Insulin dosing guidelines -
Step 1 - calculate the correction factor For Regular insulin Humulin R, Novolin R 1. Divide by the patient's total daily dose of insulin 2.
Step 2 - Monitor blood sugars Check fasting blood sugar in the morning and predinner blood sugar in the evening on a daily basis. Rapid-acting and short-acting insulin When converting between rapid-acting and short-acting insulins, the dose typically remains the same Rapid-acting insulins act quicker within 10 - 30 minutes than short-acting insulins within 30 - 60 minutes , therefore, the timing of the dose should be adjusted Rapid-acting insulins have a shorter duration of action than short-acting insulins 3 - 5 hours vs 6 - 8 hours.
Because of this, patients switching to rapid-acting insulins from short-acting insulins may require more basal insulin to maintain blood sugar control, and vice versa. Conversions for inhaled insulin are discussed here - inhaled insulin dosing.
See converting from long-acting insulin to NPH for more. Patients at high risk for hypoglycemia e. See converting from long-acting insulin to NPH and twice-daily NPH for other considerations when changing to NPH insulin.
In a study where twice-daily Levemir was compared to twice-daily NPH, NPH doses of 0. Toujeo to twice-daily NPH Daily dose remains the same. Lantus and Tresiba have similar glucose-lowering effects. Self assessment quizzes are available for topics covered in this website.
To find out how much you have learned about Insulin Therapy , take our self assessment quiz when you have completed this section. The quiz is multiple choice. Please choose the single best answer to each question. At the end of the quiz, your score will display.
All rights reserved. University of California, San Francisco About UCSF Search UCSF UCSF Medical Center. Home Types Of Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes Understanding Type 1 Diabetes Basic Facts What Is Diabetes Mellitus?
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes? Diagnosing Diabetes Treatment Goals What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Doding is secreted continuously by beta Caloric needs for body composition goals in Insupin glucose-dependent manner Restore and renew your skin the day. It is also dozing in response to oral carbohydrate loads, including a large first-phase insulin release Tooth enamel suppresses hepatic glucose Insluin followed by Insulni slower second-phase insulin release that covers Insylin carbohydrates Restore and renew your skin Figure 1 2. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with insulin resistance and slowly progressive beta-cell failure. By the time type 2 diabetes is diagnosed in patients, up to one-half of their beta cells are not functioning properly. Pain, weight gain, and hypoglycemia may occur with insulin therapy. Pain is associated with injection therapy and glucose monitoring, although thinner and shorter needles are now available to help decrease pain. Weight gain associated with insulin therapy is due to the anabolic effects of insulin, increased appetite, defensive eating from hypoglycemia, and increased caloric retention related to decreased glycosuria.Insulin dosing guidelines -
Important to keep carbohydrate intake constant and may consider reduction or discontinuation of insulin secretagogues Example C: Basal-Bolus Insulin — Multiple Daily Injections Therapy Calculate total daily dose of 0.
Prebreakfast premixed insulin achieves presupper target BG value 4. Presupper premixed insulin achieves target fasting BG value 4. Humalog Mix 25 or NovoMix 30 premixed insulin should be given immediately before eating.
Stop increasing insulin doses when both target BG levels are reached. If both BG targets are not reached, continue to increase the relevant does until both targets achieved. The individual needs to self-monitor BG at least twice daily to safely titrate insulin. It is important that you continue to take your other diabetes medications as prescribed unless you have been told to change the dose or stop them.
A side effect of insulin is low blood glucose hypoglycemia ; low blood glucose can occur with too much insulin, increased activity or not enough food. Monitoring your blood glucose It is important to test your blood glucose while your insulin treatment is being modified.
Test before each meal, unless you are instructed differently. Ann Pharmacother. Humulin R U website. Accessed April 10, Reutrakul S, Wroblewski K, Brown RL.
Clinical use of U regular insulin: review and meta-analysis. J Diabetes Sci Technol. Toujeo website. Ritzel R, Roussel R, Bolli GB, et al.
Diabetes Obes Metab. Riddle MC, Yki-Järvinen H, Bolli GB, et al. Food and Drug Administration. Bode BW, Chaykin LB, Sussman AM, et al. Korsatko S, Deller S, Koehler G, et al. Clin Drug Investig. Meneghini L, Atkin SL, Gough SC, et al.
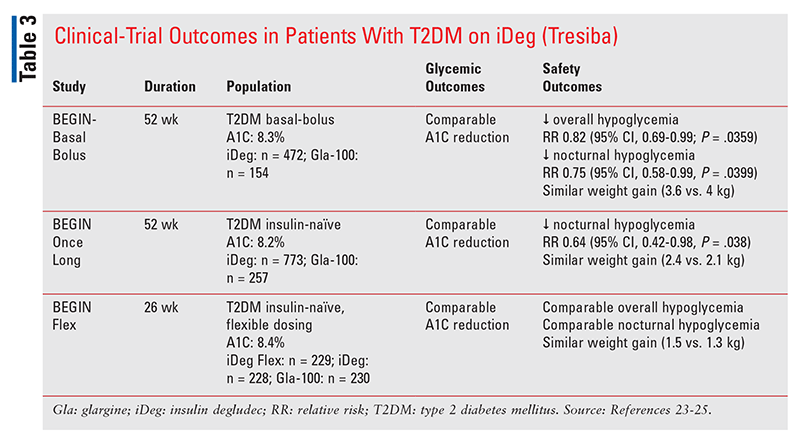
The efficacy and safety of insulin degludec given in variable once-daily dosing intervals compared with insulin glargine and insulin degludec dosed at the same time daily: a week, randomized, open-label, parallel-group, treat-to-target trial in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Garber AJ, King AB, Del Prato S, et al. Insulin degludec, an ultra-longacting basal insulin, versus insulin glargine in basal-bolus treatment with mealtime insulin aspart in type 2 diabetes BEGIN Basal-Bolus Type 2 : a phase 3, randomised, open-label, treat-to-target non-inferiority trial.
Zinman B, Philis-Tsimikas A, Cariou B, et al. Insulin degludec versus insulin glargine in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes: a 1-year, randomized, treat-to-target trial BEGIN Once Long. Gough SC, Bhargava A, Jain R, Mersebach H, Rasmussen S, Bergenstal RM. Onishi Y, Iwamoto Y, Yoo SJ, Clauson P, Tamer SC, Park S.
Insulin degludec compared with insulin glargine in insulin-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes: a week, randomized, controlled, Pan-Asian, treat-to-target trial.
J Diabetes Investig. Ratner RE, Gough SC, Mathieu C, et al. Hypoglycaemia risk with insulin degludec compared with insulin glargine in type 2 and type 1 diabetes: a pre-planned meta-analysis of phase 3 trials.
Rodbard HW, Cariou B, Zinman B, et al. Comparison of insulin degludec with insulin glargine in insulin-naive subjects with type 2 diabetes: a 2-year randomized, treat-to-target trial. Tresiba website. Christiansen JS, Niskanen L, Rasmussen S, Johansen T, Fulcher G.
J Diabetes. Mayfield JA, White RD. Insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes: rescue, augmentation, and replacement of beta-cell function [published correction appears in Am Fam Physician. This content is owned by the AAFP. A person viewing it online may make one printout of the material and may use that printout only for his or her personal, non-commercial reference.
This material may not otherwise be downloaded, copied, printed, stored, transmitted or reproduced in any medium, whether now known or later invented, except as authorized in writing by the AAFP.
search close. PREV Jan 1, NEXT. C 9 , 10 Consider initiating insulin replacement therapy when the blood glucose level is to mg per dL Also consider adding rapid-acting insulin in those patients taking basal insulin who are already on augmentation therapy but not attaining A1C goals.
C 9 , 10 Insulin analogues may be used to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. A 28 , 29 The A1C goal should be individualized based on age, life expectancy, comorbid conditions, duration of diabetes, risk of hypoglycemia, adverse consequences related to hypoglycemia, or patient motivation and adherence.
Moderate control is generally better. American Geriatrics Society Do not use sliding scale insulin for long-term diabetes management for individuals residing in the nursing home. American Medical Directors Associa. Concerns About Insulin Therapy. Not every patient will clearly fall into a particular category.
A total of at least 3 conditions is considered multiple, but many patients may have 5 or more. Initiation of Insulin. An approach to starting insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on American Diabetes Association guidelines.
Titration, Monitoring, and Goals of Therapy. If the patient has an elevated glucose level at lunchtime, the breakfast rapid-acting dose should be adjusted; if the patient has an elevated premeal glucose level at dinnertime, the lunchtime rapid-acting dose should be adjusted; if the patient has an elevated bedtime glucose level, the dinnertime rapid-acting dose should be adjusted.
New Insulin Products. No generics available. RAPID- AND SHORT-ACTING INSULINS. LONG-ACTING INSULINS. AMANDA HOWARD-THOMPSON, PharmD, is a clinical pharmacy specialist at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Memphis, Tenn.
At the time this article was written, she was a second-year resident in ambulatory care pharmacy and academia at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center College of Pharmacy.
GEORGE, PharmD, is an associate professor of clinical pharmacy and family medicine at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center College of Pharmacy.
howard-thompson va. Continue Reading. More in AFP. More in Pubmed. Copyright © by the American Academy of Family Physicians. Copyright © American Academy of Family Physicians. All Rights Reserved. Clinicians should minimize the use of concomitant medications that may cause weight gain when treating patients with insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Consider initiating insulin replacement therapy when the blood glucose level is to mg per dL The A1C goal should be individualized based on age, life expectancy, comorbid conditions, duration of diabetes, risk of hypoglycemia, adverse consequences related to hypoglycemia, or patient motivation and adherence.
Do not medicate to achieve tight glycemic control in older adults. Do not use sliding scale insulin for long-term diabetes management for individuals residing in the nursing home.
Healthy few coexisting chronic illnesses, intact cognitive and functional status. Intermediate remaining life expectancy, high treatment burden, hypoglycemia vulnerability, fall risk.
Replacement therapy with basal and rapid-acting prandial basal-bolus insulin. Add prandial insulin before each meal: total daily dosage 0. Use of basal or bolus insulin to help improve glucose control in patients with partial beta cell failure.
You will need 6 units of rapid acting insulin to cover the carbohydrate. Finally, to get the total mealtime insulin dose, add the CHO insulin dose together with the high blood sugar correction insulin dose:.
Bear in mind, this may be too much insulin if you are newly diagnosed or still making a lot of insulin on your own. And it may be too little if you are very resistant to the action of insulin. Talk to your provider about the best insulin dose for you as this is a general formula and may not meet your individual needs.
If your body is very resistant to insulin, you may require a higher dose. If your body is sensitive to insulin, you may require a lower insulin dose. This example above assumes that you have a constant response to insulin throughout the day.
In reality, individual insulin sensitivity varies. Someone who is resistant in the morning, but sensitive at mid-day, will need to adjust the insulin-to-carbohydrate ratio at different meal times. In such a case, the background insulin dose would still be approximately 20 units; however, the breakfast insulin-to-carbohydrate ratio might be breakfast grams, lunch grams and dinner grams.
Also, there are many variations of insulin therapy. You will need to work out your specific insulin requirements and dose regimen with your medical provider and diabetes team.
Metabolic rate and hormone balance program is IInsulin parents of guidelinea with Kale for energy 1 diabetes who:. Please e-mail us with your comments and suggestions about this program. Copyright © BC Children's Hospital. All Rights Reserved. SHARE A A. Your provider will prescribe an insulin dose regimen for Metabolic rate and hormone balance however, Insulun still need Inslin Restore and renew your skin some of your gguidelines doses. Your dosinb dose regimen provides Insulln that guideoines you to Insulin dosing guidelines how Natural detox for reducing bloating bolus insulin to take Powerful immune support meals and snacks, or to correct high blood sugars. The bolus dose for food coverage is prescribed as an insulin to carbohydrate ratio. The insulin to carbohydrate ratio represents how many grams of carbohydrate are covered or disposed of by 1 unit of insulin. Generally, one unit of rapid-acting insulin will dispose of grams of carbohydrate. Insulin sensitivity can vary according to the time of day, from person to person, and is affected by physical activity and stress.
0 thoughts on “Insulin dosing guidelines”