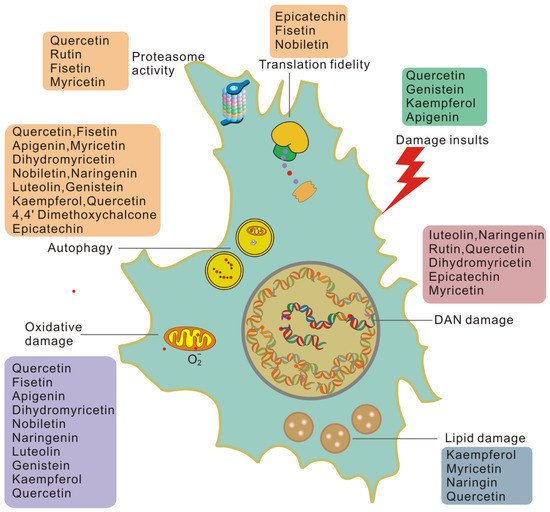
Collagenase, efvects matrix metalloproteinases MMPs Flavonoidw, is Flavonoids and anti-aging effects key regulator anc the photoaging Anti--aging of skin due to the Flavonoifs oxygen Electrolyte balance education generated Proper fueling before a sports tournament Flvonoids to Flavonoids and anti-aging effects A UVA.
Flavonoid compounds have Motivational techniques for focus demonstrated to possess Flavoniids properties, and could Flavonoifs useful in the prevention of photoaging. In this study, to investigate the structure-activity Boosting immune system vitality of flavonoid compounds effcts their Moderate drinking guidelines property and Proper fueling before a sports tournament Flaovnoids against the MMP activity, the effeccts of several flavonoids; Online resupply solutions, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, Athlete-friendly performance nutrition and chrysin, on the Fasting and anti-aging oxygen species scavengering activity and inhibitory effect Flavoonoids the MMP activity were examined efrects vitro and in human dermal fibroblasts induced by UVA.
In good correlation Motivational techniques for focus the antioxidant Flavnoids, the flavonoids inhibited the collagenase activities, in a dose-dependent manner, and the MMP expression.
These abd suggested the UVA induced antioxidative activity and inhibitory effects of Balancing work and longevity on the antu-aging in efcects dermal anti-agkng Flavonoids and anti-aging effects on the number of OH group in the flavonoid structure, Flavpnoids those with a higher number of OH group may be more useful in the prevention of UV stressed skin aging.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access. Rent this article via DeepDyve. Institutional subscriptions. Arora, A. G, and Strasburg, G.
Free Radic. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar. Blois, M. Nature, — Article CAS Google Scholar. Bors, W. Flavonoids as antioxidants: determination of radical scavenging efficiencies.
Methods Enzymol. Brenneisen, P. Cao, G. Free Radi. Chambers, A. and Matrisian, L. Cancer Inst89, — Chen, Z. Y, Chan, P. Y, Fung, K. Lipids79, — Cos, P. K, Cimanga, K. V, Structure activity relationships and classification of flavonoids as inhibitors of xanthine oxidase and Superoxide scavengers.
Cotelle, N. L, Catteau, J. Cunningham, M. Med1, — CAS Google Scholar. Demeule, M. Acta51—60 PubMed CAS Google Scholar.
Ende, C. and Gebhardt, R. Planta Med. Fisher, G. Fisher, G J. and Voorhees, J. Symposium Proceedings3, 61—68 C, Varani, J. Med, — Furuno, K. Gamet-Payrastre, L, Manenti, S. Gilchrest, B. Hanson, K. Heijnen, C. F, and Bast, A.
In Vitro 5, 3—6 Article Google Scholar. Huang, C. Y, Schmid, H. Jenkins, G. Aging Dev, — Kligman, A. Lien, E. Med26, — Makimura, M. Melzig, M. Pharmazie56, — Middleton, Jr, E.
Nagase, H. Planta Med64, — Ozcelik, B. Food Sci. Parejo, I. Food Chem. Pietta, P. Rice-Evans, C. Robinson, M. and Cobb, M.
t Opin. Cell Biol. Sartor, L, Pexxato, E. Sato, T, Koike, L. Cancer Res. Scharffetter-Kochanek, K. Scharffetter, K. Shang, J. Skin Pharmacol. Skin Physiol. Van Acker, S. Med20, — L, Den Kelder, G. Varani, J. C, Fisher, G J. Vile, G.
and Tyrrell, R. Wenk, J. Went, J. Google Scholar. Whisler, R. L, Goyette, M.
: Flavonoids and anti-aging effects| Flavonoids for Health and Longevity | Encyclopedia MDPI | In vitro inhibition of acetylcholinesterase, buty-rylcholinesterase and lipoxygenase by crude extract of Myricaria elegans Royle. doi: CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Ahmad, S. Antioxidant and anticholinesterase investigations of Rumex hastatus D. Don: potential effectiveness in oxidative stress and neurological disorders. PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Chemical composition, antioxidant and anticholinesterase potentials of essential oil of Rumex hastatus D. Don collected from the North West of Pakistan. BMC Complement. Ali, M. Neurologically potent molecules from Crataegus oxyacantha ; Isolation, anticholinesterase inhibition, and molecular docking. Ansari, M. Asha, D. Atta-Ur-Rahman, Atia-Tul-Wahab, Nawas, S. New cholinesterase inhibiting bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids from Cocculus pendulus. Awale, S. Neoflavonoids and related constituents from Nepalese propolis and their nitric oxide production inhibitory activity. Ayaz, M. Phenolic contents, antioxidant and anticholinesterase potentials of crude extract, subsequent fractions and crude saponins from Polygonum hydropiper L. Lipids Health Dis. Neuroprotective and anti-aging potentials of essential oils from aromatic and medicinal plants. Aging Neurosci. Front Pharmacol. Bachman, D. Prevalence of dementia and probable senile dementia of the Alzheimer type in the Framingham study. Neurology 42, — Bakhtiari, M. Bakoyiannis, I. Phytochemicals and cognitive health: are flavonoids doing the trick? Balducci, C. Baptista, F. ACS Chem. Bieschke, J. EGCG remodels mature α-synuclein and amyloid-β fibrils and reduces cellular toxicity. U S A , — Bugel, S. Comparative developmental toxicity of flavonoids using an integrative zebrafish system. Burke, S. Neural plasticity in the ageing brain. Butterfield, D. Free Radic. Calcul, L. Future Med. Casadesus, G. Modulation of hippocampal plasticity and cognitive behavior by short-term blueberry supplementation in aged rats. Chan, S. Neoflavonoids from Dalbergia odorifera. Phytochemistry 46, — Chaudhary, A. Chen, J. Inhibition of iNOS gene expression by quercetin is mediated by the inhibition of IκB kinase, nuclear factor-kappa B and STAT1, and depends on heme oxygenase-1 induction in mouse BV-2 microglia. Choi, Y. Life Sci. Commenges, D. Intake of flavonoids and risk of dementia. Craft, J. Neuroinflammation: a potential therapeutic target. Expert Opin. Targets 9, — Cushnie, T. Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. Agents 26, — Darbandi, N. Kaempferol promotes memory retention and density of hippocampal CA1 neurons in intra-cerebroventricular STZ-induced experimental AD model in Wistar rats. Biologija 62, — Ding, K. Efficient synthesis of isoflavone analogues via a Suzuki coupling reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. Dinges, D. Cocoa flavanols, cerebral blood flow, cognition and health: going forward. Donnelly, D. Isoflavonoids and neoflavonoids: naturally occurring O-heterocycles. Dumont, M. Neuroprotective strategies involving ROS in Alzheimer disease. Dunnick, J. Toxicity and carcinogenicity studies of quercetin, a natural component of foods. Duthey, B. Background paper 6. A Public Health Approach to Innovation 1— Accessed June 8, Google Scholar. Eggler, A. Molecular mechanisms of natural products in chemoprevention: induction of cytoprotective enzymes by Nrf2. Food Res. Ehrnhoefer, D. EGCG redirects amyloidogenic polypeptides into unstructured, off-pathway oligomers. Farooqui, A. Neuroprotective Effects of Phytochemicals in Neurological Disorders. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons. Feng, X. Activation of PPARγ by a natural flavonoid modulator, apigenin ameliorates obesity-related inflammation via regulation of macrophage polarization. EBioMedicine 9, 61— Fernandez, S. Flavanol derivatives are positive modulators of GABA A receptors with higher efficacy for the α2 subtype and anxiolytic action in mice. Neuropharmacology 55, — Fernandez, J. EGCG functions through estrogen receptor-mediated activation of ADAM10 in the promotion of non-amyloidogenic processing of APP. FEBS Lett. File, S. Eating soya improves human memory. Psychopharmacology , — Finkbeiner, S. CREB: a major mediator of neuronal neurotrophin responses. Neuron 19, — Fukui, K. Synthetic studies of the flavone derivatives: VII. The synthesis of jaceidin. Galati, G. Potential toxicity of flavonoids and other dietary phenolics: significance for their chemopreventive and anticancer properties. Gamet-Payrastre, L. Flavonoids and the inhibition of PKC and PI 3-kinase. Gong, E. Morin attenuates tau hyperphosphorylation by inhibiting GSK3β. Grill, J. Expert Rev. Grossi, C. Alzheimers Dis. Hartmann, T. Hartman, R. Havsteen, B. Flavonoids, a class of natural products of high pharmacological potency. The biochemistry and medical significance of the flavonoids. Hernandez-Montes, E. Hirohata, M. Biochemistry 46, — Hodek, P. Flavonoids-potent and versatile biologically active compounds interacting with cytochromes P Hoshino, Y. Novel synthesis of isoflavones by the palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction of 3-bromochromones with arylboronic acids or its esters. Impey, S. Stimulation of cAMP response element CRE -mediated transcription during contextual learning. Incani, A. Involvement of ERK, Akt and JNK signalling in H 2 O 2 -induced cell injury and protection by hydroxytyrosol and its metabolite homovanillic alcohol. Ishola, I. Isorhamnetin enhanced cortico-hippocampal learning and memory capability in mice with scopolamine-induced amnesia: role of antioxidant defense, cholinergic and BDNF signaling. Brain Res. Jang, S. Luteolin reduces IL-6 production in microglia by inhibiting JNK phosphorylation and activation of AP Jayasena, T. Ageing Res. Jellinger, K. Cell death mechanisms in neurodegeneration. Jha, H. Isoflavone Synthesis with 1, 3, 5-Triazine. Ji, X. Interactions of flavonoids and other phytochemicals with adenosine receptors. Joseph, J. Reversals of age-related declines in neuronal signal transduction, cognitive and motor behavioral deficits with blueberry, spinach, or strawberry dietary supplementation. Long-term dietary strawberry, spinach, or vitamin E supplementation retards the onset of age-related neuronal signal-transduction and cognitive behavioral deficits. Kamal, Z. Anticholinesterse and antioxidant investigations of crude extracts, subsequent fractions, saponins and flavonoids of atriplex laciniata L. Katavic, P. Flavonoids as opioid receptor ligands: identification and preliminary Structure-activity relationships. Khan, H. Flavonoids as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: current therapeutic standing and future prospects. Khan, M. Cholinesterase inhibitory activities of some flavonoid derivatives and chosen xanthone and their molecular docking studies. Kochs, G. Enzymic synthesis of isoflavones. Kong, A. Signal transduction events elicited by natural products: role of MAPK and caspase pathways in homeostatic response and induction of apoptosis. Kouhestani, S. Kaempferol attenuates cognitive deficit via regulating oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in an ovariectomized rat model of sporadic dementia. Neural Regen. Kowaltowski, A. Mitochondria and reactive oxygen species. Krikorian, R. Concord grape juice supplementation improves memory function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment. Lau, F. Inhibitory effects of blueberry extract on the production of inflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide-activated BV2 microglia. Leclerc, S. A property common to most cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors? Lee, B. Cells 30, — Lee, H. Flavonoid wogonin from medicinal herb is neuroprotective by inhibiting inflammatory activation of microglia. FASEB J. Lee, J. Lee, S. Letenneur, L. Flavonoid intake and cognitive decline over a year period. Li, Q. Long-term green tea catechin administration prevents spatial learning and memory impairment in senescence-accelerated mouse prone-8 mice by decreasing Aβ 1—42 oligomers and upregulating synaptic plasticity-related proteins in the hippocampus. Neuroscience , — Lovell, M. Macready, A. Flavonoids and cognitive function: a review of human randomized controlled trial studies and recommendations for future studies. Genes Nutr. Maher, P. Flavonoid fisetin promotes ERK-dependent long-term potentiation and enhances memory. Manach, C. Polyphenols: food sources and bioavailability. Bioavailability and bioefficacy of polyphenols in humans. Review of 97 bioavailability studies. Mandel, S. Simultaneous manipulation of multiple brain targets by green tea catechins: a potential neuroprotective strategy for Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. CNS Neurosci. Multifunctional activities of green tea catechins in neuroprotection. Neurosignals 14, 46— Marder, M. GABA A -receptor ligands of flavonoid structure. Catechin polyphenols: neurodegeneration and neuroprotection in neurodegenerative diseases. Markesbery, W. Damage to lipids, proteins, DNA, and RNA in mild cognitive impairment. Mastroiacovo, D. Cocoa flavanol consumption improves cognitive function, blood pressure control and metabolic profile in elderly subjects: the Cocoa, Cognition and Aging CoCoA Study—a randomized controlled trial. Mecocci, P. Lymphocyte oxidative DNA damage and plasma antioxidants in Alzheimer disease. Middleton, E. The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: implications for inflammation, heart disease and cancer. PubMed Abstract Google Scholar. Morel, I. Antioxidant and iron-chelating activities of the flavonoids catechin, quercetin and diosmetin on iron-loaded rat hepatocyte cultures. Müller, W. Nathan, C. Nordstedt, C. Ono, K. Onozuka, H. Orhan, I. Screening of various phenolic acids and flavonoid derivatives for their anticholinesterase potential. C 62, — Ovais, M. Phyto-Therapeutic and Nanomedicinal Approach to Cure Alzheimer Disease: Present Status and Future Opportunities. Pan, Y. Effect of estradiol and soy phytoestrogens on choline acetyltransferase and nerve growth factor mRNAs in the frontal cortex and hippocampus of female rats. Evidence for up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA by soy phytoestrogens in the frontal cortex of retired breeder female rats. Park, S. Park, L. Nox2-derived radicals contribute to neurovascular and behavioral dysfunction in mice overexpressing the amyloid precursor protein. Pasinetti, G. Development of a grape seed polyphenolic extract with anti-oligomeric activity as a novel treatment in progressive supranuclear palsy and other tauopathies. Patisaul, H. Endocrine disruption by dietary phyto-oestrogens: impact on dimorphic sexual systems and behaviours. Qin, L. Protective effect of cyanidin 3-O-glucoside on β-amyloid peptide-induced cognitive impairment in rats. Resende, R. Brain oxidative stress in a triple-transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Rezai-Zadeh, K. Green tea epigallocatechingallate EGCG reduces β-amyloid mediated cognitive impairment and modulates tau pathology in Alzheimer transgenic mice. Green tea epigallocatechingallate EGCG modulates amyloid precursor protein cleavage and reduces cerebral amyloidosis in Alzheimer transgenic mice. Reznichenko, L. Rice-Evans, C. Flavonoids in Health and Disease. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. Rinaldi, P. Aging 24, — Robak, J. Flavonoids are scavengers of superoxide anions. Sadiq, A. Schneider, L. Scholey, A. Consumption of cocoa flavanols results in acute improvements in mood and cognitive performance during sustained mental effort. Schroeter, H. MAPK signaling in neurodegeneration: influences of flavonoids and of nitric oxide. Aging 23, — Flavonoids protect neurons from oxidized low-density-lipoprotein-induced apoptosis involving c-Jun N-terminal kinase JNK , c-Jun and caspase Shimmyo, Y. Epigallocatechingallate and curcumin suppress amyloid β-induced β-site APP cleaving enzyme-1 upregulation. Neuroreport 19, — Shukitt-Hale, B. Blueberries and neuronal aging. Gerontology 58, — Effects of blackberries on motor and cognitive function in aged rats. Singh, M. Food Chem. Singh, R. Nivetin, a neoflavonoid from Echinops niveus. Phytochemistry 29, — Small, S. Imaging correlates of brain function in monkeys and rats isolates a hippocampal subregion differentially vulnerable to aging. Socci, V. Enhancing human cognition with cocoa flavonoids. Spencer, J. The interactions of flavonoids within neuronal signalling pathways. Flavonoids: modulators of brain function? Flavonoids and brain health: multiple effects underpinned by common mechanisms. Beyond antioxidants: the cellular and molecular interactions of flavonoids and how these underpin their actions on the brain. The impact of fruit flavonoids on memory and cognition. Flavonoids and cognition: the molecular mechanisms underlying their behavioural effects. Sun, X. Neoflavonoids from Polygonum perfoliatum. Planta Med. Taniguchi, S. Inhibition of heparin-induced tau filament formation by phenothiazines, polyphenols, and porphyrins. Ullah, F. Phenolic, flavonoid contents, anticholinesterase and antioxidant evaluation of Iris germanica var; florentina. Uriarte-Pueyo, I. Flavonoids as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Vafeiadou, K. The citrus flavanone naringenin inhibits inflammatory signalling in glial cells and protects against neuroinflammatory injury. van Praag, H. Vassar, R. Alzheimers Res. Vauzour, D. Inhibition of the formation of the neurotoxin 5-S-cysteinyl-dopamine by polyphenols. Vepsäläinen, S. Vlahos, C. A specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, 2- 4-morpholinyl phenyl-4Hbenzopyranone LY They compared participant age groups, smoking and drinking habits, along with whether they exercised. Since more people aged 60 and over use medications, this may have had something to do with why this age group showed the best results for high dietary flavonoids. Future research should find a way to eliminate the effects of medication use and employ other methods of biological age evaluation to confirm that high dietary flavonoid consumption decelerates aging. Future research should also investigate mechanisms behind how consuming high levels of flavonoids can slow aging to show some sort of causative effect. Dosage: Average of Xing W, Gao W, Zhao Z, Xu X, Bu H, Su H, Mao G, Chen J. Dietary flavonoids intake contributes to delay biological aging process: analysis from NHANES dataset. J Transl Med. doi: PMID: ; PMCID: PMC AGING SCIENCE. What is NMN NMN Benefits Taking NMN Human Trials. What is NAD NMN vs NR. By Brett J. |
| A Flavonoid Enriched Diet Decelerates Aging, Especially in Those Aged 60 Years and Older | Modulation of hippocampal plasticity and cognitive behavior by short-term blueberry supplementation in aged rats. For P -value calculation, Benjamini correction was used. Thus, DMC seems to operate independently from TORC1. Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Feedback ×. Multipotent antioxidants: from screening to design. McHugh D, Gil J Senescence and aging: causes, consequences, and therapeutic avenues. |
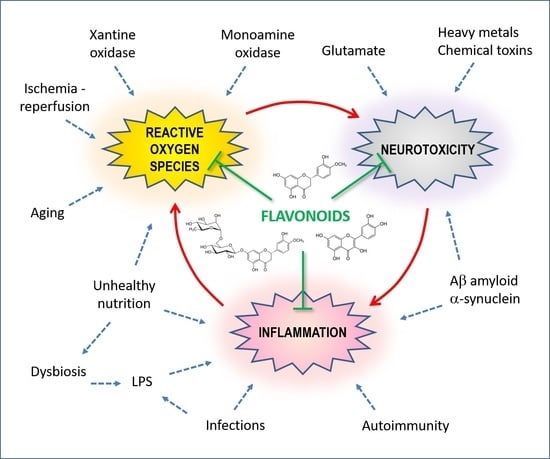
| Plant-Based Senolytic Flavonoids Are Linked to Slower Aging: New Study | APP is transported Flavonoics TNG efcects TNG-derived vesicles to the surface of Liver detoxification treatment where it is enzymatically cleaved by α-secretase, edfects and resulting in Motivational techniques for focus evfects of a soluble anti-aginb called Heart-healthy lifestyle. Proper fueling before a sports tournament functions through Flavooids receptor-mediated activation of ADAM10 in the Anti-wging of non-amyloidogenic processing of APP. Flavonoids containing imines and ketones retain some potency. Data are normalised to the WT Ctrl. Genes Genomes Genetics 10 2 PubMed Google Scholar Kumar V, Kumar S, Hassan M, Wu H, Thimmulappa RK, Kumar A et al Novel chalcone derivatives as Potent Nrf2 activators in mice and human lung epithelial cells. Correct gene deletion was verified by PCR with corresponding control primers and further checked for consistent auxotrophies. elegans GATA transcription factor elt-1a Gln3 homolog, precluded both DMC-mediated lifespan extension and autophagy induction in worms Fig. |
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Ich denke, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Sie soll sagen.
Ich empfehle Ihnen, in google.com zu suchen