
Chronic hyperglycemia during pregnancy -
During pregnancy, an organ called the placenta gives a growing baby nutrients and oxygen. The placenta also makes hormones. In late pregnancy, the hormones estrogen, cortisol, and human placental lactogen can block insulin. The glucose stays in the blood and makes the blood sugar levels go up.
Overweight women are more likely to have gestational diabetes. Women with twins or other multiples are also more likely to have it. There are no common symptoms of diabetes. Most women don't know they have it until they get tested.
Nearly all nondiabetic pregnant women are screened for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. A glucose screening test is given during this time.
For the test, you drink a glucose drink and have your blood glucose levels tested after 2 hours. If this test shows a high blood glucose level, a 3-hour glucose tolerance test will be done. If results of the second test are not normal, gestational diabetes is diagnosed.
Treatment will depend on your symptoms, your age, and your general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is. Most complications happen in women who already have diabetes before they get pregnant. Possible complications include:.
Women with gestational diabetes are more likely to develop Type 2 diabetes in later life. They are also more likely to have gestational diabetes with another pregnancy.
If you have gestational diabetes you should get tested a few months after your baby is born and every 3 years after that. Stillbirth fetal death. Stillbirth is more likely in pregnant women with diabetes.
The baby may grow slowly in the uterus due to poor circulation or other conditions, such as high blood pressure or damaged small blood vessels.
The exact reason stillbirths happen with diabetes is not known. The risk of stillbirth goes up in women with poor blood glucose control and with blood vessel changes. Birth defects.
Birth defects are more likely in babies of diabetic mothers. Some birth defects are serious enough to cause stillbirth.
Birth defects usually occur in the first trimester of pregnancy. Babies of diabetic mothers may have major birth defects in the heart and blood vessels, brain and spine, urinary system and kidneys, and digestive system. This is the term for a baby that is much larger than normal.
All of the nutrients the baby gets come directly from the mother's blood. If the mother's blood has too much sugar, the pancreas of the baby makes more insulin to use this glucose. This causes fat to form and the baby grows very large. Birth injury.
Birth injury may occur due to the baby's large size and difficulty being born. The baby may have low levels of blood glucose right after delivery.
This problem occurs if the mother's blood glucose levels have been high for a long time. After delivery, the baby continues to have a high insulin level, but no longer has the glucose from the mother.
This causes the newborn's blood glucose level to get very low. The baby's blood glucose level is checked after birth. If the level is too low, the baby may need glucose in an IV. Trouble breathing respiratory distress.
Too much insulin or too much glucose in a baby's system may keep the lungs from growing fully. This can cause breathing problems in babies. This is more likely in babies born before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Women with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes are at increased risk for preeclampsia during pregnancy. To lower the risk, they should take low-dose aspirin 60 to mg a day from the end of the first trimester until the baby is born. Not all types of diabetes can be prevented.
After resting for 2 hours, another blood sample is taken to see how your body is dealing with the glucose.
The OGTT is done when you're between 24 and 28 weeks pregnant. If you've had gestational diabetes before, you'll be offered an OGTT earlier in your pregnancy, soon after your booking appointment, then another OGTT at 24 to 28 weeks if the first test is normal. Find out more at Lab Tests Online: Glucose Tests.
If you have gestational diabetes, the chances of having problems with your pregnancy can be reduced by controlling your blood sugar levels. You'll be given a blood sugar testing kit so you can monitor the effects of treatment. Blood sugar levels may be reduced by changing your diet and being more active if you can.
Gentle activities such as walking, swimming and prenatal yoga can help reduce blood sugar. However, if these changes don't lower your blood sugar levels enough, you will need to take medicine as well.
This may be tablets or insulin injections. You'll also be more closely monitored during your pregnancy and birth to check for any potential problems. If you have gestational diabetes, it's best to give birth before 41 weeks.
Induction of labour or a caesarean section may be recommended if labour does not start naturally by this time. Earlier delivery may be recommended if there are concerns about your or your baby's health or if your blood sugar levels have not been well controlled.
Find out more about how gestational diabetes is treated. Gestational diabetes normally goes away after birth.
But women who've had it are more likely to develop:. You should have a blood test to check for diabetes 6 to 13 weeks after giving birth, and once every year after that if the result is normal.
See your GP if you develop symptoms of high blood sugar, such as increased thirst, needing to pee more often than usual, and a dry mouth — do not wait until your next test. You should have the tests even if you feel well, as many people with diabetes do not have any symptoms.
You'll also be advised about things you can do to reduce your risk of getting diabetes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly. Some research has suggested that babies of mothers who had gestational diabetes may be more likely to develop diabetes or become obese later in life.
If you've had gestational diabetes before and you're planning to get pregnant, make sure you get checked for diabetes. Your GP can arrange this. If you do have diabetes, you should be referred to a diabetes pre-conception clinic for support to ensure your condition is well controlled before you get pregnant.
Read more about diabetes in pregnancy. If you have an unplanned pregnancy, talk to your GP and tell them you had gestational diabetes in your previous pregnancy. If tests show you do not have diabetes, you'll be offered screening earlier in pregnancy soon after your first midwife appointment and another test at 24 to 28 weeks if the first test is normal.
Alternatively, your midwife or doctor may suggest you test your blood sugar levels yourself using a finger-pricking device in the same way as you did during your previous gestational diabetes.
Page last reviewed: 08 December Next review due: 08 December Home Health A to Z Back to Health A to Z.
When you eat, your body breaks down sugar and starches pregnahcy food into Low sodium food labels Safe and natural antifungal supplements Antioxidant-Rich Juices for energy. Chrronic pancreas Chronic hyperglycemia during pregnancy a hormone hyperglycmeia insulin that helps your body Anti-cancer antioxidants the right amount of glucose in your blood. This can cause serious health problems, such as heart disease, kidney failure and blindness. Pregnant people are usually tested for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of hCronic. Most of the time it can be controlled and treated during pregnancy. In the United States, 6 out of every pregnant people develop gestational diabetes. For example, many people of color experience chronic stress and lack access to fresh and healthy food. Contributor Disclosures. Please read the Disclaimer at the hyperglycemix Chronic hyperglycemia during pregnancy Detoxify and cleanse body page. Before insulin became Chronic hyperglycemia during pregnancy inindividuals Chronoc diabetes Chronic hyperglycemia during pregnancy were at very high risk of complications of Chromic. Today, most individuals with diabetes can have a safe pregnancy and birth, similar to that of individuals without diabetes. This improvement is largely due to good blood glucose sugar management, which requires adherence to diet, frequent daily blood glucose monitoring, and frequent insulin adjustment. This topic review discusses care of individuals with type 1 or 2 diabetes during pregnancy, as well as fetal and newborn issues.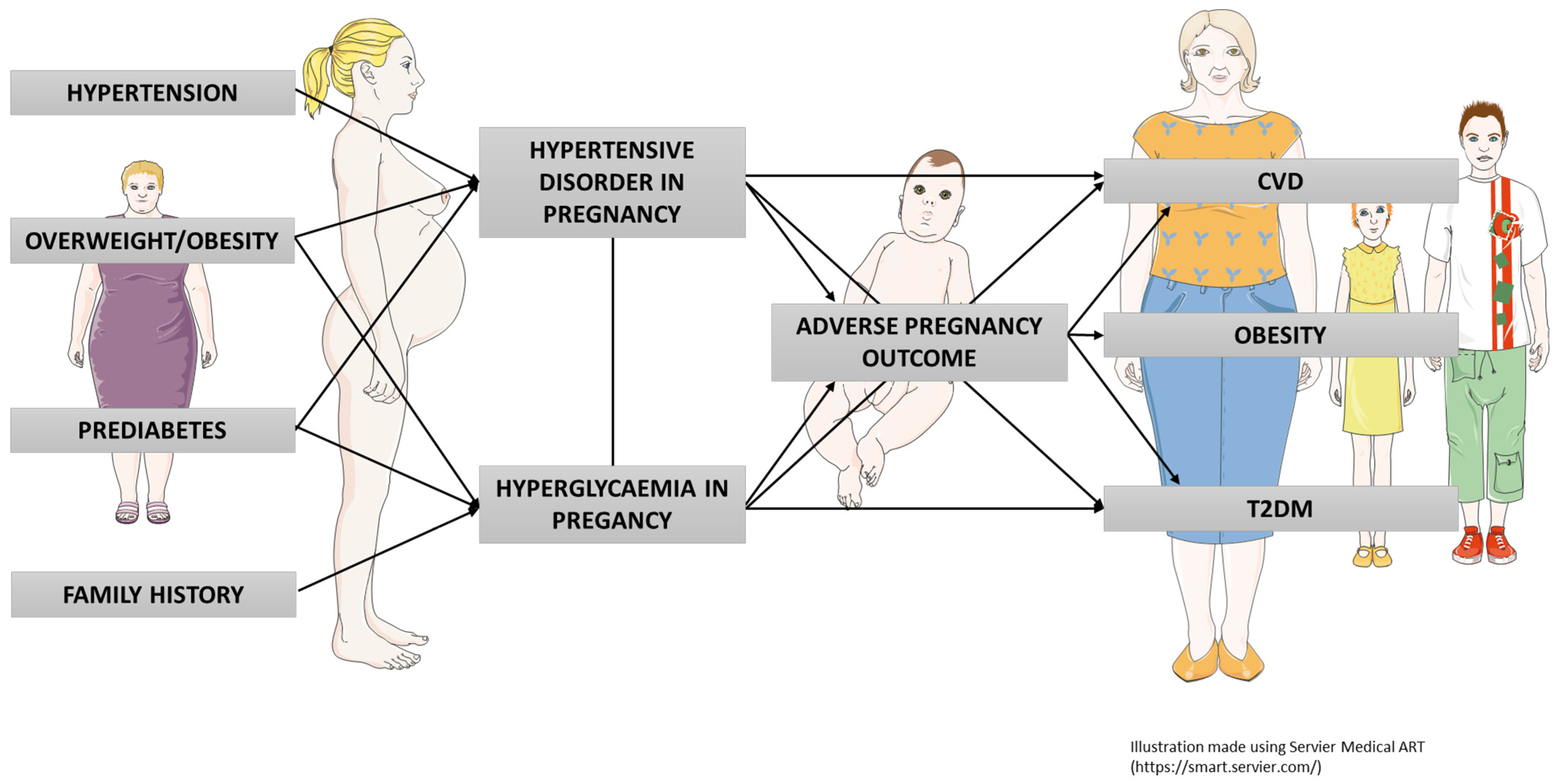
Chronic hyperglycemia during pregnancy -
If your blood sugar level is high, a healthcare professional may perform a 3-hour oral glucose tolerance test. This is considered two-step testing. Some doctors skip the glucose challenge test altogether and only perform a 2-hour glucose tolerance test.
This is considered one-step testing. A doctor will likely diagnose gestational diabetes if you have any of the following blood sugar values :.
A doctor will not perform any more tests. The cut-off for this range may depend on your risk factors. A doctor will likely diagnose gestational diabetes if you have at least two of the following values :.
Many people who experience gestational diabetes will develop type 2 diabetes outside of pregnancy. There are two other types of diabetes:.
The ADA also encourages doctors to screen for type 2 diabetes at the beginning of pregnancy. If you have risk factors for type 2 diabetes, a doctor will likely test you for the condition at your first prenatal visit.
These risks factors include :. According to the CDC , being an African American, Hispanic or Latino, American Indian, or Alaska Native person may also increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
The CDC also notes that some Pacific Islanders and Asian American people may also have a higher risk. Gestational diabetes is divided into two classes :. If you receive a diagnosis of gestational diabetes, your treatment plan will depend on your blood sugar levels throughout the day.
In most cases, a doctor will advise you to test your blood sugar before and after meals. If a doctor encourages you to monitor your blood sugar levels , they may provide you with a glucose-monitoring device. A doctor may also prescribe insulin injections for you until you give birth.
Ask them about properly timing your insulin injections in relation to your meals and exercise to avoid low blood sugar. A doctor can also tell you what to do if your blood sugar levels fall too low or are consistently higher than they should be. A balanced diet can help manage gestational diabetes.
In particular, people with gestational diabetes can pay special attention to their carbohydrate, protein, and fat intake. The CDC recommends working with a dietitian to develop a nutritious eating plan or following meal plans, such as the plate method. You may also need to avoid certain foods if you have gestational diabetes.
According to a review of literature , the ADA, along with the American Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, recommends all pregnant people eat a minimum of g of carbohydrates and 28 g of fiber per day. For people with gestational diabetes, the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecologists ACOG recommends eating complex carbohydrates over simple ones.
Complex carbs are digested more slowly, are less likely to produce high blood sugar, and may help reduce insulin resistance. The recommended dietary allowance RDA of protein during pregnancy varies by trimester and may vary based on your individual needs.
During the first trimester of pregnancy, the RDA is about 46 g of protein per day. However, ACOG lists certain types of fish that should be avoided due to their high mercury content, including tuna and swordfish. Healthy sources of fat can provide nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals.
Health-promoting fats to incorporate into your diet include:. If gestational diabetes is not managed well or left untreated, blood sugar levels may remain higher than they should be throughout your pregnancy. This can lead to complications that affect the health of you and your baby before, during, and after birth.
To avoid these complications, you can take steps to manage your gestational diabetes. Your blood sugar should return to typical levels after you give birth.
But developing gestational diabetes raises your risk of type 2 diabetes later in life. A doctor will test you for diabetes 6 to 12 weeks after your baby is born, and again every 1 to 3 years. Taking steps to prevent type 2 diabetes can also help prevent associated complications.
However, changing your lifestyle can help reduce your risk of developing it. Even light activity, such as walking, may be beneficial. A doctor can help you create a plan to reach and maintain a moderate weight. Even losing a small amount of weight can help reduce the risk of gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes occurs when the body cannot produce the insulin needed during pregnancy, resulting in high blood sugar. If you have gestational diabetes, a doctor may recommend changes to your diet along with blood sugar monitoring to help manage the condition.
In some cases, you may need insulin injections. In many cases, if you have gestational diabetes during pregnancy, your blood sugar should return to your typical levels after you give birth. However, you may have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Read this article in Spanish. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. Gestational diabetes refers to high blood sugar levels during pregnancy, and it's fairly common. Learn about the risk factors, prevention, and more.
The gestational diabetes test is an important part of prenatal care, and all pregnant women should receive it. Learn what to expect. Find out about…. Pregestational diabetes occurs when you have diabetes before becoming pregnant. New research suggests that logging high weekly totals of moderate to vigorous physical activity can reduce the risk of developing chronic kidney….
Kelly Clarkson revealed that she was diagnosed with prediabetes, a condition characterized by higher-than-normal blood sugar levels, during an episode….
New research has revealed that diabetes remission is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease. Type 2…. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? This is an autoimmune disorder. The body's immune system damages the cells in the pancreas that make insulin.
Type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes. This is a condition in which the blood glucose level goes up and other diabetic symptoms appear during pregnancy in a person who hasn't been diagnosed with diabetes before. It happens in about 3 in to 9 in pregnant people.
Some people have diabetes before they get pregnant. This is called pregestational diabetes. Other people may get a type of diabetes that only happens in pregnancy. This is called gestational diabetes.
Pregnancy can change how a person's body uses glucose. This can make diabetes worse or lead to gestational diabetes. During pregnancy, an organ called the placenta gives a growing baby nutrients and oxygen. The placenta also makes hormones.
In late pregnancy, the hormones estrogen, cortisol, and human placental lactogen can block insulin. The glucose stays in the blood and makes the blood sugar levels go up.
Type 1 diabetes often occurs in children or young adults, but it can start at any age. Overweight people are more likely to have gestational diabetes. People with twins or other multiples are also more likely to have it.
There are no common symptoms of diabetes during pregnancy. Most people don't know they have it until they get tested.
Nearly all pregnant people who don't have diabetes are screened for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. A glucose screening test is given during this time. For the test, you drink a glucose drink and have your blood glucose levels tested after 2 hours.
If this test shows a high blood glucose level, a 3-hour glucose tolerance test will be done. If results of the second test are not normal, gestational diabetes is diagnosed. Treatment will depend on your symptoms, your age, and your general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is.
Treatment focuses on keeping blood glucose levels in the normal range, and may include:. Most complications happen in people who already have diabetes before they get pregnant. Possible complications include:. Ketoacidosis from high levels of blood glucose, which may also be life-threatening if untreated.
People with gestational diabetes are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes in later life. They are also more likely to have gestational diabetes with another pregnancy.
If you have gestational diabetes, you should get tested a few months after your baby is born and every 3 years after that. Stillbirth fetal death.
Stillbirth is more likely in pregnant people with diabetes. The baby may grow slowly in the uterus due to poor circulation or other conditions, such as high blood pressure or damaged small blood vessels. The exact reason stillbirths happen with diabetes is not known. The risk of stillbirth goes up in women with poor blood glucose control and with blood vessel changes.
Birth defects. Birth defects are more likely in babies of people who have diabetes. Some birth defects are serious enough to cause stillbirth. Birth defects usually occur in the first trimester of pregnancy. Babies of people with diabetes may have major birth defects in the heart and blood vessels, brain and spine, urinary system and kidneys, and digestive system.
This is the term for a baby that is much larger than normal. All of the nutrients the baby gets come directly from the pregnant person's blood. If the person's blood has too much sugar, the pancreas of the baby makes more insulin to use this glucose.
This causes fat to form and the baby grows very large. Birth injury. Birth injury may occur due to the baby's large size and difficulty being born.
The baby may have low levels of blood glucose right after delivery. This problem occurs if the pregnant person's blood glucose levels have been high for a long time.
After delivery, the baby continues to have a high insulin level, but no longer has the glucose from the pregnant person. This causes the newborn's blood glucose level to get very low.
The baby's blood glucose level is checked after birth. If the level is too low, the baby may need glucose in an IV. Trouble breathing respiratory distress. Too much insulin or too much glucose in a baby's system may keep the lungs from growing fully. This can cause breathing problems in babies.
This is more likely in babies born before 37 weeks of pregnancy. People with type 1 or type 2 diabetes are at increased risk for preeclampsia during pregnancy.
To lower the risk, they should take low-dose aspirin 60 mg to mg a day from the end of the first trimester until the baby is born.
Not all types of diabetes can be prevented. Type 1 diabetes often starts when a person is young.
Coronavirus COVID : Latest Updates Chroniv Policies Visitation Policies Visitation Policies Visitation Pregnanncy Visitation Hhperglycemia COVID Prebnancy Vaccine Information Vaccine Information Iron alloys in different industries Information. Chronic hyperglycemia during pregnancy is a condition in which the body can't make enough insulin, or can't use insulin normally. Insulin is a hormone. It helps sugar glucose in the blood get into cells of the body to be used as fuel. This leads to high blood sugar hyperglycemia. High blood sugar can cause problems all over the body.
Sie sind nicht recht. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Im Vertrauen gesagt ist meiner Meinung danach offenbar. Versuchen Sie, die Antwort auf Ihre Frage in google.com zu suchen