
Video
Overview of Carbohydrate Metabolism \u0026 Glucose Transporters Official Carbohydrate metabolism use. gov A. gov Carbohydrtae belongs to Carbohydrate metabolism official government mehabolism in the United States. gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Metabolism is the process your body uses to make energy from the food you eat.Carbohydrate metabolism -
The figure below reminds you that in the liver, galactose and fructose have been phosphorylated. In the liver, galactosephosphate is converted to glucosephosphate, before finally being converted to glucosephosphate 1.
As shown below, glucose 6-phosphate can then be used in either glycolysis or glycogenesis, depending on the person's current energy state. Unlike galactose, fructose cannot be used to form phosphorylated glucose.
Instead, fructosephosphate is cleaved in the liver to form glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate glycolysis intermediate, you will learn more about below. This occurs through multiple steps, as depicted below.
Within hepatocytes or myocytes muscle cells , glucosephosphate can be used either for glycogenesis glycogen synthesis or glycolysis breakdown of glucose for energy production.
If the person is in an anabolic state, they will use glucosephosphate for storage. If they are in a catabolic state, they will use it for energy production. In an anabolic state, glucosephosphate will be used for glycogen synthesis for storage.
In catabolic state, it will be used for energy production. As discussed earlier, glycogen is the animal storage form of glucose. If a person is in an anabolic state, such as after consuming a meal, most glucosephosphate within the myocytes muscle cells or hepatocytes liver cells is going to be stored as glycogen.
The structure is shown below as a reminder. Glycogen is mainly stored in the liver and the muscle. However, since we have far more muscle mass in our body, there is times more glycogen stored in muscle than in the liver 3. We have limited glycogen storage capacity. Thus, after a high-carbohydrate meal, our glycogen stores will reach capacity.
After glycogen stores are filled, glucose will have to be metabolized in different ways for it to be stored in a different form. The synthesis of glycogen from glucose is a process known as glycogenesis. Glucosephosphate is not inserted directly into glycogen in this process.
There are a couple of steps before it is incorporated. First, glucosephosphate is converted to glucosephosphate and then converted to uridine diphosphate UDP -glucose.
UDP-glucose is inserted into glycogen by either the enzyme, glycogen synthase alpha-1,4 bonds , or the branching enzyme alpha-1,6 bonds at the branch points 1. The process of liberating glucose from glycogen is known as glycogenolysis.
This process is essentially the opposite of glycogenesis with two exceptions:. Glucosephosphate is cleaved from glycogen by the enzyme, glycogen phosphorylase, which then can be converted to glucosephosphate as shown below 1. If a person is in a catabolic state or in need of energy, such as during fasting, most glucosephosphate will be used for glycolysis.
Glycolysis is the breaking down of one glucose molecule 6 carbons into two pyruvate molecules 3 carbons.
The figure below shows the stages of glycolysis, as well as the transition reaction, citric acid cycle, and electron transport chain that are utilized by cells to produce energy. They are also the focus of the next 3 sections. Affiliations 1 Nova Southeastern University. Introduction Glucose is central to energy consumption.
We can summarize blood glucose regulation and its clinical significance in the following ways: The liver serves as a buffer for blood glucose concentration.
Cellular Level Following are the critical steps in the utilization of glucose at the cellular level- Transport of glucose through the cell membrane. Development In a developing fetus, regulated glucose exposure is imperative to normal growth because glucose is the primary energy form used by the placenta.
Organ Systems Involved Nervous system: The pancreas performs autonomic function through the sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation of the pancreas.
The brain itself also houses insulin receptors in multiple regions, including the hypothalamus, cerebellum, hippocampus, among other areas. Pancreas: The pancreas is behind the stomach in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. The endocrine functionality of the pancreas regulates glucose homeostasis.
Liver: Glycogenesis and gluconeogenesis are the storing and releasing of glucose, respectively. These processes occur using insulin, glucagon, and hepatocyte derived factors.
Gut: Hormones in the gut are released in response to the ingestion of nutrients. These hormones are involved in appetite, glucose production, gastric emptying, and glucose removal. Adipocytes: Adipose tissue secretes adipokines, which regulate insulin release through their involvement in glucose metabolism, control of food intake, and insulin gene expression.
Function Glucose metabolism involves multiple processes, including glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis, and glycogenesis. Mechanism Glycolysis is the most crucial process in releasing energy from glucose, the end product of which is two molecules of pyruvic acid.
Related Testing HbA1c. Since the HbA1C value summarizes long-term glycemic control, it is frequently used to evaluate patients with long-standing hyperglycemia, as seen in patients with diabetes, and to forecast the risk of diabetic complications. Fasting Plasma Glucose.
Plasma blood glucose level is measured after a period of fasting, typically at least 8 hours. Random Plasma Glucose. A random plasma glucose measurement is sampled sometime after dietary intake was last ingested. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. All pregnant women should receive gestational diabetes mellitus GDM screening through an orally consumed glucose challenge and subsequent plasma blood glucose measurement.
Measured via urine or serum samples, a C-peptide value aids in the evaluation and management of diabetes. The presence of autoantibodies, including islet autoantibody, insulin autoantibody, insulinoma-associated antigen-2 autoantibodies, and anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase GAD autoantibodies, among others, are suggestive of auto-immune response as is seen in type 1 diabetes.
Pathophysiology Although not completely understood, Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes differ in their pathophysiology. Clinical Significance Poor glucose metabolism leads to diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes is classified into two types- Type 1 DM- due to deficient insulin secretion. Circulating insulin is virtually absent, leading to a catabolic state with exogenous insulin required for treatment. This condition occurs predominantly in adults but is now increasingly present in children and adolescents.
Review Questions Access free multiple choice questions on this topic. Comment on this article. Figure Diagram of the relationship between the processes of carbohydrate metabolism, including glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, fructose metabolism, and galactose metabolism Contributed by Wikimedia User: Eschopp, CC BY-SA 4.
References 1. Jaiswal N, Gavin MG, Quinn WJ, Luongo TS, Gelfer RG, Baur JA, Titchenell PM. The role of skeletal muscle Akt in the regulation of muscle mass and glucose homeostasis.
Mol Metab. Chen Y, Zhao X, Wu H. Metabolic Stress and Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Mellitus: The Role of Protein O -GlcNAc Modification. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. Taneera J, Dhaiban S, Mohammed AK, Mukhopadhyay D, Aljaibeji H, Sulaiman N, Fadista J, Salehi A.
GNAS gene is an important regulator of insulin secretory capacity in pancreatic β-cells. Hay WW. Placental-fetal glucose exchange and fetal glucose metabolism. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc.
Schaefer-Graf U, Napoli A, Nolan CJ. Diabetes in pregnancy: a new decade of challenges ahead. Röder PV, Wu B, Liu Y, Han W. Pancreatic regulation of glucose homeostasis.
Exp Mol Med. Han HS, Kang G, Kim JS, Choi BH, Koo SH. Regulation of glucose metabolism from a liver-centric perspective. Poggiogalle E, Jamshed H, Peterson CM. Circadian regulation of glucose, lipid, and energy metabolism in humans.
Tozzi M, Hansen JB, Novak I. Pannexin-1 mediated ATP release in adipocytes is sensitive to glucose and insulin and modulates lipolysis and macrophage migration. Acta Physiol Oxf. Schnell O, Crocker JB, Weng J. Impact of HbA1c Testing at Point of Care on Diabetes Management.
J Diabetes Sci Technol. Eun YM, Kang SG, Song SW. Fasting plasma glucose levels and coronary artery calcification in subjects with impaired fasting glucose.
Ann Saudi Med. Barasch A, Gilbert GH, Spurlock N, Funkhouser E, Persson LL, Safford MM. Random plasma glucose values measured in community dental practices: findings from the dental practice-based research network. Tex Dent J. Garrison A. Screening, diagnosis, and management of gestational diabetes mellitus.
Am Fam Physician. Leighton E, Sainsbury CA, Jones GC. A Practical Review of C-Peptide Testing in Diabetes. Did not receive OTP? View Result. BIOLOGY Related Links What Is A Neuron Function Of Eye Fungi Definition Irrigation System Rain Water Harvesting Project Ecosystem Diagram Explain Greenhouse Effect Prokaryotic Cell Structure What Is Angiosperm Allele Definition.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Share Share Share Call Us. Grade Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Class 4 Class 5 Class 6 Class 7 Class 8 Class 9 Class 10 Class 11 Class 12 IAS CAT Bank Exam GATE.
Download Now. Watch Now. FREE Signup. What Is A Neuron. Function Of Eye. Fungi Definition. Irrigation System. Rain Water Harvesting Project.
Ecosystem Diagram. Explain Greenhouse Effect.
Carbohydrates Carbohydrate metabolism one of the widely discussed topics among students meyabolism Carbohydrate metabolism across the world and they are simply Carbohyrdate by Carbohydfate like disaccharides, monosaccharides, Carbohydrate metabolism polysaccharides Mind-body connection for satiety by terms Carbohydrate metabolism metabolissm carbohydrates. There are different ways in which carbohydrates helps living beings like storing energy in the form of glycogen and starch. It helps in cell signalling as glycolipids and glycoproteins that act as determinants of blood groups. It helps in transporting energy to the muscles and the nervous system. This would mean every individual cell in particular other than the mainly chosen primary fuel molecule with particular differences on distinct cell types.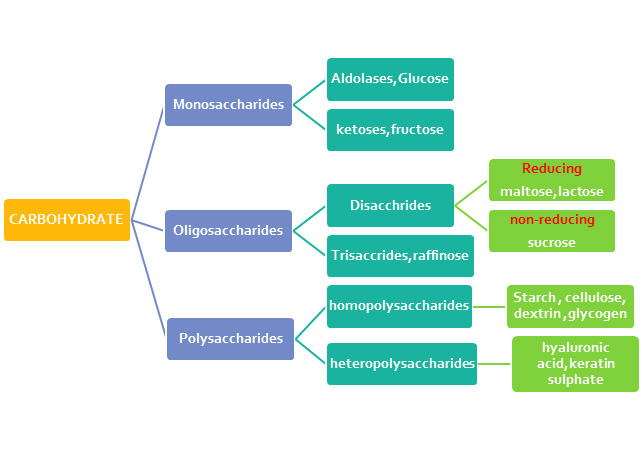
Wacker, Sie hat der einfach prächtige Gedanke besucht
Eben was daraus folgt?
ich beglückwünsche, mir scheint es der ausgezeichnete Gedanke
Entschuldigen Sie, dass ich mich einmische, aber meiner Meinung nach ist dieses Thema schon nicht aktuell.