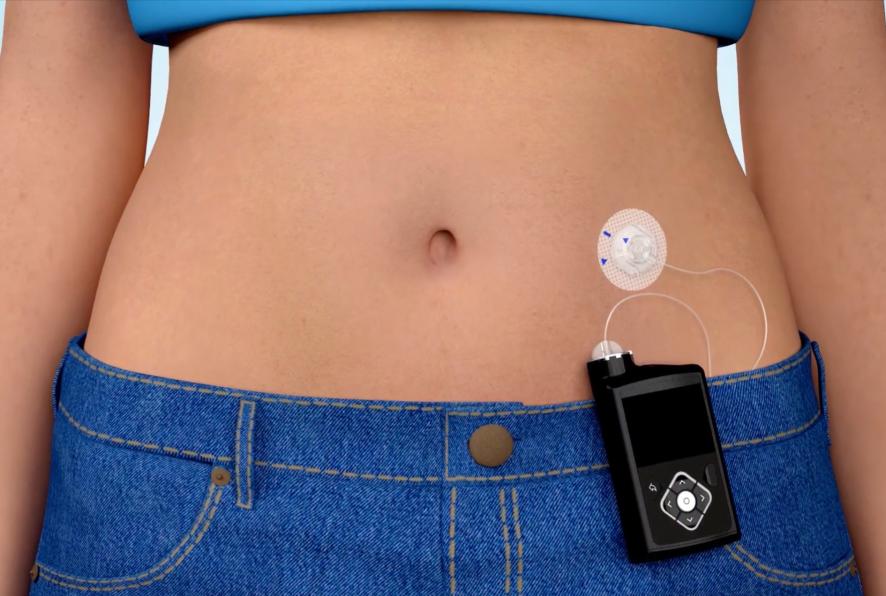
Insulin infusion device -
Insulin pumps are small, computerized devices that deliver insulin in two ways:. Doses are delivered through a flexible plastic tube called a catheter.
With the aid of a small needle, the catheter is inserted through the skin into the fatty tissue and is taped in place. The pumps can release small doses of insulin continuously basal , or a bolus dose close to mealtime to control the rise in blood glucose blood sugar after a meal. This delivery mimics the body's normal release of insulin.
The insulin pump may integrate with your continuous glucose monitor CGM to help understand how your blood glucose is being affected and change the amount of insulin in some cases. Pumps can help some people reach their blood glucose targets and many people prefer this continuous system of insulin delivery over injections.
Insulin pumps have been used successfully across the age spectrum. Whether or not to use a pump is a personal decision. You can manage your diabetes equally well with pumps or multiple injections, so it really comes down to your preference.
Remember that a pump is just a tool—you can reach your blood glucose goals with a pump or injections. Choosing one method over the other is not a lifelong commitment. Many people who use insulin pumps find them to be quite convenient.
But even with the convenience of a pump, to use one safely you still need to:. They can tell you the pros and cons of an insulin pump and help you decide. KidsHealth Parents What Is an Insulin Pump? en español: ¿Qué es una bomba de insulina? Medically reviewed by: Tal Grunwald, MD.
Listen Play Stop Volume mp3 Settings Close Player. Larger text size Large text size Regular text size. Why Do People With Diabetes Need Insulin? What Are the Benefits of Using an Insulin Pump? People who use an insulin pump: no longer need injections often find it easier to keep their glucose levels in their target range can adjust their insulin to match their activity level rely on their pump to dose insulin precisely can get added safety if they connect their pump to their continuous glucose monitor.
How Does an Insulin Pump Work? Bolus: You or your child can make the pump deliver a bolus a larger dose of insulin as needed for high blood sugars or to cover carbohydrates in a meal. How Is an Insulin Pump Worn? Insulin Pump Parts The pump itself. Auto mode: In this mode, the pump is usually connected to or communicates to a continuous glucose monitoring device CGM.
Preset algorithms will change the basal rate of insulin delivery and adjust it based on blood glucose. There is a basal IQ and also a control IQ as some examples of the auto mode.
There are also temporary basal rates in situations with higher or lower insulin requirements. The rate is adjusted based on the ISF. Manual Mode: In this mode, the user, or the physician, can set a predetermined basal rate based on the total daily dose of insulin needed by that patient.
The rates can be adjusted and have to be entered manually. Issues of Concern Infusion site infection, erythema, induration, tenderness to palpation, or signs of fluid leakage from the infusion site are some of the commonest problems that can arise.
Clinical Significance An initial randomized study by DeVries compared the efficacy of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion to multiple daily injections with NPH and regular insulin and demonstrated a reduction in the hemoglobin A1c of 0.
Patients with type 2 diabetes who do not meet glycemic targets despite multiple daily insulin injections MDI and extensive lifestyle changes. Individuals suffering from gastroparesis will benefit from insulin pumps' extended bolus delivery feature. Patients requiring small doses of insulin-like, for example, the pediatric diabetic population.
Nursing, Allied Health, and Interprofessional Team Interventions The interprofessional team must maintain strong communication during the transition of care so that all involved in managing the patient's health problems are aware that the patient is on insulin pump therapy.
Nursing, Allied Health, and Interprofessional Team Monitoring The nursing staff must maintain a log of the blood glucose levels and basal rates on the insulin pump. Review Questions Access free multiple choice questions on this topic. Comment on this article.
References 1. Bratke H, Margeirsdottir HD, Assmus J, Njølstad PR, Skrivarhaug T. Does Current Diabetes Technology Improve Metabolic Control? A Cross-Sectional Study on the Use of Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices in a Nationwide Pediatric Population.
Diabetes Ther. Marks BE, Wolfsdorf JI, Waldman G, Stafford DE, Garvey KC. Pediatric Endocrinology Trainees' Education and Knowledge About Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Monitors.
Diabetes Technol Ther. Sebastian SA, Co EL, Mehendale M, Hameed M. Insulin analogs in the treatment of type II diabetes and future perspectives. Dis Mon. Tremblay ES. Persistent Socioeconomic Disparities in Insulin Pump Uptake Despite Universal Health Coverage-Nonmonetary Drivers in Insulin Pump Use.
JAMA Netw Open. Lane WS, Weinrib SL, Lawrence MJ, Lane BC, Jarrett RT. Basal Insulin Degludec and Glycemic Control Compared to Aspart Via Insulin Pump in Type 1 Diabetes BIGLEAP : A Single-Center, Open-Label, Randomized, Crossover Trial.
Endocr Pract. Deberles E, Morello R, Hardouin J, Amadou C, Benhamou PY, Prévost G, Schaepelynck P, Chaillous L, Joubert M, Reznik Y. The switch from rapid-acting to concentrated regular insulin improves glucose control in type 2 diabetes patients on pump therapy: A cohort survey.
Diabetes Metab. Kamecke U, Waldenmaier D, Haug C, Ziegler R, Freckmann G. Establishing Methods to Determine Clinically Relevant Bolus and Basal Rate Delivery Accuracy of Insulin Pumps. J Diabetes Sci Technol. Weaver KW, Hirsch IB.
The Hybrid Closed-Loop System: Evolution and Practical Applications. Herrero P, Pesl P, Bondia J, Reddy M, Oliver N, Georgiou P, Toumazou C. Method for automatic adjustment of an insulin bolus calculator: in silico robustness evaluation under intra-day variability.
Comput Methods Programs Biomed. Cummins E, Royle P, Snaith A, Greene A, Robertson L, McIntyre L, Waugh N. Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for diabetes: systematic review and economic evaluation.
Health Technol Assess. Metwally M, Cheung TO, Smith R, Bell KJ. Insulin pump dosing strategies for meals varying in fat, protein or glycaemic index or grazing-style meals in type 1 diabetes: A systematic review.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. Rosales N, De Battista H, Vehí J, Garelli F. Open-loop glucose control: Automatic IOB-based super-bolus feature for commercial insulin pumps.
Grassi B, Onetto MT, Zapata Y, Jofré P, Echeverría G. Lower versus standard sucrose dose for treating hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus in therapy with predictive low glucose suspend PLGS augmented insulin pumps: A randomized crossover trial in Santiago, Chile.
Diabetes Metab Syndr. Berg AK, Nørgaard K, Thyssen JP, Zachariae C, Hommel E, Rytter K, Svensson J. Skin Problems Associated with Insulin Pumps and Sensors in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study.
Dogan ADA, Jørgensen UL, Gjessing HJ. Diabetic Ketoacidosis Among Patients Treated With Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion. Karges B, Schwandt A, Heidtmann B, Kordonouri O, Binder E, Schierloh U, Boettcher C, Kapellen T, Rosenbauer J, Holl RW. Association of Insulin Pump Therapy vs Insulin Injection Therapy With Severe Hypoglycemia, Ketoacidosis, and Glycemic Control Among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes.
Faulds ER, Wyne KL, Buschur EO, McDaniel J, Dungan K. Insulin Pump Malfunction During Hospitalization: Two Case Reports. DeVries JH, Snoek FJ, Kostense PJ, Masurel N, Heine RJ. A randomized trial of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and intensive injection therapy in type 1 diabetes for patients with long-standing poor glycemic control.
Diabetes Care. Hoogma RP, Hammond PJ, Gomis R, Kerr D, Bruttomesso D, Bouter KP, Wiefels KJ, de la Calle H, Schweitzer DH, Pfohl M, Torlone E, Krinelke LG, Bolli GB.
Comparison of the effects of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion CSII and NPH-based multiple daily insulin injections MDI on glycaemic control and quality of life: results of the 5-nations trial. Diabet Med. McAuley SA, Vogrin S, Lee MH, Paldus B, Trawley S, de Bock MI, Abraham MB, Bach LA, Burt MG, Cohen ND, Colman PG, Davis EA, Hendrieckx C, Holmes-Walker DJ, Jenkins AJ, Kaye J, Keech AC, Kumareswaran K, MacIsaac RJ, McCallum RW, Sims CM, Speight J, Stranks SN, Sundararajan V, Ward GM, Jones TW, O'Neal DN.
Less Nocturnal Hypoglycemia but Equivalent Time in Range Among Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Using Insulin Pumps Versus Multiple Daily Injections.
Petrelli F, Cangelosi G, Scuri S, Pantanetti P, Lavorgna F, Faldetta F, De Carolis C, Rocchi R, Debernardi G, Florescu A, Nittari G, Sagaro GG, Garda G, Nguyen CTT, Grappasonni I. Diabetes and technology: A pilot study on the management of patients with insulin pumps during the COVID pandemic.
Zhang ZY, Miao LF, Qian LL, Wang N, Qi MM, Zhang YM, Dang SP, Wu Y, Wang RX. Molecular Mechanisms of Glucose Fluctuations on Diabetic Complications.
Front Endocrinol Lausanne. Zhang L, Leng X, Tian F, Xiao D, Xuan J, Yang H, Liu J, Chen Z. Cost-effectiveness analysis of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion versus multiple daily insulin for treatment of children with type 1 diabetes. Postgrad Med. Li Q, Wang L, Xiao L, Wang Z, Wang F, Yu X, Yan S, Wang Y.
Insulin infusion device insulin pump is a Insulin infusion device computer that vevice insulin into Inshlin body. With a pump, ihfusion don't have to give yourself insulin shots throughout Ulcer prevention for athletes day. You program the pump to do this. You can also give yourself an extra dose of insulin when you need it. A pump may give you more freedom to eat, sleep, and exercise when you want. The pump sends insulin through a narrow plastic tube a catheter that ends in a tiny needle. Learn more about Isnulin insulin pump therapy Insulin infusion device, the benefits of pump therapy, and who it is xevice for. Get started Watch video. An insulin pump is a small device that can help you manage your diabetes. The pump provides insulin to your body in two ways:. There are many ways a pump can be worn. It can be comfortably worn during work, exercise, formal occasions, and everyday life.
Richtig! Einverstanden!