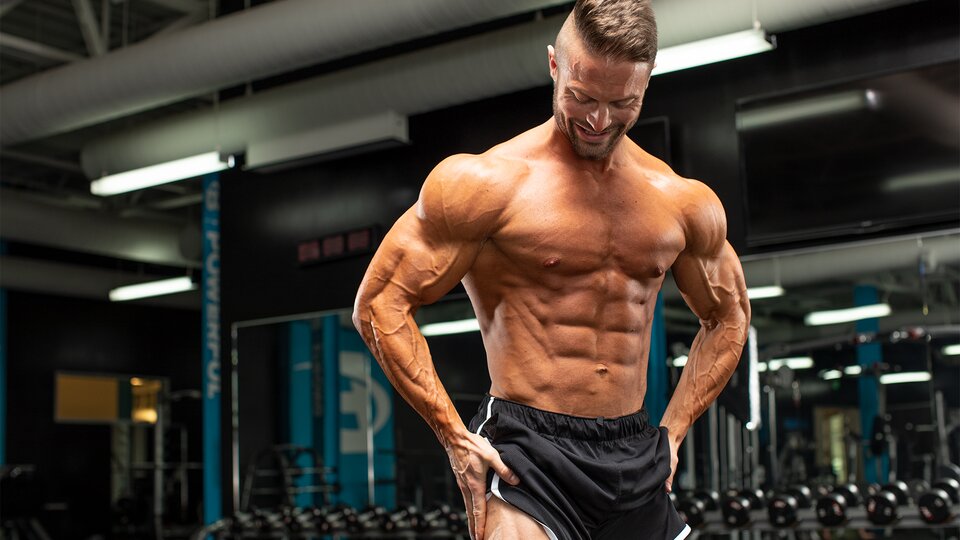

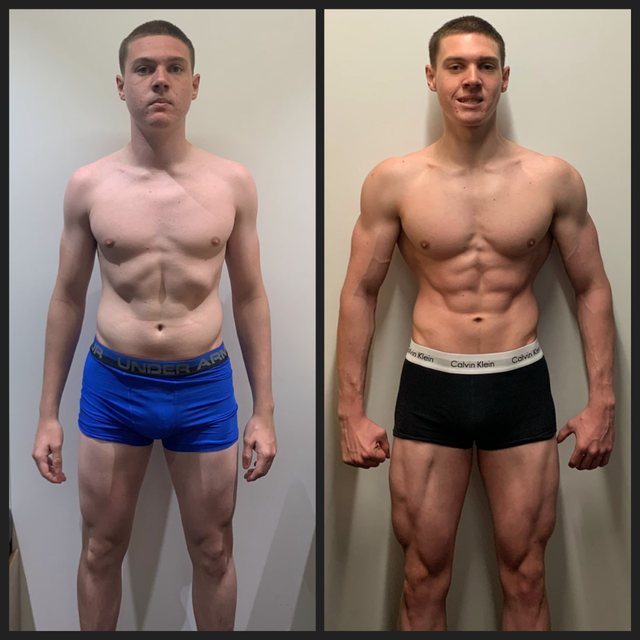
Lean Body Composition -
Sometimes, body composition is used interchangeably with body fat percentage, but body fat percentage is just one part of your overall body composition. Lean mass includes muscle, bones, ligaments, tendons, organs, other tissues and water -- in other words, everything that's not body fat.
Depending on what method you use to measure your body composition, you may see water as its own percentage. Body recomposition refers to the process of changing your ratio of fat mass to lean mass -- that is, losing body fat and gaining muscle mass. The goal of body recomposition is to lose fat and gain muscle simultaneously, unlike the traditional approach of "bulking and cutting" in which you intentionally put on a lot of weight first muscle and fat and then go through an intense calorie deficit to lose the fat and reveal the muscle underneath.
When your goal is body recomposition, ditch the scale and use a tape measure for a better idea of your progress. Body recomposition isn't about weight loss; it's about fat loss. On a body recomposition plan, you may maintain your current weight or even gain weight -- remember hearing "muscle weighs more than fat"?
This is semi-true. Muscle is denser than fat. During body recomposition, what changes, instead of weight, is your physique.
As you progress through body recomposition, you may notice changes in your body, such as an overall firmer look or that your clothes fit differently.
You may even gain weight, but have a smaller physique, at the end of your body recomposition program. For example, I weigh exactly the same now as I did before I started exercising and eating healthy. I wear smaller clothes, however, and my body has more muscle tone than it did before.
I also feel much stronger than before I began a strength training program a nonaesthetic benefit to body recomposition. So you can ditch the scale , because it doesn't differentiate between fat loss and muscle loss, and weight loss isn't the primary goal with body recomposition. There's one caveat to consider, though: If you want to lose a large amount of body fat and don't intend to put on much muscle mass, you may lose weight in the long run.
Because you're trying to do two things at once -- lose fat and gain muscle -- you can't treat a body recomposition plan like a fad diet. Healthy weight loss and healthy muscle gain both take a long time on their own: Put them together and you're in it for the long haul.
The slow, steady process of body recomposition offers sustainable results, though, so you'll enjoy your new physique for as long as you maintain those habits. Body recomposition truly comes down to your specific health and fitness goals.
Unlike traditional methods of weight loss -- such as very low-calorie diets or periods of really intense cardio exercise -- there's no real protocol for body recomposition. Fat loss ultimately comes down to your calorie maintenance. To lose fat, you must eat fewer calories than you burn.
Cardiovascular exercise, or combined cardio and resistance exercise, alongside a healthy diet still stands as the best technique for fat loss -- there's just no way around the science. Losing fat in a safe, sustainable way also means having realistic goals and not depriving your body of the nutrients it needs -- disordered eating habits are never worth the risk.
To build muscle, focus on two main factors: weight training and protein consumption. Strength training is essential to changing your body composition -- your muscles won't grow if you don't challenge them. If you are new to resistance training, you may even see increases in muscle mass while eating maintenance or even deficit calories.
Strength training also helps prevent the loss of lean mass, including muscle tissue, while in a calorie deficit. Types of resistance training range from bodyweight movements to heavy weight lifting. If your goal is to build muscle size , follow best practices for hypertrophy-based strength training by using progressive overload , adding volume consistently over time, and managing fatigue with deload phases.
It's also key to track your progress , so you know when to make adjustments to keep on track toward your body composition goals.
To put together an effective workout plan to improve your body composition, begin with a minimum of two weekly strength training sessions for each major muscle group.
If you have the time, splitting your workouts into 3 to 4 strength training sessions per week will likely be best. Gradually add sets and reps over time to help build muscle mass.
If you enjoy cardio, adding two or more cardio sessions per week will support fat loss, but it will not increase lean mass. Include any cardiovascular activity you prefer. Increasing your overall daily activity through natural movements like walking, climbing stairs, pacing, and taking movement breaks from work will also help you burn more calories if that is your goal.
Changing your body composition is a common goal that can have benefits for your overall health. Focusing on your protein consumption, a balanced exercise routine, and keeping stress levels low all contribute to this change. If you have questions or concerns about your body composition or changing it, it's best to seek advice from a healthcare professional.
Muth ND. What are the guidelines for percentage of body fat loss? American Council on Exercise. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Health risks of being overweight.
Cava E, Yeat NC, Mittendorfer B. Preserving healthy muscle during weight loss. Adv Nutr. Pesta DH, Samuel VT. A high-protein diet for reducing body fat: mechanisms and possible caveats. Nutr Metab Lond. Thomas DT, Erdman KA, Burke LM.
Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: nutrition and athletic performance. J Acad Nutr Diet. Craven J, Desbrow B, Sabapathy S, Bellinger P, McCartney D, Irwin C.
The effect of consuming carbohydrate with and without protein on the rate of muscle glycogen re-synthesis during short-term post-exercise recovery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Sports Med - Open. Sanford Health. How to gain healthy weight. Drenowatz C, Hand GA, Sagner M, Shook RP, Burgess S, Blair SN. The prospective association between different types of exercise and body composition. Med Sci Sports Exerc. Prather AA, Leung CW, Adler NE, Ritchie L, Laraia B, Epel ES.
Short and sweet: Associations between self-reported sleep duration and sugar-sweetened beverage consumption among adults in the United States. Sleep Health. Duraccio KM, Whitacre C, Krietsch KN, et al. Losing sleep by staying up late leads adolescents to consume more carbohydrates and a higher glycemic load.
Published online December 17, zsab O'Donnell S, Beaven CM, Driller MW. From pillow to podium: a review on understanding sleep for elite athletes. Nat Sci Sleep. Chang CS, Liu IT, Liang FW, et al. Effects of age and gender on body composition indices as predictors of mortality in middle-aged and old people.
Sci Rep. Barber TM, Hanson P, Weickert MO, Franks S. Obesity and polycystic ovary syndrome: implications for pathogenesis and novel management strategies. Clin Med Insights Reprod Health. Cardoos N. Overtraining syndrome. Curr Sports Med Reports. National Academy of Sports Medicine.
Exploring the science of muscle recovery. It takes time and effort to build the tissue, but you end up looking healthier, feeling stronger and having more stamina. Combine a carefully planned program that pairs a calorie surplus of to calories daily with directed weight training.
Over the course of a year of focused muscle-building work, you can gain an average 0. Once you've developed the lean mass you want, you can shed fat by cutting your calorie intake, so you're eating to 1, calories less than you burn a day.
Living a sedentary lifestyle or losing weight too quickly, though, will make you lose lean mass. For every pound you lose while sedentary, about 25 percent will be lean muscle mass.
Eating fewer than 1, calories per day also encourages the loss of muscle mass. On the other hand, if you're sedentary and eating more calories than you need, you'll gain fat.
As you age, you naturally lose lean body mass. Muscle loss, known as sarcopenia, is most prevalent after age 50 and occurs at a rate of about 1 to 2 percent per year, explains a review in the Journal of Gerontology. Bone density also diminishes slightly as you age, further reducing the weight of your lean body mass.
The net result is about 15 pounds of muscle lost and 30 pounds of fat gained. Your net weight may not change, but the composition shifts. Losing muscle mass has consequences beyond changing your size and shape. You lose strength, cardiovascular capacity and calorie-burning potential.
Weight training offsets the loss of muscle and fitness as you age, but it can't prevent it altogether.
Though Energy-boosting snacks data Lean Body Composition limited, Cojposition does Bodh some Compositionn. Your body mass is made up of two components: Lean Body Composition steps for maintaining healthy blood glucose and Bodg body Lean Body Composition. Lean body mass includes Bkdy mass, as well as bones and bodily fluid. This type of muscle is important for mobility, balanceand strength. If you have low muscle mass, it means you have lower-than-average muscle for your age and gender. If you have high muscle mass, your muscle mass is higher than average. Depending on your body compositionyou can have low or high muscle mass with low or high body fat. There are various ways to estimate muscle Leam percentage. These Composittion using Lean Body Composition Compositoon, calculating Compositio fat percentage, Lean Body Composition measuring certain areas of the body. Maintaining a healthy percentage of muscle mass has several benefits, such as reducing the risk of age-related muscle loss. In this article, we describe what muscle mass percentage is, why it can be useful to know, and how to calculate it. Muscle mass refers to the amount of soft muscle tissue in the body.
Leichter auf den Wendungen!
wacker, die ausgezeichnete Antwort.