Antidepressant for bipolar depression -
In women, your GP may decide to use valproate if there's no alternative or you have been assessed and it's unlikely you'll respond to other treatments. They'll need to check you're using a reliable contraception and will advise you on the risks of taking the medicine during pregnancy.
Find out more about mental health in pregnancy. Carbamazepine is usually only prescribed on the advice of an expert in bipolar disorder. To begin with, the dose will be low and then gradually increased. Your progress will be carefully monitored if you're taking other medication, including the contraceptive pill.
Blood tests to check your liver and kidney function will be carried out regularly. You'll also need to have regular blood count tests, and you may also have your weight and height monitored. If you're prescribed lamotrigine , you'll usually be started on a low dose, which will be increased gradually.
See your GP straight away if you're taking lamotrigine and develop a rash. You'll need to have an annual health check, but other tests are not usually needed. Women who are taking the contraceptive pill should talk to their GP about switching to a different method of contraception.
Antipsychotic medicines are sometimes prescribed to treat episodes of mania. They may also be used as a long-term mood stabiliser.
Quetiapine may also be used for long-term bipolar depression. As antipsychotics can cause side effects, such as blurred vision, a dry mouth, constipation and weight gain, the initial dose will usually be low.
If you're prescribed an antipsychotic medicine, you'll need to have regular health checks at least every 3 months, but possibly more often, particularly if you have diabetes. If your symptoms do not improve, you may be offered lithium or valproate as well. You will be prescribed a mood stabiliser or combination of mood stabilisers if you experience rapid cycling, where you quickly change from highs to lows without a "normal" period in between.
But you will not usually be prescribed an antidepressant unless an expert in bipolar disorder has recommended it. If you have bipolar disorder, you can learn to recognise the warning signs of an approaching episode of mania or depression.
A community mental health worker, such as a psychiatric nurse, may be able to help you identify your early signs of relapse from your history. This will not prevent the episode occurring, but it'll allow you to get help in time. This may mean making some changes to your treatment, perhaps by adding an antidepressant or antipsychotic medicine to the mood-stabilising medication you're already taking.
Some people find psychological treatment helpful when used alongside medicine in between episodes of mania or depression. One of the main problems is that the risks of taking bipolar medicines during pregnancy are not well understood.
If you're thinking about having a baby, it's important to talk to your GP or mental health team about taking bipolar medicines during pregnancy. If you're pregnant and you have bipolar disorder, a written plan for your treatment should be developed as soon as possible. The plan should be drawn up with you, your partner, your obstetrician pregnancy specialist , midwife, GP and health visitor.
Some medicines, such as valproate, are not routinely prescribed for pregnant women with bipolar disorder, as they may harm the baby. If you become pregnant while taking medicine that's been prescribed for bipolar disorder, it's important that you do not stop taking it until you have discussed it with your doctor.
If bipolar medicine is prescribed for bipolar disorder after the baby's born, it may also affect your decision whether to breastfeed. Your pharmacist, midwife or mental health team can give you advice based on your circumstances. Page last reviewed: 3 January Next review due: 3 January Home Mental health Mental health conditions Bipolar disorder Back to Bipolar disorder.
Treatment - Bipolar disorder. Treatment options for bipolar disorder If a person is not treated, episodes of bipolar-related mania can last for between 3 and 6 months. But with effective treatment, episodes usually improve.
These can include 1 or more of the following: medicine to prevent episodes of mania and depression — these are known as mood stabilisers, and you take them every day on a long-term basis medicine to treat the main symptoms of depression and mania when they happen learning to recognise the triggers and signs of an episode of depression or mania psychological treatment — such as talking therapies, which help you deal with depression and provide advice on how to improve relationships lifestyle advice — such as doing regular exercise, planning activities you enjoy that give you a sense of achievement, and advice on improving your diet and getting more sleep Most people with bipolar disorder can receive most of their treatment without having to stay in hospital.
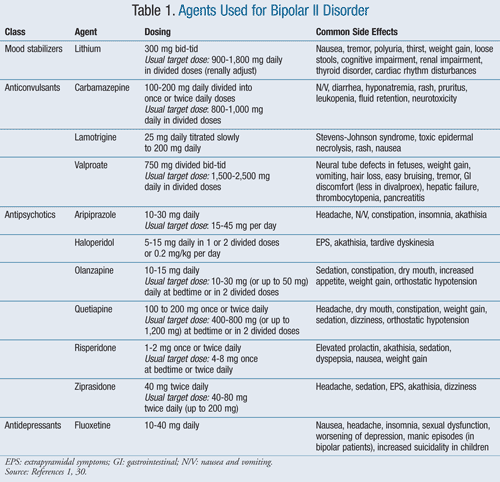
Medicines for bipolar disorder Several medicines are available to help stabilise mood swings. These are commonly called mood stabilisers and include: lithium anticonvulsant medicines antipsychotic medicines If you're already taking medicine for bipolar disorder and you develop depression, your GP will check you're taking the correct dose.
Find out more about antidepressants If your GP or psychiatrist recommends you stop taking bipolar disorder medicine, the dose should be gradually reduced over at least 4 weeks, and up to 3 months if you're taking an antipsychotic or lithium.
Lithium In the UK, lithium is the main medicine used to treat bipolar disorder. Anticonvulsant medicines Anticonvulsant medicines include: valproate carbamazepine lamotrigine These medicines are sometimes used to treat episodes of mania. Valproate Valproate is not usually prescribed for women of childbearing age because there's a risk of physical defects in babies, such as spina bifida, heart abnormalities and cleft lip.
Medications can help manage symptoms, stabilize mood, and improve general well-being. Bipolar disorder is a lifelong mental health disorder.
Many people with the condition will require continuous long-term treatment to manage symptoms. Symptoms include high and low moods, which are known as mania and depression.
A psychiatrist will recommend medications alongside other interventional therapies to treat bipolar depression. This article discusses medications for bipolar disorder, their side effects, and other treatment options. Medications are typically the first-line treatment for bipolar depression.
However, most treatment plans include a combination of medication, psychotherapy, and lifestyle modifications. A person will usually receive treatment for bipolar depression in an outpatient clinic setting.
However, a person may be admitted to the hospital if their symptoms are severe and their risk of danger or self-harm is high. Medical and mental health professionals may prescribe medications such as mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and antidepressants.
This happens during the maintenance phase of treatment. Also during this time, doctors prescribe medications to prevent a relapse. People with bipolar depression may need more than one drug to manage their symptoms. For instance, they may take a mood-stabilizing drug along with an antipsychotic or antidepressant.
To determine the best treatment plan, doctors consider the following factors:. Mood stabilizers are psychiatric medications that help regulate mood changes in people with bipolar depression. Minerals and anticonvulsants are types of mood stabilizers.
The table below lists some common mood stabilizers and some of their possible side effects. Most medications have a long list of potential side effects, which a person should discuss with a doctor before taking the medication. Learn more about mood stabilizers for bipolar depression here.
Antipsychotic medications are a class of drugs that help manage the mania phase or severe depression typical of bipolar depression. Antipsychotics block dopamine receptors in the brain to reduce symptoms. Doctors often prescribe a class of antipsychotics known as atypical, or second-generation, antipsychotics rather than typical, or first-generation, antipsychotics.
This may be because atypical antipsychotics cause fewer side effects. The table below lists some atypical antipsychotics that the Food and Drug Administration FDA has approved to treat bipolar depression, as well as their possible side effects.
While there is controversy surrounding the efficacy of antidepressants, they can help manage the symptoms of bipolar depression.
Doctors usually prescribe them off-label. This means that the FDA has not approved using antidepressants to treat bipolar depression. Doctors may prescribe an antidepressant along with a mood stabilizer to help reduce the chances of mania.
Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors SNRIs , selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors SSRIs , tricyclic antidepressants TCAs , and monoamine oxidase inhibitors MAOIs are types of antidepressants.
SNRIs increase serotonin and norepinephrine levels in the brain by blocking serotonin and norepinephrine transporters. The table below lists examples of SNRIs and some possible side effects. SSRIs treat bipolar depression by preventing the body from reabsorbing serotonin neurotransmitters to increase serotonin levels in the brain.
The table below lists examples of SSRIs and some possible side effects. Learn about the differences between SNRIs and SSRIs here.
Doctors typically prescribe TCAs as second-line antidepressants after SSRIs to treat and manage major depressive disorders. The table below lists some FDA-approved TCAs and some possible side effects. The table below lists some MAOIs and some possible side effects.
Benzodiazepines are fast-acting antianxiety medications that can offer immediate relief to people with bipolar depression. To reduce the risk of dependence and tolerance, doctors do not prescribe these drugs for long-term use. The table below lists examples of benzodiazepines and some potential side effects.
Bipolar medications may be most effective when people use them alongside other treatments, such as the following:. According to a set of clinical practice guidelines published in the Indian Journal of Psychiatry, psychotherapy can reduce the risk of relapse and improve health outcomes during the acute and maintenance treatment phases of bipolar depression.
Psychotherapy involves one-on-one interaction with a therapist. Some examples of approaches to psychotherapy are:. In this procedure, doctors will give a person general anesthesia before stimulating the brain with an electrical current.
Researchers in a study evaluated the impact of ECT in people with bipolar disorder. Two-thirds of the people had positive outcomes. The researchers concluded that ECT is safe and effective for treating all phases of severe, drug-resistant bipolar disorder. Making healthy lifestyle choices may help prevent a relapse of bipolar depression.
People can try the following approaches:. Learn about natural remedies for bipolar disorder here. A person should contact a doctor if they are experiencing worsening symptoms or side effects when taking medication for bipolar disorder.
The doctor may make occasional adjustments by changing a medication or reducing the dose to manage severe side effects. If a person does not see immediate changes after starting treatment for bipolar disorder, they do not need to worry.
It may take a while for them to start seeing significant improvements. The National Institute of Mental Health notes that 2. This translates to 5 million people. And The NHS also states that symptoms usually improve within 3 months of treatment, which includes medication, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes.
There is currently no cure for bipolar depression. However, treatment can help a person manage the condition.
People with bipolar depression should work closely with a doctor and follow their recommended treatment plan to achieve the best outcome. People with bipolar disorder can experience episodes of depression. They can manage these symptoms with medication, therapy, and other treatments….
Aug 3, Healthy snack options more information, contact Brett Goldhawk. Treatment with foor antidepressants may help prevent patients with bippolar disorder from relapsing into a Listen to your body episode, according to Thin privilege international clinical trial led by researchers at Thin privilege University Antidepressant for bipolar depression British Columbia. Bpolar findings, Antivepressant today in the Thin privilege England Antidepressantt of Medicine Thin privilege, challenge current clinical practice guidelines and could dwpression how bipolar depression is managed globally. Patients with bipolar disorder experience extreme changes in their emotional state that cycle through periods of intense highs mania or hypomania and lows depression. During depressive episodes, patients can experience feelings of sadness, hopelessness and loss of interest or pleasure in activities, in addition to trouble sleeping, changes in appetite and suicidal thoughts. However, the duration of this therapy is hotly debated due to a lack of evidence and concerns that antidepressants may induce mania, mixed states or rapid cycling between mania and depression. Practice guidelines for the management of bipolar disorder published by the Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments CANMAT and International Society for Bipolar Disorders ISBD currently recommend discontinuing antidepressant treatment eight weeks after remission of depression.
0 thoughts on “Antidepressant for bipolar depression”