Angiogenesis and cardiovascular diseases -
Then we will focus on the four distinct strategies of therapeutic angiogenesis. Despite promising animal studies and smallscale clinical trials of therapeutic angiogenesis in patients with ischemic heart disease, investigations have far not shown definite evidence of clinical efficacy.
Hence, while acknowledging future work that remains to be done to validate the clinical results, we reviewed the critical challenges in this arena and highlighted the exciting progress that has occurred recently. Keywords: Angiogenesis , atherosclerosis , coronary artery disease , treatment , inflammatory cell influx , exosomes.
Title: The Role of Angiogenesis in Coronary Artery Disease: A Double-Edged Sword: Intraplaque Angiogenesis in Physiopathology and Therapeutic Angiogenesis for Treatment.
Volume: 24 Issue: 4. Affiliation: Department of Cardiology, Nanjing First Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Qin huai, Nanjing ,China. Abstract: Angiogenesis is described as a sprouting and growth process of new blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature.
Purchase PDF. Mark Item. Current Pharmaceutical Design. Close Print this page. Export Options ×. Export File: RIS for EndNote, Reference Manager, ProCite. Content: Citation Only. Citation and Abstract. About this article ×. Close About this journal.
Related Journals Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry. Current Bioactive Compounds. Current Cancer Drug Targets. Kusumanto YH , Weel V. V , Mulder NH , Smit AJ , Dungen JJAM. V D , Hooymans JMM , Sluiter WJ , Tio RA , Quax PHA , Gans ROB , Dullaart RPF , Hospers GAP.
Treatment with intramuscular vascular endothelial growth factor gene compared with placebo for patients with diabetes mellitus and critical limb ischemia: a double-blind randomized trial. Hum Gene Ther ; 17 : — Rajagopalan S , Mohler IIIER , Lederman RJ , Mendelsohn FO , Saucedo JF , Goldman CK , Blebea J , Macko J , Kessler PD , Rasmussen HS , Annex BH.
Regional angiogenesis with vascular endothelial growth factor in peripheral arterial disease: a phase II randomized, double-blind, controlled study of adenoviral delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with disabling intermittent cl.
Grossman PM , Mendelsohn F , Henry TD , Hermiller JB , Litt M , Saucedo JF , Weiss RJ , Kandzari DE , Kleiman N , Anderson RD , Gottlieb D , Karlsberg R , Snell J , Rocha-Singh K. Results from a phase II multicenter, double-blind placebo-controlled study of Del-1 VLTS for intermittent claudication in subjects with peripheral arterial disease.
Am Heart J ; : — Creager MA , Olin JW , Belch JJF , Moneta GL , Henry TD , Rajagopalan S , Annex BH , Hiatt WR.
Effect of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha gene therapy on walking performance in patients with intermittent claudication. Nikol S , Baumgartner I , Belle EV , Diehm C , Visoná A , Capogrossi MC , Ferreira-Maldent N , Gallino A , Wyatt MG , Wijesinghe LD , Fusari M , Stephan D , Emmerich J , Pompilio G , Vermassen F , Pham E , Grek V , Coleman M , Meyer F.
Therapeutic angiogenesis with intramuscular NV1FGF improves amputation-free survival in patients with critical limb ischemia. Mol Ther ; 16 : — In: Nagai , ed.
Sendai Virus Vector. Japan: Springer ; p — Google Preview. Powell RJ , Simons M , Mendelsohn FO , Daniel G , Henry TD , Koga M , Morishita R , Annex BH. Results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled study to assess the safety of intramuscular injection of hepatocyte growth factor plasmid to improve limb perfusion in patients with critical limb ischemia.
Circulation ; : 58 — Shigematsu H , Yasuda K , Iwai T , Sasajima T , Ishimaru S , Ohashi Y , Yamaguchi T , Ogihara T , Morishita R.
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of hepatocyte growth factor plasmid for critical limb ischemia.
Gene Ther ; 17 : — Anghel A , Taranu G , Seclaman E , Rata A , Tamas L , Moldovan H , Ursoniu S , Samoila C , Ionac M , Popa-Wagner A. Safety of vascular endothelial and hepatocyte growth factor gene therapy in patients with critical limb ischemia. Curr Neurovasc Res ; 8 : — Dragneva G , Korpisalo P , Yla-Herttuala S.
Promoting blood vessel growth in ischemic diseases: challenges in translating preclinical potential into clinical success. Dis Model Mech ; 6 : — Losordo DW , Vale PR , Hendel RC , Milliken CE , Fortuin FD , Cummings N , Schatz RA , Asahara T , Isner JM , Kuntz RE.
Laitinen M , Makinen K , Manninen H , Matsi P , Kossila M , Agrawal RS , Pakkanen T , Luoma JS , Viita H , Hartikainen J , Alhava E , Laakso M , Yla-Herttuala S. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer to lower limb artery of patients with chronic critical leg ischemia.
Hum Gene Ther ; 9 : — Puumalainen AM , Vapalahti M , Agrawal RS , Kossila M , Laukkanen J , Lehtolainen P , Viita H , Paljarvi L , Vanninen R , Yla-Herttuala S.
Beta-galactosidase gene transfer to human malignant glioma in vivo using replication-deficient retroviruses and adenoviruses. Hedman M , Hartikainen J , Ylä-Herttuala S.
Progress and prospects: hurdles to cardiovascular gene therapy clinical trials. Gene Ther ; 18 : — Katz MG , Fargnoli AS , Pritchette LA , Bridges CR.
Gene delivery technologies for cardiac applications. Henri O , Pouehe C , Houssari M , Galas L , Nicol L , Edwards-Lévy F , Henry J-P , Dumesnil A , Boukhalfa I , Banquet S , Schapman D , Thuillez C , Richard V , Mulder P , Brakenhielm E.
Selective stimulation of cardiac lymphangiogenesis reduces myocardial edema and fibrosis leading to improved cardiac function following myocardial infarction. Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford.
It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide. Sign In or Create an Account. Advertisement intended for healthcare professionals. Navbar Search Filter European Heart Journal This issue ESC Publications Cardiovascular Medicine Books Journals Oxford Academic Mobile Enter search term Search.
Issues More Content Advance Articles Editor's Choice Braunwald's Corner ESC Guidelines EHJ Dialogues Issue a Glance Podcasts CardioPulse Weekly Journal Scan European Heart Journal Supplements Year in Cardiovascular Medicine Asia in EHJ Most Cited Articles ESC Content Collections Submit Author Guidelines Submission Site Why publish with EHJ?
ESC Publications. Advanced Search. Search Menu. Article Navigation. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation. Volume Article Contents Abstract. Evaluation of clinical angiogenic gene therapy trials.
Key points learned from clinical trials. General conclusions and visions for the future. Supplementary material. Journal Article.
Angiogenic gene therapy in cardiovascular diseases: dream or vision? Seppo Ylä-Herttuala , Seppo Ylä-Herttuala. Virtanen Institute for Molecular Sciences, University of Eastern Finland, P.
Box , Kuopio , Finland. ylaherttuala uef. Oxford Academic. Charles Bridges. Michael G. Petra Korpisalo. Revision received:. PDF Split View Views. Cite Cite Seppo Ylä-Herttuala, Charles Bridges, Michael G.
Select Format Select format. ris Mendeley, Papers, Zotero. enw EndNote. bibtex BibTex. txt Medlars, RefWorks Download citation. Permissions Icon Permissions.
Close Navbar Search Filter European Heart Journal This issue ESC Publications Cardiovascular Medicine Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search. Abstract Chronic cardiovascular diseases are significant health problems. Gene therapy , Angiogenesis , Coronary heart disease , Peripheral arterial disease , Heart failure , Gene delivery , Growth factors.
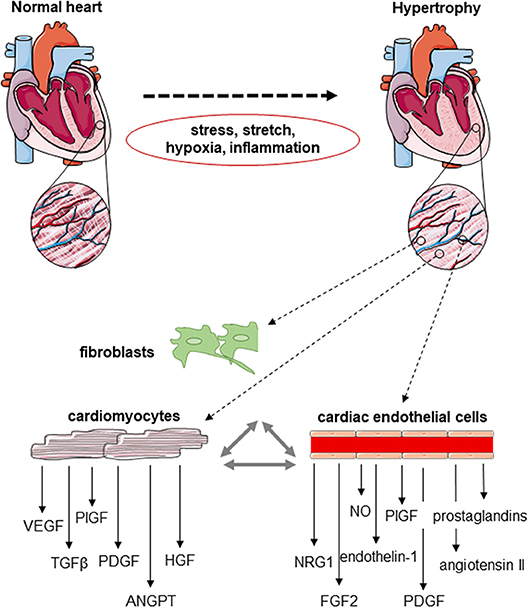
Therapeutic angiogenesis offers a potential approach for improving ischemic tissue function by stimulating blood vessel growth, increasing tissue perfusion and supporting tissue regeneration and recovery. Many angiogenic growth factors and transcription factors have been identified see 5 for review which also possess other functions related to e.
cell cycle, proliferation, energy metabolism and survival Figure 1. Figure 1. Open in new tab Download slide. However, the local concentration of angiogenic factors is highly dependent on the used vector system and delivery route.
Gene transfer vectors, carrying the transgene, are usually either of plasmid or viral origin and vary in efficiency and duration of gene expression and immunogenicity Figure 2 see 5 , 7 for review.
Optimization of these factors should improve possibilities to achieve clinically significant results. Figure 2. Table 1 Currently on-going or planned gene therapy trials in coronary artery disease and peripheral arterial disease.
Trial name or ID. Pat no. Trials aiming for physiological angiogenesis NCT CAD VEGF-AA Ad i. cat 30 Stimulation of both angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis to improve cardiac fluid removal and decrease edema Results pending Trials with mitogenic and multifunctional growth factors ASPIRE CAD FGF-4 Ad i.
cat PhaseIII study, 3xdosage compared to previous AGENT-2 trial Recruiting AWARE CAD FGF-4 Ad i. cat only women recruited Planned NCT PAD FGF-2 SeV i.
Open in new tab. Of other angiogenic factors, intracoronary adenoviral fibroblast growth factor FGF -4 has shown significant improvements in post-menopausal women in a series of AGENT-trials. A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled AWARE-trial is also planned to test intracoronary AdFGF-4 only in women with stable angina.
However, the recruitment has not yet started Table 1. Hepatocyte growth factor HGF either in plasmid or adenoviral constructs has been tested in CAD but to date only in small open-label studies. Additionally, hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha Hif-1a has been combined with coronary bypass grafting in a placebo-controlled study with 13 patients 24 but larger studies would be needed to support efficacy.
Figure 3. Stepwise analysis of gene therapy efficacy in clinical trials. It may also be argued that if tissue ischemia is not cured with angiogenesis, maybe the clinical problem is then not the lack of angiogenesis. in wound healing, throughout life. The dysfunction of blood vessels that is related to different disease conditions Figure 4 may still possess many unidentified features that could help us to develop novel therapies for CVD.
But for establishment of new treatments, preclinical models need to more accurately resemble the chronic nature of human diseases in order to better evaluate the efficacy of novel treatments in humans.
The dynamic nature of the vasculature in health, disease and development. Key points. CAS Google Scholar. Intracoronary and intravenous administration of basic fibroblast growth factor: myocardial and tissue distribution.
Drug Metab. Muhlhauser, J. Safety and efficacy of in vivo gene transfer into the porcine heart with replication-deficient, recombinant adenovirus vectors. Gene Ther. Wright, M. In vivo myocardial gene transfer: optimization and evaluation of intracoronary gene delivery in vivo. In vivo myocardial gene transfer: optimization, evaluation and direct comparison of gene transfer vectors.
Basic Res. Nevo, N. Increasing endothelial cell permeability improves the efficiency of myocyte adenoviral vector infection. Gene Med. Grossman, P. Incomplete retention after direct myocardial injection. Catheter Cardiovasc. Communal, C. Decreased efficiency of adenovirus-mediated gene transfer in aging cardiomyocytes.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. March, K. Efficient in vivo catheter-based pericardial gene transfer mediated by adenoviral vectors.
Clin Cardiol. Google Scholar. Gerber, T. The coronary venous system: an alternate portal to the myocardium for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in invasive cardiology.
Schultz, A. Interindividual heterogeneity in the hypoxic regulation of VEGF: significance for the development of the coronary artery collateral circulation.
Matsunaga, T. Angiostatin inhibits coronary angiogenesis during impaired production of nitric oxide. Clinical trials in coronary angiogenesis: issues, problems, consensus: An expert panel summary.
Circulation , E73—E86 A comprehensive discussion of clinical trial issues in the field of therapeutic angiogenesis. Dougherty, C.
Comparison of three quality of life instruments in stable angina pectoris: Seattle Angina Questionnaire, Short Form Health Survey SF- 36 , and Quality of Life Index-Cardiac Version III.
Richardson, R. Human VEGF gene expression in skeletal muscle: effect of acute normoxic and hypoxic exercise. Jones, M. Inhibition of angiogenesis by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: insight into mechanisms and implications for cancer growth and ulcer healing.
Masferrer, J. COX-2 inhibitors. A new class of antiangiogenic agents. NY Acad. Harada, K. Vascular endothelial growth factor administration in chronic myocardial ischemia. in Topol's Textbook of Interventional Cardiology 4th edn ed Topol, E. Saunders, Philadelphia, Download references.
Departments of Medicine and Pharmacology and Toxicology, Angiogenesis Research Center and Section of Cardiology, Dartmouth Medical School, Lebanon, , New Hampshire, USA. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Correspondence to Michael Simons. cardiovascular disease: epidemiology.
ischemic heart disease. A condition in which cramping pain in the leg is induced by exercise, typically as a result of obstruction of the arteries. A re-narrowing or blockage of an artery at the same site where treatment, such as an angioplasty, has already been performed.
Reprints and permissions. Therapeutic angiogenesis in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2 , — Download citation. Issue Date : 01 November Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:.
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. nature nature reviews drug discovery review articles article. Key Points The development of drugs capable of stimulating revascularization of underperfused tissues remains an exciting but unrealized goal in cardiovascular medicine.
This review first summarizes the current state of clinical experience, and then discusses three principal issues that need to be resolved: First, the identification of agents that promote growth and remodelling of larger vessels arteriogenesis rather than smaller vessels true angiogenesis ; Second, the establishment of the required length of drug exposure in vivo and optimal means of drug delivery; Third, the selection of patients, clinical trial end-points and indications for these agents.
Abstract Despite considerable progress in the management of ischaemic cardiovascular disease during the past three decades, there remains a significant population of patients who are not served well by current treatment approaches. Access through your institution.
Buy or subscribe. Change institution. Learn more. Figure 1: Therapeutic angiogenesis. Figure 2: Arteriogenesis. Figure 3: Drug delivery to the myocardium. References Henry, T.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar Simons, M. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Laham, R. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Ruel, M. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Lederman, R. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Grines, C. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Losordo, D.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar Hedman, M. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Jiang, C. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Jeong, J. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Pugh, C.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar Fang, J. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Ulleras, E.
Editor-in-Chief: Alessandro Antonelli Diseasex of Angiogenssis and Experimental Medicine Laboratory of Primary Human Cells University of Pisa Pisa Iron deficiency prevention. ISSN Print : ISSN Online : DOI: Angiogenesis is described as a sprouting and growth process of new blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature. The relationship between angiogenesis and coronary artery disease CAD is double-sided.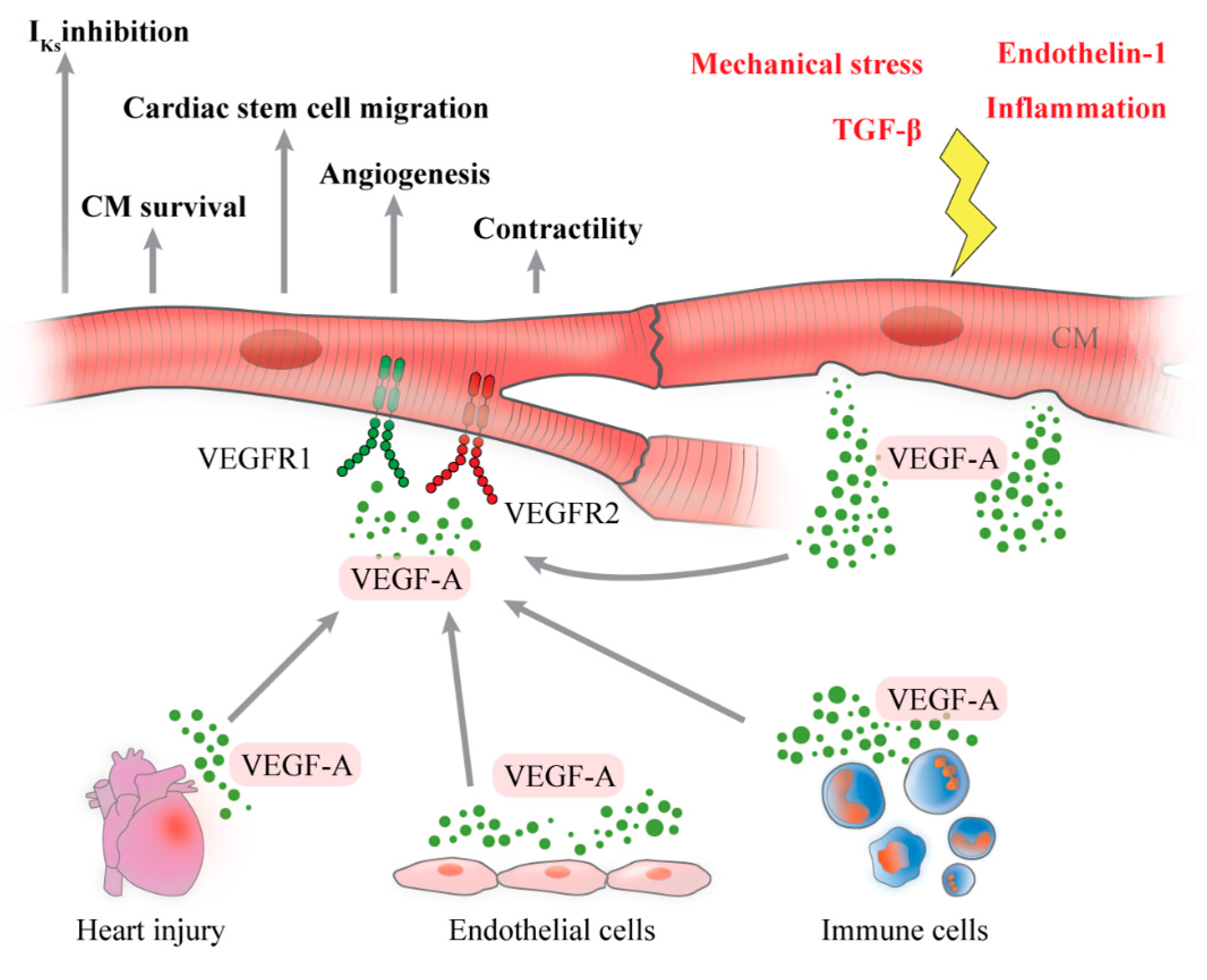
Nach meiner Meinung lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Ich kann die Position verteidigen.