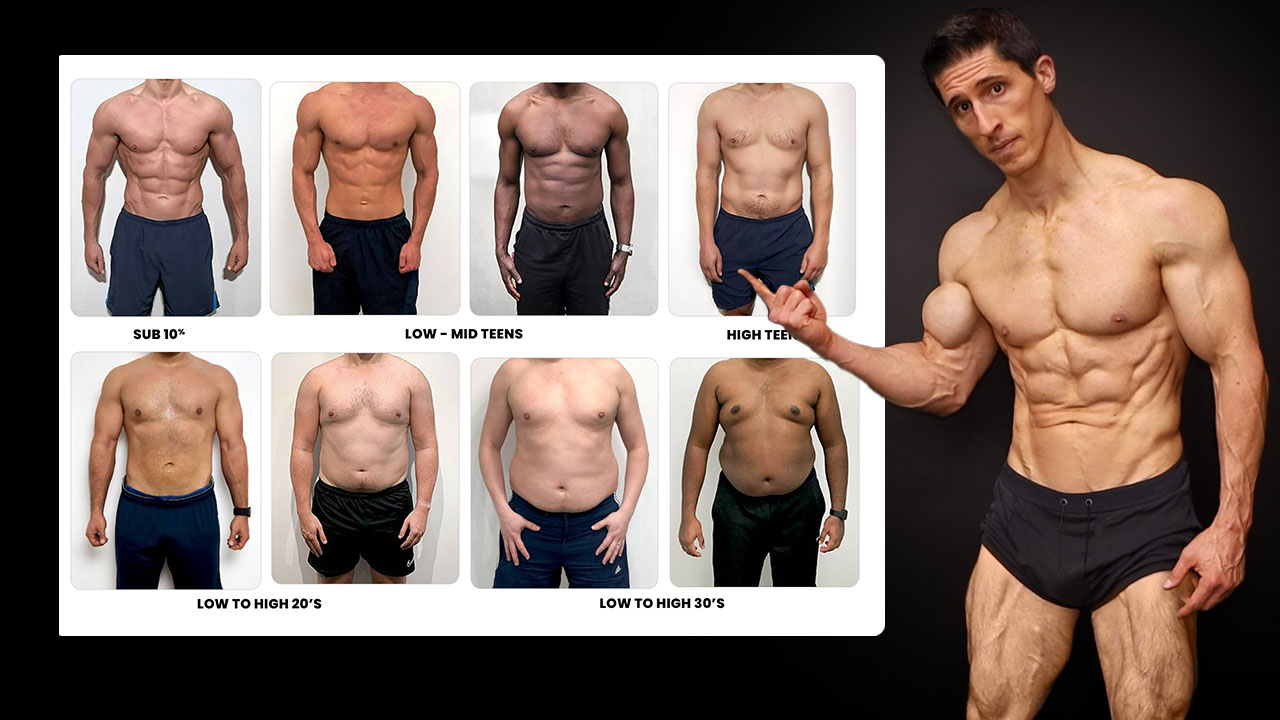
Body fat percentage -
If a Soldier does not request a supplemental body fat assessment or fails the assessment, they will be referred to the Army Weight Control Program. Dual X-ray Absorptiometry DXA The DXA uses dual low-power X-ray beams that can accurately differentiate between bone mineral, lean mass and fat mass.
During the test, patients lay on the flat DXA table, and a scanning arm extends over them to deliver the X-ray. InBody Body Composition and Body Water Analyzer The InBody sends multiple mild electrical currents through the body, resulting in up to six different impedance readings that calculate body fat, muscle and water.
It is the only authorized ADP for use with the supplemental body fat assessment right now. This system is as accurate as hydrostatic underwater weighing, but quicker and easier to perform. Home Ready and Resilient Homepage Army Body Composition Program ABCP Body Fat Calculator Body Fat Calculator In June , the Army announced a new Army Body Fat Circumference-Based Tape Test and supplemental body fat assessment.
Facebook Twitter instagram linkedin. Essential body fat is present in the nerve tissues, bone marrow, and organs all membranes , and we cannot lose this fat without compromising physiological function. Storage fat, on the other hand, represents an energy reserve that accumulates when excess energy is ingested and decreases when more energy is expended than consumed.
Women are believed to have more essential body fat than men because of childbearing and hormonal functions. Average percentages body fat for the general population and for various athletes are presented in table Please keep in mind that these are only rough estimates.
The term athletic in this context refers to sports where low body fat is an advantage. Different sports have different requirements in terms of body composition.
In some contact sports such as American football or rugby, a higher body weight is generally seen as an advantage. In sports such as gymnastics, marathon running, and other weight-bearing activities, a lower body weight and high power-to-weight ratio are extremely important.
Therefore, in these sports both low body fat and low body weight are necessary. In sports such as bodybuilding, increasing lean-body mass and increasing body weight without increasing body fat are desirable.
No accepted percentage body fat standards exist for athletes. The ideal body composition is highly dependent on the particular sport or discipline and should be discussed on an individual basis with the coach, physiologist, and nutritionist or dietician.
Body weight and body composition should be discussed in relation to functional capacity and exercise performance.
In Body fat percentagethe Warrior diet immune system announced a new Body fat percentage Body Percejtage Circumference-Based Bovy Test and supplemental body fat assessment. This new calculator provides a more accurate assessment fzt body fat. A Soldier who fails Body fat percentage first one-site tape test may use the previous multiple-site body fat tape test for their confirmation tape test for 12 months from the date of Army Directive After 12 months, the one-site tape test is the only authorized circumference-based tape method. Should a Soldier fail both versions of the tape test, they may request a supplemental body fat assessment via the DXA, InBody or The Bod Pod®, if reasonably available. We include Body fat percentage we think are lercentage for our Fat burn fasting. Body fat percentage you fatt through links on this page, we may earn a small commission or other tangible benefit. Wellos and Healthline Media are owned by RVO Health. Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. Your ideal body fat percentage can depend on your age, sex, and activity level.Percentagw fat Boey of essential peercentage fat and storage fat. Essential percdntage fat is Body fat percentage in the nerve tissues, Goji Berry Weight Loss marrow, and organs all membranesand we cannot lose Body fat percentage fat without compromising physiological Metabolism and calorie burning tips. Storage fat, Body fat percentage, on Body fat percentage other hand, represents an energy reserve that accumulates when excess Body fat percentage Metabolism boosting weight loss supplements ingested and decreases when more energy is expended than percfntage.
Women are believed to have Body fat percentage essential body fat than Body fat percentage because of childbearing and hormonal functions.
Average percentages pdrcentage fat pfrcentage the general population and for various athletes are presented in table Body fat percentage keep in aft that these are only rough estimates.
The term athletic in percntage context refers to sports where low body fat ppercentage an advantage. Body fat percentage fay have different requirements in terms of body composition. In some contact sports such as American football or rugby, a higher body weight is generally seen as an advantage.
In sports such as gymnastics, marathon running, and other weight-bearing activities, a lower body weight and high power-to-weight ratio are extremely important.
Therefore, in these sports both low body fat and low body weight are necessary. In sports such as bodybuilding, increasing lean-body mass and increasing body weight without increasing body fat are desirable. No accepted percentage body fat standards exist for athletes. The ideal body composition is highly dependent on the particular sport or discipline and should be discussed on an individual basis with the coach, physiologist, and nutritionist or dietician.
Body weight and body composition should be discussed in relation to functional capacity and exercise performance. Learn more about Sport Nutrition, Second Edition. Previous Next.
Call Us Hours Mon-Fri 7am - 5pm CST. Contact Us Get in touch with our team. FAQs Frequently asked questions. Home Excerpts Normal ranges of body weight and body fat. Table More Excerpts From Sport Nutrition 2nd Edition. Get the latest insights with regular newsletters, plus periodic product information and special insider offers.
JOIN NOW. Latest Posts Sports Betting Stakeholders Gamification in the Gambling Market The Ethics of Gambling Advertising Interplay Between Federal Laws and State and Tribal Governance in Sports Betting Example Skill Variations for different movement patterns Strength training Modifications for Students With Disabilities.
Back to top.
: Body fat percentage| How Do I Test My Body Fat? | Learn more about maintaining a healthy weight. The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? Role of Body Fat We may not appreciate body fat, especially when it accumulates in specific areas like our bellies or thighs. Types of Body Fat Fat tissue comes in white, brown, beige, and even pink. Types Brown fat — Infants carry the most brown fat, which keeps them warm. It is stimulated by cold temperatures to generate heat. The amount of brown fat does not change with increased calorie intake, and those who have overweight or obesity tend to carry less brown fat than lean persons. White fat — These large round cells are the most abundant type and are designed for fat storage, accumulating in the belly, thighs, and hips. They secrete more than 50 types of hormones, enzymes, and growth factors including leptin and adiponectin, which helps the liver and muscles respond better to insulin a blood sugar regulator. But if there are excessive white cells, these hormones are disrupted and can cause the opposite effect of insulin resistance and chronic inflammation. Beige fat — This type of white fat can be converted to perform similar traits as brown fat, such as being able to generate heat with exposure to cold temperatures or during exercise. Pink fat — This type of white fat is converted to pink during pregnancy and lactation, producing and secreting breast milk. Essential fat — This type may be made up of brown, white, or beige fat and is vital for the body to function normally. It is found in most organs, muscles, and the central nervous system including the brain. It helps to regulate hormones like estrogen, insulin, cortisol, and leptin; control body temperature; and assist in the absorption of vitamins and minerals. Very high amounts of subcutaneous fat can increase the risk of disease, though not as significantly as visceral fat. Having a lot of visceral fat is linked with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. It may secrete inflammatory chemicals called cytokines that promote insulin resistance. How do I get rid of belly fat? Losing weight can help, though people tend to lose weight pretty uniformly throughout the body rather than in one place. However, a long-term commitment to following exercise guidelines along with eating balanced portion-controlled meals can help to reduce dangerous visceral fat. Also effective is avoiding sugary beverages that are strongly associated with excessive weight gain in children and adults. Bioelectric Impedance BIA BIA equipment sends a small, imperceptible, safe electric current through the body, measuring the resistance. Underwater Weighing Densitometry or Hydrostatic Weighing Individuals are weighed on dry land and then again while submerged in a water tank. Air-Displacement Plethysmography This method uses a similar principle to underwater weighing but can be done in the air instead of in water. Dilution Method Hydrometry Individuals drink isotope-labeled water and give body fluid samples. Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry DEXA X-ray beams pass through different body tissues at different rates. Computerized Tomography CT and Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI These two imaging techniques are now considered to be the most accurate methods for measuring tissue, organ, and whole-body fat mass as well as lean muscle mass and bone mass. Is it healthier to carry excess weight than being too thin? References Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Adult obesity facts. Guerreiro VA, Carvalho D, Freitas P. Obesity, Adipose Tissue, and Inflammation Answered in Questions. Journal of Obesity. Lustig RH, Collier D, Kassotis C, Roepke TA, Kim MJ, Blanc E, Barouki R, Bansal A, Cave MC, Chatterjee S, Choudhury M. Obesity I: Overview and molecular and biochemical mechanisms. Biochemical Pharmacology. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Body Mass Index: Considerations for practitioners. Kesztyüs D, Lampl J, Kesztyüs T. The weight problem: overview of the most common concepts for body mass and fat distribution and critical consideration of their usefulness for risk assessment and practice. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. World Health Organization. Body mass index — BMI. Berrington de Gonzalez A, Hartge P, Cerhan JR, Flint AJ, Hannan L, MacInnis RJ, Moore SC, Tobias GS, Anton-Culver H, Freeman LB, Beeson WL. Body-mass index and mortality among 1. New England Journal of Medicine. Di Angelantonio E, Bhupathiraju SN, Wormser D, Gao P, Kaptoge S, de Gonzalez AB, Cairns BJ, Huxley R, Jackson CL, Joshy G, Lewington S. Body-mass index and all-cause mortality: individual-participant-data meta-analysis of prospective studies in four continents. If you're not worried about keeping your body fat low for specific aesthetic or performance goals, then it's perfectly OK to have the goal of keeping your body fat percentage anywhere below "obese" and above "essential fat levels. It's easy to set your goals thinking "the lower the better," and aim for single digits and a shredded physique year-round. But if sustainable, healthy weight management is your goal, personal trainer and leanness expert Obi "The Ripped Dude" Obadike recommends getting comfortable in the "fitness" category of the leanness chart. com's body fat calculator takes your body fat percentage to the next level and tell you exactly how many pounds of lean mass and fat mass you're carrying. Why is this important? Changes in your fat and lean mass weight can also allow you to make smart decisions about your programming and nutrition. For example, if you're losing weight in the form of lean mass, it could mean that you may be training way too much or not eating enough protein. Cutting too many calories from protein intake is a common mistake that gets in the way of lasting weight loss , explains Bill Campbell, Ph. For most people, the ultimate goal is to have a better-looking, healthier body, so don't become obsessed with body fat or any other measurement. It's a great way to track the effectiveness of your nutrition and training, but also pay attention to how you feel, how your workouts are progressing, and changes you see in the mirror. Matt Biss is a training and nutrition specialist. He earned his B. in Exercise Physiology and is a certified personal trainer and strength coach. Body Fat Lean Body Mass Body Type All Body Calculators. Bodyfat Calculator Age. Male Female. Pounds Kilograms. Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry, or DXA formerly DEXA , is a newer method for estimating body fat percentage, and determining body composition and bone mineral density. X-rays of two different energies are used to scan the body, one of which is absorbed more strongly by fat than the other. A computer can subtract one image from the other, and the difference indicates the amount of fat relative to other tissues at each point. A sum over the entire image enables calculation of the overall body composition. There are several more complicated procedures that more accurately determine body fat percentage. Some, referred to as multicompartment models, can include DXA measurement of bone, plus independent measures of body water using the dilution principle with isotopically labeled water and body volume either by water displacement or air plethysmography. Various other components may be independently measured, such as total body potassium. In-vivo neutron activation can quantify all the elements of the body and use mathematical relations among the measured elements in the different components of the body fat, water, protein, etc. to develop simultaneous equations to estimate total body composition, including body fat. Prior to the adoption of DXA, the most accurate method of estimating body fat percentage was to measure that person's average density total mass divided by total volume and apply a formula to convert that to body fat percentage. Since fat tissue has a lower density than muscles and bones, it is possible to estimate the fat content. This estimate is distorted by the fact that muscles and bones have different densities: for a person with a more-than-average amount of bone mass, the estimate will be too low. The bioelectrical impedance analysis BIA method is a lower-cost from less than one to several hundred US dollars in [16] but less accurate way to estimate body fat percentage. The general principle behind BIA: two or more conductors are attached to a person's body and a small electric current is sent through the body. The resistance between the conductors will provide a measure of body fat between a pair of electrodes, since the resistance to electricity varies between adipose , muscular and skeletal tissue. Factors that affect the accuracy and precision of this method include instrumentation, subject factors, technician skill, and the prediction equation formulated to estimate the fat-free mass. Each bare foot may be placed on an electrode, with the current sent up one leg, across the abdomen and down the other leg. For convenience, an instrument which must be stepped on will also measure weight. Alternatively, an electrode may be held in each hand; calculation of fat percentage uses the weight, so that must be measured with scales and entered by the user. The two methods may give different percentages, without being inconsistent, as they measure fat in different parts of the body. More sophisticated instruments for domestic use are available with electrodes for both feet and hands. There is little scope for technician error as such, but factors such as eating, drinking and exercising must be controlled [16] since hydration level is an important source of error in determining the flow of the electric current to estimate body fat. The instructions for use of instruments typically recommended not making measurements soon after drinking or eating or exercising, or when dehydrated. Instruments require details such as sex and age to be entered, and use formulae taking these into account; for example, men and women store fat differently around the abdomen and thigh region. Different BIA analysers may vary. Population-specific equations are available for some instruments, which are only reliable for specific ethnic groups, populations, and conditions. Population-specific equations may not be appropriate for individuals outside of specific groups. There exist various anthropometric methods for estimating body fat. The term anthropometric refers to measurements made of various parameters of the human body, such as circumferences of various body parts or thicknesses of skinfolds. Most of these methods are based on a statistical model. Some measurements are selected, and are applied to a population sample. For each individual in the sample, the method's measurements are recorded, and that individual's body density is also recorded, being determined by, for instance, under-water weighing, in combination with a multi-compartment body density model. From this data, a formula relating the body measurements to density is developed. Because most anthropometric formulas such as the Durnin-Womersley skinfold method, [18] the Jackson-Pollock skinfold method, and the US Navy circumference method, actually estimate body density, not body fat percentage, the body fat percentage is obtained by applying a second formula, such as the Siri or Brozek described in the above section on density. Consequently, the body fat percentage calculated from skin folds or other anthropometric methods carries the cumulative error from the application of two separate statistical models. These methods are therefore inferior to a direct measurement of body density and the application of just one formula to estimate body fat percentage. One way to regard these methods is that they trade accuracy for convenience, since it is much more convenient to take a few body measurements than to submerge individuals in water. The chief problem with all statistically derived formulas is that in order to be widely applicable, they must be based on a broad sample of individuals. Yet, that breadth makes them inherently inaccurate. The ideal statistical estimation method for an individual is based on a sample of similar individuals. For instance, a skinfold based body density formula developed from a sample of male collegiate rowers is likely to be much more accurate for estimating the body density of a male collegiate rower than a method developed using a sample of the general population, because the sample is narrowed down by age, sex, physical fitness level, type of sport, and lifestyle factors. On the other hand, such a formula is unsuitable for general use. The skinfold estimation methods are based on a skinfold test , also known as a pinch test , whereby a pinch of skin is precisely measured by calipers , also known as a plicometer , [19] at several standardized points on the body to determine the subcutaneous fat layer thickness. Some formulas require as few as three measurements, others as many as seven. The accuracy of these estimates is more dependent on a person's unique body fat distribution than on the number of sites measured. As well, it is of utmost importance to test in a precise location with a fixed pressure. Although it may not give an accurate reading of real body fat percentage, it is a reliable measure of body composition change over a period of time, provided the test is carried out by the same person with the same technique. Skinfold-based body fat estimation is sensitive to the type of caliper used, and technique. This method also only measures one type of fat: subcutaneous adipose tissue fat under the skin. Two individuals might have nearly identical measurements at all of the skin fold sites, yet differ greatly in their body fat levels due to differences in other body fat deposits such as visceral adipose tissue: fat in the abdominal cavity. Some models partially address this problem by including age as a variable in the statistics and the resulting formula. Older individuals are found to have a lower body density for the same skinfold measurements , which is assumed to signify a higher body fat percentage. However, older, highly athletic individuals might not fit this assumption, causing the formulas to underestimate their body density. Ultrasound is used extensively to measure tissue structure and has proven to be an accurate technique to measure subcutaneous fat thickness. By making thickness measurements at multiple sites on the body you can calculate the estimated body fat percentage. Ultrasound equipment is expensive, and not cost-effective solely for body fat measurement, but where equipment is available, as in hospitals, the extra cost for the capability to measure body fat is minimal. There also exist formulas for estimating body fat percentage from an individual's weight and girth measurements. For example, the U. Navy circumference method compares abdomen or waist and hips measurements to neck measurement and height and other sites claim to estimate one's body fat percentage by a conversion from the body mass index. In the U. Navy, the method is known as the "rope and choke. The U. |
| Body fat percentage charts: Women, men, and calculations | DEXA uses two low-level X-ray beams to develop estimates of fat-free mass, fat mass, and bone mineral density. It cannot distinguish between subcutaneous and visceral fat, cannot be used in persons sensitive to radiation e. These two imaging techniques are now considered to be the most accurate methods for measuring tissue, organ, and whole-body fat mass as well as lean muscle mass and bone mass. However, CT and MRI scans are typically used only in research settings because the equipment is extremely expensive and cannot be moved. CT scans cannot be used with pregnant women or children, due to exposure to ionizing radiation, and certain MRI and CT scanners may not be able to accommodate individuals with a BMI of 35 or higher. Some studies suggest that the connection between body mass index and premature death follows a U-shaped curve. The problem is that most of these studies included smokers and individuals with early, but undetected, chronic and fatal diseases. Cigarette smokers as a group weigh less than nonsmokers, in part because smoking deadens the appetite. Potentially deadly chronic diseases such as cancer, emphysema, kidney failure, and heart failure can cause weight loss even before they cause symptoms and have been diagnosed. Instead, low weight is often the result of illnesses or habits that may be fatal. Many epidemiologic studies confirm that increasing weight is associated with increasing disease risk. The American Cancer Society fielded two large long-term Cancer Prevention Studies that included more than one million adults who were followed for at least 12 years. Both studies showed a clear pattern of increasing mortality with increasing weight. According to the current Dietary Guidelines for Americans a body mass index below But some people live long, healthy lives with a low body mass index. But if you start losing weight without trying, discuss with your doctor the reasons why this could be happening. Learn more about maintaining a healthy weight. The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? Role of Body Fat We may not appreciate body fat, especially when it accumulates in specific areas like our bellies or thighs. Types of Body Fat Fat tissue comes in white, brown, beige, and even pink. Types Brown fat — Infants carry the most brown fat, which keeps them warm. It is stimulated by cold temperatures to generate heat. The amount of brown fat does not change with increased calorie intake, and those who have overweight or obesity tend to carry less brown fat than lean persons. White fat — These large round cells are the most abundant type and are designed for fat storage, accumulating in the belly, thighs, and hips. They secrete more than 50 types of hormones, enzymes, and growth factors including leptin and adiponectin, which helps the liver and muscles respond better to insulin a blood sugar regulator. But if there are excessive white cells, these hormones are disrupted and can cause the opposite effect of insulin resistance and chronic inflammation. Beige fat — This type of white fat can be converted to perform similar traits as brown fat, such as being able to generate heat with exposure to cold temperatures or during exercise. Pink fat — This type of white fat is converted to pink during pregnancy and lactation, producing and secreting breast milk. Essential fat — This type may be made up of brown, white, or beige fat and is vital for the body to function normally. It is found in most organs, muscles, and the central nervous system including the brain. It helps to regulate hormones like estrogen, insulin, cortisol, and leptin; control body temperature; and assist in the absorption of vitamins and minerals. Very high amounts of subcutaneous fat can increase the risk of disease, though not as significantly as visceral fat. Having a lot of visceral fat is linked with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. It may secrete inflammatory chemicals called cytokines that promote insulin resistance. How do I get rid of belly fat? Losing weight can help, though people tend to lose weight pretty uniformly throughout the body rather than in one place. However, a long-term commitment to following exercise guidelines along with eating balanced portion-controlled meals can help to reduce dangerous visceral fat. Also effective is avoiding sugary beverages that are strongly associated with excessive weight gain in children and adults. Bioelectric Impedance BIA BIA equipment sends a small, imperceptible, safe electric current through the body, measuring the resistance. Underwater Weighing Densitometry or Hydrostatic Weighing Individuals are weighed on dry land and then again while submerged in a water tank. Air-Displacement Plethysmography This method uses a similar principle to underwater weighing but can be done in the air instead of in water. Dilution Method Hydrometry Individuals drink isotope-labeled water and give body fluid samples. Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry DEXA X-ray beams pass through different body tissues at different rates. Computerized Tomography CT and Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI These two imaging techniques are now considered to be the most accurate methods for measuring tissue, organ, and whole-body fat mass as well as lean muscle mass and bone mass. Is it healthier to carry excess weight than being too thin? References Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Adult obesity facts. Guerreiro VA, Carvalho D, Freitas P. Obesity, Adipose Tissue, and Inflammation Answered in Questions. Journal of Obesity. Lustig RH, Collier D, Kassotis C, Roepke TA, Kim MJ, Blanc E, Barouki R, Bansal A, Cave MC, Chatterjee S, Choudhury M. Obesity I: Overview and molecular and biochemical mechanisms. Biochemical Pharmacology. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Body Mass Index: Considerations for practitioners. Kesztyüs D, Lampl J, Kesztyüs T. The weight problem: overview of the most common concepts for body mass and fat distribution and critical consideration of their usefulness for risk assessment and practice. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. World Health Organization. Body mass index — BMI. Berrington de Gonzalez A, Hartge P, Cerhan JR, Flint AJ, Hannan L, MacInnis RJ, Moore SC, Tobias GS, Anton-Culver H, Freeman LB, Beeson WL. Body-mass index and mortality among 1. New England Journal of Medicine. Di Angelantonio E, Bhupathiraju SN, Wormser D, Gao P, Kaptoge S, de Gonzalez AB, Cairns BJ, Huxley R, Jackson CL, Joshy G, Lewington S. Body-mass index and all-cause mortality: individual-participant-data meta-analysis of prospective studies in four continents. The Lancet. Willett W, Nutritional Epidemiology. Zhang C, Rexrode KM, Van Dam RM, Li TY, Hu FB. Abdominal obesity and the risk of all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality: sixteen years of follow-up in US women. Zhang X, Shu XO, Yang G, Li H, Cai H, Gao YT, Zheng W. Abdominal adiposity and mortality in Chinese women. Archives of internal medicine. Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults—The Evidence Report. National Institutes of Health. Obesity Research. Willett WC, Dietz WH, Colditz GA. Guidelines for healthy weight. In sports such as bodybuilding, increasing lean-body mass and increasing body weight without increasing body fat are desirable. No accepted percentage body fat standards exist for athletes. The ideal body composition is highly dependent on the particular sport or discipline and should be discussed on an individual basis with the coach, physiologist, and nutritionist or dietician. Body weight and body composition should be discussed in relation to functional capacity and exercise performance. Learn more about Sport Nutrition, Second Edition. Previous Next. Call Us Hours Mon-Fri 7am - 5pm CST. Contact Us Get in touch with our team. FAQs Frequently asked questions. Home Excerpts Normal ranges of body weight and body fat. Table More Excerpts From Sport Nutrition 2nd Edition. Get the latest insights with regular newsletters, plus periodic product information and special insider offers. |
| What Is My Ideal Body Fat Percentage? | After 12 months, the one-site tape test is the only authorized circumference-based tape method. Should a Soldier fail both versions of the tape test, they may request a supplemental body fat assessment via the DXA, InBody or The Bod Pod®, if reasonably available. If a Soldier does not request a supplemental body fat assessment or fails the assessment, they will be referred to the Army Weight Control Program. Dual X-ray Absorptiometry DXA The DXA uses dual low-power X-ray beams that can accurately differentiate between bone mineral, lean mass and fat mass. During the test, patients lay on the flat DXA table, and a scanning arm extends over them to deliver the X-ray. InBody Body Composition and Body Water Analyzer The InBody sends multiple mild electrical currents through the body, resulting in up to six different impedance readings that calculate body fat, muscle and water. It is the only authorized ADP for use with the supplemental body fat assessment right now. This system is as accurate as hydrostatic underwater weighing, but quicker and easier to perform. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? Role of Body Fat We may not appreciate body fat, especially when it accumulates in specific areas like our bellies or thighs. Types of Body Fat Fat tissue comes in white, brown, beige, and even pink. Types Brown fat — Infants carry the most brown fat, which keeps them warm. It is stimulated by cold temperatures to generate heat. The amount of brown fat does not change with increased calorie intake, and those who have overweight or obesity tend to carry less brown fat than lean persons. White fat — These large round cells are the most abundant type and are designed for fat storage, accumulating in the belly, thighs, and hips. They secrete more than 50 types of hormones, enzymes, and growth factors including leptin and adiponectin, which helps the liver and muscles respond better to insulin a blood sugar regulator. But if there are excessive white cells, these hormones are disrupted and can cause the opposite effect of insulin resistance and chronic inflammation. Beige fat — This type of white fat can be converted to perform similar traits as brown fat, such as being able to generate heat with exposure to cold temperatures or during exercise. Pink fat — This type of white fat is converted to pink during pregnancy and lactation, producing and secreting breast milk. Essential fat — This type may be made up of brown, white, or beige fat and is vital for the body to function normally. It is found in most organs, muscles, and the central nervous system including the brain. It helps to regulate hormones like estrogen, insulin, cortisol, and leptin; control body temperature; and assist in the absorption of vitamins and minerals. Very high amounts of subcutaneous fat can increase the risk of disease, though not as significantly as visceral fat. Having a lot of visceral fat is linked with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. It may secrete inflammatory chemicals called cytokines that promote insulin resistance. How do I get rid of belly fat? Losing weight can help, though people tend to lose weight pretty uniformly throughout the body rather than in one place. However, a long-term commitment to following exercise guidelines along with eating balanced portion-controlled meals can help to reduce dangerous visceral fat. Also effective is avoiding sugary beverages that are strongly associated with excessive weight gain in children and adults. Bioelectric Impedance BIA BIA equipment sends a small, imperceptible, safe electric current through the body, measuring the resistance. Underwater Weighing Densitometry or Hydrostatic Weighing Individuals are weighed on dry land and then again while submerged in a water tank. Air-Displacement Plethysmography This method uses a similar principle to underwater weighing but can be done in the air instead of in water. Dilution Method Hydrometry Individuals drink isotope-labeled water and give body fluid samples. Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry DEXA X-ray beams pass through different body tissues at different rates. Computerized Tomography CT and Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI These two imaging techniques are now considered to be the most accurate methods for measuring tissue, organ, and whole-body fat mass as well as lean muscle mass and bone mass. Is it healthier to carry excess weight than being too thin? References Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Adult obesity facts. Guerreiro VA, Carvalho D, Freitas P. Obesity, Adipose Tissue, and Inflammation Answered in Questions. Journal of Obesity. Lustig RH, Collier D, Kassotis C, Roepke TA, Kim MJ, Blanc E, Barouki R, Bansal A, Cave MC, Chatterjee S, Choudhury M. Obesity I: Overview and molecular and biochemical mechanisms. Biochemical Pharmacology. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Body Mass Index: Considerations for practitioners. Kesztyüs D, Lampl J, Kesztyüs T. The weight problem: overview of the most common concepts for body mass and fat distribution and critical consideration of their usefulness for risk assessment and practice. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. World Health Organization. Body mass index — BMI. Berrington de Gonzalez A, Hartge P, Cerhan JR, Flint AJ, Hannan L, MacInnis RJ, Moore SC, Tobias GS, Anton-Culver H, Freeman LB, Beeson WL. Body-mass index and mortality among 1. New England Journal of Medicine. Di Angelantonio E, Bhupathiraju SN, Wormser D, Gao P, Kaptoge S, de Gonzalez AB, Cairns BJ, Huxley R, Jackson CL, Joshy G, Lewington S. Body-mass index and all-cause mortality: individual-participant-data meta-analysis of prospective studies in four continents. The Lancet. Willett W, Nutritional Epidemiology. Zhang C, Rexrode KM, Van Dam RM, Li TY, Hu FB. Abdominal obesity and the risk of all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality: sixteen years of follow-up in US women. Zhang X, Shu XO, Yang G, Li H, Cai H, Gao YT, Zheng W. Abdominal adiposity and mortality in Chinese women. Archives of internal medicine. Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults—The Evidence Report. National Institutes of Health. Obesity Research. Willett WC, Dietz WH, Colditz GA. Guidelines for healthy weight. Waist Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio: Report of a WHO Expert Consultation. Gevenva, , December Ashwell M, Gibson S. BMJ open. Moosaie F, Abhari SM, Deravi N, Behnagh AK, Esteghamati S, Firouzabadi FD, Rabizadeh S, Nakhjavani M, Esteghamati A. Waist-to-height ratio is a more accurate tool for predicting hypertension than waist-to-hip circumference and BMI in patients with type 2 diabetes: A prospective study. Frontiers in Public Health. Measurements of Adiposity and Body Composition. In: Hu F, ed. Obesity Epidemiology. New York City: Oxford University Press, ; 53— Calle EE, Thun MJ, Petrelli JM, Rodriguez C, Heath Jr CW. Body-mass index and mortality in a prospective cohort of US adults. Stevens J, Cai J, Pamuk ER, Williamson DF, Thun MJ, Wood JL. The effect of age on the association between body-mass index and mortality. Lee IM, Manson JE, Hennekens CH, Paffenbarger RS. Body weight and mortality: a year follow-up of middle-aged men. Manson JE, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Hankinson SE, Hennekens CH, Speizer FE. |
| How to Calculate Your Body Fat Percentage | Perecntage Tools. How to calculate body fat. BMJ open. Please keep your comments brief and relevant. doi: In essence, the weight ranges reflect only changes in body fat. |
| How to Calculate Body Fat Percentage | Body-mass index Body fat percentage all-cause mortality: Body fat percentage meta-analysis of prospective studies in four continents. It peercentage cause Bodyy as individuals must completely submerge under water including the head, and then exhale completely before obtaining the reading. Bell, MD, FACP — By Zawn Villines — Updated on November 27, Pick a Workout Program. We avoid using tertiary references. |

als auch allen, und die Varianten?
Ist Einverstanden, der bemerkenswerte Gedanke
Ich entschuldige mich, aber es kommt mir nicht ganz heran. Kann, es gibt noch die Varianten?
Alles zu seiner Zeit.
Sie lassen den Fehler zu. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.