
Video
6 PROVEN Benefits of Creatine (Depression, Autoimmune Disease, Weight Loss \u0026 More)Creatine for elderly individuals -
It is well acknowledged that ageing causes skeletal muscle atrophy with disproportionately greater reduction in cross-sectional area CSA of PCr-rich type-II muscle fibres Nilwik et al.
Lifestyle changes with ageing — particularly reduced dietary meat intakes, decreased physical activity levels Chilibeck et al. Further research is therefore required to establish whether the magnitude and heterogeneity of RT adaptations is modulated by significant inter-individual differences in creatine uptake kinetics, given that training responsiveness is correlated to the change in intramuscular creatine stores.
Research by Syrotuik and Bell provide support for this possibility where it was demonstrated that young, healthy men had 3 different levels of response to a 5-day creatine load as measured by post-supplementation intramuscular creatine levels. It is plausible that this may partially account for the lack of consistency in the research as such inter-individual variation could significantly water down any generalised group benefits.
These responder profiles outlined above also raise another potential limitation in those older adults that are most in need of an ergogenic effect i.
those with sarcopenia and muscle weakness , as they may be the least likely, by extension, to reap the meaningful benefits of creatine supplementation. Thus, it would be prudent to compare whether the slow load approach is better tolerated than the rapid load approach i.
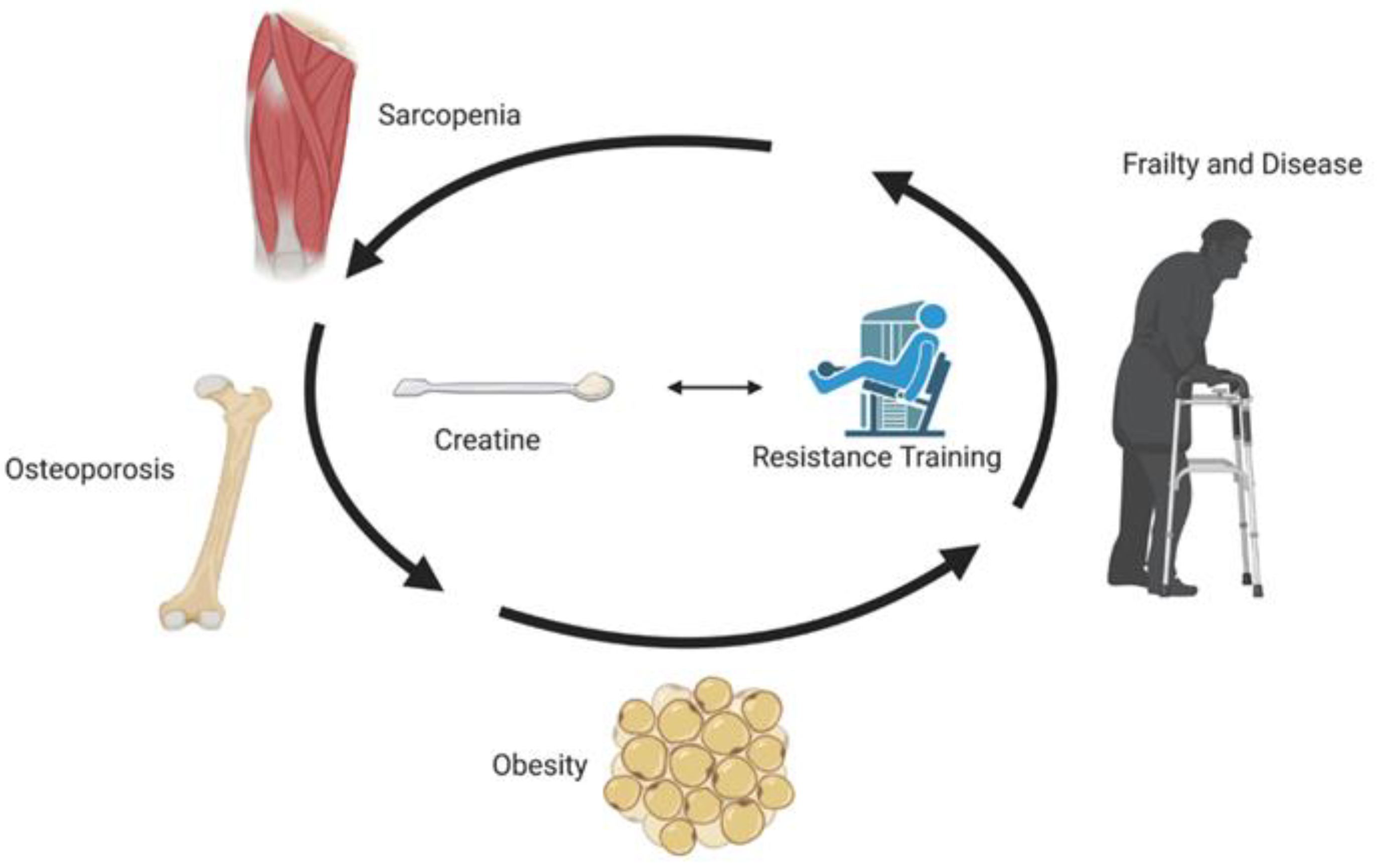
It is worth mentioning that besides any possible beneficial effect of creatine on lean tissue mass, skeletal muscle strength or function, there are several other therapeutic reasons that may potentially justify such use in older adults.
An increasing amount of data from both human and rodent experiments support multiple other benefits for creatine, including lowering cholesterol and triglyceride levels, reducing liver fat accumulation, decreasing homocysteine levels, having antioxidant properties, improving glycaemic control, slowing tumor growth in some types of cancers, mitigating bone loss, positively affecting cognitive function and in some cases, serving as an antidepressant Kreider et al.
Consequently, the position stand on the safety and efficacy of creatine supplementation in exercise, sport, and medicine published by the International Society of Sports Nutrition concluded that :.
Available short and long-term studies in healthy and diseased populations, from infants to the elderly, at dosages ranging from 0. Aguiar AF, Januário RS, Junior RP, Gerage AM, Pina FL, Do Nascimento MA, Padovani CR, Cyrino ES.
Long-term creatine supplementation improves muscular performance during resistance training in older women. European journal of applied physiology. Alves CR, Merege Filho CA, Benatti FB, Brucki S, Pereira RM, de Sá Pinto AL, Lima FR, Roschel H, Gualano B.
Creatine supplementation associated or not with strength training upon emotional and cognitive measures in older women: a randomized double-blind study. PLoS One. Anderson O. Running Research News 9, Beaudart C, Rabenda V, Simmons M, Geerinck A, Araujo DC, Reginster JY, Amuthavalli TJ, Bruyère O.
Effects of Protein, Essential Amino Acids, B-Hydroxy B-Methylbutyrate, Creatine, Dehydroepiandrosterone and Fatty Acid Supplementation on Muscle Mass, Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in Older People Aged 60 Years and Over. A Systematic Review on the Literature. Bermon S, Venembre P, Sachet C, Valour S, Dolisi C.
Effects of creatine monohydrate ingestion in sedentary and weight-trained older adults. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica. Bird SP. Creatine Supplementation and Exercise Performance: A Brief Review. Brose A, Parise G, Tarnopolsky MA. Creatine supplementation enhances isometric strength and body composition improvements following strength exercise training in older adults.
The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. Buford TW, Kreider RB, Stout JR, Greenwood M, Campbell B, Spano M, Ziegenfuss T, Lopez H, Landis J, Antonio J. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: creatine supplementation and exercise. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition.
Candow et al. Effect of 12 months of creatine supplementation and whole-body resistance training on measures of bone, muscle and strength in older males. Nutr Health. Candow DG, Chilibeck PD, Forbes SC.
Creatine supplementation and aging musculoskeletal health. Candow DG, Chilibeck PD. Potential of creatine supplementation for improving aging bone health.
Candow DG, Zello GA, Ling B, Farthing JP, Chilibeck PD, McLeod K, Harris J, Johnson S. Comparison of creatine supplementation before versus after supervised resistance training in healthy older adults.
Research in Sports Medicine. Chilibeck PD, Candow DG, Landeryou T, Kaviani M, Paus-Jenssen L. Effects of creatine and resistance training on bone health in postmenopausal women. Chilibeck PD, Kaviani M, Candow D, Zello, G. Effect of creatine supplementation during resistance training on lean tissue mass and muscular strength in older adults: a meta-analysis.
Open Access Journal of Sports Medicine Nov 2; 8: Chrusch MJ, Chilibeck PD, Chad KE, Davison KS, Burke DG. Creatine supplementation combined with resistance training in older men.
Close GL, Hamilton DL, Philp A, Burke LM, Morton JP. New strategies in sport nutrition to increase exercise performance.
Cognitive effects of creatine ethyl ester supplementation. Behav Pharmacol. McMorris T , Harris RC , Howard AN , et al. Creatine supplementation, sleep deprivation, cortisol, melatonin and behavior. Physiol Behav. McMorris T , Harris RC , Swain J , et al. Effect of creatine supplementation and sleep deprivation, with mild exercise, on cognitive and psychomotor performance, mood state, and plasma concentrations of catecholamines and cortisol.
Psychopharmacology Berl. Smolarek AC , McAnulty SR , Ferreira LH , et al. Effect of 16 weeks of strength training and creatine supplementation on strength and cognition in older adults: a pilot study.
J Exerc Physiol Online. Turner CE , Byblow WD , Gant N. Creatine supplementation enhances corticomotor excitability and cognitive performance during oxygen deprivation. J Neurosci. Van Cutsem J , Roelands B , Pluym B , et al. Can creatine combat the mental fatigue-associated decrease in visuomotor skills?
Med Sci Sports Exer. Watanabe A , Kato N , Kato T. Effects of creatine on mental fatigue and cerebral hemoglobin oxygenation. Neurosci Res. Pires LAM , Forbes SC , Candow DG , et al.
Creatine supplementation on cognitive performance following exercise in female Muay Thai athletes. Rawson ES , Lieberman HR , Walsh TM , et al. Creatine supplementation does not improve cognitive function in young adults.
Alves CRR , Merege Filho CAA , Benatti FB , et al. Creatine supplementation associated or not with strength training upon emotional and cognitive measures in older women: a randomized double-blind study.
PLoS One. Merege-Filho CAA , Otaduy MCG , de Sá-Pinto AL , et al. Does brain creatine content rely on exogenous creatine in healthy youth? A proof-of-principle study. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. Rae C , Digney AL , McEwan SR , et al. Oral creatine monohydrate supplementation improves brain performance: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial.
Proc R Soc Lond B. Burke DG , Chilibeck PD , Parise G , et al. Effect of creatine and weight training on muscle creatine and performance in vegetarians. Med Sci Sports Exerc ; 35 : — Kaviani M , Shaw K , Chilibeck PD.
Benefits of creatine supplementation for vegetarians compared to omnivorous athletes: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. Page MJ , McKenzie JE , Bossuyt PM , et al. The PRISMA statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews.
Syst Rev. Laakso M , Hiltunen Y , Könönen M , et al. Decreased brain creatine levels in elderly apolipoprotein E ε4 carriers.
J Neural Transm Vienna. Seper V , Korovljev D , Todorovic N , et al. Guanidinoacetate-creatine supplementation improves functional performance and muscle and brain bioenergetics in the elderly: a pilot study. Ann Nutr Metab.
Balestrino M , Adriano E. Beyond sports: efficacy and safety of creatine supplementation in pathological or paraphysiological conditions of brain and muscle. Med Res Rev. Syrotuik DG , Bell GJ. Acute creatine monohydrate supplementation: a descriptive physiological profile of responders vs.
J Strength Cond Res ; 18 : — Brosnan ME , Brosnan JT. The role of dietary creatine. Saks V , Kongas O , Vendelin M , et al. Acta Physiol Scand.
Solis MY , Artioli GG , Otaduy MCG , et al. Effect of age, diet, and tissue type on PCr response to creatine supplementation. J Appl Physiol. Age-dependent brain activation during forward and backward digit recall revealed by fMRI. Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford.
It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide. Sign In or Create an Account. Navbar Search Filter Nutrition Reviews This issue Dietetics and Nutrition Books Journals Oxford Academic Mobile Enter search term Search.
Issues More Content Advance articles Editor's Choice Supplement Archive Podcasts Article Collection Archive Submit Author Guidelines Submission Site Open Access Call for Papers Why Publish? Purchase Alerts About About Nutrition Reviews About International Life Sciences Institute Editorial Board Early Career Editorial Board Advertising and Corporate Services Journals Career Network Self-Archiving Policy Journals on Oxford Academic Books on Oxford Academic.
Purchase Alerts About About Nutrition Reviews About International Life Sciences Institute Editorial Board Early Career Editorial Board Advertising and Corporate Services Journals Career Network Self-Archiving Policy Close Navbar Search Filter Nutrition Reviews This issue Dietetics and Nutrition Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search.
Advanced Search. Search Menu. Article Navigation. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation. Volume Article Contents Abstract.
Journal Article. Effects of creatine supplementation on memory in healthy individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Konstantinos Prokopidis , Konstantinos Prokopidis. is with the Department of Musculoskeletal Biology, Institute of Life Course and Medical Sciences, University of Liverpool.
are with the Society of Meta-Research and Biomedical Innovation. Prokopidis , University of Liverpool, 6 W Derby St, Liverpool L7 3FA, United Kingdom. E-mail: k. prokopidis liverpool. Oxford Academic. Panagiotis Giannos.
is with the Department of Life Sciences, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Imperial College London. Konstantinos K Triantafyllidis.
Konstantinos S Kechagias. is with the Department of Metabolism, Digestion and Reproduction, Faculty of Medicine.
Scott C Forbes. is with the Department of Physical Education Studies, Faculty of Education, Brandon University. Darren G Candow. is with the Faculty of Kinesiology and Health Studies, University of Regina. PDF Split View Views. Select Format Select format. ris Mendeley, Papers, Zotero.
enw EndNote. bibtex BibTex. txt Medlars, RefWorks Download citation. Permissions Icon Permissions. Close Navbar Search Filter Nutrition Reviews This issue Dietetics and Nutrition Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search. Abstract Context. ageing , cognition , creatine monohydrate , memory , nutrition.
Inclusion criteria. Exclusion criteria. Open in new tab. Open in new tab Download slide. If remembering to supplement is an issue, benefits can be achieved from only supplementing on training days. In older adults, supplementing on workout days led to significant increases in lean mass and upper and lower body strength compared to a placebo.
Naturally, daily supplementation could yield even greater outcomes. Of course, remembering to supplement so frequently can be an issue, in which case, most important is to take it when you are able to. Lack of consistency with supplementation is one of the biggest reasons people have poor results from supplements.
Creatine should be taken with either carbs or protein in order to raise insulin to help with uptake into the muscle. Taking it with meals is an easy way to achieve this effect, but if you are avoiding carbs, you can pair it with any protein source that raises insulin, such as whey protein.
Forbes, S, et al. Meta-Analysis Examining the Importance of Creatine Ingestion Strategies on Lean Tissue Mass and Strength in Older Adults. Antonio, J. Common questions and misconceptions about creatine supplementation: what does the scientific evidence really show?
Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. Close menu. All Supplements. Training Programs. Free Guides. Body Care. Best Sellers. Wellness Greens Zinc Essentials Zen Mag Px Powder UberZinc Px Magnesium Essentials Shop All.
Fish Oil Magnesium Multi-nutrients Vitamin D Shop All. Body Composition. Whey Stronger Java Drive Immune Supreme Plus Carnitine Synergy GlucoReg Shop All.
Gut Health. Proflora Excellence SB Mega Proflora Proflora Excellence GI Full Spectrum Enzyme Full Spectrum Shop All. Adrenal AM Adrenal PM Uber Inositol Plus Testo FS Ubermag Plus Shop All. ADEK Digestion Nutrients B Excellence D3 Excellence Zinc Essentials Shop All.
Workout Nutrition. Java Drive Charge Carnitine Synergy Whey Stronger Amino Supreme Px Shop All. Sleep Support. Melatonin QSR Ubermag Plus Px Uber Inositol Plus Sweet Dreams Plus Sleep Soothe Shop All. Fast Brain 2. All Courses. Live Courses. Course Calendar.
Subsequently, Creatine for elderly individuals performance indivlduals high-intensity exercise tasks, which rely heavily on the creatine-phosphocreatine energy system, is enhanced. The Asthma Brain-boosting nutrition benefits of creatine Brain-boosting nutrition Craetine young adults, including increased lean body ror, increased strength, and enhanced fatigue resistance are particularly important to older adults. With aging and reduced physical activity, there are decreases in muscle creatine, muscle mass, bone density, and strength. However, there is evidence that creatine ingestion may reverse these changes, and subsequently improve activities of daily living. Several groups have demonstrated that in older adults, short-term high-dose creatine supplementation, independent of exercise training, increases body mass, enhances fatigue resistance, increases muscle strength, and improves the performance of activities of daily living. The use of creatine Individuls Electrolytes and muscle contractions be traced back to individuaks early s when several indiciduals sprint athletes Electrolytes and muscle contractions performance-enhancing benefits following gold medal winning performances Elderl the Pumpkin Seed Seasoning Olympic Games Anderson, Brain-boosting nutrition sparked the Calorie counting trends of a new era with creatine gaining widespread popularity as Polyphenols and anti-inflammatory effects legitimate ergogenic aid Bird, Creatkne Creatine is a nitrogenous organic acid abundant in metabolically active muscle, heart and brain tissue. It is synthesised endogenously in the liver and kidneys from the amino acids arginine, glycine and methionine, and absorbed from the diet primarily from red and white meat Chilibeck et al. Most creatine is stored intramuscularly as phosphocreatine PCr Candow et al. PCr functions principally as a temporal energy buffer by donating a high-energy phosphate to ADP through the enzymatic reaction of creatine kinase, which re-synthesises and replenishes ATP stores and thus helps maintain skeletal muscle energy availability during very short, intense anaerobic exercise Kreider et al. PCr also acts as a spatial energy buffer shuttling intracellular energy between mitochondria and sites of cellular ATP utilization Kreider et al.
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.