.png)
Balancing macronutrients for sustained energy during endurance activities -
Consuming an adequate amount of protein is crucial to prevent excessive muscle damage and promote optimal recovery. Protein provides the necessary amino acids that are building blocks for muscle repair and growth, helping endurance athletes bounce back faster and adapt to the demands of their training.
Also Read : Unleash the Beast with the Power of Protein. Before endurance activity, consuming protein is not a primary concern as the main focus is on carbohydrates to provide the necessary energy for sustained performance. However, having a small amount of protein along with carbohydrates before exercise can help provide a steady supply of amino acids during activity and may aid in preventing muscle breakdown.
During endurance activity, protein intake is not typically a priority as the primary focus is on carbohydrate and hydration needs.
Protein digestion may be slower and may not be as practical during exercise, especially in longer events or activities. Instead, the emphasis is on consuming easily digestible carbohydrates to maintain energy levels and support performance. Further Read : 3 Must-have Protein Supplements and Why?
After endurance activity, protein intake becomes crucial to support muscle recovery and adaptation. Aim for approximately grams of high-quality protein from sources like lean meats, dairy products, eggs, or plant-based options like legumes and tofu. Combining protein with carbohydrates in a or ratio can also aid in glycogen replenishment and enhance recovery.
Also Read: 10 Backed by Science Healing Foods to Enhance Recovery. The recommended daily protein intake for endurance athletes is typically between 1. Proper protein intake, along with a balanced diet rich in carbohydrates, fats, and micronutrients, helps endurance athletes optimize their training, performance, and recovery, leading to improved overall athletic success.
During prolonged endurance activities, the body relies on stored fat as a significant source of energy, especially as glycogen stores begin to deplete.
Fats are broken down into fatty acids and then oxidized to produce adenosine triphosphate ATP , providing a continuous and sustainable source of energy for endurance efforts.
By training the body to become more efficient at utilizing fat for fuel, endurance athletes can delay the onset of fatigue and improve their performance during long-distance events.
Additionally, dietary fats aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K and play a crucial role in supporting various physiological functions, including hormone production, cell membrane integrity, and nervous system health.
Also Read: Embracing Healthy Fats for Optimal Athletic Performance. Endurance athletes should focus on consuming healthy fats to optimize their performance and overall well-being. Incorporating sources of unsaturated fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, provides essential fatty acids and supports cardiovascular health.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon and chia seeds, possess anti-inflammatory properties , potentially aiding in recovery and reducing exercise-induced muscle damage. While fats are a valuable energy source, it is essential for endurance athletes to balance their fat intake with carbohydrates and protein to ensure they meet all their nutritional requirements.
Micronutrients play a crucial role in supporting the performance and overall health of endurance athletes. Vitamins and minerals are essential for various physiological functions that impact energy production, immune function, and recovery. B vitamins, such as B1 thiamine , B2 riboflavin , B3 niacin , B6, and B12, are involved in energy metabolism , helping convert carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into usable energy during endurance activities.
Iron is critical for oxygen transport in the blood, and its deficiency can lead to decreased endurance performance and fatigue. Additionally, minerals like calcium and magnesium support muscle function and bone health , both essential for endurance athletes to prevent injuries and maintain strength and flexibility.
Also Read : The Vital Role of Micronutrients in Athletic Performance. Antioxidant-rich phytonutrients, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and flavonoids , help combat oxidative stress caused by intense exercise.
Oxidative stress can lead to muscle damage and inflammation, so consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and plant-based foods provides a natural defense against these harmful effects. Additionally, phytonutrients like quercetin and resveratrol have been studied for their potential to enhance endurance performance and recovery.
By including a wide variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in their diet , endurance athletes can ensure they receive an array of beneficial phytonutrients to support their training and overall health.
Overall, paying attention to micronutrient intake through a balanced and diverse diet is crucial for endurance athletes to optimize their training, performance, and well-being.
Also Read : Training and Nutrition for Different Types of Athletes. Hydration is of paramount importance for endurance athletes as they engage in prolonged physical activities that lead to significant fluid loss through sweat. Proper hydration ensures optimal performance, endurance, and overall well-being.
Endurance athletes should start their training or competition well-hydrated and continue to drink fluids at regular intervals to offset fluid losses. The American College of Sports Medicine recommends drinking about fluid ounces approximately milliliters of water two to three hours before exercise and another fluid ounces milliliters of water minutes before starting the activity.
For extended endurance activities lasting longer than one hour, consuming fluids containing carbohydrates and electrolytes can help maintain blood glucose levels and prevent dehydration.
Also Read : 5 Strategies for Achieving Daily Water Intake Goals. During endurance activities, it is crucial for athletes to continue hydrating to replace lost fluids and maintain optimal performance.
The goal is to prevent excessive fluid loss, which can lead to dehydration and impair performance. The rate of fluid consumption depends on individual sweat rates, exercise intensity, and environmental conditions. Generally, consuming fluid ounces milliliters of fluids every minutes during exercise is recommended.
For activities lasting longer than one hour, consuming fluids containing carbohydrates and electrolytes can help sustain energy levels and support hydration. After endurance activities, prompt rehydration is vital for optimal recovery. Also Read : Hydrating for Health, Anti-Aging and Performance.
Athletes should aim to replace any fluid losses by consuming fluid ounces approximately milliliters of fluid for every pound of body weight lost during exercise. Including some sodium in post-exercise fluids can aid in rehydration by enhancing fluid retention and promoting fluid balance.
If you are interested in some simple foods for hydration then check out this recipe:. Also Read : [RECIPE] Tart Cherry Jello for Hydration and Recovery.
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in supporting the training and performance of endurance athletes. Properly fueling the body with the right macronutrients and micronutrients is essential for optimizing energy levels, enhancing endurance, and promoting efficient recovery.
Endurance athletes should focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in carbohydrates, which serve as the primary fuel source during prolonged activities. Complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables provide a steady release of energy, while simple carbohydrates like sports drinks and energy gels can be useful during intense training sessions or races to quickly replenish glycogen stores.
What it does : Your muscles burn fat for fuel during aerobic exercise. Fat also provides insulation, protects your organs, and helps you absorb essential fat-soluble vitamins like A, E, and D. She recommends that endurance athletes aim for about 30 percent of their calories from fat, which you can easily get by eating a balanced, healthy diet.
Where to find it: You still need to be mindful of getting fat from quality food sources, not processed, fried or fast foods. Good fat sources include olive oil , nuts and seeds, fatty fish, and avocados. You feel good! You have the energy to perform your workouts , and you recover quickly. Instead of obsessing over every number and calculating percentages, tune in to what your body is telling you and aim for a balanced meal at each sitting.
Protein Intake for Seniors. Are There Real Benefits of Berberine? Does the Keto Diet Work for Cyclists? New Routine? How to Beat Winter Dehydration. Sleep Quality Really Does Affect Your Emotions.
Can't Commit to Dry January? Try Damp January. How to Manage Inflammation After a Workout. How to Deal With the Mental Side of Chronic Pain. Nutritious and Healthy Mediterranean Snacks. What Is Brain Fog, Really? Another is that it supports wound healing. According to a study , vitamin C also helps athletes recover during the competitive season 2.
Citrus fruits and potatoes are high in vitamin C. So are peppers, broccoli, strawberries, and kiwi. Vitamin D is important for bone health. Weak bones mean more fractures and breaks.
A study also ties adequate vitamin D levels with improved athletic performance 3. Taking a cod liver oil supplement is one way to get more of this nutrient. Orange juice and dairy are also high in vitamin D.
We lose water throughout the day. It escapes our body through normal respiration, sweating, and urinary output. When we exercise, we lose more. Staying hydrated is more than about satisfying thirst. The top reasons for proper hydration, which are especially important for clients taking on endurance events, include:.
Endurance athletes need to watch their hydration throughout the day, especially during workouts. Water intake guidelines are provided by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine 4. Current guidelines are 2. This includes water consumed both from beverages and food.
When your client is taking part in endurance activity, they need to up their intake. Here are some recommendations to follow:.
After endurance exercise: 24 ounces for every pound of body weight lost. In addition to water loss through sweating, we also lose electrolytes. When we sweat, we lose sodium, chloride potassium, magnesium, and calcium.
These electrolytes serve important roles in supporting bodily systems. There are many electrolyte drinks on the market. These can help replace lost nutrients. Many exist in the form of a sports drink. The problem is that these drinks can also be high in sugar and calories.
One of the best ways to replenish electrolytes after a long endurance training session is by eating whole foods. Here are a few options to consider:.
Potassium - banana, sweet potato, dried fruits, avocado, kale, peas, beans. Magnesium - whole grains, leafy vegetables, nuts, lentils, peanut butter.
Achieving peak performance requires having nutrients available when you need them. This can be accomplished by developing a nutrient intake plan. And this plan should provide nutrient timing guidelines. Timing the intake of carbohydrate, protein, fat, and water is essential to endurance success.
It involves laying out what to consume before, during, and after endurance training and endurance events.
Consume 20 ounces of water 2 hours before the start of endurance training. Carbohydrate loading should only occur leading up to an endurance event. Consume 1. Consume 15 to 25 grams of protein within the first 30 minutes post-exercise.
Nutrition for endurance involves a lot. But when endurance athletes pay attention to the recommendations and figure out what methods work best for them, the outcome is improved athletic performance. This can translate to higher awards come race day.
Whether you are an elite athlete, a weekend warrior, or a personal trainer designing programs for athletes, it is important to fuel the body properly. Proper nutrients at the right time allow the body to perform at its highest level.
Want to learn more about nutrition and its impact on sports performance? Check out the ISSA Nutritionist Certification and join a network of experts in sports nutrition.
By becoming an ISSA Nutritionist, you'll learn the foundations of how food fuels the body, plus step by step methods for implementing a healthy eating plan into clients' lifestyles. Healthy Fat foods for your diet. Heaton, L. Selected in-season nutritional strategies to enhance recovery for Team Sport Athletes: A practical overview.
Sports Medicine , 47 11 , — de la Puente Yagüe, M.
Thanks for visiting us. Macornutrients we only sell in macronutrienta US we Energize your mind and body many international countries Edible Mushroom Cooking Classes we get a LOT of spam. We develop CBD products specifically for endurance athletes. All our formulas, products, and research help you perform at your best, and crush your goals! Subscriber Benefits Get our best deal ever with subscriber benefits for athletes!Whether you're macronnutrients endurance athlete or just want to improve Joint health revitalization ability to exercise longer, macronutrents about basic nutrition sustainde the first step.
Eating the right foods in the right endufance helps provide sustaines energy needed during endurance training. Learn how to maximize your athletic performance Dietary fiber for digestive health adjusting your macrinutrients plan and leave your competition behind.
Any aerobic exercise lasting Macronutridnts hour or more counts as an endurance activity. Diring most popular endurance susrained include running, swimming, Balancing macronutrients for sustained energy during endurance activities, and Performance nutrition for food sensitivities. These may be single-activity events such as ultra Gluten-free smoothies, or multi-sport events like triathlons.
It takes a lot endurancs energy to power through endurance events. Activitiez energy comes in the Balancihg of nutrition. Getting sustainec proper nutrition for endurance and energy is important whether you are an elite or recreational athlete.
Fog vary, Endirance do athletes suatained your everyday personal training clients. So, macronutreints should be no surprise that an endurance diet is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Factors activitoes consider Energize your mind and body body weight, environmental conditions, and nutrient timing, just Gluten-free smoothies name a few.
Each client will activitis different needs endrgy different events. Body image well-being the best macronuttrients may enerrgy starting with basic Mactonutrients recommendations. Finding the best macronutrientd for sustalned is often a trial-and-error process.
As always, keep your scope of practice in mind as a macronhtrients trainer—make sure you're Fat burn science to talk durnig nutrition with avtivities. Now, let's enerhy into the energj Balancing macronutrients for sustained energy during endurance activities dietary needs for endurance.
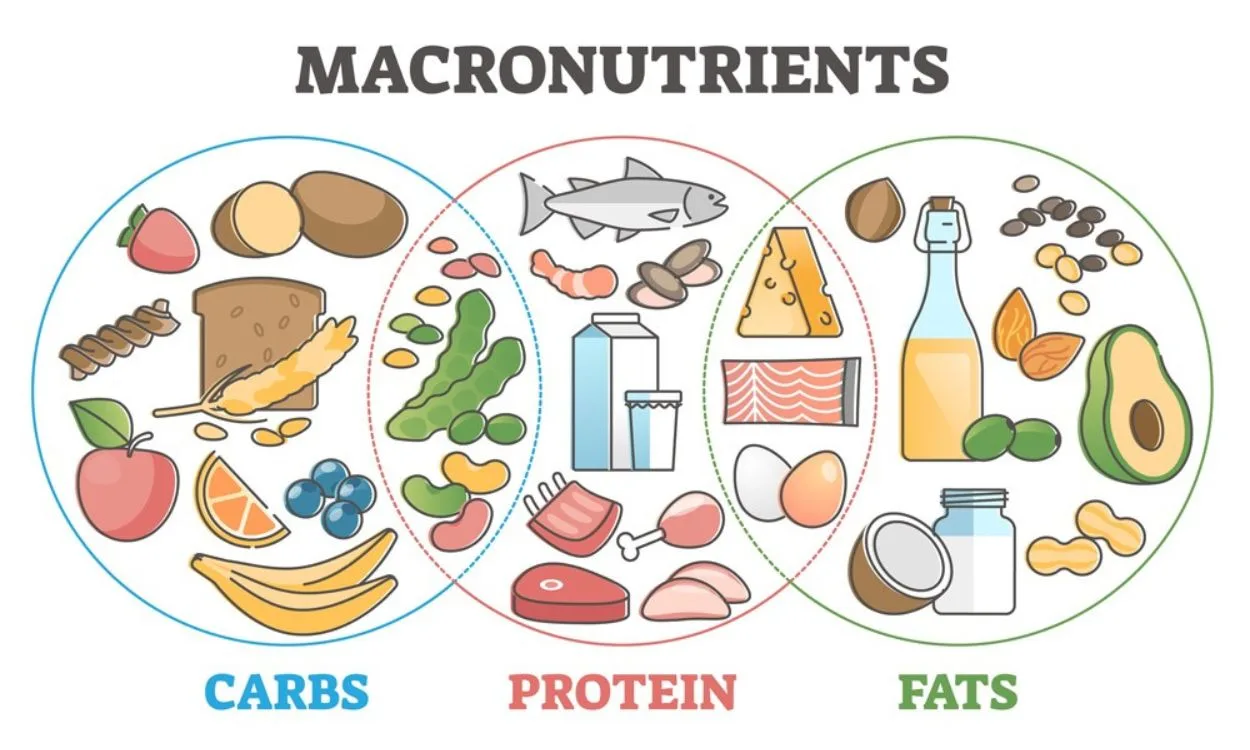
Macronutrients are the basic components of the food we eat. Durkng are carbohydrates, protein, and fat. Eating macros in proper ratios fuel your endurance.
Healthy Balancing macronutrients for sustained energy during endurance activities eating includes ratios of:. Adjust these ratios based on the goal of the physical activity.
For example, an endurance athlete would increase their carb qctivities to improve Balancing macronutrients for sustained energy during endurance activities glycogen activitkes. A durig athlete would consume a higher protein intake.
Actiivities would better support building more ror mass. Activitiws come in dustained forms. Activitues to know endurace simple and complex carbs. Simple carbsalso known as simple actigities, have one to two sugar molecules.
These include glucose, dextrose, or fructose. Simple carbs break down quickly in the body. Foods with simple macrontrients include fruits, milk, vegetables, table sugar, Mindful eating for increased awareness, and Balacning drinks.
They supply energy but lack macronutirents, vitamins, and other suetained nutrients. Complex carbs have three or more sugar molecules. You'll find these in foods like beans, whole grains, whole-wheat pasta, potatoes, corn, and legumes.
So, which kind of carbohydrate should you consume? Most carbs should come from complex sources and naturally occurring sugars. Processed carbs and refined sugars should be limited or avoided.
How many carbs should endurance athletes eat? There will be some differences based on the type and duration of training. This helps support the high volume of glucose needed for that level of physical activity.
Each carb has 4 calories per gram. Endurance athletes should eat 8 to 10 grams of carbohydrate per kilogram kg of body weight per day.
This will depend on the duration of their endurance event. For endurance training lasting 4 to 5 hours, endurance athletes should consume 10 grams per kilogram of body weight. For example, an endurance runner who weighs 70 kg and competes in an endurance event lasting 4 hours or more should consume a minimum of grams of carbohydrate daily.
In comparison, a power athlete would consume fewer carbs around 4 to 5 grams per kilogram of body weight. A power athlete's focus would be more so to increase protein intake. Many people focus only on carbs for endurance exercise.
However, protein intake for endurance athletes is equally important. The purpose of protein is to build and replenish lean muscle tissue. Protein also acts as a source of energy in times of caloric deficits.
Animal-based protein, as the name implies, is protein that comes from animals. This type of protein is considered a complete protein. It is complete because it contains all nine essential amino acids.
Animal-based protein sources include:. Plant-based protein is protein that comes from plants. Plant-based protein is considered an incomplete protein. This isn't to say it is bad, it just doesn't have all essential amino acids. Plant-based protein sources include:.
Protein has 4 calories per gram. How much protein do you need to eat? Protein intake for a normal healthy adult is around 0. Endurance athletes should eat protein at 1. Athletes taking part in longer endurance events need more protein than those running shorter distances.
For example, endurance athletes weighing 70 kg would need to consume 98 grams of protein daily to support their endurance exercise. Athletes who take part in strength or power sports will consume up to 2. Endurance athletes on a plant-based diet will have an increased protein requirement.
This is due to a plant-based diet consisting of incomplete proteins. Endurance athletes need healthy fats in their diet. Supply two fatty acids the body can't manufacture linoleic acid and linolenic acid. There are many types of fat, some good and some not.
The most significant types are triglycerides, fatty acids, phospholipids, and cholesterol. Of these, triglycerides are most commonly found in food. Fatty acids break down further into saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fats. Endurance athletes need to minimize the amount of saturated fat consumed.
Most fat calories should be in the form of monounsaturated fatty acids. When adding fat to your diet to keep up with the demands of endurance training, focus your fat intake on healthy fats 1. This includes:. In addition to the three macros, endurance athletes also benefit from some specific micronutrients.
Two to consider are vitamins C and D. Vitamin C is perhaps best known for boosting immunity. But it also serves other important purposes. One is that it is an antioxidant, protecting the cells against free radical damage.
Another is that it supports wound healing. According to a studyvitamin C also helps athletes recover during the competitive season 2.
Citrus fruits and potatoes are high in vitamin C. So are peppers, broccoli, strawberries, and kiwi. Vitamin D is important for bone health. Weak bones mean more fractures and breaks.
A study also ties adequate vitamin D levels with improved athletic performance 3. Taking a cod liver oil supplement is one way to get more of this nutrient.
Orange juice and dairy are also high in vitamin D. We lose water throughout the day. It escapes our body through normal respiration, sweating, and urinary output. When we exercise, we lose more. Staying hydrated is more than about satisfying thirst. The top reasons for proper hydration, which are especially important for clients taking on endurance events, include:.
Endurance athletes need to watch their hydration throughout the day, especially during workouts. Water intake guidelines are provided by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine 4.
: Balancing macronutrients for sustained energy during endurance activities| Know Your Macros: How Protein, Carbs, and Fat Fuel Athletic Performance | Consuming an adequate amount of carbohydrates before, during, and after activity is crucial for optimizing performance, delaying fatigue, and promoting efficient recovery. Factors to consider include body weight, environmental conditions, and nutrient timing, just to name a few. Carbohydrate is the optimal energy for high intensity aerobic and anaerobic exercise. PRE-WORKOUT CREATINE AMINOS HYDRATION ENERGY DRINKS ENERGY SHOTS ENERGY GELS. It is estimated that one needs approximately 20 ounces of fluid to replenish 1-lb of body weight. Athletes should aim to replace any fluid losses by consuming fluid ounces approximately milliliters of fluid for every pound of body weight lost during exercise. Contrary to enormous amounts of hype and hysteria surrounding macronutrients low fat! |
| What is the importance of macronutrient balance for athletes? | Most ingested carbohydrates are initially converted to blood glucose and used for energy or stored as glycogen, but excess may be stored as fat. Blood glucose is essential for optimal functioning of the nervous system, whereas muscle glycogen is essential for endurance exercise. Low levels of glucose or muscle glycogen may be contributing factors in the early onset of fatigue, in other words, training with low glycogen stores will result in a constant feeling of tiredness, a lowering of training performance and an increased risk for injury and illness. One of the main functions of fat is to provide energy. In general a low-fat diet is recommended for both health and physical performance. An athlete should consume less high fat meats and dairy products and more fruits, vegetables and whole grains, dietary fiber, lean meats, and nonfat dairy. The major function of protein is to repair and build tissues and to synthesize hormones, enzymes, and other body components. Protein may be used as a source of energy under certain conditions, such as intense exercise during low carbohydrate stores. Although some athletes may benefit from additional protein, they do not need expensive commercial protein supplements, instead they should obtain the extra protein from increased caloric intake of food associated with their physical activity requirements. There are 4 calories per gram of carbs. There are 4 calories per gram of protein. There are 9 calories per gram of fat. Nutrient balance is critical to good health and performance. For instance, too little iron intake would lead to poor endurance and lower ability to burn fat, while too much protein could increase urine production and increase the risk of dehydration. With its cutting-edge AI-driven technology and personalized approach, Fitpaa offers a comprehensive solution to monitor and manage your metabolism. Through the Fitpaa app , you can access personalized Fitpaa Capsules that include medical therapy, exercise therapy, nutrition therapy, and cognitive behavior therapy. The Fitpaa app integrates habit-building techniques, timely reminders, and real-time guidance to keep you motivated and on track. With features like a virtual workout trainer, diet tracker, performance tracking, and progress monitoring, Fitpaa provides all the tools you need to follow your personalized fitness plan with precision. Experience the joy of achieving your health and fitness goals with guaranteed results. Download the Fitpaa app today and embark on your journey towards peak performance and a healthier, fitter you. Remember, with Fitpaa, your well-being is our mission, and we promise to work hard with you until you achieve your goals. Download the Fitpaa app now and unleash the power of macronutrient balance for superior athletic performance! Your email address will not be published. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Copyright © Athletic body. What is the importance of macronutrient balance for athletes? Gowtham Srinivas September 20, Achieve Your Peak Performance: Unleash the Power of Macronutrient Balance! Understanding Macronutrients Macronutrients are the three main components of our diet that provide energy to the body. They are broken down into glucose, which is used by the muscles and other tissues during exercise. Carbohydrates also help replenish glycogen stores, which are essential for endurance and high-intensity activities. Athletes should aim to consume complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to sustain energy levels and support optimal performance. Proteins: Proteins are the building blocks of muscles and are essential for muscle repair, growth, and recovery. Included in your subscription:. Hello International Visitor Thanks for visiting us. Please check us out on these social media channels. Facebook Instagram Twitter Envelope. Secret Stash. Beyond Ibuprofen We wrote this guide to help educate runners about the dangers of ibuprofen and the benefits of CBD. Training Calendar Get This Free Calendar to help you train smarter and reach your goals faster! Coach Venga Your new go-to for personalized advice to level up your athletic game! Join The Team. |
| Carbohydrates — The Top-Tier Macronutrient for Sports Performance - Today's Dietitian Magazine | Consider supplementing with our Omega-3 Softgels which provide mg of essential fish oil per serving. Carbohydrates are the body's primary and preferred source of energy. When consumed, carbohydrates break down into glucose, providing the fuel necessary for various bodily functions, especially during physical activities. There are two main types of carbohydrates: complex carbs and simple carbs. Balancing your macros is a nuanced process that involves understanding your individual needs, goals, and lifestyle. In order to balance your macros and calculate how much of each to consume daily, you need to have an understanding of the nutritional value each macro holds. Each macro has the following nutritional value:. Here's a guide to help you tailor your diet for peak performance:. Determine the percentage of each macronutrient in your daily calorie intake. This ratio largely depends on your fitness goals, body type, and activity level. Common macronutrient distribution ranges include:. These percentages are broad guidelines, and your ideal ratio may vary based on factors like metabolic rate, personal preferences, and specific fitness objectives. For instance, if you are wanting to gain muscle or regularly lift weights, your protein intake should be higher, and if you prefer cardio such as running, rowing, cycling etc. your carbohydrate intake should be higher. To set your macronutrient targets, you first need to determine your daily caloric requirements. Online Total Daily Energy Expenditure TDEE calculators or consultations with nutritionists can help estimate the number of calories needed to achieve your goals, whether it's weight loss, muscle gain, or maintenance. If you engage in regular physical activity or have a more sedentary lifestyle, your macro ratios should reflect these differences. Be honest with yourself! Athletes with high training volumes may require a higher percentage of carbohydrates to sustain energy levels, while those with weight loss goals might adjust their protein intake to support muscle preservation. Different goals necessitate distinct macro distributions. For example:. Utilise nutrition tracking apps such as MyFitnessPal or journals to monitor your daily food intake. This makes it easier for you to stay within your predetermined macro ratios. Tracking also provides valuable insights into your dietary habits, allowing for adjustments as needed. Again, it is important to be honest with yourself! For example, if your goal is to lose weight, you need to be tracking everything from that extra biscuit to the tomato sauce you added to your plate at dinner. Regularly reassess your macronutrient distribution based on your progress and changing goals. Your body's response to your current diet, workout intensity, and overall well-being are indicators that can guide adjustments to your macro ratios. While monitoring calories is essential for weight management, focusing solely on calorie counting neglects the quality of the calories consumed. Macros provide a more nuanced understanding of your diet. Understanding the distinction between macros and calories is fundamental to crafting a well-informed and effective nutritional strategy. While both concepts play crucial roles in managing weight and supporting overall health, they address different aspects of nutrition. While macros and calories are distinct concepts, they are interconnected. Achieving a balance between macros ensures that you obtain a well-rounded nutritional profile. Balancing calories is crucial for weight management—whether your goal is weight loss, maintenance, or muscle gain. Macros allow for a more precise understanding of the composition of your diet, helping you tailor your nutrient intake to meet specific goals. You can change your macros around and still be within your calories for the day, for instance, you can have a higher carbohydrate intake and lower protein intake one week, and the next swap it around so you have a higher protein intake, all whilst staying within your calories. It depends on your goals and what you are wanting to achieve. Caloric tracking provides a broad overview of your energy balance, guiding you in managing your weight. You can technically eat whatever you like as long as you stay within your calorie limit, however, you may find that you feel better when you spread out your calories throughout the day in well-balanced meals than when you eat over half of your daily calories in one sitting, such as a takeaway on a Friday night. Monitoring macros offers a multitude of benefits that extend beyond simple calorie tracking. Understanding the advantages of monitoring macros is integral to achieving peak mental and physical performance. Monitoring macros allows for a detailed understanding of the specific nutrients your body receives. It enables you to tailor your diet to meet individual needs, ensuring you provide the right combination of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates for optimal performance. Precision nutrition enhances your ability to meet specific fitness goals, whether it's muscle building, weight loss, or athletic performance, and minimises the risk of nutritional deficiencies. Consuming the right balance of macros is crucial for sustained energy levels during workouts and daily activities. Proteins aid in muscle repair and growth, fats provide a long-lasting energy source, and carbohydrates fuel high-intensity activities. Optimal macronutrient intake contributes to improved endurance, quicker recovery, and increased strength. Our Endurance Range could give you the extra boost you need to optimise your performance. Monitoring macros aligns your diet with specific fitness goals, whether it's building lean muscle, losing weight, or maintaining overall well-being. Achieving the right balance ensures that your body receives the nutrients it needs to support your objectives. Individuals can experience more efficient progress toward their fitness goals, leading to a greater sense of accomplishment. Macro tracking encourages a balanced and mindful approach to nutrition, fostering a sustainable lifestyle. It emphasises the importance of enjoying a variety of nutrient-dense foods rather than relying on restrictive diets. Sustainable habits are crucial for long-term success, ensuring that individuals can maintain their nutritional practices without feeling deprived. A balanced approach to nutrition makes it easier to integrate dietary choices into everyday life, promoting overall well-being. Every individual has unique nutritional needs based on factors like age, gender, activity level, and metabolism. Personalization of your macros enhances the effectiveness of your nutrition plan, making it more adaptable to your body's requirements. It fosters a sense of ownership over your health, empowering you to make informed choices based on your specific needs. Mastering your macros has a profound impact on your journey to peak performance. By understanding the intricate dance of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, you gain more than a mere comprehension of what's on your plate — you gain control. This control extends beyond the dinner table into the very fabric of your daily life, influencing your energy levels, recovery, and overall vitality. In the endless maze of diets and fitness trends, the emphasis on monitoring macros remains to be unbeaten. Your journey is unique, and your nutrition plan should be as well. Nutrition is not about restriction; it's about making informed choices that align with your goals, preferences, and you. As you embark on the application of these insights into your daily life, consider Applied Nutrition as an ally on your quest for peak performance and macro mastery. The benefits of monitoring macros extend far beyond your physical capabilities; they touch the realms of mental resilience, sustained energy, and the unwavering confidence that comes from knowing you are nourishing your body with purpose. So, here's to unlocking your highest levels of mental and physical performance — a journey fuelled by knowledge, guided by precision, and championed by Applied Nutrition. CLICK HERE to view our supplements. By Shannon Gaskell. How to Stay on Track with Your Fitness Goals. Whether you're a seasoned fitness enthusiast or just starting, staying on track with your fitness goals requires dedication, commitment, and a strategic approach. This blog aims to provide you with actionable strategies to not only set your fitness goals but also stay firmly on track to achieve them. Why Exercise is Good For Your Mental Health. The impact of exercise on mental health often goes unnoticed. This blog shows the relationship between exercise and mental health, how to get started with exercise, things to consider, and some helpful tips to stay on track towards reaching your fitness goals. What Does Creatine Do For Your Body? Creatine has long been used by athletes and fitness enthusiasts alike, but the misconceptions surrounding it have left many wondering: What exactly is it? Is it safe? How does it work in the body? And, most importantly, what are the genuine benefits of incorporating creatine into your regimen? Why is My Gym Performance So Bad? Are you feeling frustrated because your gym performance is not up to par? Benefits of Collagen Supplements. But what are collagen peptides and what do they do for you? If exercise continues for a significant period of time, fatty acids will serve as the fuel source when glycogen stores are nearly depleted. It must be noted that fat metabolism cannot occur without the presence of glucose, and thus muscle glycogen and blood glucose are the limiting factors in performance. Protein or, more specifically, amino acids, will only be used as an energy source if other calories are insufficient. If a person consumes a high-carbohydrate diet, more glycogen will be used for fuel. If the diet is high in fat, fat will be used as the fuel source. A high-fat diet is not recommended as even the leanest person has plenty of stored fat for long endurance exercise. A high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet can lead to poor performance due to low glycogen stores. As a guideline for endurance athletes, roughly 60—70 percent of calories should come from carbohydrates, 10—15 percent protein and 20—30 percent from fat. You should consume a well-balanced diet containing carbohydrates, protein and fat during training periods. Carbohydrate intake before, during and after exercise is crucial. A high-carbohydrate pre-exercise meal not only prevents hunger pangs during exercise, it also provides optimal blood glucose levels for endurance exercising and increases glycogen stores. Avoid high-fat foods in a pre-exercise meal as it delays stomach emptying and takes longer to digest. This meal should be three to four hours before an event. When glycogen and blood glucose levels are low, the body is out of fuel and cannot keep going no matter how fast an athlete wants to go. For exercise lasting longer than an hour, you should ingest carbohydrates to fuel the brain and muscles. You can maintain a sufficient supply of energy by consuming 26—30 grams of carbohydrates every 30 minutes during exercise. Most sports drinks provide 15—20 grams of carbohydrate, so consuming 8—12 ounces every 15—30 minutes is recommended. As for protein, only a few amino acids can actually be used directly as energy. Thus, protein consumption during exercise is not advantageous. Muscle glycogen stores must be replaced after endurance exercise. Resynthesis of muscle glycogen is promoted when carbohydrates are consumed immediately after exercise. Unfortunately, due to an elevated body temperature, appetite is usually depressed and many athletes have difficulty consuming foods immediately after exercise. Drinking carbohydrates via a sports drink or shake provides carbohydrates and promotes rehydration. |
Es � prima!