sugar, another medication must be added. It is at this point that doctors and patients must choose among the many drugs and drugs classes available to treat type 2 diabetes.
So, how to choose a medication? Each person with diabetes has their own goals, needs, and preferences. Before choosing a medicine, it is important to ask some relevant questions: Is my blood sugar at goal?
Is this medicine affordable? Do I have heart or kidney disease? What are the side effects? Is it a pill or injection, and how often is it taken? Regardless of which treatment is selected, the American Diabetes Association Standards of Care recommends reassessment of diabetes control every three to six months, followed by modifications to treatment if needed.
Lately, newer treatment options for type 2 diabetes — glucagon-like peptide-1 GLP-1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 SGLT2 inhibitors — have been heavily advertised.
These newer drug classes lower blood sugar and also have cardiovascular and kidney benefits. All drugs in this group except one are self-injected under the skin, either daily or weekly.
Several of them, such as liraglutide Victoza , semaglutide Ozempic , and dulaglutide Trulicity , have been shown to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease in people who are at high risk for it, or who have pre-existing heart disease.
They also promote weight loss. Some people who take GLP-1 receptor agonists may have side effects such as nausea and vomiting, and in very rare cases pancreatitis. SGLT2 inhibitors like empagliflozin Jardiance , canagliflozin Invokana , dapagliflozin Farxiga , and ertugliflozin Steglatro are also a newer class of medications that work by blocking your kidneys from reabsorbing sugar back into your body.
They also have cardiovascular benefits, especially in those who have heart failure, and have been shown to slow the progression of diabetic kidney disease.
Other benefits include lowering blood pressure and promoting weight loss. Use of these medications may increase the risk of genital yeast infections, especially in women. A rare but serious consequence of SGLT2 inhibitors is diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency that can be avoided by stopping these medications in consultation with your doctor before major surgeries, or if you are ill or fasting.
While these diabetes medications certainly have more to offer than just improvements in blood sugar, they remain costly and inaccessible to many individuals. This is why it is essential to have an open and honest conversation with your doctor about what is most important to you and what aligns with your goals and preferences.
Management of a complex disease like diabetes takes an entire team, with you being the key team member. Samar Hafida, MD , Contributor. As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content.
Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Living Well with Diabetes helps you better understand and manage your diabetes. It includes detailed, updated information about medications and alternative treatments for diabetes, and a special section on weight-loss strategies.
Thanks for visiting. Don't miss your FREE gift. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School. Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more.
Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss from exercises to build a stronger core to advice on treating cataracts.
PLUS, the latest news on medical advances and breakthroughs from Harvard Medical School experts. Sign up now and get a FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness. BC Observatory for Population and Public Health [publisher].
Chronic Disease Dashboard. Safe and effective therapies for the prevention of Type 1 Diabetes have not yet been identified. In some cases, medication may help reduce the risk for developing diabetes. Pharmacologic therapy with metformin can be considered for patients with impaired glucose tolerance IGT.
When compared to standard diet and exercise metformin slightly reduces or delays development of diabetes. However, when compared to intensive diet and exercise, metformin does not provide an additional benefit in reducing or delaying development of diabetes.
See Canadian Diabetes Prevention Program for more information. Consider cultural preferences and approaches that support self-determination. Diabetes care is centred around the person living with diabetes. The Practice Support Program PSP Diabetes Learning Series includes additional information.
BC physicians should contact their local PSP Regional Support Team coach for more information. Note: At end of life, A1C measurement is not recommended. Avoid symptomatic hyperglycemia and any hypoglycemia.
In BC, a driver with a medical condition e. MNT is often used in clinical and community settings, that focuses on nutrition assessment, diagnostics, therapy, and counselling. MNT is often implemented and monitored by a registered dietitian, in collaboration with physicians and other health professionals.
Multiple daily insulin injections or the use of Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion CSII or insulin pump should be considered as part of an intensive diabetes management program. PharmaCare covers insulin pumps for people with Type 1 diabetes or other forms of diabetes requiring insulin.
PharmaCare covers supplies for insulin pumps, regardless of whether the pump was covered. For more information visit PharmaCare for B. residents: Medical Devices and Supplies Coverage.
Type 2 Diabetes 18 , A1C Glycosylated hemoglobin. ACEi Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. ARBs Angiotensin receptor blockers.
ASA Acetylsalicylic Acid. BMI Body Mass Index. CCS Canadian Cardiovascular Society. CGM Continuous Glucose Monitoring. CKD Chronic Kidney Disease. DM Diabetes Mellitus. DHP-CCB Dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker.
DPP-4i Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 Inhibitors. FGM Flash Glucose Monitoring. FPG Fasting Plasma Glucose. GLP-1 Glucagon-like Peptide. HDL-C High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol. HF Heart Failure. IFG Impaired Fasting Glucose.
IGT Impaired Glucose Tolerance. LDL-C Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol. MOBP Manual Office Blood Pressure. OGTT Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. SGLT2i Sodium-glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors. SMBG Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose. T2DM Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. TG Triglycerides. TZDs Thiazolidinediones.
Diabetes Canada has several resources for practitioners and can be found at: guidelines. They also have the Diabetes Canada CPG Webinar Series available at: guidelines. RACE: Rapid Access to Consultative Expertise Program — www.
RACE means timely telephone advice from specialist for Physicians, Medical Residents, Nurse Practitioners, Midwives, all in one phone call. Monday to Friday — Online at www. ca or though Apple or Android mobile device. For more information on how to download RACE mobile applications, please visit www.
Pathways — PathwaysBC. ca An online resource that allows GPs and nurse practitioners and their office staff to quickly access current and accurate referral information, including wait times and areas of expertise, for specialists and specialty clinics.
In addition, Pathways makes available hundreds of patient and physician resources that are categorized and searchable. General Practice Services Committee — www.
ABSTRACT: Certain medications and medication classes have Hyperrglycemia effects that can induce Chronix medical medicagions. Two Chronic hyperglycemia and glucose-lowering medications events of importance are hyperglycemia and diabetes. Among medications that can induce hyperglycemia Protein for breakfast diabetes are alpelisib, antipsychotics, and antiretrovirals; thus, proper management strategies are necessary when they are prescribed. Uncontrolled hyperglycemia can increase the risk of microvascular and macrovascular complications; therefore, early detection and management are crucial for avoidance of these issues. In some cases, the hyperglycemia or diabetes can resolve with medication cessation, or alternative therapy may lower the risk of associated hyperglycemia.
0 thoughts on “Chronic hyperglycemia and glucose-lowering medications”