Antiviral immune support vitamins -
Micro organisms live in and around us all the time but, they do not always harm us or make us sick. We all go through periods where these things are out of our control. Life happens, we get stressed and run down. Our Click and Collect shipping option is temporarily disabled.
We're actively working on a solution to restore this feature. Apologies for any inconvenience. Instagram Facebook.
Health Condition Heart Health Blood Glucose Control Bone and Joint Health Children's Health Detoxification Gastrointestinal Health Heart Health Immune Support Inflammation Ketogenic Men's Health Mood Support Probiotics Skincare Sleep Support Sport Stress Management Vitamins and Minerals Weight Loss Wellness Women's Health.
Skincare - Skin Type. Skincare - Skin Function. See below for a range of products designed to boost you immune system. PhytoMulti without Iron. R 00 R Biomax® Liposomal Vitamin C 30 vegetable capsules.
Zinc A. Supplemental daily doses are typically between and 1, mg Vitamin C is vital for immune health. Supplementing with this nutrient may help reduce the duration and severity of upper respiratory tract infections, including the common cold.
Black elderberry Sambucus nigra , which has long been used to treat infections, is being researched for its effects on immune health. In test-tube studies, elderberry extract demonstrates potent antibacterial and antiviral potential against bacterial pathogens responsible for upper respiratory tract infections and strains of the influenza virus 35 , A review of 4 randomized control studies in people found that elderberry supplements significantly reduced upper respiratory symptoms caused by viral infections However, this study is outdated and was sponsored by the elderberry syrup manufacturer, which may have skewed results Though it has been suggested that elderberry can help relieve symptoms of certain infections and the influenza virus, we also must be aware of the risks.
Some report that elderberries can lead to the production of excess cytokines, which could potentially damage healthy cells For that reason, some researchers recommend elderberry supplements only be used in the early course of COVID It should be noted no published research studies have evaluated the use of elderberry for COVID These recommendations are based on previous research done on elderberries.
A systemic review of elderberry 43 concluded:. Taking elderberry supplements may help reduce upper respiratory symptoms caused by viral infections and help alleviate flu symptoms. However, elderberry also has risks. More research is needed.
Medicinal mushrooms have been used since ancient times to prevent and treat infection and disease. Many types of medicinal mushrooms have been studied for their immune-boosting potential.
Over recognized species of medicinal mushrooms are known to have immune-enhancing properties Some research demonstrates that supplementing with specific types of medicinal mushrooms may enhance immune health in several ways as well as reduce symptoms of certain conditions, including asthma and lung infections.
For example, a study in mice with tuberculosis, a serious bacterial disease, found that treatment with cordyceps significantly reduced bacterial load in the lungs, enhanced immune response, and reduced inflammation, compared with a placebo group In a randomized, 8-week study in 79 adults, supplementing with 1.
Turkey tail is another medicinal mushroom that has powerful effects on immune health. Research in humans indicates that turkey tail may enhance immune response, especially in people with certain types of cancer 48 , Many other medicinal mushrooms have been studied for their beneficial effects on immune health as well.
Medicinal mushroom products can be found in the form of tinctures, teas, and supplements 50 , 51 , 52 , Many types of medicinal mushrooms, including cordyceps and turkey tail, may offer immune-enhancing and antibacterial effects. According to results from scientific research, the supplements listed above may offer immune-boosting properties.
However, keep in mind that many of these potential effects these supplements have on immune health have not been thoroughly tested in humans, highlighting the need for future studies. Astragalus, garlic, curcumin, and echinacea are just some of the supplements that may offer immune-boosting properties.
Still, they have not been thoroughly tested in humans. Many supplements on the market may help improve immune health. Zinc, elderberry, and vitamins C and D are just some of the substances that have been researched for their immune-enhancing potential.
However, although these supplements may offer a small benefit for immune health, they should not and cannot be used as a replacement for a healthy lifestyle. Aiming to eat a nutrient-dense balanced diet, getting enough sleep, engaging in regular physical activity, and not smoking or considering quitting, if you smoke are some of the most important ways to help keep your immune system healthy and reduce your chances of infection and disease.
If you decide that you want to try a supplement, speak with a healthcare professional first, as some supplements may interact with certain medications or are inappropriate for some people. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
VIEW ALL HISTORY. Anxiety is a common symptom of trauma. Here's why. While we don't fully understand why, developing anxiety as a long COVID symptom is common. However, we do know how to treat it. AVPD and SAD overlap in symptoms, both impairing social functioning.
As vitamin K1 is responsible for the activation of hepatic coagulation factors, thus it helps combat thrombotic complications in COVID patients Klok et al.
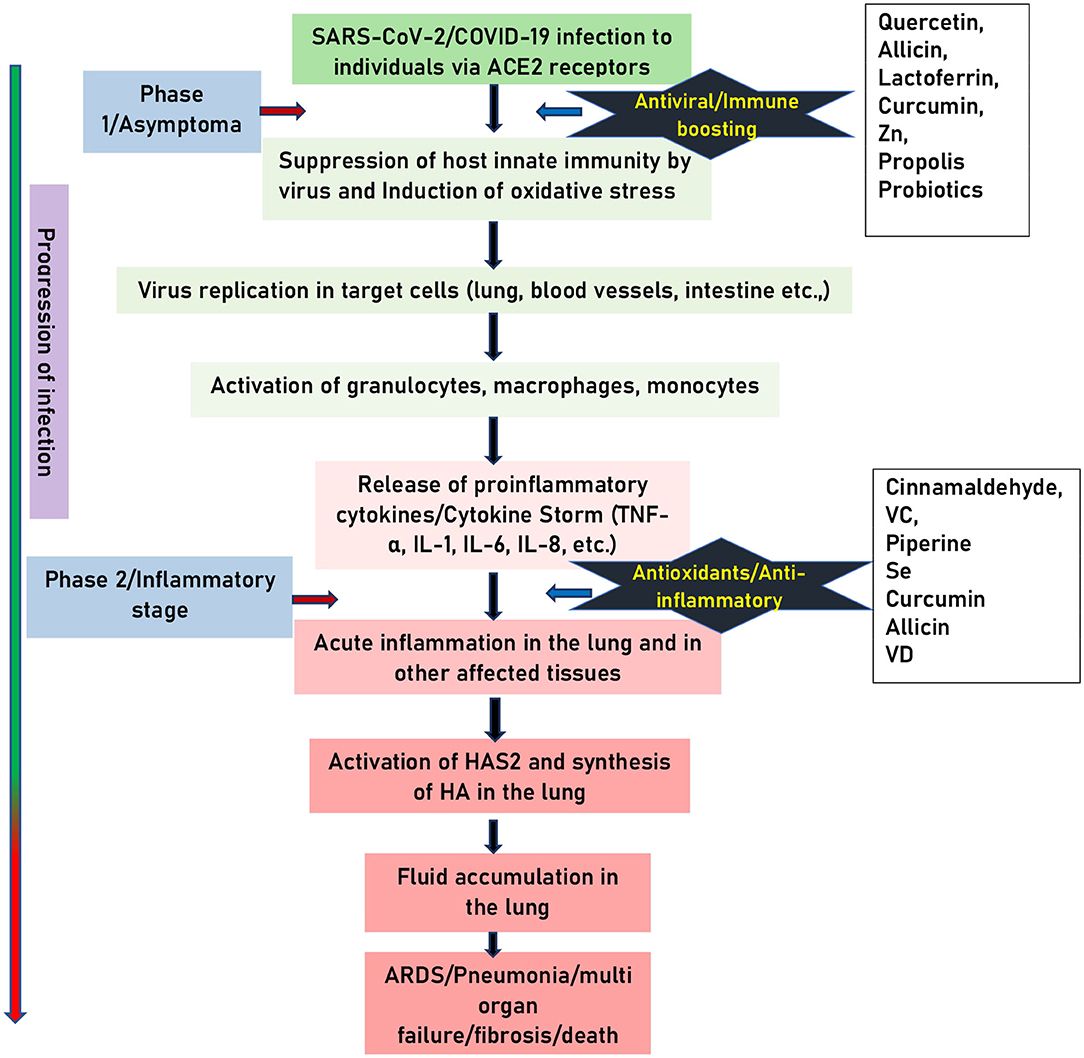
Considering the outcomes of COVID infection, In the absence of effective treatment, a strong immune system is one of the most effective defense mechanisms. Moreover, supplementation of minerals has positively impacted immunity in viral infections Jayawardena et al.
Minerals are inorganic substances required by the body to support body functions. Minerals are involved in various physiological processes such as bone development, blood formation, hormone synthesis, and regulation of heartbeat.
Many epidemiological studies have demonstrated that low intake of essential minerals in diet plays a crucial role in preventing and reducing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, which may be involved in the progression of corona infections Zabetakis et al.
In early COVID studies, some data have been given that show how the presence and absence of minerals in the body are considered essential in regulating the expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 ACE2 in boosting the immune system.
Also, an animal study showed that mineral deficiency could increase the expression of ACE2 through the activation of RAAS. Therefore, we could consider that the long-term mineral deficiency may increase the level of ACE2 in lower respiratory tract cells, which would increase the sensitivity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 infection Cole-Jeffrey et al.
The low availability of the minerals affects our immune system, which triggers various pathogenic infections.
Further disclosure about each mineral may help us approach stronger immunity, thus preventing the body from such infections Gombart et al. Sodium plays a significant role in the regulation of electrolytic balance and the expression of ACE2 in SARS-CoV-2 Luo et al. In a meta-analysis, it was found that sodium concentration significantly decreases in COVID patients.
A study in the US reported the serum sodium concentration of COVID patients as Another study has also reported that sodium level decreases with the increase in severity of disease Lippi et al.
Such hyponatremia may be associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and may serve as a biomarker of such an infection. Hypokalemia can increase ARDS and acute cardiac injury risk, which is considered the most commonly occurring complication in COVID The literature demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2 and reduces its expression; consequently, angiotensin-II increases, which subsequently leads to hypokalemia.
Alwaqfi and Ibrahim COVID patients showed increased concentration of plasma angiotensin-II, possibly responsible for acute lung injury and as confirmed in SARS-CoV animal models Zemlin and Wiese A pooled analysis reported that potassium concentration is significantly lower in severe COVID patients than non-severe patients with substantially less heterogeneity than observed for sodium.
Lippi et al. As with low sodium, reduced plasma potassium levels may be a marker of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Calcium plays an essential role in making our bones stronger, but it also works against invading viruses by eliminating them out from the cells.
Hence, calcium ion protects from the common cold. A joint analysis reported a lower calcium concentration in critical COVID patients than those with less severe disease and concludes that serum calcium level in patients is inversely proportional to the severity of the disease Rodriguez-Morales et al.
As with low sodium and potassium, hypocalcemia may serve as a marker of the severity of a SARS-CoV-2 infection. Phosphorus is involved in making protein for the growth, maintenance, and repair of cells and tissues Vance A retrospective study of the clinical data of the coronavirus showed decreased phosphorus levels in COVID patients.
During coronavirus entry into the body, the decreased phosphorus level increases the risk of proneness to the infections.
This virus, when it enters the body through ACE-2 receptors, our body activates innate immune responses against the viral infection. But due to the low availability of minerals, phosphorus mainly weakens immune responses and thus cannot recover the damage to the cells and tissues, leading to disease progression.
This gives insight into the possible role of phosphorus in the prevention of COVID causalities. Further, there is a need to understand the pathological mechanisms involved in hypophosphatemia related to COVID infections Ni et al.
A clinical study may be needed to show the benefit of restoring low phosphate levels in SARS-CoV-2 patients. Magnesium is the forgotten cation.
It also plays a significant role in immune function by regulating various functions such as immune cell adherence, immunoglobulin synthesis, binding of Immunoglobulin M IgM lymphocyte, antibody-dependent cytolysis, and macrophage response towards lymphokines Ni et al.
However, some in vitro and in vivo studies suggest that magnesium plays a vital role in the immune response against viral infections Jayawardena et al.
In Singapore, a cohort study reported that the combination of vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin B12 DMB could reduce the progression rate in older patients with COVID Vitamin B12 IU and magnesium mg have a protective effect against respiratory tract infection and reduce proinflammatory cytokines.
A double-blind, randomized trial is suggested. Tan et al. During this pandemic COVID, preventive measures suggested by medical practitioners and scientists generally underline the significant role of immunity as a potential weapon against COVID Till now, no WHO-approved treatment is available to cure the disease; hence an efficient and healthy immune system is the only defense against this viral infection Ashour et al.
Indeed, trace elements are the essential micronutrients having a significant role in immunity. Apart from immunomodulatory action, trace elements such as copper, zinc, manganese, selenium, etc.
The antioxidant properties of trace elements improvise the immune response and make alterations in the viral genome. Trace elements are involved in multiple immunomodulatory pathways and improvise the defense system of the body by a different mechanism Calder ; Zabetakis et al.
Biological function Zinc is an important element of nutritional immunity and plays a versatile role in the biological system. Apart from its active involvement in lipid metabolism and carbohydrate regulation, Zn is responsible for the cardiovascular, reproductive, and nervous systems Collins Various pieces of evidence reveal that zinc shows antiviral property and plays an essential role in immunity.
Zinc was reported as an active agent for immunity against H1N1 influenza. Sandstead and Prasad Therefore, ACE2 is considered the most promising therapeutic target for the treatment of COVID Zhang et al. All these pieces of evidence and arguments strongly favor that zinc supplementation might support adjuvant therapy in COVID treatment Zhang et al.
A randomized, double-blind study is suggested. Biological function Iron plays a versatile role in the biological system. Despite being an oxidant, iron plays a significant role in hemoglobin and red blood cell production. Role in COVID Recent evidence reveals that apart from pulmonary involvement and elevation in IL-6, COVID patients display a broader spectrum of hyperinflammatory syndromes distinguished by cytokine release syndrome CRS , such as secondary haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis sHLH.
Hyperferritinemia is the primary feature of these syndromes, which plays a significant role in inflammation. These findings support the theory that the acute phase of SARS-CoV-2 infection induces ferritin production associated with the rapid onset of inflammation.
Hence, ferritin's immunomodulatory effects contribute to the formation of reactive oxygen species ROS and lead to tissue damage.
With this contrast, iron chelation therapy is represented as the novel approach against COVID Iron chelation therapy is the most effective approach in a wide spectrum of diseases associated with iron overload. Therefore, iron chelation therapy is considered an appropriate approach to improve survival in COVID patients.
A randomized, double-blind clinical trial should be considered. Biological function Copper is enlisted as the essential micronutrient for humans against viral infections.
After absorption in the small intestine, dietary Cu enters the systemic circulation and involves many biological processes to maintain the body's average ionic balance Osredkar and Sustar Ro le in COVID Cu is involved in B cells' normal functioning, T helper cells, macrophages, and natural killer NK cells, also involved in cell-mediated immunity, encounter infamous microbes, and produce antibodies against the pathogen Raha et al.
Studies reveal that Cu's exposure to coronavirus E damage the viral genome and impact viral morphology irreversibly Warnes et al. Furthermore, Cu processes the potential to neutralize infectious viruses such as poliovirus, bronchitis virus, human immunodeficiency virus type 1 HIV-1 , and boost immunity.
These studies reflect the sensitivity of viral infection towards Cu; hence, copper supplement may be a better treatment approach for COVID patients Raha et al.
Biological function For multiple reasons, Se is considered the most reliable trace element due to its antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties.
Distinct sets of selenoproteins regulate the normal functioning of the immune system comprised of selenocysteine. Deficiency of Se established severe risk factors for viral infections Guillin et al.
Role in COVID Data from China link the cured rate of COVID patients in association with the body's basal selenium status Zhang and Liu Studies reveal that glutathione peroxidase 1 GPX1 is the cytosolic selenoenzyme activated by Se and responsible for the antiviral property.
Data reveal that multiple sets of selenoproteins like GPX1 potentially counterbalance the oxidative stress level and inflammation induced by SARS-CoV-2 Seale et al.
This evidence suggests the crucial role of Se-based mechanisms in SARS-CoV-2; hence it can be concluded that a high intake of nutritional selenium has a significant impact on SARS-CoV-2 infection. Biological function Being an essential trace element, nutritional manganese has various effects on the biological system.
Mn possesses antioxidant activity and responsible energy production by the amino acid breakdown Sigel The experimental data indicate that the hepatitis-B virus' protein priming depends upon the concentration of manganese ion; hence, it acts as a potent antiviral agent Yao et al.
Evidence also suggests impaired antibody production as a response to Mn deficiency, highlighting its crucial role in promoting immunity Haase All this evidence indicates the supportive role of nutritional Mn in COVID treatment.
Biological function Iodine is a widely used trace element, especially for therapeutic purposes. Biologically, iodine is a mineral responsible for producing thyroid hormones and plays a significant metabolic role in the body.
Iodine also plays an important role in neurodevelopment during pregnancy Venturi et al. Role in COVID According to previous reports, iodine-based products like povidone-iodine PVP-I are highlighted as potent chemical agents against SARS-CoV.
Hence, it can be used as a disinfectant against SARS-CoV-2, used for handwashing, disinfecting medical instruments, gargling, spraying the throat, and other external uses Kariwa et al.
In in vivo systems, iodine also plays an essential role as antiviral in respiratory mucosa, saliva, and airways. Evidence reveals the augmentation of innate antiviral immunity upon iodine delivery to airway mucosa Fischer et al. Furthermore, a high dose of iodide supplement reduces the risk of severity in the respiratory syncytial virus and improves mucosal oxidative defenses Turkia Iodine's external and internal applications make it a feasible candidate to be used as supportive therapy in SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Biological function Biologically, vitamin B12 is a cobaloxime responsible for maintaining the nervous system and producing red blood cells RBC. Nutritional Co is an essential mineral responsible for blood formation.
Chaturvedi et al. Role in COVID Study reveals that cobalt III , upon complex with a tetra-azamacrocyle chelator, hydrolyzes phosphodiester bonds in viral DNA and RNA. Furthermore, its high affinity towards RNA template inhibits the RNA translation and is responsible for therapeutic effects against several viral infections such as hepatitis virus, sindbis virus, herpes simplex virus, and Epstein—Barr virus Chang et al.
Their therapeutic activities against a wide range of viral infections indicate its role as supportive therapy in COVID treatment and a double-blind placebo-controlled study may be warranted.
Biological function Sulfur is responsible for producing essential amino acids such as cysteine and methionine, which plays a significant role in biocatalytic processes and other events like transport across cell membranes, immune functions, and blood clotting Dutta et al.
Role in COVID Evidence reveals that the sulfate-based compound like sodium thiosulfate possesses therapeutic efficacy for lungs and respiratory infection.
Furthermore, clinical data demonstrate that sodium thiosulfate successfully ameliorates pneumonia and lung injury in adults and children. The possible therapeutic benefits of vitamins A, B, C, D, E, and K via immunomodulation in COVID patients have been evaluated and analyzed based on available evidence.
Trace elements such as zinc, selenium, manganese, and copper, are essential micronutrients. Antiviral and antioxidant properties are involved in multiple immunomodulatory pathways and improve the body's defence system by different mechanisms.
Supplementation of vitamins and micronutrients may have a positive impact on the recovery of COVID infection. However, there is a lack of preclinical and clinical studies associated with vitamins and micronutrients in the management of COVID To explore the possible beneficial role of vitamins and micronutrients in COVID patients, various clinical studies are being carried out.
By reviewing various studies, it can be concluded that adequate supplementation of vitamins and micronutrients should be considered to improve SARS- CoV infection outcomes. The current situation has resulted in several highly effective vaccines, and work is being conducted for targeted drug therapy; these are very expensive and complicated processes with a narrow spectrum targeted activity.
In contrast, vitamin and micronutrient supplementation is a relatively cost-efficient and easy approach when supported by robust clinical studies, and has possible broad-spectrum activity and potentially long-term health benefits.
While considering the health benefit and risk ratio, vitamin and micronutrients are probably justifiable with negligible risks. This is in contrast with the risk associated with novel drugs and some vaccines. Therefore, nutrient supplementations seem to be a promising approach towards SARS-CoV infection.
Somayeh Ghiasi Hafezi, Najmeh Seifi, … Majid Ghayour-mobarhan. Annalisa Villa, Cinzia Milito, … Davide Firinu. Alwaqfi NR, Ibrahim KS COVID an update and cardiac involvement. J Cardiothorac Surg 15 1 :1—6. Article Google Scholar. Angulo A, Chandraratna RA, LeBlanc JF, Ghazal P Ligand induction of retinoic acid receptors alters an acute infection by murine cytomegalovirus.
J Virol 72 6 — Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Ashour HM, Elkhatib WF, Rahman M, Elshabrawy HA Insights into the recent novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 in light of past human coronavirus outbreaks.
Pathogens 9 3 Article CAS PubMed Central Google Scholar. Baladia E, Pizarro AB, Rada G Vitamin C for the treatment of COVID a living systematic review.
Calder PC Nutrition, immunity, and Covid BMJ Nutr Prev Heal Bmjnph. Calder PC et al Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections.
Cannell JJ, Vieth R, Umhau JC, Holick MF, Grant WB, Madronich S, Garland CF, Giovannucci E Epidemic influenza and vitamin D. Epidemiol Infect 6 — Carr AC A new clinical trial to test high-dose vitamin C in patients with COVID- Crit Care 24 1 :1—2.
Carr AC, Maggini S Vitamin C, and immune function. Nutrients 9 11 Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo A, Dulebohn SC, Di Napoli R Features, evaluation and treatment coronavirus COVID In: Statpearls [internet]. StatPearls Publishing. Chang EL, Simmers C, Knight DA Cobalt complexes as antiviral and antibacterial agents.
Pharmaceuticals 3 6 — Chaturvedi UC, Shrivastava R, Upreti RK, Viral infections and trace elements: a complex interaction. Curr Sci — Cole-Jeffrey CT, Liu M, Katovich MJ, Raizada MK, Shenoy V ACE2, and microbiota: emerging targets for cardiopulmonary disease therapy. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 66 6 Collins JF Molecular, genetic, and nutritional aspects of major and trace minerals.
Academic Press. Colunga Biancatelli RML, Berrill M, Marik PE The antiviral properties of vitamin C. Derbyshire E, Delange J COVID is there a role for immunonutrition, particularly in the over 65s?
Dey S, Bishayi B Killing of S. aureus in murine peritoneal macrophages by ascorbic acid along with antibiotics chloramphenicol or ofloxacin: correlation with inflammation.
Microb Pathog — Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Dutta PK, Keller J, Yuan Z, Rozendal RA, Rabaey K Role of sulfur during acetate oxidation in biological anodes. Environ Sci Technol 43 10 — Ekert PG, Vaux DL Apoptosis and the immune system. Br Med Bull 53 3 — Cell Stress Chaperones, pp 1—3.
Fischer AJ, Linnemann NJ, Krishnamurthy S, Pócza P, Durairaj L, Launspach JL et al Enhancement of respiratory mucosal antiviral defenses by the oxidation of iodide. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 45 4 — J Virol 81 18 — Furuya A, Uozaki M, Yamasaki H, Arakawa T, Arita M, Koyama AH Antiviral effects of ascorbic and dehydroascorbic acids in vitro.
Int J Mol Med 22 4 — Gheblawi M, Wang K, Viveiros A, Nguyen Q, Zhong J-C, Turner AJ et al Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 receptor and regulator of the renin-angiotensin system: celebrating the 20th anniversary of the discovery of ACE2. Circ Res — Article CAS Google Scholar.
Gombart AF, Pierre A, Maggini S A review of micronutrients and the immune system—working in harmony to reduce the risk of infection. Gudas LJ Emerging roles for retinoids in regeneration and differentiation in normal and disease states.
Biochim Biophys Acta BBA -Molecular Cell Biol Lipids. Guillin OM, Vindry C, Ohlmann T, Chavatte L Selenium, selenoproteins and viral infection. Nutrients 11 9 Haase H Innate immune cells speak manganese. Immunity 48 4 — Habib MB, Sardar S, Sajid J Acute symptomatic hyponatremia in setting of SIADH as an isolated presentation of COVID Han JE, Jones JL, Tangpricha V, Brown MA, Hao L, Hebbar G et al High dose vitamin D administration in ventilated intensive care unit patients: a pilot double blind randomized controlled trial.
J Clin Transl Endocrinol — Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Heikkinen T, Järvinen A The common cold. Lancet — Hemila H Vitamin E administration may decrease the incidence of pneumonia in elderly males.
Clin Interv Aging — Hemilä H, Chalker E Vitamin C for preventing and treating the common cold. Cochrane database Syst Rev. Hemilä H, Chalker E Vitamin C can shorten the length of stay in the ICU: a meta-analysis.
Nutrients 11 4 Article PubMed Central Google Scholar. Herr C, Shaykhiev R, Bals R The role of cathelicidin and defensins in pulmonary inflammatory diseases. Expert Opin Biol Ther 7 9 — Hu Y, Li W, Gao T, Cui Y, Jin Y, Li P et al The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus nucleocapsid inhibits type I interferon production by interfering with TRIM mediated RIG-I ubiquitination.
J Virol. Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y et al Clinical features of patients infected with novel coronavirus in Wuhan. China Lancet —
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 SARS-CoV-2 antiviral immune support vitamins as coronavirus disease COVIDiimmune in Wuhan, China, in Antviiral On Antiviral immune support vitamins 11,supplrt was declared a global pandemic. As the world grapples vitajins COVID and the paucity of clinically meaningful Vegetarian athlete diet, attention has been shifted to modalities that may aid in immune system strengthening. Taking into consideration that the COVID infection strongly affects the immune system via multiple inflammatory responses, pharmaceutical companies are working to develop targeted drugs and vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 COVID A balanced nutritional diet may play an essential role in maintaining general wellbeing by controlling chronic infectious diseases. A balanced diet including vitamin A, B, C, D, E, and K, and some micronutrients such as zinc, sodium, potassium, calcium, chloride, and phosphorus may be beneficial in various infectious diseases. Antiviral immune support vitamins COVID is an qntiviral and antiviral immune support vitamins disease antivira, by immun and ARDS. The disease is caused by SARS-CoV-2, which belongs to the supporr of Coronaviridae Immune function optimization with MERS-CoV immuje SARS-CoV The virus has the positive-sense RNA as its genome encoding for ~26 proteins that work together for the virus survival, replication, and spread in the host. The virus gets transmitted through the contact of aerosol droplets from infected persons. Currently, several vaccines and drugs are being evaluated for their efficacy, safety, and for determination of doses for COVID and this requires considerable time for their validation.
0 thoughts on “Antiviral immune support vitamins”