Coenzyme Q and cholesterol -
The novel single-stage restricted cubic spline regression model was applied to explore nonlinear dose-response relationships. Results: Fifty randomized controlled trials with a total of participants were included in the qualitative synthesis. The pooled analysis revealed that CoQ10 supplementation significantly reduced total cholesterol TC MD Keywords: CoQ10 supplementation; dyslipidemia; lipid profiles; meta-analysis.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.
According to the literatures to date, it seems that the antioxidant effects of CoQ 10 vary depending on the physiological status of animals, dosage and duration of CoQ 10 level, environmental conditions, etc.
Therefore, it could be concluded that dietary CoQ 10 had beneficial effects on the hepatic antioxidant defense system under cholesterol-induced hyperlipidemic stress in SD rats. The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
The datasets are available in the data sheet of In-Surk Jang repository. Acosta MJ, Vazquez Fonseca L, Desbats MA, C C, Zordan R, Trevisson E, Salviati L. Coenzyme Q biosynthesis in health and disease.
Biochim Biophys Acta. Article CAS Google Scholar. Crane FL. Biochemical function of coenzymes Q J Am Coll Nutr. Littarru GP, Tiano L, Belardinelli R, Watts GF. Coenzyme Q 10 , endothelial function, and cardiovascular disease. Quiles JL, Ochoa JJ, Battino M, Gutierrez-Rios P, Nepomuceno EA, Frias ML, Huertas JR, Mataix J.
Life-long supplementation with a low dosage of coenzyme Q 10 in the rat: effects on antioxidant status and DNA damage. Turunen M, Olsson J, Dallner G. Metabolism and function of coenzyme Q. Ahmadvand H, Tavafi M, Khosrowbeygi A.
Amelioration of altered antioxidant enzymes activity and glomerulosclerosis by coenzyme Q 10 in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J Diabetes Complicat. Article Google Scholar. Fouad AA, Jresat I. Hepatoprotective effect of coenzyme Q 10 in rats with acetaminophen toxicity.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. Song MH, Kim HN, Lim Y, Jang IS. Effects of coenzyme Q 10 on the antioxidant system in SD rats exposed to lipopolysaccharide-induced toxicity. Lab Anim Res. Bullon P, Roman-Malo L, Marin-Aguilar F, Alvarez-Suarez JM, Giampieri F, Battino M, Cordero MD.
Lipophilic antioxidants prevent lipopolysaccharide-induced mitochondrial dysfunction through mitochondrial biogenesis improvement.
Pharmacol Res. Kwong LK, Kamzalov S, Rebrin I, Bayne AC, Jana CK, Morris P, Forster MJ, Sohal RS. Effects of coenzyme Q 10 administration on its tissue concentrations, mitochondrial oxidant generation, and oxidative stress in the rat.
Free Radic Biol Med. Sohal RS, Kamzalov S, Sumien N, Ferguson M, Rebrin HKR, Forster MJ. Effect of coenzyme Q 10 intake on endogenous coenzyme Q content, mitochondrial electron transport chain, antioxidative defenses, and life span of mice.
Zhang Y, Aberg F, Appelkvist EL, Dallner G, Ernster L. Uptake of dietary coenzyme Q supplement is limited in rats. J Nutr. CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Shetty RA, Ikonne US, Forster MJ, Sumien N.
Coenzyme Q 10 and α-tocopherol reversed age-associated functional impairments in mice. Exp Gerontol. Abdelbaset M, Safar MM, Mahmoud SS, Negm SA, Agha AM.
Red yeast rice and coenzyme Q 10 as safe alternatives to surmount atorvastatin-induced myopathy in hyperlipidemic rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. Jimenez-Santos MA, Juarez-Rojop IE, Tovilla-Zarate CA, Espinosa-Garcia MT, Juarez-Oropeza MA, Ramon-Frías T, Bermudez-Ocana DY, Diaz-Zagoya JC. Coenzyme Q 10 supplementation improves metabolic parameters, liver function and mitochondrial respiration in rats with high doses of atorvastatin and a cholesterol-rich diet.
Lipids Health Dis. Li S, Zeng XY, Zhou X, Wang H, Jo E, Robinson SR, Xu A, Ye JM. Dietary cholesterol induces hepatic inflammation and blunts mitochondrial function in the liver of high-fat-fed mice.
J Nutr Biochem. Schroepfer GJ Jr. Oxysterols: modulators of cholesterol metabolism and other processes. Physiol Rev. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 -ΔΔCT Method.
Kupfer D, Levin E. Monooxygenase drug metabolizing activity in CaCl 2 -aggregated hepatic microsomes from rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. Tappel AL. Glutathione peroxidase and hydroperoxides. Methods Enzymol. Habig WH, Phobst MJ, Jakoby WB.
Glutathione S-transferase: the first enzymatic steps in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem. Bidlack WR, Tappel AL. Damage to microsomal membrane by lipid peroxidation. Matias I, Petrosino S, Racioppi A, Capasso R, Izzo AA, Di Marzo V.
Dysregulation of peripheral endocannabinoid levels in hyperglycemia and obesity: effect of high fat diets.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. Ramalho L, da Jornada MN, Antunes LC, Hidalgo MP. Metabolic disturbances due to a high-fat diet in a non-insulin-resistant animal model. Nutr Diabetes. Millan J, Pinto X, Munoz A, Zuniga M, Rubies-Prat J, Pallardo LF, Masana L, Mangas A, Hernandez-Mijares A, Gonzalez-Santos P, Ascaso JF, Pedro-Botet J.
Lipoprotein ratios: physiological significance and clinical usefulness in cardiovascular prevention. Vasc Health Risk Manag. CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Hu X, Wang T, Li W, Jin F, Wang L. Effects of NS Lactobacillus strains on lipid metabolism of rats fed a high-cholesterol diet.
Ramirez-Tortosa MC, Granados S, Ramirez-Tortosa CL, Ochoa JJ, Camacho P, García-Valdés L, Battino M, Quiles JL. Oxidative stress status in liver mitochondria and lymphocyte DNA damage of atherosclerotic rabbits supplemented with water soluble coenzyme Q Ratnam DV, Chandraiah G, Meena AK, Ramarao P, Kumar MN.
The co-encapsulated antioxidant nanoparticles of ellagic acid and coenzyme Q 10 ameliorates hyperlipidemia in high fat diet fed rats. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. Mohseni M, Vafa MR, Hajimiresmail SJ, Zarrati M, Rahimi Forushani A, Bitarafan V, Shidfar F. Effects of coenzyme Q 10 supplementation on serum lipoproteins, plasma fibrinogen, and blood pressure in patients with hyperlipidemia and myocardial infarction.
Iran Red Crescent Med J. Nemes K, Aberg F, Gylling H, Isoniemi H. Cholesterol metabolism in cholestatic liver disease and liver transplantation: from molecular mechanisms to clinical implications. World J Hepatol.
Espinosa-Diez C, Miguel V, Mennerich D, Kietzmann T, Sanchez-Perez P, Cadenas S, Lamas S. Antioxidant responses and cellular adjustments to oxidative stress. Redox Biol. Chou ST, Peng HY, Hsu JC, Lin CC, Shih Y.
Achillea millefolium L. essential oil inhibits LPS-induced oxidative stress and nitric oxide production in RAW Int J Mol Sci. Niklowitz P, Menke T, Andler W, Okun JG. Simultaneous analysis of coenzyme Q10 in plasma, erythrocytes and platelets: comparison of the antioxidant level in blood cells and their environment in healthy children and after oral supplementation in adults.
Clin Chim Acta. Spolarics Z. Endotoxin stimulates gene expression of ROS-eliminating pathways in rat hepatic endothelial and Kupffer cells. Am J Phys. CAS Google Scholar. Sena CM, Nunes E, Gomes A, Santos MS, Proenca T, Martins MI, Seica RM. Supplementation of coenzyme Q 10 and α-tocopherol lowers glycated hemoglobin level and lipid peroxidation in pancreas of diabetic rats.
Nutr Res. Novoselova EG, Lunin SM, Novoselova TV, Khrenov MO, Glushkova OV, Avkhacheva NV, Safronova VG, Fesenko EE.
Naturally occurring antioxidant nutrients reduce inflammatory response in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. Lee CK, Pugh TD, Klopp RG, Edwards J, Allison DB, Weindruch R, Prolla TA.
The impact of alpha-lipoic acid, coenzyme Q 10 and caloric restriction on life span and gene expression patterns in mice. Kamzalov S, Sumien N, Forster MJ, Sohal RS. Coenzyme Q intake elevates the mitochondrial and tissue levels of coenzyme Q and alpha-tocopherol in young mice.
Download references. The authors thank the Regional Animal Research Center at GNTECH to provide analytical instrument for conducting this research project. The authors thank the Regional Animal Research Center at GNTECH to support this research project. Department of Animal Science and Biotechnology, and the Regional Animal Research Center, Gyeongnam National University of Science and Technology, Chilam-Dong , Jinju, Gyeongnam, , Korea.
Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, Dong-Eui Univerisity, Busan, , Korea. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. H-NL: analysis of Real-Time PCR for antioxidant genes. D-GJ: animal care for the experiment.
YL: analysis of blood biochemical profiles. I-SJ: analysis of antioxidant enzyme activity. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Correspondence to In-Surk Jang. All members agreed to submit this manuscript to La Anim Res. Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4. Reprints and permissions. Kim, HN. et al. The effects of coenzyme Q 10 supplement on blood lipid indices and hepatic antioxidant defense system in SD rats fed a high cholesterol diet.
Lab Anim Res 35 , 13 Download citation. Received : 06 May Accepted : 24 July Published : 08 August Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative.
Skip to main content. Search all BMC articles Search.
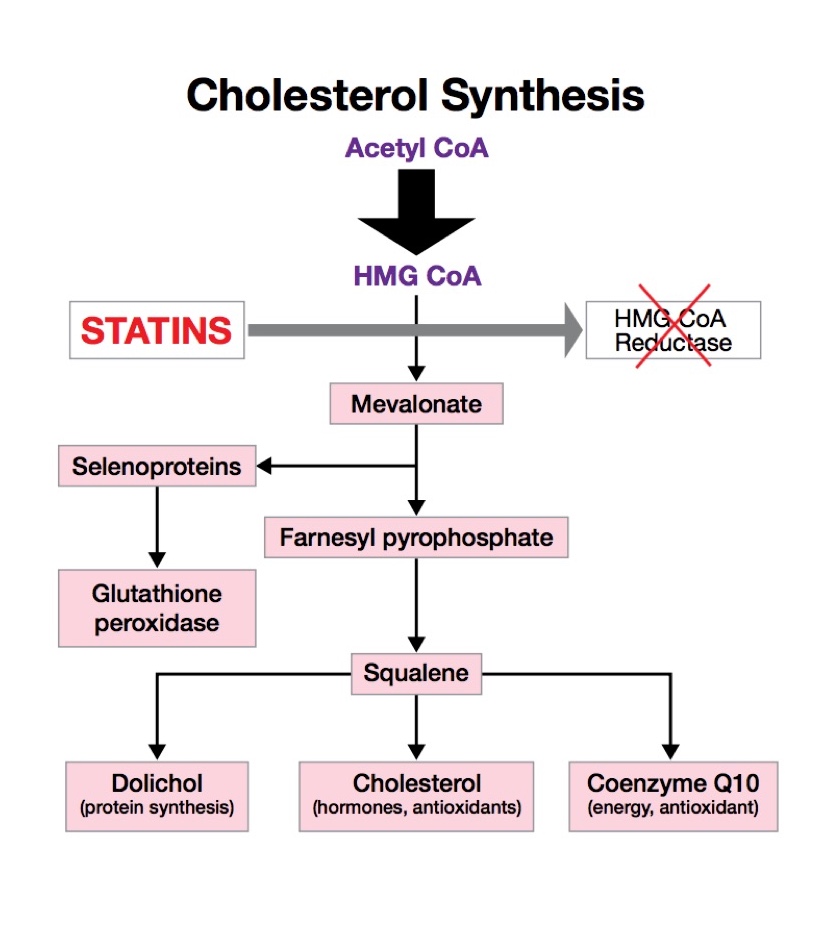
Coenzyme Q 10 is a member of the ubiquinone family of Coenzyme Q and cholesterol. Choleaterol Coenzyme Q and cholesterol, including humans, can synthesize ubiquinones, hence, coenzyme Q 10 is cuolesterol considered a vitamin 1. Low-calorie breakfast ideas Coenzyme Q and cholesterol ubiquinone Rev up your metabolism to the ubiquitous presence of anc compounds in living organisms and Coezyme chemical structure, which contains a functional group known as a benzoquinone. Ubiquinones are fat-soluble molecules with anywhere from 1 to 12 isoprene 5-carbon units. The ubiquinone found in humans, ubidecaquinone or coenzyme Q 10has a "tail" of 10 isoprene units a total of 50 carbon atoms attached to its benzoquinone "head" Figure 1 1. Coenzyme Q 10 is soluble in lipids fats and is found in virtually all cell membranesincluding mitochondrial membranes. The ability of the benzoquinone head group of coenzyme Q 10 to accept and donate electrons is a critical feature to its function. Laboratory Animal Research volume 35Hair growth remedies number: snd Cite this article. Coenzyme Q and cholesterol details. Coenzymf body weight, weight gain, liver weight and abdominal fat pads were unaffected by 0. The activities hepatic GPX and GST were unaffected by CoQ 10 and cholesterol supplements in rats. In conclusion, 0.
0 thoughts on “Coenzyme Q and cholesterol”