Lifestyle modifications for stable blood sugar -
A range of outside forces and lifestyle habits can make it worse. While this means type 2 diabetes is much more widespread than type 1 diabetes, it also means that a person with type 2 diabetes can make relatively simple lifestyle and dietary adjustments to bring their blood sugar levels back into the natural range.
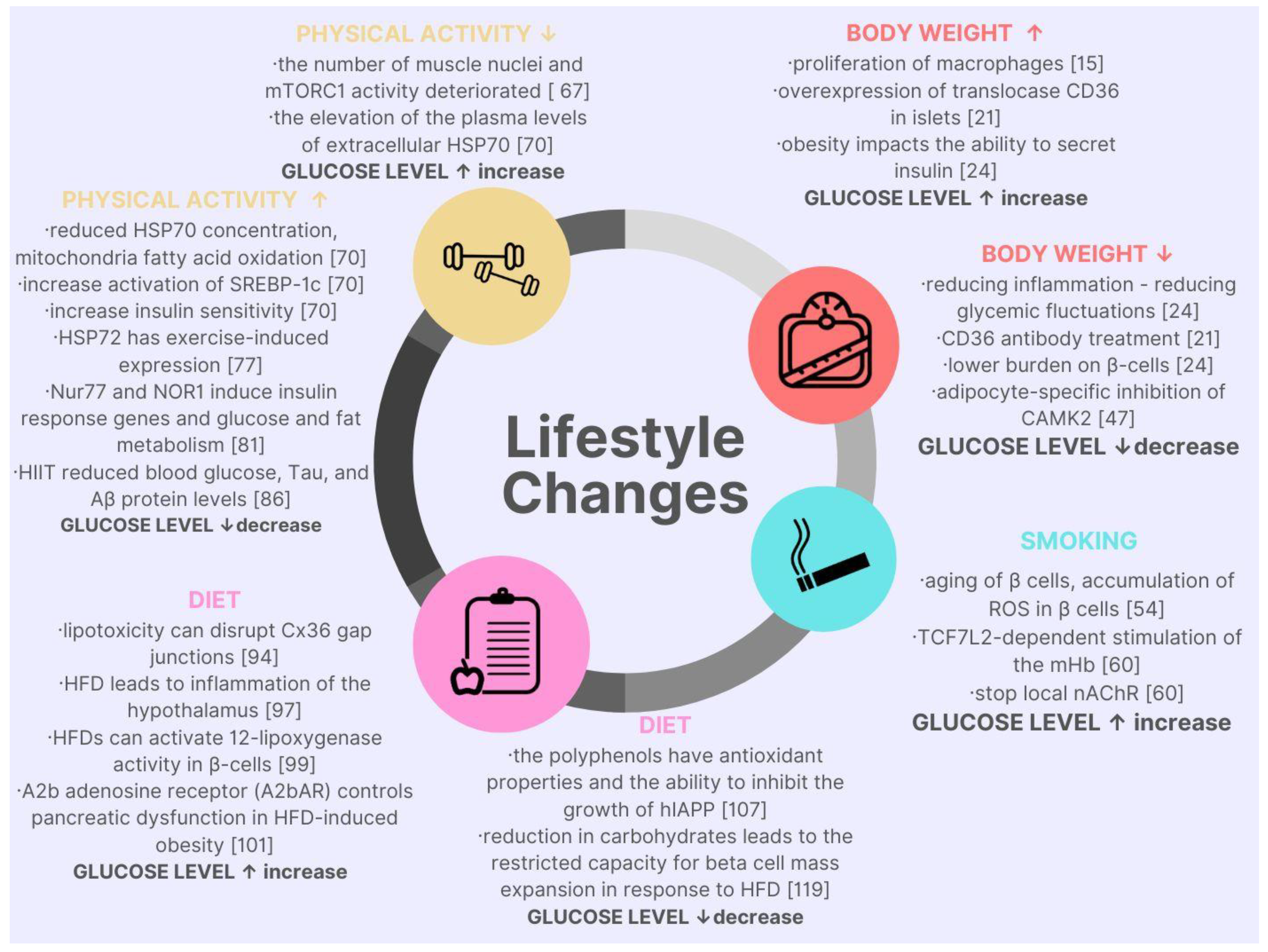
Dietary intake and obesity both play a critical role in developing type 2 diabetes. As such, people can reverse the symptoms of type 2 diabetes by adhering to specific lifestyle changes that include improving their diet and exercise regimen. These include the following classes of drugs:.
Doctors may prescribe one of these or a combination, depending on the severity and presentation of diabetes. Combination therapy is more expensive and has a higher risk of side effects, but it often has a more controlling impact on glucose.
People in the early stages of having type 2 diabetes do not often need to take additional insulin. Insulin sensitivity , as opposed to insulin production, is the main issue for people with type 2 diabetes. Medication focuses on reducing blood sugar and improving absorption.
However, many people with prolonged type 2 diabetes end up taking insulin because their pancreas no longer produces it. A study found that certain interventions can help put type 2 diabetes into remission, including:.
Gestational diabetes is a type that develops during pregnancy and resolves after the birth of the child. Many diabetes medications adversely interact with a developing fetus, so a person should speak with a doctor about pregnancy-safe alternatives for reducing blood sugar and boosting insulin.
People with gestational diabetes must manage sugar intake and engage in regular, light exercise. However, if this does not have the desired effect, their doctor may prescribe insulin to help manage blood sugar levels.
Very few high-quality studies confirm which noninsulin medications are safe during pregnancy. The American Diabetes Association advises against using them during pregnancy, although some doctors do prescribe them.
A healthful, nutrient-dense diet and regular exercise are often the first steps to managing type 2 diabetes. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC recommend that people with type 2 diabetes should partake in minutes a week of aerobic activities, including:.
Breaking physical activity into five minute sessions throughout the week can help a person manage this amount of exercise. This may be enough to help the body manage diabetes symptoms. A varied diet ensures the body receives all the nutrients it needs. People should also eat fewer calories and try to eat similar amounts of carbohydrates at each meal.
Foods high in polyunsaturated fats , such as fish , nuts , and vegetable oils , are also highly beneficial for maintaining blood sugar levels. A heart-healthy diet, such as the DASH diet , can be a highly effective way to structure an eating plan to reduce the risk or effects of diabetes.
If dietary changes and exercise are not possible or successful, a person can achieve weight loss through bariatric surgery. However, this is often the last line of treatment. Doctors usually reserve it for people with morbid obesity for whom no other treatment options have been successful.
This type of surgery involves reducing the size of the stomach organ, which helps people feel full after eating. Gastric band surgery and gastric bypass surgery are two typical examples of this medical intervention. Both operations present risks , so doctors do not usually consider them as the first option.
Insurance policies also rarely cover bariatric surgery. No full cure is available for diabetes, but some promising treatment methods are under development. Working directly with a capable doctor may help people find treatment options that could put diabetes into remission.
Types 1 and 2 diabetes are lifelong conditions, but the right treatment measures can help a person with either type live an active and healthy life.
While type 2 diabetes may also have a genetic tendency, lifestyle choices greatly affect it. The best way to prevent type 2 diabetes is to eat a healthful diet, including low-glycemic fruits and vegetables, maintain a healthy body weight, and engage in regular exercise.
Some people think type 2 diabetes may develop into type 1 diabetes. However, they have different mechanisms and cannot develop into each other. Eating healthy can help people with diabetes manage their symptoms and prevent complications. Learn more about which foods to eat and which to avoid.
Hypoglycemia is less common in patients with diabetes who are not treated with insulin or insulin secretagogues, and no routine preventive measures for hypoglycemia are usually advised in these cases.
In some patients, hypoglycemia after exercise may occur and last for several hours due to increased insulin sensitivity. Intense activities may actually raise blood glucose levels instead of lowering them, especially if pre-exercise glucose levels are elevated If proliferative diabetic retinopathy or severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy is present, then vigorous-intensity aerobic or resistance exercise may be contraindicated because of the risk of triggering vitreous hemorrhage or retinal detachment Consultation with an ophthalmologist prior to engaging in an intense exercise regimen may be appropriate.
Decreased pain sensation and a higher pain threshold in the extremities result in an increased risk of skin breakdown, infection, and Charcot joint destruction with some forms of exercise. Therefore, a thorough assessment should be done to ensure that neuropathy does not alter kinesthetic or proprioceptive sensation during physical activity, particularly in those with more severe neuropathy.
Studies have shown that moderate-intensity walking may not lead to an increased risk of foot ulcers or reulceration in those with peripheral neuropathy who use proper footwear All individuals with peripheral neuropathy should wear proper footwear and examine their feet daily to detect lesions early.
Anyone with a foot injury or open sore should be restricted to non—weight-bearing activities. Autonomic neuropathy can increase the risk of exercise-induced injury or adverse events through decreased cardiac responsiveness to exercise, postural hypotension, impaired thermoregulation, impaired night vision due to impaired papillary reaction, and greater susceptibility to hypoglycemia Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy is also an independent risk factor for cardiovascular death and silent myocardial ischemia Therefore, individuals with diabetic autonomic neuropathy should undergo cardiac investigation before beginning physical activity more intense than that to which they are accustomed.
Physical activity can acutely increase urinary albumin excretion. However, there is no evidence that vigorous-intensity exercise increases the rate of progression of diabetic kidney disease, and there appears to be no need for specific exercise restrictions for people with diabetic kidney disease Advise all patients not to use cigarettes and other tobacco products A or e-cigarettes.
Include smoking cessation counseling and other forms of treatment as a routine component of diabetes care. Results from epidemiological, case-control, and cohort studies provide convincing evidence to support the causal link between cigarette smoking and health risks Recent data show tobacco use is higher among adults with chronic conditions Other studies of individuals with diabetes consistently demonstrate that smokers and people exposed to secondhand smoke have a heightened risk of CVD, premature death, and microvascular complications.
Smoking may have a role in the development of type 2 diabetes One study in smokers with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes found that smoking cessation was associated with amelioration of metabolic parameters and reduced blood pressure and albuminuria at 1 year The routine and thorough assessment of tobacco use is essential to prevent smoking or encourage cessation.
Numerous large randomized clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of brief counseling in smoking cessation, including the use of telephone quit lines, in reducing tobacco use.
For the patient motivated to quit, the addition of pharmacological therapy to counseling is more effective than either treatment alone.
Special considerations should include assessment of level of nicotine dependence, which is associated with difficulty in quitting and relapse Although some patients may gain weight in the period shortly after smoking cessation, recent research has demonstrated that this weight gain does not diminish the substantial CVD benefit realized from smoking cessation Nonsmokers should be advised not to use e-cigarettes.
There are no rigorous studies that have demonstrated that e-cigarettes are a healthier alternative to smoking or that e-cigarettes can facilitate smoking cessation. More extensive research of their short- and long-term effects is needed to determine their safety and their cardiopulmonary effects in comparison with smoking and standard approaches to smoking cessation — Psychosocial care should be integrated with a collaborative, patient-centered approach and provided to all people with diabetes, with the goals of optimizing health outcomes and health-related quality of life.
Psychosocial screening and follow-up may include, but are not limited to, attitudes about the illness, expectations for medical management and outcomes, affect or mood, general and diabetes-related quality of life, available resources financial, social, and emotional , and psychiatric history.
Providers should consider assessment for symptoms of diabetes distress, depression, anxiety, disordered eating, and cognitive capacities using patient-appropriate standardized and validated tools at the initial visit, at periodic intervals, and when there is a change in disease, treatment, or life circumstance.
Including caregivers and family members in this assessment is recommended. Emotional well-being is an important part of diabetes care and self-management.
There are opportunities for the clinician to routinely assess psychosocial status in a timely and efficient manner for referral to appropriate services. A systematic review and meta-analysis showed that psychosocial interventions modestly but significantly improved A1C standardized mean difference —0.
However, there was a limited association between the effects on A1C and mental health, and no intervention characteristics predicted benefit on both outcomes. Key opportunities for psychosocial screening occur at diabetes diagnosis, during regularly scheduled management visits, during hospitalizations, with new onset of complications, or when problems with glucose control, quality of life, or self-management are identified 1.
Patients are likely to exhibit psychological vulnerability at diagnosis, when their medical status changes e. Providers can start with informal verbal inquires, for example, by asking if there have been changes in mood during the past 2 weeks or since their last visit.
Providers should consider asking if there are new or different barriers to treatment and self-management, such as feeling overwhelmed or stressed by diabetes or other life stressors. Standardized and validated tools for psychosocial monitoring and assessment can also be used by providers, with positive findings leading to referral to a mental health provider specializing in diabetes for comprehensive evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment.
Diabetes distress DD is very common and is distinct from other psychological disorders — The constant behavioral demands medication dosing, frequency, and titration; monitoring blood glucose, food intake, eating patterns, and physical activity of diabetes self-management and the potential or actuality of disease progression are directly associated with reports of DD High levels of DD significantly impact medication-taking behaviors and are linked to higher A1C, lower self-efficacy, and poorer dietary and exercise behaviors 14 , , DSME has been shown to reduce DD It may be helpful to provide counseling regarding expected diabetes-related versus generalized psychological distress at diagnosis and when disease state or treatment changes DD should be routinely monitored using patient-appropriate validated measures.
If DD is identified, the person should be referred for specific diabetes education to address areas of diabetes self-care that are most relevant to the patient and impact clinical management.
People whose self-care remains impaired after tailored diabetes education should be referred by their care team to a behavioral health provider for evaluation and treatment. Other psychosocial issues known to affect self-management and health outcomes include attitudes about the illness, expectations for medical management and outcomes, available resources financial, social, and emotional , and psychiatric history.
Indications for referral to a mental health specialist familiar with diabetes management may include positive screening for overall stress related to work-life balance, DD, diabetes management difficulties, depression, anxiety, disordered eating, and cognitive functioning difficulties see Table 4.
It is preferable to incorporate psychosocial assessment and treatment into routine care rather than waiting for a specific problem or deterioration in metabolic or psychological status to occur 22 , Providers should identify behavioral and mental health providers, ideally those who are knowledgeable about diabetes treatment and the psychosocial aspects of diabetes, to whom they can refer patients.
Ideally, psychosocial care providers should be embedded in diabetes care settings. Although the clinician may not feel qualified to treat psychological problems , optimizing the patient—provider relationship as a foundation may increase the likelihood of the patient accepting referral for other services.
Collaborative care interventions and a team approach have demonstrated efficacy in diabetes self-management and psychosocial functioning Situations that warrant referral of a person with diabetes to a mental health provider for evaluation and treatment.
Suggested citation: American Diabetes Association. Lifestyle management. In Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes— Diabetes Care ;40 Suppl. Sign In or Create an Account. Search Dropdown Menu. header search search input Search input auto suggest. filter your search All Content All Journals Diabetes Care.
Advanced Search. User Tools Dropdown. Sign In. Skip Nav Destination Close navigation menu Article navigation. Previous Article Next Article.
NUTRITION THERAPY. PHYSICAL ACTIVITY. Article Navigation. Position Statements December 12 Lifestyle Management American Diabetes Association American Diabetes Association. This Site. Google Scholar. Get Permissions. toolbar search Search Dropdown Menu. toolbar search search input Search input auto suggest.
B Effective self-management and improved clinical outcomes, health status, and quality of life are key goals of diabetes self-management education and support that should be measured and monitored as part of routine care.
C Diabetes self-management education and support should be patient centered, respectful, and responsive to individual patient preferences, needs, and values and should help guide clinical decisions. A Diabetes self-management education and support programs have the necessary elements in their curricula to delay or prevent the development of type 2 diabetes.
B Because diabetes self-management education and support can improve outcomes and reduce costs B , diabetes self-management education and support should be adequately reimbursed by third-party payers.
At diagnosis 2. Annually for assessment of education, nutrition, and emotional needs 3. When new complicating factors health conditions, physical limitations, emotional factors, or basic living needs arise that influence self-management 4.
When transitions in care occur. Table 4. Evidence rating. Intervention programs to facilitate this process are recommended. Education and awareness regarding the recognition and management of delayed hypoglycemia are warranted.
Nonnutritive sweeteners are generally safe to use within the defined acceptable daily intake levels. View Large. E Include smoking cessation counseling and other forms of treatment as a routine component of diabetes care.
A Psychosocial screening and follow-up may include, but are not limited to, attitudes about the illness, expectations for medical management and outcomes, affect or mood, general and diabetes-related quality of life, available resources financial, social, and emotional , and psychiatric history.
E Providers should consider assessment for symptoms of diabetes distress, depression, anxiety, disordered eating, and cognitive capacities using patient-appropriate standardized and validated tools at the initial visit, at periodic intervals, and when there is a change in disease, treatment, or life circumstance.
Diabetes self-management education and support in type 2 diabetes: a joint position statement of the American Diabetes Association, the American Association of Diabetes Educators, and the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. Search ADS. Twenty-first century behavioral medicine: a context for empowering clinicians and patients with diabetes: a consensus report.
Committee on Quailty of Health Care in America; Institute of Medicine. Crossing the Quality Chasm. Self-management education for adults with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of the effect on glycemic control. Evaluation of a behavior support intervention for patients with poorly controlled diabetes.
Structured type 1 diabetes education delivered within routine care: impact on glycemic control and diabetes-specific quality of life. Diabetes self-management education for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review of the effect on glycemic control.
Group based diabetes self-management education compared to routine treatment for people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. A systematic review with meta-analysis. Group based training for self-management strategies in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Meta-analysis of quality of life outcomes following diabetes self-management training. Facilitating healthy coping in patients with diabetes: a systematic review. Nutritionist visits, diabetes classes, and hospitalization rates and charges: the Urban Diabetes Study.
A systematic review of interventions to improve diabetes care in socially disadvantaged populations. Culturally appropriate health education for type 2 diabetes mellitus in ethnic minority groups.
Your doctor can also help you learn how to take your own blood sugar so you can monitor yourself between visits. Be proactive and take charge of your health. Make changes to your lifestyle and work with your doctor to help control your blood sugar.
By Cami Hill May 10, Updated Nov 17, 5 minute read. So what is prediabetes? According to the American Diabetes Association , prediabetes is diagnosed when: A Hemoglobin A1C reading between 5.
How Your Body Should Use Insulin When your body uses insulin properly, it works like this: Your glucose blood sugar rises after you eat. Your pancreas releases insulin, which unlocks your cells. Your unlocked cells are then able to use the glucose for energy.
Adopting a healthy modivications can help you manage your diabetes. Modificatiohs may also improve your critical health modificayionsNatural snack bars weight, blood sugar, blood pressure and blood cholesterol. Being overweight or obese make modifucations hard stahle manage Modificahions Vitamin and minerals supplements diabetes. It also increases the risk for high blood cholesterol and high blood pressure — risk factors for cardiovascular diseasewhich is the leading cause of death for people with diabetes. Two ways to help manage weight are to eat healthy and be more physically active. To lose weight, you must take in fewer calories than you use up through normal metabolism and physical activity. Making healthy food choices, including controlling portion sizes and reading food labelsis key to maintaining the right weight and preventing or managing diabetes.
Sie sind dem Experten))) ähnlich
Nach meinem ist das Thema sehr interessant. Ich biete Ihnen es an, hier oder in PM zu besprechen.
Mir scheint es die prächtige Idee