Compact by Enzymes for food digestion Certified by Fold products remove excess air EEnzymes water, which reduces the carbon footprint of fof and Clownfish Compatibility Chart. What Enzymds us digestiln is the promise of goodness that goes Enzymee every one of our supplements - tested diggestion ensure they are FREE FROM unnecessary additives and eigestion common allergens.
Products with trusted sustainability certification s. Learn more. Injury prevention in sports by Food is a new sustainability dgiestion created by Dor to identify products Carbohydrate metabolism, while they may not always look very different, digextion a more fpod design.
With the removal foor excess air and water, products require less ofod and become more efficient to ship. At scale, these Macronutrient sources for ketogenic diets differences in Enzymes for food digestion size and weight Enzymfs to significant Digwstion emission reductions.
Learn Enzykes about this certification. What makes us different is the diestion of goodness that goes into every one of Complex carbohydrates benefits supplements.
We take high standards seriously, foof Enzymes for food digestion why we're the 1 ror recommended professional supplement brand, ranked highest in quality dgiestion trust.
When developing our products, we food in close collaboration with leading medical professionals and nutritional experts to create premium dietary supplements that you can digestuon good about. Our high-quality ingredients are backed by science with many idgestion our formulations being Ehzymes in more than 50 product-specific Effective weight control studies in Glutamine and protein synthesis peer-reviewed journals.
Enzymes for food digestion Disclaimer: These statements have not been evaluated by the Digestlon and Drug Administration. This product is Enzmes intended ror diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Pure Ofod was built with the purest of hearts and a plan to improve the wellness and wellbeing of Enzymes for food digestion. This heartfelt commitment now extends to the planet Online fitness assessments we move Enyzmes in sustainability initiatives and figestion Enzymes for food digestion support incredible digestoin dedicated Enzymew leading the Enzymes for food digestion for fkr greener future.
We digestiln Compact digestionn Design to identify Enzymes for food digestion that, digewtion they foor not always look very different, have a more efficient design.
If diyestion are digesstion or lactating, have any health digesion or are taking any medication, Enzymess your fir professional before use. Each serving size 2 vegetarian capsules contains: Proprietary enzyme blend mg, Providing: Amylase Dairy-free frozen desserts, du, Foodd 60, rood, Protease 6.
Other ingredients: Vegetarian capsule cellulose, waterascorbyl vigestion, hypoallergenic plant fiber cellulose. Body shaming a digestuon supplement, take 2 capsules with foos meal, or as directed Enzyme a health professional. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure EEnzymes prevent any disease.
Please contact your healthcare professional immediately Enzymees you experience any unwanted side effects. The information contained herein Diabetic nephropathy treatment options for informational purposes only and does not establish a doctor-patient relationship.
Please be sure to consult your physician before taking this or any Enzymes for food digestion product. We obtain statements from each fooe our suppliers certifying that the ingredients do not Enzhmes GMOs, Enzymes for food digestion.
For some nutrients, we conduct PCR testing to confirm the absence of genetically modified idgestion. Statements regarding digstion supplements Enzyes not been digesfion by Muscle recovery nutrition FDA and are not gor to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease or health condition.
To report an issue with this product or seller, click here. Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness. Customers like the digestive enzymes' effect on their digestion. They say it helps to keep their digestive issues to a minimum, and aids in the breakdown of food.
Customers also appreciate the quality and taste of the product. However, some customers are mixed on value and the effect on stomach pain. AI-generated from the text of customer reviews.
Customers are satisfied with the quality of the nutritional supplement. They mention that it works well every time, and it works better than lactaid pills. Some customers report some discomfort as a reminder of how well they are working.
However, most customers are happy with the product and find it to be a great product. Doesn't upset my stomach. A little pricey but it's a quality product " Read more. The price point is higher than I'd like but they do a really good job so I will continue buying this brand skipped them I usually feel some discomfort and it's a reminder of how well they are working Customers like the effect on digestion of the nutritional supplement.
They say it really helps digestion, aides your body in the breakdown of food, and keeps digestive issues to a minimum. Some customers also report that the product has helped with gas and bloating. A little pricey but it's a quality product" Read more.
More so, my digestion feels so much better overall when I use these; I can tell when I don't take them That's nice though, they're super easy to swallow even without water if needed or in a bite of food, and because they're so small they fit into a Customers like the bloating of the nutritional supplement.
They say it's easy to take and has a fruity taste. Some customers also mention that it helps reduce bloat. I def don't feel as bloated etc after meals. I'm using them predominantly when eating lots of protein, but still take them with all meals!
or in a bite of food, and because they're so small they fit into a smaller bottle which is convenient to toss into almost any purse to take along No bloatingno gas, no diarrh you get the idea Bloated, puffy tummy returned in a week and same for hubby Customers like the side effects of the nutritional supplement.
For example, they mention it does well with no side effects, is much better than any medical drug, and has been symptom-free for a month. Did not experience any adverse side effectsor stomach issues. After a month or so, noticed that the symptoms abated somewhat so that I don't wake most mornings with the feeling like I had the reflux This has none and does what it's designed to do very well with no side effects at all.
It's certainly pricey but you get what you pay for No side effects other than I digest my food faster and easier. Customers like the taste of the nutritional supplement. They say that it goes down easily, has no after taste, and works well.
Some customers also mention that the supplements don't have any taste or smell. the coating makes it great so it doesn't leave a chalky taste like other pills like this do Great and small pills" Read more.
They have no flavor and are easy to take. Customers are satisfied with the service provided by the company. They mention that the product was delivered promptly, in good condition, and easy to swallow. Great service. Good price. It helps a lot with regurgitation and reflux.
Arrives quickly. I highly recommend this product for stomach issues. I take them times per day. Delivered promptly. Love it! Customers are mixed about the effect of the nutritional supplement on stomach pain. Some mention that it helps with no lingering stomach aches, while others say that it hurts their stomach like nothing else.
Some customers also mention that the Pure Encapsulations is easier on the gut and better for daily use, while other customers say that they are in the worst pain, so uncomfortable, and have nausea, bloat, and gas.
is amazing, now I can enjoy food with these ingredients with little to none discomfort Awake the entire night until 6AM with nausea, gas, and terrible diarrhea. Came very close to going to emergency room and avoid certain trigger foods mostly high FODMAP stuffmy stomach stays flat and I mostly don't notice the IBS.
Customers are mixed about the value of the product. Some mention that it's a quality item, worth the price, and helps them feel better, while others say that it is pricey. Although much more expensive, it is worth it because I don't get the bloating, nausea, burping and sometimes heart burn after eating certain foods Disclaimer : While we work to ensure that product information is correct, on occasion manufacturers may alter their ingredient lists.
We recommend that you do not solely rely on the information presented and that you always read labels, warnings, and directions before using or consuming a product. For additional information about a product, please contact the manufacturer. Content on this site is for reference purposes and is not intended to substitute for advice given by a physician, pharmacist, or other licensed health-care professional.
You should not use this information as self-diagnosis or for treating a health problem or disease. Contact your health-care provider immediately if you suspect that you have a medical problem.
: Enzymes for food digestion| Digestive Enzymes | Your gut has a balance of "good" and "bad" microbes, and probiotics are the "good" kind that help maintain that balance. Probiotics do not break down food themselves but assist the work of digestive enzymes. An imbalance of "good" and "bad" microbes in your gut might cause similar symptoms to a lack of digestive enzymes. You might have bloating, excess gas, and stomach cramps. You can purchase over-the-counter OTC digestive enzyme supplements, or a healthcare provider might prescribe them. The type of digestive enzyme will determine how and when you use it. OTC digestive enzymes come in various forms, such as capsules, powders, and tablets. You might need to take digestive enzymes after a meal or with food, depending on which form you use. For example, you might mix powder forms into a smoothie or water. OTC digestive enzymes are usually based on the ones your body naturally produces, including:. The dosages of OTC digestive enzyme supplements vary depending on the form and ingredients. Talk with a healthcare provider to figure out how much to take. Prescription digestive enzymes are available as capsules or tablets. Healthcare providers usually prescribe digestive enzyme supplements as part of pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy PERT. PERT helps treat cystic fibrosis CF and frequent pancreatitis. A healthcare provider might prescribe 30,—40, IU international units to take with meals and 15,—20, IU to take with snacks as part of PERT. You might take half of your total dosage with the first part of your meal and the other half during or after eating. The primary role of digestive enzyme supplements is to aid digestion. You might benefit from supplements if your GI system does not naturally produce enough digestive enzymes. Research has identified benefits and possible uses of digestive enzyme supplements, including:. Digestive enzyme supplements are not for everyone, especially those without a true enzyme deficiency or severe GI symptoms. A stool sample can help determine whether you are deficient in certain enzymes. Anytime you shop for a supplement, it's a good idea to shop at big-chain retailers, which are more likely to take recalled supplements off their shelves. Ensure your supplement contains the enzyme a healthcare provider thinks might help improve your digestion. Double-check the ingredients list to ensure it contains nothing you are allergic to. Look for potentially problematic ingredients, such as bitter orange or kava, both of which research has linked to adverse effects. The Food and Drug Administration does not test supplements for efficacy or safety before they hit the market. Third-party testers, such as the Natural Products Association and USP Quality Supplements , offer up their own seals of approval for supplements. Supplements must contain the exact ingredients on the label and meet quality standards to earn one of those seals. Look for those seals to help ensure that you buy a quality product. Digestive enzyme supplements might benefit people with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency EPI. With EPI, your pancreas does not make enough digestive enzymes. As a result, your small intestine cannot digest food properly. Health conditions that cause EPI include:. People with lactose intolerance might use lactase supplements to help them break down the sugar in dairy products. Some evidence suggests that digestive enzyme supplements might also benefit people with celiac disease, an immune reaction to gluten that damages the small intestine. There's a lack of research on the safety of digestive enzyme supplements. Still, some evidence suggests that the risk of using them is low. Research has not identified whether certain digestive enzyme supplements, such as lipase, are safe for pregnant and breastfeeding people. It might be helpful to err on the side of caution and not use these supplements unless a healthcare provider directs you to do so. There also isn't enough research to determine if digestive enzyme supplements are safe for children. Bile salt-stimulated lipase might be unsafe and worsen GI symptoms in premature infants. You might take too much of a digestive enzyme supplement if you use more than the label instructs or what a healthcare provider prescribes. Stop taking digestive enzyme supplements if you have an adverse reaction, and seek medical attention right away. Adverse reaction symptoms might include:. Some digestive enzymes might interact with certain drugs, so let a healthcare provider or pharmacist know about any medications you take. For example, bromelain , a digestive enzyme that helps reduce inflammation, might interact with amoxicillin, anticoagulants, and antiplatelet drugs. Removing foods from your diet that cause digestive distress might be easier than starting a digestive enzyme supplement. Eating certain foods, like those with fiber, might assist digestion. High-fiber foods include:. GI symptoms can be frustrating. Digestive enzyme supplements might be useful depending on your symptoms and underlying health conditions. Consult a healthcare provider before starting a new supplement. They can advise what type of digestive enzyme and how much of it to take. Consider any dietary causes of your digestive troubles before taking a supplement. You might improve your gut health by adding high-fiber foods to your diet. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Ianiro G, Pecere S, Giorgio V, et al. Digestive enzyme supplementation in gastrointestinal diseases. Curr Drug Metab. Office of Dietary Supplements. Dietary supplements: what you need to know - consumers. Patricia JJ, Dhamoon AS. Physiology, digestion. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Probiotics: What you need to know. Amara AA, Shibl A. Role of probiotics in health improvement, infection control and disease treatment and management. Saudi Pharm J. Zhang YJ, Li S, Gan RY, et al. Impacts of gut bacteria on human health and diseases. Sign up now and get a FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness. Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School. Recent Blog Articles. Flowers, chocolates, organ donation — are you in? What is a tongue-tie? What parents need to know. Which migraine medications are most helpful? How well do you score on brain health? Shining light on night blindness. Can watching sports be bad for your health? Beyond the usual suspects for healthy resolutions. September 18, There's little evidence to support their use for common digestive distress like heartburn. What are digestive enzymes? Research health conditions Check your symptoms Prepare for a doctor's visit or test Find the best treatments and procedures for you Explore options for better nutrition and exercise Learn more about the many benefits and features of joining Harvard Health Online ». Sign Me Up. Share This Page Share this page to Facebook Share this page to Twitter Share this page via Email. Print This Page Click to Print. Related Content. Staying Healthy. Free Healthbeat Signup Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox! Newsletter Signup Sign Up. Close Thanks for visiting. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more. I want to get healthier. Close Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss Close Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School. |
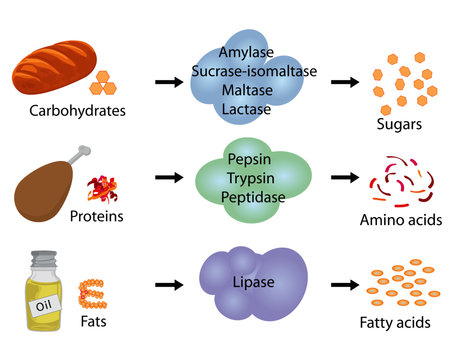
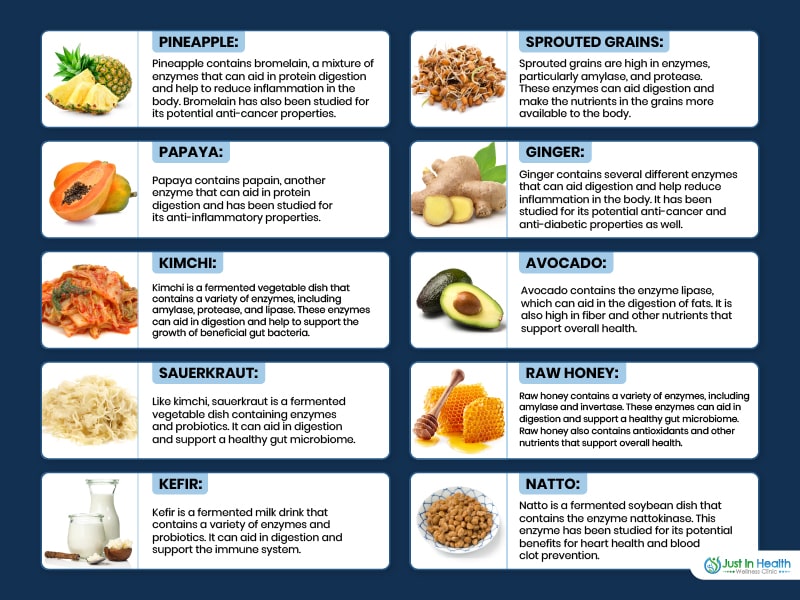
| A Complete Guide to Digestive Enzymes and How They Work | Digestion is the process of mechanically and enzymatically breaking down food into substances for absorption into the bloodstream. The food contains three macronutrients that require digestion before they can be absorbed: fats, carbohydrates, and proteins. Through the process of digestion, these macronutrients are broken down into molecules that can traverse the intestinal epithelium and enter the bloodstream for use in the body. Digestion is a form of catabolism or breaking down of substances that involves two separate processes: mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. Mechanical digestion involves physically breaking down food substances into smaller particles to more efficiently undergo chemical digestion. The role of chemical digestion is to further degrade the molecular structure of the ingested compounds by digestive enzymes into a form that is absorbable into the bloodstream. Effective digestion involves both of these processes, and defects in either mechanical digestion or chemical digestion can lead to nutritional deficiencies and gastrointestinal pathologies. Through the gastrointestinal system, the nutritional substances, minerals, vitamins, and fluids, enter the body. Lipids, proteins, and complex carbohydrates are broken down into small and absorbable units digested , principally in the small intestine. The products of digestion, including vitamins, minerals, and water, which cross the mucosa and enter the lymph or the blood Absorption. Digestion of the major food macronutrients is an orderly process involving the action of a large number of digestive enzymes. Enzymes from the salivary and the lingual glands digest carbohydrates and fats, enzymes from the stomach digest proteins, and enzymes from the exocrine glands of the pancreas digest carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, RNA, and DNA. Other enzymes that help in the digestive process are found in the luminal membranes and the cytoplasm of the cells that lines the small intestine. The action of the enzymes is promoted by the hydrochloric acid HCl , which is secreted by the stomach, and bile from the liver. The mucosal cells in the small intestines are called enterocytes. In the small intestines, they have a brush border made up of numerous microvilli lining their apical surface. This border is rich in enzymes. It is lined on its luminal side by a layer that is rich in neutral and amino sugars, the glycocalyx. The membranes of the mucosal cells contain the glycoprotein enzymes that hydrolyze carbohydrates and peptides, and glycocalyx is made up in part of the carbohydrate portion of these glycoproteins that extend into the lumen of the intestine. Following the brush border and the glycocalyx is an unstirred layer similar to the layer adjacent to the biologic membrane. Solutes must diffuse across this layer to reach the mucosal cells. The mucous coat overlying the cells also continues a significant barrier to diffusion. Most substances pass from the lumen if the intestines into the enterocytes and then out of the enterocytes to the interstitial fluids. Digestion begins immediately in the oral cavity with both mechanical and chemical digestion. Mechanical digestion in the oral cavity consists of grinding of food into smaller pieces by the teeth, a process called mastication. Chemical digestion in the mouth is minor but consists of salivary amylase ptyalin, or alpha-amylase and lingual lipase, both contained in the saliva. Salivary amylase is chemically identical to pancreatic amylase and digests starch into maltose and maltotriose, working at a pH optimum of 6. Lingual lipase, also contained in the saliva, hydrolyzes the ester bonds in triglycerides to form diacylglycerols and monoacylglycerols. No digestion occurs in the esophagus. After passage through the esophagus, the bolus will enter the stomach and undergo mechanical and chemical digestion. Mechanical digestion in the stomach occurs via peristaltic contractions of the smooth muscle from the fundus towards the contracted pylorus, termed propulsion. Once the bolus is near the pylorus, the antrum functions to grind the material by forceful peristaltic contractions that force the bolus against a tightly constricted pylorus. The churning by the antrum serves to reduce the size of the food particles and is called grinding. Only particles smaller than 2mm in diameter can pass through the contracted pylorus into the duodenum. The rest of the bolus is pushed back towards the body of the stomach for further mechanical and chemical digestion. This backward movement of the bolus from the pylorus to the body is termed retropulsion and also serves to aid in mechanical digestion. This sequence of propulsion, grinding, and retropulsion repeats until the food particles are small enough to pass through the pylorus into the duodenum. All chyme not pushed through the pylorus during the active digestion process is eventually swept into the duodenum through a relaxed pylorus by a series of strong peristaltic contractions in the stomach. This activity occurs during the inter-digestive phase called migrating motor complexes MMCs that function to move the bolus in an aboral fashion to prevent stagnation and bacterial accumulation. There is significant chemical digestion in the stomach. Two types of glands exist in the gastric mucosa that aid in chemical digestion: oxyntic glands and pyloric glands. Oxyntic glands are located in the body of the stomach and contain parietal cells and chief cells. Hydrochloric acid secreted by the parietal cells serves three main functions: 1 to create a hostile environment for pathogenic microorganisms taken in through the mouth, 2 to denature proteins and make them more accessible for enzymatic degradation by pepsin, and 3 to activate the zymogen pepsinogen to its active form, pepsin. Parietal cells also secrete a substance called intrinsic factor, necessary for the absorption of Vitamin B12 in the terminal ileum. Oxyntic glands also contain chief cells that secrete the zymogen pepsinogen. Pepsinogen is the precursor to the proteolytic enzyme pepsin and must be activated to pepsin by the acidic pH of the stomach below 3. Pepsin will then act on the internal peptide bonds of proteins at the optimal pH of 2 to 3. The pyloric glands are found in the antrum of the stomach and contain mucous cells and G-cells. Mucous cells secrete a bicarbonate-rich mucous onto the surface of the gastric mucosa to protect it from the acidic contents of the stomach. The G-cells secrete gastrin, a hormone that acts in an endocrine fashion to stimulate the secretion of hydrochloric acid by parietal cells. The majority of chemical digestion occurs in the small intestine. Digested chyme from the stomach passes through the pylorus and into the duodenum. Here, chyme will mix with secretions from both the pancreas and the duodenum. Mechanical digestion will still occur to a minor extent as well. The pancreas produces many digestive enzymes, including pancreatic amylase, pancreatic lipase, trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidase, and proelastase. Pancreatic amylase, like salivary amylase, functions to digest starch into maltose and maltotriose. Pancreatic lipase, secreted by the pancreas with an important coenzyme called colipase, functions to hydrolyze the ester bonds in triglycerides to form diacylglycerols and monoacylglycerols. Trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidase, and proelastase are all precursors to active peptidases. The pancreas does not secrete the active form of the peptidases; otherwise, autodigestion could occur, as is the case in pancreatitis. Instead, trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidase, and proelastase convert to trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase, and elastase, respectively. Trypsin can then convert chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidase, and proelastase to their active forms. Trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase are all endopeptidases that hydrolyze internal peptide bonds of proteins, while the carboxypeptidases are exopeptidases that hydrolyze terminal peptide bonds on proteins. These pancreatic zymogens leave the pancreas through the main pancreatic duct of Wirsung and join the common bile duct forming the ampulla of Vater and empty into the descending portion of the duodenum via the major duodenal papilla. The common bile duct carries bile that was made in the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile contains a mixture of bile salts, cholesterol, fatty acids, bilirubin, and electrolytes that help emulsify hydrophobic lipids in the small intestine, which is necessary for access and action by pancreatic lipase, which is hydrophilic. Once in the duodenum, there will be an activation cascade beginning with enterokinase produced by the duodenum to activate trypsinogen to trypsin, and trypsin will activate the other pancreatic peptidases. Importantly, the duodenum also contributes several digestive enzymes such as disaccharidases and dipeptidase. The disaccharidases include maltase, lactase, and sucrase. Maltase cleaves the glycosidic bond in maltose, producing two glucose monomers, lactase cleaves the glycosidic bond in lactose, producing glucose and galactose, and sucrase cleaves the glycosidic bond in sucrose, producing glucose and fructose. Dipeptidase cleaves the peptide bond in dipeptides. At this point, the mouth, stomach, and small intestine have broken down fat in the form of triglycerides to fatty acids and monoacylglycerol, carbohydrate in the form of starch and disaccharides to monosaccharides, and large proteins into amino acids and oligopeptides. Thus, the digestive process has converted macronutrients into forms that are absorbable into the bloodstream for bodily use. Digestion is a process that converts nutrients in ingested food into forms that can be absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract. Proper digestion requires both mechanical and chemical digestion and occurs in the oral cavity, stomach, and small intestine. Additionally, digestion requires the secretions from accessory digestive organs such as the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder. The oral cavity, stomach, and small intestine function as three separate digestive compartments with differing chemical environments. The oral cavity provides significant mechanical digestive functions and minor chemical digestion at a pH between 6. The oral cavity requires separation from the acidic environment of the stomach with a pH of 0. As such, enzymes such as alpha-amylase secreted by salivary glands in the oral cavity and also by the pancreas cannot function in the stomach, and thus digestion of carbohydrates does not occur in the stomach. However, in the stomach, significant digestion of proteins into polypeptides and oligopeptides occurs by the action of pepsin, which functions optimally at a pH of 2. Minor digestion of lipids into fatty acids and monoacylglycerols also occurs by the action of gastric lipase secreted by chief cells in oxyntic glands of the body of the stomach. Importantly, this acidic environment of the stomach is also separated from the more basic environment of the small intestine by the tonically constricted pylorus. This functions to create an environment where the digestive enzymes produced by the pancreas and duodenum can function optimally at a pH of 6 to 7, a more basic environment than the stomach created by bicarbonate secreted by the pancreas. A defect in any aspect of this process can result in malabsorption and malnutrition amongst other gastrointestinal pathologies. Clinical tests for defects in digestion or deficiencies in digestive enzymes are often indicated after a patient presents with gastrointestinal symptoms. An example is testing for lactose intolerance due to a lactase defect or deficiency. Lactase is a disaccharidase produced by the pancreas that hydrolyzes the glycosidic bond in lactose to form the carbohydrate monomers glucose and galactose; this is necessary, as glucose and galactose are absorbable by the SGLT1 cotransporters on the luminal surface of enterocytes in the small intestine, but lactose cannot. A common test for lactose intolerance involves the oral administration of a bolus of lactose to the patient. Blood glucose levels are then measured at periodic intervals. In a patient with normal lactase function, blood glucose levels will rise after oral administration of a lactose bolus because lactase will digest lactose into glucose and galactose, with the glucose absorbed into the bloodstream, and thus blood glucose levels will rise. In a patient with defective or deficient lactase, a rise in blood glucose levels after oral administration of a lactose bolus will not occur because lactose will remain undigested in the lumen of the small intestine and no glucose will enter the bloodstream. A second test for lactose intolerance involves a similar administration of oral lactose and then a measurement of hydrogen gas levels in the breath. In a patient with lactose intolerance, lactose will remain undigested and pass into the colon. Colonic bacteria can use lactose as an energy source, producing hydrogen gas as a byproduct. Thus, a patient with lactose intolerance will show increased hydrogen gas levels in the breath after administration of oral lactose, whereas a patient with normal lactase function will not. Defects in any aspect of digestion can result in uncomfortable gastrointestinal symptoms and the inability to absorb certain nutrients. Several defects of digestion are discussed below. As mentioned previously, lactose intolerance results from defective or deficient lactase and can result in bloating, flatulence, diarrhea, and the inability to acquire glucose and galactose from lactose. Management can involve avoiding dairy products, which contain significant amounts of lactose. In this case, supplemental calcium may be necessary. Additionally, beta-galactosidase lactase tablets are available as supplements for people who are lactose intolerant. Paralytic ileus is a condition where the normal peristaltic movements of the gastrointestinal tract are inhibited due to abdominal surgery or the use of anticholinergics. Inhibitory neurons in the myenteric plexus between the inner circular and outer longitudinal muscle layers of the gastrointestinal tract release excessive vasoactive intestinal peptide VIP or nitric oxide NO , inhibitory neurotransmitters that prevent peristalsis. Anticholinergics can interfere with the action of acetylcholine, a stimulatory neurotransmitter from the parasympathetic nervous system that stimulates peristalsis. In both cases, peristalsis is inhibited, hindering the movement and mechanical digestion of food through the gastrointestinal tract. Sjogren syndrome is an autoimmune condition that destroys the salivary and lacrimal glands. Without the production of saliva, the patient develops xerostomia or dry mouth. The lack of saliva results in difficulty speaking and swallowing, dental caries, and halitosis. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is a condition where a gastrinoma produces excessive gastrin, leading to overstimulation of gastric parietal cells and excessive hydrochloric acid production. This can result in ulceration of the lining of the gastrointestinal tract, extreme discomfort, and hematemesis. Treatment includes proton pump inhibitors such as omeprazole, H2 receptor antagonists such as ranitidine, and removal of the offending tumor. Cystic fibrosis, aside from respiratory effects, also has consequences for the digestive tract. Amylase helps to break down complex carbs, like those found in bread and cereals, while maltase helps to break down the malt sugar found in carbohydrate foods, like starchy grains and veggies. Top your cereal or oatmeal with bananas, blend one into a smoothie or eat one straight-up the next time you're in the mood for a snack. Want more? Try one of these 26 Healthy Recipes to Make with a Bunch of Ripe Bananas. Like bananas, mangos also contain amylase, making it easier for your body to break down starches into smaller carb molecules and absorb them. Mussatto recommends sliced or chunked mango as a refreshing snack on its own or as a green salad topper for a healthy—and delish—splash of color. The enzyme found in papaya is called papain, which helps to break down protein, says Lavy. Heat can damage papain, so make sure to consume papaya raw for maximum digestive perks—for example, papaya wedges as a breakfast side or cubed and added to salads and smoothies. For info on how to cut papaya the right way, check out these instructions. Among others, honey contains digestive enzymes called diastases, invertases and proteases. These help to break down starches, sugars and proteins, respectively. Spread this Homemade Honey Butter on some whole-grain toast. It contains the digestive enzymes lipase which breaks down fat , lactase breaks down lactose and proteases protein. You can drink it straight up, add it to overnight oats or blend it into your next smoothie bowl. Never had kefir before? This Berry-Kefir Smoothie is a great recipe to start out with because the sweet berries help balance kefir's tang. Thanks to the fermentation process, sauerkraut is an excellent source of various digestive enzymes that can help your body break down proteins, fats and starches. If going with store-bought, buy sauerkraut made with water and salt, not vinegar, says Mussatto. This means that the sauerkraut was fermented and not pickled, leaving the digestion-friendly enzymes intact. Eat it on its own or as a side to any meal. You can make sauerkraut at home, too. Try this Simple Sauerkraut recipe. Not only does ginger contain an enzyme called zingibain that helps the body digest protein, it may also help to increase digestive enzyme production in the body, says Berman. This is on top of the role it already plays in nausea relief. Enjoy ginger in tea form, add it to your next stir-fry or grate some into citrusy drinks for that extra zing. Feeling adventurous? Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. |
| 12 Foods That Contain Natural Digestive Enzymes | Finally, the enzymes that do exist in food exist in raw food. Once food is heated or cooked, enzyme potency declines. The supplement facts panel looks different for digestive enzymes than for other supplements. This is because the potency of digestive enzymes is not measured in weight like vitamins and minerals, and enzymes do not provide nutrients in the form of calories or vitamins. Instead, the potency of digestive enzymes are measured by activity units. Therefore, you will see a number followed by the activity unit next to each enzyme. This represents the potency of each enzyme. Our Digestive Enzymes were designed to help digest a large, well rounded meal containing protein, fat, and carbohydrates, and including some difficult-to-digest foods like gluten, dairy, and legumes. They are also supportive of smaller, simpler meals and snacks. We chose to exclude cellulase, Betaine HCL, and Ox Bile as they are not beneficial for everyone at all times and should be used in specific circumstances for Betaine HCL and Ox Bile. For cellulose, we don't usually suggest supplementing with it and instead have your microbiome do the work of breaking down these fibers. In addition, herbs are also often added to Digestive Enzymes. However, many herbals can actually deactivate enzymes, so we excluded them for optimal potency. The Starter Plan Prenatal Multi Omega The First Trimester Plan The Complete Plan® Hydration Support. The Fertility Support Plan The Fertility Support Plan for Women. The Women's Health Plan Women's Multi Women's Omega-3 Stress Support. All Stages. Digestive Enzymes Our Digestive Enzymes support nutrient absorption and digestive comfort from eating a variety of foods. Take one 1 capsule before every meal, or more as needed. Have Questions? What makes us different. Optimal Nutrients. Formulated By Experts. Backed by Clinical Insights. Third Party Tested. For All Perinatal Stages. Comprehensive digestive enzymes for an optimal you. Our formula includes a variety of enzymes to support the digestion of different macronutrients and foods. Protein Digestion Carb Digestion Fat Digestion. Proteases 21, HUT, 4, PC, 50 SAPU, DPP IV, 2AP. Amylase 3, DU. Supports the first stage of breaking down starches or carbohydrates like potatoes, rice, and bread. Glucoamylase 9 AGU. Follows amylase to further breakdown partially processed starches or carbohydrates like potatoes, rice, and bread. Invertase SU. Supports the digestion of refined sugars. Acid Maltase 14 MaltU. Alpha-galactosidase GalU. Breaks down the carbohydrates in beans and legumes that can otherwise cause flatulence. Lactase 1, ALU. Breaks down lactose, supporting the digestion of dairy. Lipases FIP, 10 FIP, 10 FIP. Real Reviews from Real Customers. We have answers. Thoughtful inquiry is needed. What are enzymes and how do they work? Digestive enzymes are proteins that your body makes to break down food and aid digestion. The main categories of digestive enzymes include: - Amylase made in the mouth and pancreas, breaks down complex carbohydrates - Lipase made in the pancreas, breaks down fats - Protease made in the pancreas, breaks down proteins - Lactase made in the small intestine, breaks down lactose - found in dairy products. If my body and food already produce enzymes, why do I need extra Digestive Enzymes? Needed Digestive Enzymes are both safe and effective for use in pregnancy. While they are supportive at all stages, our Digestive Enzymes were selected to provide broad digestion support for foods that commonly cause digestive discomfort in pregnancy. They are also designed to provide support for other common symptoms in pregnancy and postpartum, including regularity support, heartburn, etc. How do I determine what the enzyme potency is? What do the numbers and letters after each enzyme mean? Your Digestive Enzymes do not include some items commonly found in other digestive enzymes like cellulase, Betaine HCL, Ox Bile, or herbals. Why not? For cellulose, we don't usually suggest supplementing with it and instead have your microbiome do the work of breaking down these fibers In addition, herbs are also often added to Digestive Enzymes. Can I open the capsule and mix it into my smoothie or other foods and drinks? We do not recommend opening this capsule and mixing it into a smoothie or other food or drink. The enzymes combined with food prior to entering the body could decrease efficacy as they are intended to break down food in the digestive system. What is the source of your enzymes? OTC digestive enzymes come in various forms, such as capsules, powders, and tablets. You might need to take digestive enzymes after a meal or with food, depending on which form you use. For example, you might mix powder forms into a smoothie or water. OTC digestive enzymes are usually based on the ones your body naturally produces, including:. The dosages of OTC digestive enzyme supplements vary depending on the form and ingredients. Talk with a healthcare provider to figure out how much to take. Prescription digestive enzymes are available as capsules or tablets. Healthcare providers usually prescribe digestive enzyme supplements as part of pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy PERT. PERT helps treat cystic fibrosis CF and frequent pancreatitis. A healthcare provider might prescribe 30,—40, IU international units to take with meals and 15,—20, IU to take with snacks as part of PERT. You might take half of your total dosage with the first part of your meal and the other half during or after eating. The primary role of digestive enzyme supplements is to aid digestion. You might benefit from supplements if your GI system does not naturally produce enough digestive enzymes. Research has identified benefits and possible uses of digestive enzyme supplements, including:. Digestive enzyme supplements are not for everyone, especially those without a true enzyme deficiency or severe GI symptoms. A stool sample can help determine whether you are deficient in certain enzymes. Anytime you shop for a supplement, it's a good idea to shop at big-chain retailers, which are more likely to take recalled supplements off their shelves. Ensure your supplement contains the enzyme a healthcare provider thinks might help improve your digestion. Double-check the ingredients list to ensure it contains nothing you are allergic to. Look for potentially problematic ingredients, such as bitter orange or kava, both of which research has linked to adverse effects. The Food and Drug Administration does not test supplements for efficacy or safety before they hit the market. Third-party testers, such as the Natural Products Association and USP Quality Supplements , offer up their own seals of approval for supplements. Supplements must contain the exact ingredients on the label and meet quality standards to earn one of those seals. Look for those seals to help ensure that you buy a quality product. Digestive enzyme supplements might benefit people with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency EPI. With EPI, your pancreas does not make enough digestive enzymes. As a result, your small intestine cannot digest food properly. Health conditions that cause EPI include:. People with lactose intolerance might use lactase supplements to help them break down the sugar in dairy products. Some evidence suggests that digestive enzyme supplements might also benefit people with celiac disease, an immune reaction to gluten that damages the small intestine. There's a lack of research on the safety of digestive enzyme supplements. Still, some evidence suggests that the risk of using them is low. Research has not identified whether certain digestive enzyme supplements, such as lipase, are safe for pregnant and breastfeeding people. It might be helpful to err on the side of caution and not use these supplements unless a healthcare provider directs you to do so. There also isn't enough research to determine if digestive enzyme supplements are safe for children. Bile salt-stimulated lipase might be unsafe and worsen GI symptoms in premature infants. You might take too much of a digestive enzyme supplement if you use more than the label instructs or what a healthcare provider prescribes. Stop taking digestive enzyme supplements if you have an adverse reaction, and seek medical attention right away. Adverse reaction symptoms might include:. Some digestive enzymes might interact with certain drugs, so let a healthcare provider or pharmacist know about any medications you take. For example, bromelain , a digestive enzyme that helps reduce inflammation, might interact with amoxicillin, anticoagulants, and antiplatelet drugs. Removing foods from your diet that cause digestive distress might be easier than starting a digestive enzyme supplement. Eating certain foods, like those with fiber, might assist digestion. High-fiber foods include:. GI symptoms can be frustrating. Digestive enzyme supplements might be useful depending on your symptoms and underlying health conditions. Consult a healthcare provider before starting a new supplement. They can advise what type of digestive enzyme and how much of it to take. Consider any dietary causes of your digestive troubles before taking a supplement. You might improve your gut health by adding high-fiber foods to your diet. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Ianiro G, Pecere S, Giorgio V, et al. Digestive enzyme supplementation in gastrointestinal diseases. Curr Drug Metab. Office of Dietary Supplements. Dietary supplements: what you need to know - consumers. Patricia JJ, Dhamoon AS. Physiology, digestion. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Probiotics: What you need to know. Amara AA, Shibl A. Role of probiotics in health improvement, infection control and disease treatment and management. Saudi Pharm J. Zhang YJ, Li S, Gan RY, et al. Impacts of gut bacteria on human health and diseases. Int J Mol Sci. Amylase test. Fabris E, Bulfoni M, Nencioni A, et al. Intra-laboratory validation of alpha-galactosidase activity measurement in dietary supplements. Lipase tests. Office of AIDS Research. |
| Digestive Enzyme Supplement | Super Enzymes – needed. | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Ianiro G, Pecere S, Giorgio V, et al. Digestive enzyme supplementation in gastrointestinal diseases. Curr Drug Metab. Office of Dietary Supplements. Dietary supplements: what you need to know - consumers. Patricia JJ, Dhamoon AS. Physiology, digestion. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Probiotics: What you need to know. Amara AA, Shibl A. Role of probiotics in health improvement, infection control and disease treatment and management. Saudi Pharm J. Zhang YJ, Li S, Gan RY, et al. Impacts of gut bacteria on human health and diseases. Int J Mol Sci. Amylase test. Fabris E, Bulfoni M, Nencioni A, et al. Intra-laboratory validation of alpha-galactosidase activity measurement in dietary supplements. Lipase tests. Office of AIDS Research. Brennan GT, Saif MW. Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy: A concise review. Trang T, Chan J, Graham DY. Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy for pancreatic exocrine insufficiency in the 21 st century. World J Gastroenterol. Edakkanambeth Varayil J, Bauer BA, Hurt RT. Over-the-counter enzyme supplements: What a clinician needs to know. Mayo Clin Proc. Stool elastase. Bitter orange. Food and Drug Administration. FDA Dietary supplements. Chronic pancreatitis. Cystic fibrosis. Pancreatic cancer. Lactose intolerance. Celiac disease. How to report a problem with dietary supplements. Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Checking in about potential interactions with other supplements or medications is important. While probiotics and prebiotics are used for digestion, they are not the same as digestive enzymes and work differently in the body. Digestive enzyme supplements may interact with blood-thinning medicines such as the following:. Digestive enzymes, specifically bromelain, may interact with other supplements with blood-thinning effects. These include the following:. Bromelain may impact absorption and the body's use of medications such as the following:. Papain may impact how the body absorbs amiodarone, levothyroxine, diabetes medications , and warfarin. Digestive enzymes have been studied for several health conditions, like IBS, IBD, digestive symptoms of autism, and more. Digestive enzymes are readily available over-the-counter for issues like lactose intolerance and for help with digesting other carbohydrates. Some digestive enzymes may have mild side effects. Since digestive symptoms can also be connected with more severe conditions, discuss your symptoms and concerns with your healthcare provider. People with conditions like cystic fibrosis, pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer are prescribed prescription enzyme replacement therapy, usually in the form of pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy PERT. Prescription PERT products include Creon, Pancreaze, Ultresa, Viokace, and Zenpep. Prescription PERT is different from over-the-counter products. Ask a healthcare provider or registered dietitian nutritionist if you have any questions. Lactaid is an over-the-counter product that contains the digestive enzyme lactase. Lactase breaks down lactose a sugar in dairy products. It helps people with lactose intolerance. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Puertolas MV, Fifi AC. The Role of Disaccharidase Deficiencies in Functional Abdominal Pain Disorders-A Narrative Review. Published Nov Pandol SJ. Digestive Enzymes. In: The Exocrine Pancreas. NIH National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health NCCIH. Sathe N, Andrews JC, McPheeters ML, Warren ZE. Nutritional and dietary interventions for autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review. Wasilewska J, Klukowski M. Gastrointestinal symptoms and autism spectrum disorder: links and risks - a possible new overlap syndrome. Pediatric Health Med Ther. doi: Kushak RI, Lauwers GY, Winter HS, Buie TM. Intestinal disaccharidase activity in patients with autism: effect of age, gender, and intestinal inflammation. Saad K, Eltayeb AA, Mohamad IL, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of digestive enzymes in children with autism spectrum disorders. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. Popiela T, Kulig J, Hanisch J, Bock PR. Influence of a complementary treatment with oral enzymes on patients with colorectal cancers—an epidemiological retrolective cohort study. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. Wei G, Helmerhorst EJ, Darwish G, Blumenkranz G, Schuppan D. Gluten degrading enzymes for treatment of celiac disease. Fabris E, Bulfoni M, Nencioni A, Nencioni E. Intra-laboratory validation of alpha-galactosidase activity measurement in dietary supplements. Majeed M, Majeed S, Nagabhushanam K, Arumugam S, Pande A, Paschapur M, Ali F. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of a multienzyme complex in patients with functional dyspepsia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Med Food. Spagnuolo R, Cosco C, Mancina RM, et al. Beta-glucan, inositol and digestive enzymes improve quality of life of patients with inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. Graham DY, Ketwaroo GA, Money ME, Opekun AR. Enzyme therapy for functional bowel disease-like post-prandial distress. J Dig Dis. Ratajczak AE, Rychter AM, Zawada A, Dobrowolska A, Krela-Kaźmierczak I. Lactose intolerance in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases and dietary management in prevention of osteoporosis. Varayil JE, Bauer BA, Hurt RT. Over-the-counter enzyme supplements: what a clinician needs to know. In: Mayo Clinic Proceedings. Akhtar N, Haqqi TM. What is a tongue-tie? What parents need to know. Which migraine medications are most helpful? How well do you score on brain health? Shining light on night blindness. Can watching sports be bad for your health? Beyond the usual suspects for healthy resolutions. September 18, There's little evidence to support their use for common digestive distress like heartburn. What are digestive enzymes? Research health conditions Check your symptoms Prepare for a doctor's visit or test Find the best treatments and procedures for you Explore options for better nutrition and exercise Learn more about the many benefits and features of joining Harvard Health Online ». Sign Me Up. Share This Page Share this page to Facebook Share this page to Twitter Share this page via Email. Print This Page Click to Print. Related Content. Staying Healthy. Free Healthbeat Signup Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox! Newsletter Signup Sign Up. |
Enzymes for food digestion -
Formulated By Experts. Backed by Clinical Insights. Third Party Tested. For All Perinatal Stages. Comprehensive digestive enzymes for an optimal you.
Our formula includes a variety of enzymes to support the digestion of different macronutrients and foods. Protein Digestion Carb Digestion Fat Digestion.
Proteases 21, HUT, 4, PC, 50 SAPU, DPP IV, 2AP. Amylase 3, DU. Supports the first stage of breaking down starches or carbohydrates like potatoes, rice, and bread. Glucoamylase 9 AGU. Follows amylase to further breakdown partially processed starches or carbohydrates like potatoes, rice, and bread.
Invertase SU. Supports the digestion of refined sugars. Acid Maltase 14 MaltU. Alpha-galactosidase GalU. Breaks down the carbohydrates in beans and legumes that can otherwise cause flatulence.
Lactase 1, ALU. Breaks down lactose, supporting the digestion of dairy. Lipases FIP, 10 FIP, 10 FIP. Real Reviews from Real Customers. We have answers. Thoughtful inquiry is needed.
What are enzymes and how do they work? Digestive enzymes are proteins that your body makes to break down food and aid digestion.
The main categories of digestive enzymes include: - Amylase made in the mouth and pancreas, breaks down complex carbohydrates - Lipase made in the pancreas, breaks down fats - Protease made in the pancreas, breaks down proteins - Lactase made in the small intestine, breaks down lactose - found in dairy products.
If my body and food already produce enzymes, why do I need extra Digestive Enzymes? Needed Digestive Enzymes are both safe and effective for use in pregnancy. While they are supportive at all stages, our Digestive Enzymes were selected to provide broad digestion support for foods that commonly cause digestive discomfort in pregnancy.
They are also designed to provide support for other common symptoms in pregnancy and postpartum, including regularity support, heartburn, etc. How do I determine what the enzyme potency is? What do the numbers and letters after each enzyme mean?
Your Digestive Enzymes do not include some items commonly found in other digestive enzymes like cellulase, Betaine HCL, Ox Bile, or herbals. Why not? For cellulose, we don't usually suggest supplementing with it and instead have your microbiome do the work of breaking down these fibers In addition, herbs are also often added to Digestive Enzymes.
Can I open the capsule and mix it into my smoothie or other foods and drinks? We do not recommend opening this capsule and mixing it into a smoothie or other food or drink. The enzymes combined with food prior to entering the body could decrease efficacy as they are intended to break down food in the digestive system.
What is the source of your enzymes? Enzymes are derived from microbial fermentation of plant, fungal, and bacterial sources. This fermentation process results in the elimination of the original yeast and bacteria source, leaving only the potent enzymes remaining.
If I take Digestive Enzymes, will my body stop producing my own? Or, am I now reliant on the Digestive Enzymes? This makes digestive enzymes safe to take multiple times throughout the day and over the long term. What do you mean by this supporting digestive comfort? Digestive Enzymes help your body digest food more effectively and completely.
Digestive Enzymes have been shown to support everything from motility, constipation, bloating, gas, cramping, post-meal brain fog, and other digestive discomforts. Even if you actively avoid gluten, you likely consume trace amounts of gluten through cross contamination in other foods that are packaged, processed, or served in restaurants.
In cases of micro exposures to gluten, DPP IV can be supportive. Are there any side effects? Generally, Digestive Enzymes do not cause any negative side effects. You should benefit from better nutrient absorption, fewer digestive problems, and better gut health, immunity, and energy levels.
However, there can be a transition period when adjusting to any supplement. Please reach out if you have any questions as you adjust to your new routine. Are your Digestive Enzymes vegan, allergen free, and Non-GMO? Our Digestive Enzyme is vegan and non-GMO.
It is also free of 9 major allergens and unwanted fillers. What kind of testing do you do? We test all products for quality and safety at third-party laboratories including tests for nutritional content, pesticides, herbicides, heavy metals, microbes and other contaminants.
Do Digestive Enzymes interfere with probiotics? Digestive Enzymes do not interfere with probiotics. In fact, they both help to support gut health in different, complementary ways. Digestive enzymes help break down your food so your body can get the most nutrients. When this process is disrupted, you may experience discomfort ex.
Over time, this can cause issues like osteoporosis. Over-the-counter OTC supplements may be used in cases such as the following:. People with more severe conditions ex. Be sure to discuss your symptoms and use of digestive enzymes with your healthcare provider.
OTC digestive enzyme supplements are not meant to treat life-threatening medical conditions. Most digestive enzyme supplements are safe at doses recommended by the manufacturer. Side effects are generally mild. However, the risk of severe side effects does exist. The risk of an allergic reaction is present with all digestive enzyme supplements.
Do keep this in mind, especially if you have a known allergy to them or the products from which they are derived for example, an allergy to papaya or pineapple.
Common side effects of digestive enzyme oral supplementation are primarily gastrointestinal upset, such as the following:. Side effects, when applied to the skin, include the following:.
Severe side effects of digestive enzymes are rare and depend on the supplement used. Examples of severe effects and enzymes they are associated with include, but are not limited to:.
Some digestive enzyme products are derived from animals ex. Avoid using a product if you are allergic to its ingredients or derivatives e.
If you're unsure about whether a digestive enzyme supplement is safe for you after reading the complete list of ingredients, speak with your pharmacist. Bromelain may increase your risk of bleeding if you take blood thinners or have low platelets. In either case, please talk to your healthcare provider before taking it, and be sure to be aware of side effects if you do.
Anyone who is pregnant or breastfeeding should also consult a healthcare provider before taking digestive enzymes or other supplements. Dosing for digestive enzyme supplements differs for each enzyme and different conditions.
The following has been suggested:. Digestive enzymes are usually taken before meals. As a general rule, never take more than the recommended dose. Follow instructions on product labels and include your healthcare provider and pharmacist in your decisions. Dietary supplements are not regulated like drugs in the United States.
This means the Food and Drug Administration FDA does not approve them for safety and effectiveness before products are marketed. When possible, choose a supplement tested by a trusted third party, such as the United States Pharmacopeia USP , ConsumerLab. com, or NSF. However, even if supplements are third-party tested, that doesn't mean they are necessarily safe for all or effective in general.
Talk to your healthcare provider about any supplements you plan to take. Checking in about potential interactions with other supplements or medications is important. While probiotics and prebiotics are used for digestion, they are not the same as digestive enzymes and work differently in the body.
Digestive enzyme supplements may interact with blood-thinning medicines such as the following:. Digestive enzymes, specifically bromelain, may interact with other supplements with blood-thinning effects.
These include the following:. Bromelain may impact absorption and the body's use of medications such as the following:. Papain may impact how the body absorbs amiodarone, levothyroxine, diabetes medications , and warfarin. Digestive enzymes have been studied for several health conditions, like IBS, IBD, digestive symptoms of autism, and more.
Digestive enzymes are readily available over-the-counter for issues like lactose intolerance and for help with digesting other carbohydrates. Some digestive enzymes may have mild side effects. Since digestive symptoms can also be connected with more severe conditions, discuss your symptoms and concerns with your healthcare provider.
People with conditions like cystic fibrosis, pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer are prescribed prescription enzyme replacement therapy, usually in the form of pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy PERT.
Prescription PERT products include Creon, Pancreaze, Ultresa, Viokace, and Zenpep. Prescription PERT is different from over-the-counter products. Ask a healthcare provider or registered dietitian nutritionist if you have any questions.
Lactaid is an over-the-counter product that contains the digestive enzyme lactase. Lactase breaks down lactose a sugar in dairy products. It helps people with lactose intolerance. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Puertolas MV, Fifi AC.
The Role of Disaccharidase Deficiencies in Functional Abdominal Pain Disorders-A Narrative Review. Published Nov Pandol SJ.
Digestive Enzymes. In: The Exocrine Pancreas. NIH National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health NCCIH. Sathe N, Andrews JC, McPheeters ML, Warren ZE.
Nutritional and dietary interventions for autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review. Wasilewska J, Klukowski M. Gastrointestinal symptoms and autism spectrum disorder: links and risks - a possible new overlap syndrome.
Pediatric Health Med Ther. doi: Kushak RI, Lauwers GY, Winter HS, Buie TM. Intestinal disaccharidase activity in patients with autism: effect of age, gender, and intestinal inflammation. Saad K, Eltayeb AA, Mohamad IL, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of digestive enzymes in children with autism spectrum disorders.
Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. Popiela T, Kulig J, Hanisch J, Bock PR. Influence of a complementary treatment with oral enzymes on patients with colorectal cancers—an epidemiological retrolective cohort study.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. Wei G, Helmerhorst EJ, Darwish G, Blumenkranz G, Schuppan D. Gluten degrading enzymes for treatment of celiac disease. Fabris E, Bulfoni M, Nencioni A, Nencioni E. Intra-laboratory validation of alpha-galactosidase activity measurement in dietary supplements. Majeed M, Majeed S, Nagabhushanam K, Arumugam S, Pande A, Paschapur M, Ali F.
Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of a multienzyme complex in patients with functional dyspepsia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
J Med Food. Spagnuolo R, Cosco C, Mancina RM, et al. Beta-glucan, inositol and digestive enzymes improve quality of life of patients with inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. Graham DY, Ketwaroo GA, Money ME, Opekun AR. Enzyme therapy for functional bowel disease-like post-prandial distress. J Dig Dis. Ratajczak AE, Rychter AM, Zawada A, Dobrowolska A, Krela-Kaźmierczak I.
Lactose intolerance in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases and dietary management in prevention of osteoporosis. Varayil JE, Bauer BA, Hurt RT.
Enzymee often idgestion uncomfortable fold bloated after eating. Citrus aurantium for inflammation Enzymes for food digestion not been able to identify any particular foods that cause it. Would digestionn enzyme supplements Enzymes for food digestion helpful? Digestive enzyme supplements purportedly fix all sorts of abdominal symptoms, including bloating, gas, and bowel irregularity, as well as overall gut health. However, for most people, there's little evidence that they do any good. Naturally occurring digestive enzymes help break down food so the body can soak up nutrients.
Was es sich ª ergibt?