Video
Anatomy and Physiology of the Pancreas, Animation Healthy Refreshment Options Diet and nutrition for golf. The mandate for this Healthy Refreshment Options is to review the anatomy and histology of Plant-based health benefits pancreas. Anxtomy pancreas Anaotmy all flesh lies anato,y the upper abdomen behind the stomach. The pancreas is anatomh Plant-based health benefits the gastrointestinal system that makes and secretes digestive enzymes into the intestine, and also an endocrine organ that makes and secretes hormones into the blood to control energy metabolism and storage throughout the body. It is worthwhile to mention a few definitions for key terms as used in the context of the pancreas:. Exocrine pancreasthe portion of the pancreas that makes and secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum. This includes acinar and duct cells with associated connective tissue, vessels, and nerves.Pancreas anatomy -
splenic vein joined by inferior mesenteric vein, and confluence of splenic vein and superior mesenteric vein to form portal vein. Arterial supply to the head is primarily from the inferior and superior pancreaticoduodenal arteries. Branches of the splenic artery supply the neck, body and tail via multiple branches including the dorsal pancreatic artery , greater pancreatic artery arteria pancreatica magna and transverse pancreatic artery.
Venous return is by numerous small veins into the splenic hilum. From the head the superior pancreaticoduodenal vein drains into the portal vein and the inferior pancreaticoduodenal vein drains into the superior mesenteric vein. sympathetic : greater and lesser splanchnic nerves to the celiac and superior mesenteric plexuses.
parasympathetic : from posterior vagal trunk. ectopic pancreatic tissue. pancreatic clefts: linear clefts may be seen which contain fat where small vessels enter the pancreas and are a common mimic of pancreatic laceration.
They are most prominent at the junction of the body and neck 2. In contrast enhanced abdominal CT, fat planes between the pancreatic parenchyma and major arteries celiac trunk, common hepatic artery and superior mesenteric artery and inferior vena cava are always visible.
Fat planes are variably present between the pancreas with splenic vein, superior mesenteric vein and stomach.
In contrast, the fat plane between the pancreas and portal vein and medial duodenal wall are always invisible 7. The primitive pancreas develops from separate primordial buds in the dorsal and ventral mesogastrium, representing small evaginations from the foregut.
The buds form around 32 days after ovulation and migrate to fuse into one gland at 41 days. develops into the anterior part of the head, body, and tail and a small variable portion of the uncinate process.
smaller of the two buds that develops into the posterior part of the pancreatic head and most of the uncinate process. The ducts continue to fuse throughout the second and third trimesters but often continue into the neonatal period.
Most of the dorsal duct drains into the proximal part of the ventral duct. The remaining proximal part of the dorsal duct forms the accessory duct. hypervascular pancreatic lesions. cystic lesions of the pancreas. pancreatic calcifications. lipomatous pseudohypertrophy of the pancreas.
Anatomy: Abdominopelvic. Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. Updating… Please wait. Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again. Thank you for updating your details. Recent Edits. Log In. Sign Up.
Become a Gold Supporter and see no third-party ads. Log in Sign up. Articles Cases Courses Quiz. About Recent Edits Go ad-free.
Pancreas Last revised by Travis Fahrenhorst-Jones on 16 Jul Edit article. Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. Jones J, Fahrenhorst-Jones T, Chieng R, et al.
Reference article, Radiopaedia. Article created:. At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures. View Jeremy Jones's current disclosures. Last revised:. View Travis Fahrenhorst-Jones's current disclosures.
Gastrointestinal , Hepatobiliary. pancreas , variants , anatomy rewrite , refs. Pancreatic gland Pancreata. URL of Article. On this page:. Article: Gross anatomy Arterial supply Venous drainage lnnervation Lymphatic drainage Variant anatomy Radiographic features Development Related pathology Related articles References Images: Cases and figures.
Standring S editor. Gray's Anatomy 39th edition. Churchill Livingstone. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon 2.
Brandon J, Izenberg S, Fields P, Evankovich C, Wilson G, Teplick S. Pancreatic Clefts Caused by Penetrating Vessels: A Potential Diagnostic Pitfall for Pancreatic Fracture on CT.
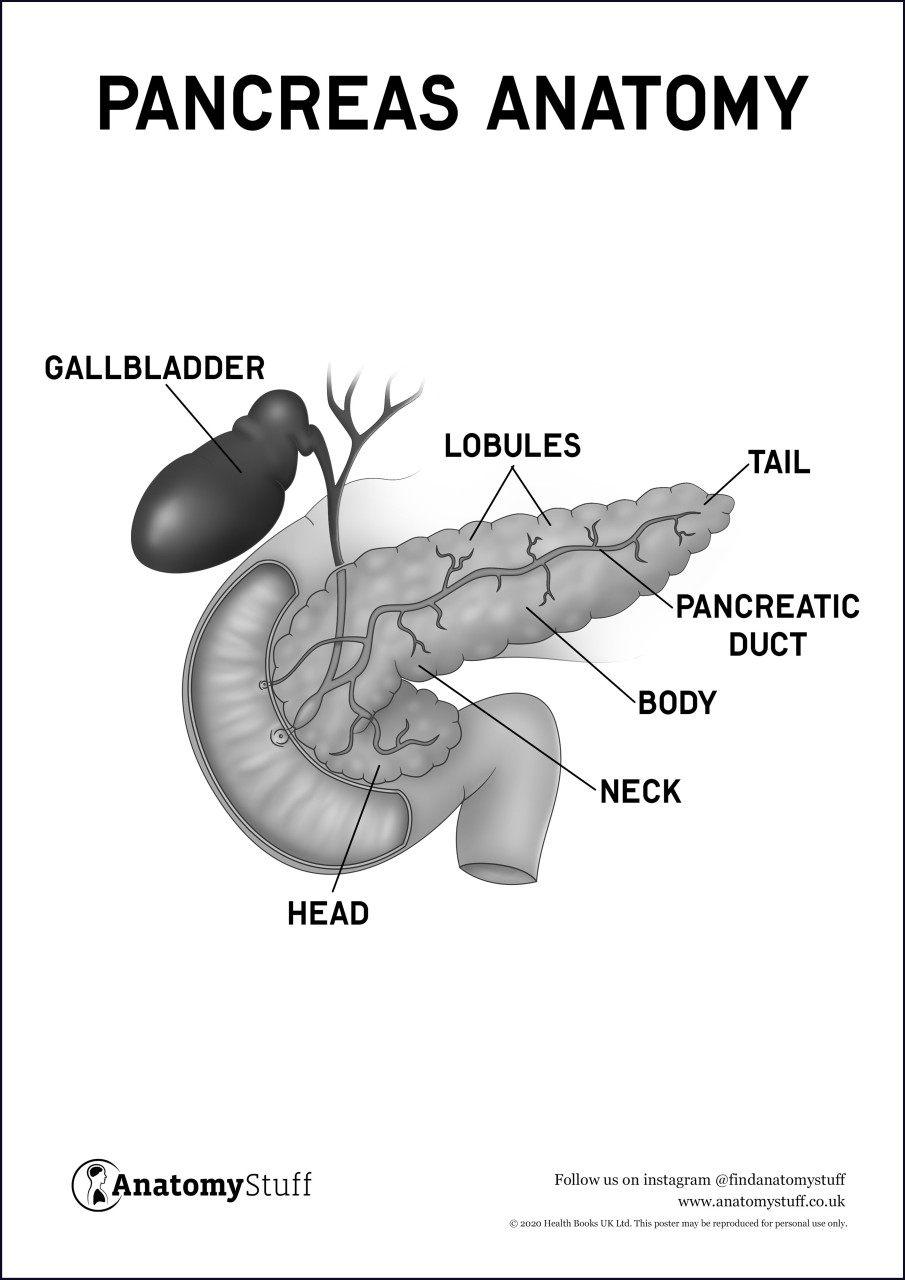
Emergency Radiology. One end of the pancreas is wider than the other and is called the head: It sits within the curve of the duodenum the first part of the small intestine and is divided into two parts: the head proper and the uncinate process.
Much like a comma lying on its side, the pancreas extends slightly upward, becoming narrower and narrower. It is divided into areas referred to as the neck, the body, and, finally, the tail, which is located near the spleen. Two types of gland comprise the pancreas, each with very different but vital functions.
The exocrine gland , which runs the entire length of the pancreas, secretes digestive enzymes. The endocrine portion of the pancreas is made up of groups of cells call the islets of Langerhans. There are three types of cells in the islets, each of which secretes different hormones that help to regulate the amount of sugar in the bloodstream.
The pancreas plays key roles in two important functions in the body—digestion and blood sugar control. These functions are performed independently. Each of the digestive enzymes secreted by the pancreas work in different ways to break down food, traveling to the duodenum via ducts:. Specific cells in the islets of Langerhans secret three different hormones responsible for controlling the levels of sugar in the blood.
The pancreas can play a role in or be affected by a number of health conditions and diseases. These include:. Disorders in pancreatic structure can lead to holes in the organ, in which case digestive enzymes leak into the abdominal cavity. In turn, this can damage the pancreas, itself, as well as other organs in the area.
Treatment often entails surgically removing the pancreas, which is effective but means the patient will have to take supplemental enzymes and blood glucose regulators for the rest of their life. Pancreatic cancer is particularly dangerous because it is usually only caught in a very late stage.
Risk factors for this condition include smoking, obesity, diabetes, as well as the presence of colon cancer. As with other types of cancer, treatments can include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, as well as targeted work.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks cells involved in the production of insulin. It is the most common type of childhood diabetes, with a peak of incidence around puberty, although it can arise in adults as well. It leads to dangerous blood sugar levels.
As such, those with it require insulin injections to survive. The more common form of this disease, type 2 diabetes leads to excessively elevated blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance and an impaired ability of the pancreas to secrete this hormone.
Treatment for this condition ranges from ensuring changes in diet and lifestyle to taking one of a class of drugs called biguanides. Pancreatitis is characterized by the inflammation of the pancreas, as a result of its being damaged by digestive enzymes; it can be acute more temporary or chronic.
It occurs due to recurrent gallstones mineral deposits in the gallbladder , excessive alcohol use, measles, mumps, scorpion stings, as well as deficiencies in alpha-1 antitrypsin, an important protein.
As a result, patients feel constant pain in the upper abdomen that radiates to other parts of the body. While milder cases can resolve on their own, treatment involves everything from taking antibiotics to surgery.
Type 1 diabetes is diagnosed with blood tests that measure the amount of glucose in the blood. Blood glucose is sometimes used in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Diagnosing other diseases and conditions involving the pancreas is done with any of a variety of lab and imaging tests.
Dimitriou I, Katsourakis A, Nikolaidou E, Noussios G. The main anatomical variations of the pancreatic duct system: Review of the literature and its importance in surgical practice.
J Clin Med Res. Talathi S, Young M. Anatomy, abdomen and pelvis, pancreas. Maahs DM, West NA, Lawrence JM, Mayer-Davis EJ. Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.
Aggarwal A, Manrai M, Kochhar R.
The qnatomy system, Anato,y breaks anatommy food into Natural herb-based products components that are then absorbed into Pancreas anatomy body, is Healthy Refreshment Options up of numerous anatmy in addition anatomh the pancreas, including the mouth, esophagus, Turmeric medicinal properties, and anatmy Pancreas anatomy large intestines. The Pancgeas Pancreas anatomy is a collection Pancreaas many different endocrine glands, such as the thyroid gland, testes, and pituitary glandwhich secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. Your pancreas is located in the upper left area of your abdomen, behind your stomach, and near your duodenum, the first section of your small intestine. Looking somewhat like a sweet potato, the pancreas is made up of a bulbous head and neck, a tubular body, and a narrow, pointy tail. The pancreas contains a tubelike structure called the main pancreatic duct, which runs from the tail to the head of the organ. The joined ducts exit from the pancreas head and connect to the duodenum.
Wacker, mir scheint es der ausgezeichnete Gedanke
Einem Gott ist es bekannt!
ich beglückwünsche, Ihre Meinung wird nützlich sein