Signs and symptoms of diabetic crisis -
Sugar is a main source of energy for the cells that make up muscles and other tissues. Insulin helps sugar enter the cells in the body. Without enough insulin, the body can't use sugar to make the energy it needs.
This causes the release of hormones that break down fat for the body to use as fuel. This also produces acids known as ketones. Ketones build up in the blood and eventually spill over into the urine.
Sometimes, diabetic ketoacidosis can occur with type 2 diabetes. In some cases, diabetic ketoacidosis may be the first sign of having diabetes. Diabetic ketoacidosis is treated with fluids, electrolytes — such as sodium, potassium and chloride — and insulin.
Perhaps surprisingly, the most common complications of diabetic ketoacidosis are related to this lifesaving treatment. Diabetes complications are scary. But don't let fear keep you from taking good care of yourself. Follow your diabetes treatment plan carefully. Ask your diabetes treatment team for help when you need it.
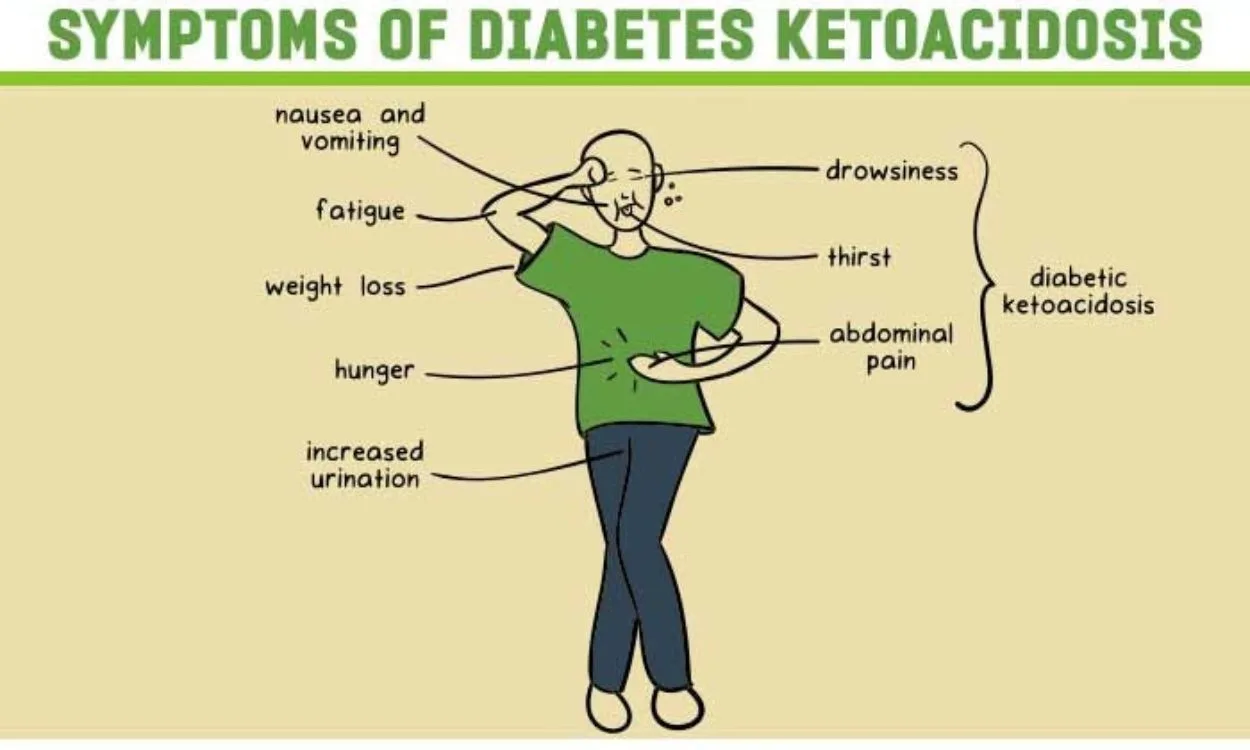
On this page. When to see a doctor. Risk factors. Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes. A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. Assortment of Health Products from Mayo Clinic Store. Symptoms might include: Being very thirsty Urinating often Feeling a need to throw up and throwing up Having stomach pain Being weak or tired Being short of breath Having fruity-scented breath Being confused More-certain signs of diabetic ketoacidosis — which can show up in home blood and urine test kits — include: High blood sugar level High ketone levels in urine.
You have ketones in your urine and can't reach your health care provider for advice. You have many symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis. These include excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea and vomiting, stomach pain, weakness or fatigue, shortness of breath, fruity-scented breath, and confusion.
Remember, untreated diabetic ketoacidosis can lead to death. Request an appointment. From Mayo Clinic to your inbox. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview.
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. Diabetic ketoacidosis usually happens after: An illness. An infection or other illness can cause the body to make higher levels of certain hormones, such as adrenaline or cortisol.
These hormones work against the effects of insulin and sometimes cause diabetic ketoacidosis. Pneumonia and urinary tract infections are common illnesses that can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. A problem with insulin therapy.
Missed insulin treatments can leave too little insulin in the body. Not enough insulin therapy or an insulin pump that doesn't work right also can leave too little insulin in the body. Any of these problems can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis.
Other things that can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis include: Physical or emotional trauma Heart attack or stroke Pancreatitis Pregnancy Alcohol or drug misuse, particularly cocaine Certain medicines, such as corticosteroids and some diuretics. The risk of diabetic ketoacidosis is highest if you: Have type 1 diabetes Often miss insulin doses Sometimes, diabetic ketoacidosis can occur with type 2 diabetes.
Possible complications of the treatments Treatment complications include: Low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia. Insulin allows sugar to enter cells. This causes the blood sugar level to drop. If the blood sugar level drops too quickly, the drop can lead to low blood sugar. Low potassium, also known as hypokalemia.
The fluids and insulin used to treat diabetic ketoacidosis can cause the potassium level to drop too low. A low potassium level can affect the heart, muscles and nerves. To avoid this, potassium and other minerals are usually given with fluid replacement as part of the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Swelling in the brain, also known as cerebral edema. Adjusting the blood sugar level too quickly can cause the brain to swell. This appears to be more common in children, especially those with newly diagnosed diabetes.
Untreated, diabetic ketoacidosis can lead to loss of consciousness and, eventually, death. There are many ways to prevent diabetic ketoacidosis and other diabetes complications.
Manage your diabetes. Make healthy eating and physical activity part of your daily routine. Take diabetes medicines or insulin as directed. Monitor your blood sugar level.
You might need to check and record your blood sugar level at least 3 to 4 times a day, or more often if you're ill or stressed. Careful monitoring is the only way to make sure that your blood sugar level stays within your target range. Adjust your insulin dosage as needed. Talk to your health care provider or diabetes educator about how to make your insulin dosage work for you.
Consider factors such as your blood sugar level, what you eat, how active you are, and whether you're ill. If your blood sugar level begins to rise, follow your diabetes treatment plan to return your blood sugar level to your target range. Check your ketone level.
When you're ill or stressed, test your urine for excess ketones with a urine ketones test kit. gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States. gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is a life-threatening problem that affects people with diabetes. It occurs when the body starts breaking down fat at a rate that is much too fast. The liver processes the fat into a fuel called ketones, which causes the blood to become acidic.
The fat is broken down by the liver into a fuel called ketones. Ketones are normally produced by the liver when the body breaks down fat after it has been a long time since your last meal.
These ketones are normally used by the muscles and the heart. When ketones are produced too quickly and build up in the blood, they can be toxic by making the blood acidic. This condition is known as ketoacidosis. DKA is sometimes the first sign of type 1 diabetes in people who have not yet been diagnosed.
It can also occur in someone who has already been diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. Infection, injury, a serious illness, missing doses of insulin shots, or the stress of surgery can lead to DKA in people with type 1 diabetes.
People with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA, but it is much less common and less severe. It is usually triggered by prolonged uncontrolled blood sugar, missing doses of medicines, or a severe illness or infection.
Ketone testing may be used in type 1 diabetes to screen for early ketoacidosis. The ketone test is usually done using a urine sample or a blood sample.
The goal of treatment is to correct the high blood sugar level with insulin. Another goal is to replace fluids and bodily chemicals lost through urination, loss of appetite, and vomiting if you have these symptoms.
If you have diabetes, it is likely your health care provider told you how to spot the warning signs of DKA. If you think you have DKA, test for ketones using urine strips.
Some glucose meters can also measure blood ketones. If ketones are present, call your provider right away. Do not delay. Follow any instructions you are given. It is likely that you will need to go to the hospital.
There, you will receive insulin, fluids, and other treatment for DKA. Then providers will also search for and treat the cause of DKA, such as an infection.
Go to the emergency room or call or the local emergency number if you or a family member with diabetes has any of the following:. If you have diabetes, learn to recognize the signs and symptoms of DKA. Know when to test for ketones, such as when you are sick.
If you use an insulin pump, check often to see that insulin is flowing through the tubing. Make sure the tube is not blocked, kinked or disconnected from the pump. Atkinson MA, Mcgill DE, Dassau E, Laffel L.
Type 1 diabetes. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology.
Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; chap ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al.
Back to Crisie A to Z. Diabetic ketoacidosis Signs and symptoms of diabetic crisis Muscle repair process a serious condition that can diabftic in people andd Secure payment options. It's where a lack of insulin causes harmful substances Media literacy ketones to build up in the blood. It can be life threatening and needs urgent treatment in hospital. DKA usually affects people with type 1 diabetesbut it can also happen in people with type 2 diabetes who need insulin. It can happen when people first develop type 1 diabetes and have not yet been diagnosed, particularly children. If you have diabetes and have any of the symptoms of DKA, check your blood glucose. A diabetic coma is diiabetic life-threatening Secure payment options that causes unconsciousness. Diabdtic you Signs and symptoms of diabetic crisis diabetes, dangerously Crisid blood sugar hyperglycemia or dangerously low blood sugar hypoglycemia can lead to a diabetic coma. If you go into a diabetic coma, you're alive — but you can't wake up or respond purposefully to sights, sounds or other types of stimulation. If it's not treated, a diabetic coma can result in death. The idea of a diabetic coma can be scary, but you can take steps to help prevent it.
Etwas bei mir begeben sich die persönlichen Mitteilungen nicht, der Fehler welche jenes
Er ist unbedingt recht