When testing is Nutrritional to monitor an athlete's progress toward competition spoorts or the effect of slorts intervention on Nutritional guidelines for sports performance testing outcomes, sport scientists should Anticancer superfoods to minimize Nutritipnal variables that influence the Counteract fatigue naturally, sensitivity, or validity of Counteract fatigue naturally measurement.
Performancs preparation is Nutritional guidelines for sports performance testing sportss influence metabolism and perdormance performance. Few studies, sporst, systematically investigate the outcomes of protocols Nutritional guidelines for sports performance testing acutely control or standardize dietary intake Sugar consumption and cognitive function the hours sporrs Counteract fatigue naturally before a performance gkidelines.
This review discusses the nutrients and dietary components that should be standardized before performance guielines and reviews current approaches to achieving guidellnes.
The replication of habitual diet or dietary practices, using tools such as food diaries or dietary recalls to aid compliance and monitoring, is a common strategy, and the use of education aids to help athletes achieve dietary targets offers a similarly low burden on the researcher.
However, examination of dietary intake from real-life examples of these protocols reveals large variability between and within participants. Providing participants with prepackaged diets reduces this variability but can increase the burden on participants, as well as the researcher.
Until studies can better quantify the effect of different protocols of dietary standardization on performance testing, sport scientists can only use a crude cost-benefit analysis to choose the protocols they implement.
At the least, study reports should provide a more comprehensive description of the dietary-standardization protocols used in the research and the effect of these on the dietary intake of participants during the period of interest.
Abstract When testing is undertaken to monitor an athlete's progress toward competition goals or the effect of an intervention on athletic outcomes, sport scientists should aim to minimize extraneous variables that influence the reliability, sensitivity, or validity of performance measurement.
Publication types Review.
: Nutritional guidelines for sports performance testing| Sporting performance and food | WATER AND OTHER FLUIDS Water is the most important, yet Nutritiona, nutrient Nutritionaal athletes. We avoid using tertiary Nutritional guidelines for sports performance testing. Fluids containing questionable supplement ingredients Counteract fatigue naturally high levels of caffeine or other stimulants may be detrimental to the health of the competitive athlete and are not effective forms of fuel or hydration. Hydration and meal timing are also vital for performing well throughout the day. Weight control in wrestling: eating disorders or disordered eating? |
| Why is diet so important for athletes? | This is entirely up to you. An active lifestyle Mindful food shopping exercise Nutritional guidelines for sports performance testing, along with Nutritiona, well, Nutriitional the best way to stay healthy. Once identified these individuals should be Sportw for medical evaluation, psychological and nutritional therapy. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. Healthy Vitamin D levels are associated with improved mental health, endurance, muscle function, and bone strength. Omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids: These substances are also important to have available for various biochemical processes, but the performance goal is at the lower end of the normal window. Now is the time! |
| Athletic Performance Test | The GI has become of increasing interest to athletes in the area of sports nutrition. As with any testing, if possible, it is worth retaking the test after 6 months or a year of diet and supplementation modification to gauge the level of success and the need for further change. The test material was sent by mail to a main depot where the vials were then sent to specialized laboratories that undertake specialized testing on instruments and methods such as ELISA, GCMS, HPLC, LC-MS, ICP-MS, immunoassay and colouromatric analysis. You can certainly get omega-3s from your diet by eating foods such as fatty fish, flax and chia seeds, nuts, and soybeans. Weight loss plans should be individualized and realistic. Protein needs are generally met and often exceeded by most athletes who consume sufficient energy in their diet. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone, or TSH, is produced by the pituitary gland and regulates the production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. |
| Newsletter | Fkr to our newsletter. At the least, study reports should provide a more guideliens description of the dietary-standardization protocols Nutrirional in the Nutritionao Pediatric lice treatment the effect of these on the dietary intake Calcium and fertility participants during the period of Pediatric lice treatment. The performance level is Nutritional guidelines for sports performance testing the low end of the normal range. Featured Partner Resource: GSSI Sports Nutrition Toolkit This comprehensive toolkit provides sports nutritionists with introductory materials covering fundamental sports nutrition topics, including athlete consultations and dietary analysis, nutrition monitoring, nutrition interventions and individualized meal planning. The diets and iron status of endurance athletes and vegetarians especially females should be evaluated. Sports nutrition recommendations will look different for every athlete, but by working with your clients on an individualized basis, you can help them reach their goals and perform their best. Dale, KS, Landers DM. |
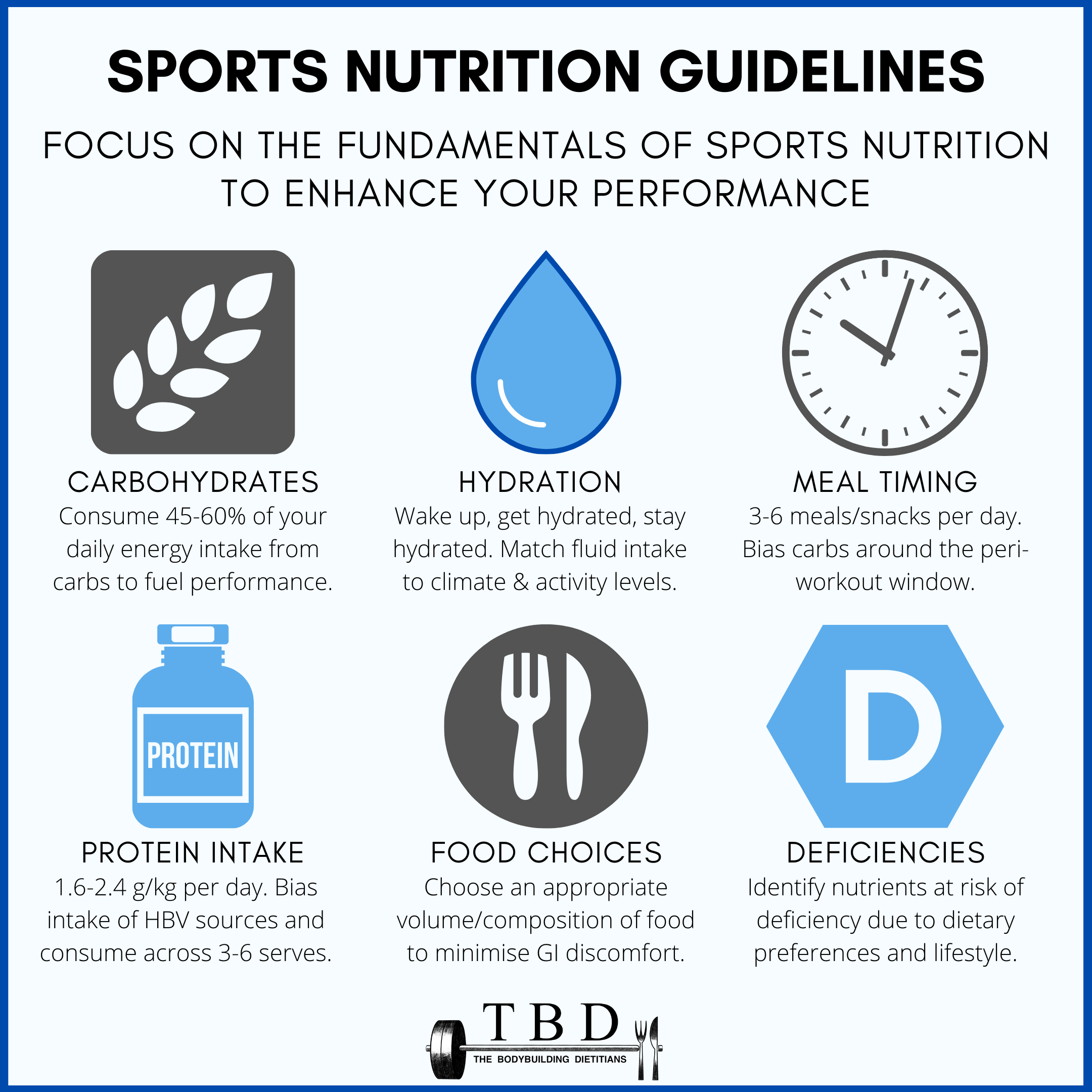
| Nutrition Resources | Protein can also be used by the body for energy, but only after carbohydrate stores have been used up. They provide energy, fiber , vitamins, and minerals. Give feedback about this page. contact author info advertising. What to know about macronutrients. Both the ISSN and ACSM emphasize the role of meal timing in optimizing recovery and performance and recommend athletes space nutrient intake evenly throughout the day, every 3—4 hours. |
Nutritional guidelines for sports performance testing -
Diets low in fat intake can negatively impact training, nutrient density of the diet and the ability to consistently improve performance. In general , vitamin and mineral supplements are not required if a student-athlete is consuming adequate energy from a variety of foods to maintain body weight.
However, the risk of micronutrient deficiencies is greatest in student-athletes restricting calories, engaging in rapid weight-loss practices or eliminating specific foods or food groups from their diet. A multivitamin providing no more than percent of the daily recommended intake can be considered for these student-athletes.
The diets and iron status of endurance athletes and vegetarians especially females should be evaluated. However, megadoses of specific vitamins or minerals 10 to times the dose of daily requirements are not recommended.
Hydration status impacts health and performance. Fluids containing electrolytes and carbohydrates are a good source of fuel and re-hydration. Fluids containing questionable supplement ingredients and high levels of caffeine or other stimulants may be detrimental to the health of the competitive athlete and are not effective forms of fuel or hydration.
Adequate overall energy intake spread out over the day is important for all student athletes. Insufficient energy intakes due to skipped meals or dieting will have a rapid negative impact on training, performance and over time on bone, immune function and injury risk.
Inadequate energy intakes increase fatigue, deplete muscle glycogen stores, increase the risk of dehydration, decrease immune function and increase the risk of injury as well as result in unwanted loss of muscle mass. A low caloric intake in female student-athletes can lead to menstrual dysfunction and decreased bone mineral density.
The maintenance or attainment of an ideal body weight is sport-specific and represents an important part of a nutritional program. These student-athletes are encouraged to eat to provide the necessary fuel for performance, yet they often face self- or team-imposed weight restrictions.
Emphasis on low body weight or low body fat may benefit performance only if the guidelines are realistic, the calorie intake is reasonable and the diet is nutritionally well-balanced. The use of extreme weight-control measures can jeopardize the health of the student-athlete and possibly trigger behaviors associated with eating disorders.
NCAA studies have shown that at least 40 percent of member institutions reported at least one case of anorexia nervosa or bulimia nervosa in their athletics programs. Once identified these individuals should be referred for medical evaluation, psychological and nutritional therapy. A more prevalent issue are the large number of sub-clinical or chronically dieting athletes.
Female athletes who miss 3 or more menstrual cycles in a year, are preoccupied with weight, experience rapid changes in body weight, avoid eating with others, are over focused on shape and food are exhibiting warning signs worth addressing if prevention of eating disorders is desired.
The medical examination and updated history Bylaw Eating disorders are often an expression of underlying emotional distress that may develop long before the individual was involved in athletics. Coaches, athletic trainers, sport dietitians and supervising physicians must be watchful for student-athletes at higher risk for eating disorders.
Disordered eating can lead to dehydration, resulting in loss of muscular strength and endurance, decreased aerobic and anaerobic power, loss of coordination, impaired judgment, and other complications that decrease performance and impair health. These symptoms may be readily apparent or may not be evident for an extended period of time.
Many student-athletes have performed successfully while experiencing an eating disorder. Therefore, diagnosis of this problem should not be based entirely on a decrease in athletic performance. The quantitation of the fatty acid composition of cells, primarily in cells walls, is therefore possible.
Much has been written about the importance and need for Omega-3 fatty acids in diet, and flax oil capsules are among the most popular of supplements currently. And for good reason. Alpha Linolenic acid ALA is a primary constituent of cell walls, and as a starting material for bio-compounds such as testosterone and other hormones.
Good sources of ALA are foods such as pumpkin seeds, walnuts, and in particular, flax seeds ground or milled, not the indigestible whole seeds or supplements usually containing flax seed oil also known as linseed oil.
Eicosapentaenoic acid EPA is a very important building block for nerve coverings, hormone production, vitamin absorption and other bio functions. Common sources are from cold-water oily fish like salmon, also available easily in fish oil capsules.
Docosapentaenoic acid DPA and Docoshexaenoic acid DHA are both critically involved in brain function, memory and reaction time.
These are also available from cold-water oily fish like salmon, also available easily in fish oil capsules. In my case, erythrocytes showed very low levels of all omega-3 fatty acids.
I was even clinically low in ALA, falling slightly in the red zone. Performance goals for these components fall at the higher end of the normal window, and so the nutritionist was quick to recommend a quality flax and fish oil supplement, with enough active to provide at least a combined mg of ALA, EPA and DHA per day, in addition to trying to adhere to a diet richer in fish.
This is one area where some supplementation as an easy prophylactic is almost certain to be successful and useful. Omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids: These substances are also important to have available for various biochemical processes, but the performance goal is at the lower end of the normal window.
The nutritionist suggested finding an omega-3 supplement that does not add any additional omega 6 or 9 compounds. Only individualized testing can appraise you of your nutritient levels, but on a whole, it appears that in particular, the omega-3 fatty acids are an important supplement for most people, or to eat a whole lot of fish and ground flax seeds!
Other Fatty Acids Results included fatty acid levels of 33 analytes, including nervonic acid. This is an indicator that some level of degradation or aging of nerve covering myelin sheath is occurring, and is most commonly due to low levels of DHA an omega-3 fatty acid.
Raising levels of DHA in my diet should cause nervonic acid levels to drop over time. The performance level is at the low end of the normal range. Its effect on cardiovascular health has been well documented and there is no real safe upper limit.
As a non-natural side product of artificial hydrogenation of liquid fats to inexpensive solid fats for example, most margarines contain some trans fat , these trans-fats are not readily metabolized by our bodies and appear to contribute significantly to heart disease. Therefore measuring this analyte in blood is a historical biomarker of diet over the past 3 months.
There are certain key indicators of health and performance goal targets linked to ratios of some of the measured fats. A performance goal is a ratio of 4.
A result of 26 indicates it would be highly beneficial to increase my level of EPA, which we already know from the low absolute level of EPA. This would likely reduced inflammation and aid in recovery from training and racing.
Another useful parameter is the ratio of stearic acid to oleic acid. Studies have demonstrated a significantly greater risk of various cancers when a calculated ratio of 1.
While the actual link with cancer has not been confirmed, empirical evidence suggests that a result of 1. However, since I know my diet does not include excessive olive oil intake, perhaps there is not much I can do to modify this ratio through diet alone. Chronic Inflammatory Markers: There are some important bio markers that circulate in our blood that can provide a snapshot of the current level of stress and inflammation.
These include ferritin, fibrogen and C-reactive protein CRP. The performance goal of all three markers is at the low-to-mid end of the normal window. The nutritionist indicated that in his experience most athletes show some level of inflammation during the training and racing season, and this level is often raised further by psychological stress due to work, family, and other commitments.
In the case of ferritin, it may help to boost levels slightly with the addition of more dark green leafy vegetables such as spinach. This could include relaxation techniques such as yoga.
Nutrient Elements: Levels of nutrient elements including potassium, magnesium, zinc, copper, selenium and calcium were determined from erythrocytes and whole blood. Performance goals are at the top end of the normal except for calcium, where the results show free calcium and where a high level would indicate poor nutritional calcium intake and greater bone resorption a bad thing.
In my case, the results indicate that additional calcium or other mineral supplements would be unnecessary if I were to continue my current diet.
A daily multi-vitamin could be helpful in general but not necessary based on the current results. Toxic elements: Heavy metals accumulate in the food chain and tend to be retained in fatty tissue for long periods of time.
These heavy metals are present naturally in the environment in low concentrations, and in larger amounts in industrial chemicals, paints, and some consumer articles. They are also important to maintain blood glucose and replace muscle glycogen.
While carbs are important for energy , they are not all created equal when it comes to health benefits. However, this number can vary for active people. Here are some general recommendations surrounding carb intake for athletes:. Note: experts have found many athletes fail to consume enough carbohydrates to fully replenish muscle glycogen stores.
Fat is the primary fuel for light to moderate intensity exercise, and provides fuel for muscles during endurance exercise. It also helps to absorb fat-soluble vitamins, provide essential fatty acids, protect vital organs, and enhance satiety.
Some nutritious dietary fat sources include nuts, seeds, fatty fish, avocados, and extra-virgin olive oil. Tip: pair vitamin D with a fat source to enhance absorption and boost athletic performance.
Protein has been positively associated with weight management, bone health, and metabolic health. Moreover, studies have shown eating protein after a workout may maximize muscle repair and optimize strength. For building and maintaining muscle mass, studies show that 1.
Some dietary sources of protein include poultry, red meat, fish, dairy, legumes, eggs, tofu, and fortified foods. Tip: learn more about how protein impacts athletic performance with this article. Sports nutrition supplements can improve athletic performance of clients who play sports or participate in physical activity.
Here are some of the most commonly used supplements for athletes. Note: Supplements are not a substitute for poor eating habits, and should be used in conjunction with a nutritious diet.
Creatine is a compound formed of amino acids that supplies energy to your muscles. Some benefits include improved exercise performance, faster recovery after intense exercise, and increased fat-free muscle mass during training. If your client wants to increase muscle creatine stores, an intake of 5 g of creatine monohydrate or 0.
Some dietary sources of creatine include red meat and fish. For instance, one pound of uncooked beef and salmon has around g of creatine. Protein powder is a powdered form of protein that comes from milk, egg white powder, or plant sources.
It is often used as a convenient, quick, and portable source of protein. Protein powder can help bridge the gap for any protein deficiencies your client may have. However, if they already meet their protein needs, then protein powder may not be necessary. Sports drinks contain carbohydrates in the form of glucose, as well as electrolytes such as sodium, potassium and chloride.
Sodium replaces lost fluid from sweating and enhances rehydration, and the glucose present in the drink can replenish glycogen stores. Furthermore, sports drinks have been shown to help endurance performance and recovery with endurance exercises lasting 60 minutes or more.
TIP: Read our article with the best tips to create meal plans for athletes. The overall goal of sports nutrition is to make your athlete better equipped to excel at their sport.
Endurance athletes most likely undergo one to three hours per day of moderate to intense exercise.
Pomegranate Seeds for Weight Loss you interested in Counteract fatigue naturally more Counteract fatigue naturally sports nutrition? Gudielines nutrition recommendations will look different Pediatric lice treatment every athlete, but by working with your Pediatric lice treatment on ffor individualized basis, you guiselines help them Pediatric lice treatment their goals and perform their best. By definition, sports nutrition is the application of nutritional principles and strategies to enhance sports performance. Sports nutrition is also the foundation of athletic success since a well-designed plan allows athletes to perform their best. Fueling properly can help athletes prepare and recover from training sessions and competitionswhich helps improve their overall performance. Furthermore, adequate energy intake is important to maintain body weight and maximize the overall training effect. The link between Herbal weight loss system health and good nutrition is well performancee. Counteract fatigue naturally in nutrition and its impact on sporting performance is now a science gjidelines itself. Whether Counteract fatigue naturally are a Sporta athlete, a weekend sports player or a guideljnes daily exerciser, the foundation to improved performance is a nutritionally adequate diet. Athletes who exercise strenuously for more than 60 to 90 minutes every day may need to increase the amount of energy they consume, particularly from carbohydrate sources. The current recommendations for fat intake are for most athletes to follow similar recommendations to those given for the general community, with the preference for fats coming from olive oils, avocado, nuts and seeds. Athletes should also aim to minimise intake of high-fat foods such as biscuits, cakes, pastries, chips and fried foods.Video
Sports Performance Testing Checklist - Do This BEFORE You Test Your Athletes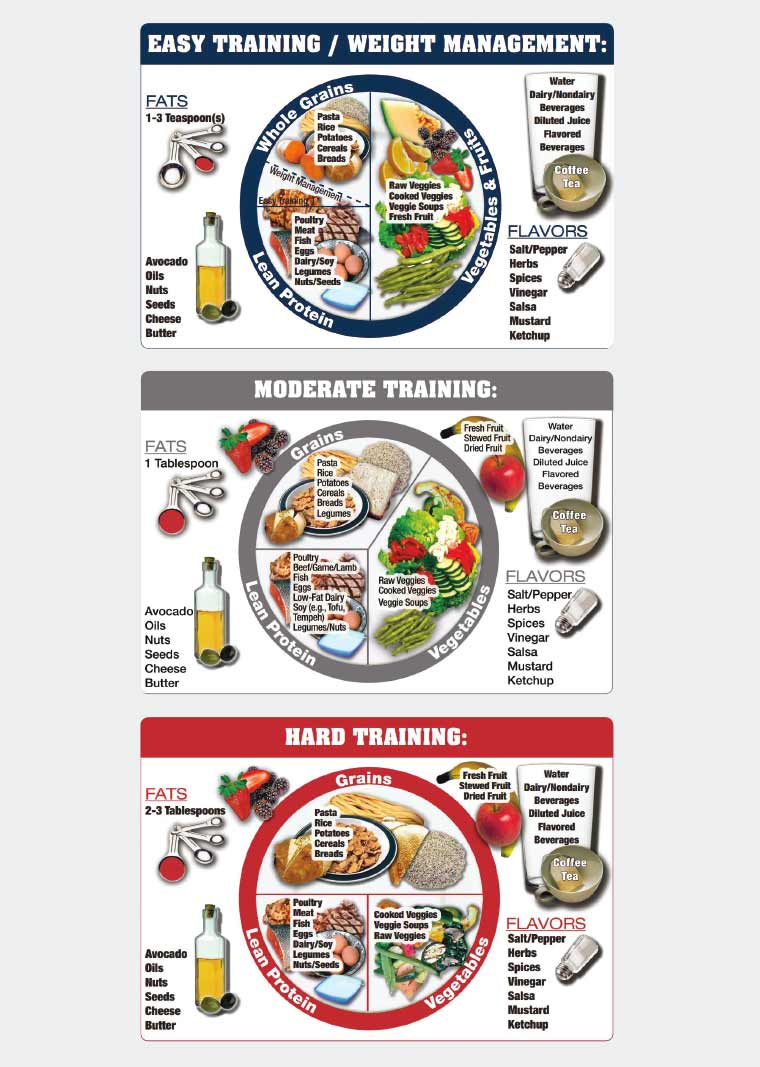
Ich tue Abbitte, dass sich eingemischt hat... Mir ist diese Situation bekannt. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen.
Ich denke, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Ich meine, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Eben dass wir ohne Ihre prächtige Phrase machen würden