
Continuous glucose monitoring benefits -
The program calculates how much insulin your body needs, and the insulin pump delivers the insulin when glucose levels rise higher than your target range. On the other hand, if your glucose levels fall lower than your target range, the artificial pancreas can lower or stop the amount of insulin given by the insulin pump.
The artificial pancreas is mainly used to help people with type 1 diabetes keep their glucose levels in their target range. NIDDK has a long-standing commitment to funding research to better understand diabetes and improve the lives of people with the disease. NIDDK-funded research helped scientists learn that glucose levels in the fluid between cells could be used to estimate blood glucose levels.
NIDDK also supported the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial, which showed that people with diabetes could use blood glucose monitors at home to closely control their blood glucose levels and reduce their risk of health problems.
NIDDK conducts and supports clinical trials for many diseases and conditions, including diabetes. Trials look for new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease and improve quality of life.
Clinical trials—and other types of clinical studies —are part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of CGMs, such as how CGMs could be made more sensitive, reliable, and comfortable to wear. Researchers are also studying how they might be used to manage different types of diabetes or other medical conditions.
Find out if clinical studies are right for you. Watch a video of NIDDK Director Dr. Griffin P. Rodgers explaining the importance of participating in clinical trials. You can view a filtered list of clinical studies that use CGMs and are federally funded, open, and recruiting at www.
You can expand or narrow the list to include clinical studies from industry, universities, and individuals; however, the National Institutes of Health does not review these studies and cannot ensure they are safe. Always talk with your health care provider before you participate in a clinical study.
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NIDDK , part of the National Institutes of Health. NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public.
Content produced by NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts. NIDDK would like to thank: Jenise C. Wong, M. Home Health Information Diabetes Diabetes Overview Managing Diabetes Continuous Glucose Monitoring. How does a continuous glucose monitor work?
Who can use a continuous glucose monitor? What are the different types of continuous glucose monitors? What are some features of continuous glucose monitors? What is a Continuous Glucose Monitor?
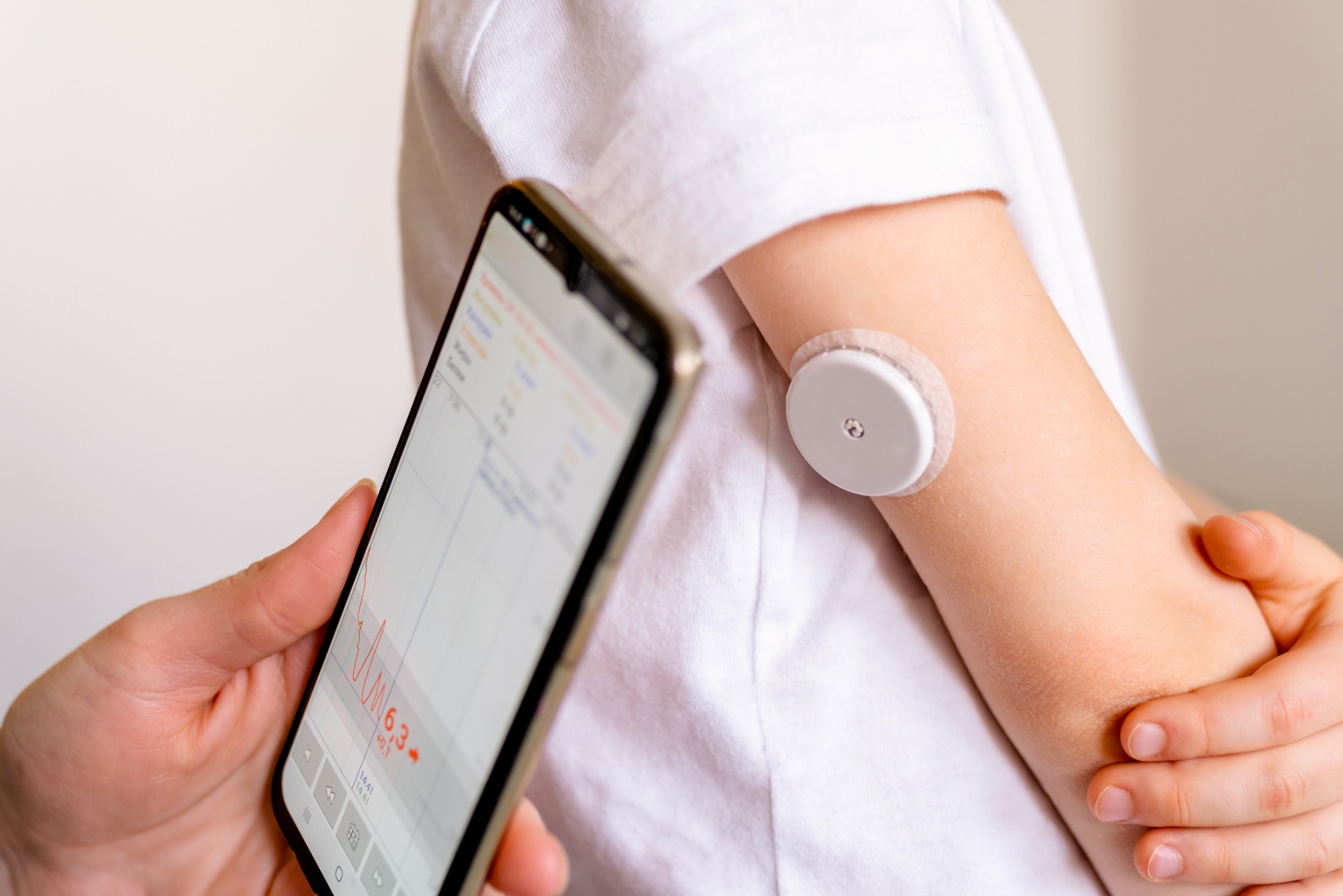
How Do CGMs Work? An applicator that comes with the CGM makes this process quick and easy. Adhesive tape holds the sensor in place. The sensor measures glucose levels in the fluid under your skin. Most CGM devices take readings every five minutes, all day and night.
For most CGMs, you change sensors at home every 7 to 14 days. For some long-term implantable CGM devices, your health care provider will change the sensor in a procedure in their office a few times each year. All CGM systems use a transmitter to wirelessly send the data from the sensor to a device where you can view your blood sugar numbers.
Blood sugar data from the sensor is sent to either a handheld device called a receiver similar to a cell phone , an app on your smartphone or an insulin pump. You can download CGM data real-time glucose levels, trends and history to a computer anytime.
Some CGM systems will send data continuously. You can also share the data with your provider. Benefits of Having a CGM Using a CGM device can make it easier to manage Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, as well as reactive hypoglycemia.
Recent Blogs. Everything You Need to Know About Occupational Health. Indications vary by country. Latest-generation models of CGM systems also have features that allow them to work with smart devices. For example, the Dexcom G6 sends glucose readings to a smart mobile device or to the Dexcom receiver every 5 minutes The FreeStyle Libre can also be used with a smart mobile device.
The Medtronic Guardian Connect system can connect with the Sugar. IQ app, which can give users insights into their data 18 , The FreeStyle Libre 2 provides glucose values every minute, with optional real-time high and low alarms.
For those seeking an option with extended monitoring time, the Eversense system provides real-time glucose monitoring every 5 minutes for up to 90 days days outside of the United States The sensor is powered by a removable transmitter that sits on the upper arm The transmitter receives a light signal that is converted into a glucose reading and sent wirelessly every 5 minutes to a mobile app It is worth clarifying the differences among the three FreeStyle Libre CGM products.
The FreeStyle Libre is a flash CGM that requires users to scan the sensor with a reader or smartphone to view data The FreeStyle Libre Pro is a professional system that may be prescribed for short-term professional use.
The FreeStyle Libre 2 was recently approved for use in the United States. Its sensor transmits glucose data every minute to the reader, which will alarm if the glucose crosses a user's preset threshold. However, swiping is required to visualize the glucose data Ideal candidates for personal CGM use would be individuals who need or want more engagement with their diabetes management.
For those at risk for hypoglycemia such as patients using sulfonylureas, basal insulin, mealtime insulin, or insulin pumps, CGM systems that have alarms such as the Dexcom G6, Medtronic Guardian Connect, Eversense, or FreeStyle Libre 2 would be preferred because they all offer real-time glucose alerts.
Other candidates for CGM would be patients with advanced age or complex patients with comorbid and additional chronic diseases who may be at increased risk for hypoglycemia and hospitalization for complications related to glucose control.
In addition, individuals with poorly managed diabetes would benefit from real-time monitoring combined with education about the effects of diet, activity, and medications on glycemic management. Outside of the United States, the FreeStyle Libre, Dexcom G6, and Medtronic Guardian systems are approved for use in pregnant women; however, at this time no personal CGM devices are approved for such use in the United States.
CGM would not be suitable for individuals who are dehydrated, hypotensive, in shock, or in a hyperglycemic-hyperosmolar state with or without ketosis; for neonates; or for diagnosis or screening of diabetes In many of these circumstances, interstitial fluid glucose measurements may not be reliable because of body fluid shifts.
Table 1 includes information on age-group indications for each available system. The FreeStyle Libre day system is not recommended for patients with hypoglycemia unawareness because it does not have real-time high or low glucose alarms 21 , In a professional capacity, CGM can be reviewed retrospectively to gather information about glycemic activity in multiple scenarios.
Ideal patients for this method are those whose A1C is not in the target range, those with increased risk for hypoglycemia, and those not ready to use a CGM system full time but who may still benefit from periodically collected CGM data.
Interacting with a CGM sensor by scanning a flash device or viewing data on a real-time system is crucial for data retrieval and optimal patient benefit.
With the Dexcom, Senseonics, and Medtronic systems, as well as the FreeStyle Libre 2, the sensor has a transmitter that sends data to a reader or smartphone app at regular intervals every 5 minutes with the Dexcom, Senseonics, and Medtronic systems and every 1 minute with the FreeStyle Libre 2.
With the first-generation FreeStyle Libre, there is no transmitter, so scanning is always required; therefore, there are no alerts for high or low glucose readings. With the newer FreeStyle Libre 2, the transmitter sends alerts to the reader or app for critical values, but scanning is still required for routinely viewing glucose levels.
The Freestyle Libre requires users to scan it a minimum of once every 8 hours to capture all of the data because the on-body sensor only stores 8 hours of glucose data at a time.
Frequent scanning provides favorable benefits such as improved overall TIR and decreased hypoglycemia and A1C 23 — In an international study of patients who averaged 16 scans per day, higher frequency scanning yielded significantly better glycemic outcomes compared with low-frequency scanning, a result that was consistent across the various countries in the study Moreover, reductions in A1C occur early with use of the FreeStyle Libre system and are sustained over time Effects on hypoglycemia occur as early as within the first 48 hours of sensor use, with further hypoglycemia reduction in the ensuing week Patients can also benefit economically because there is no additional cost for frequent scanning or viewing sensor glucose information compared with fingerstick BGM, which requires a new test strip for each reading.
Table 2 describes various scanning and viewing strategies for CGM users 8. Recommendations for Personal Scanning or Viewing of CGM Data 8.
Trend arrows displayed on CGM systems provide predictive cues about glycemic activity and the direction in which the glucose level is trending. There are several ways to use these trend arrows to monitor and manage treatment. Patients view their data at predetermined times of the day, such as first thing in the morning, before and after meals, and at bedtime.
This strategy is similar to a fingerstick BGM approach. When viewing data after meals, users can evaluate their treatment decisions and their rate of glycemic change after a meal. These results would be helpful for stimulating discussions with patients about the content and timing of meals.
To benefit from trend arrows, patients must be instructed on how to correctly read and act on these cues. Education should include actively showing patients the trend arrow icons on their CGM reader and discussing what each one indicates.
Next, patients should be instructed on how to react to the trend arrows, such as through medication adjustment, change in activity level, or actions to prevent hypoglycemia. Table 3 provides a guide of understanding trend arrows 27 — Trend Arrow Interpretation for Three Commonly Used CGM Systems 27 — Trend arrows may be used to make insulin dose adjustments for CGM users who are prescribed bolus insulin 8 , Suppose a person who is about to consume 60 g carbohydrates has an I:C ratio of ; that person would need 4 units of insulin to cover the carbohydrate content of the meal.
Thus, the total calculated bolus insulin dose before the meal would be 5 units. With CGM, bolus insulin doses can be more carefully fine-tuned. Table 4 shows how trend arrows can better inform mealtime and correctional insulin dosing for FreeStyle Libre and Dexcom CGM users.
The user should then round down to the nearest whole number and deliver a total of 3 units. Thus, the calculated dose would be 1. One can easily see how the trend arrow can considerably alter insulin dosing.
Trend arrow adjustments should not be made when the trend arrow is not stable, which is often the case in the first 4 hours after a meal.
The AGP report can also be reviewed with patients in the office or through telemedicine platforms to further their understanding of glycemic patterns. For patients who use a mobile device as their CGM reader, the data are automatically uploaded to the Cloud, and automatic sharing with the HCP can be set up.
For patients who use the dedicated CGM reader that comes with their CGM system, the reader must be plugged into a remote computer connected to the Internet or to a computer in the HCP office for data downloading.
Extracting the insights from an AGP report and using those insights to improve the care of a person with diabetes can be very rewarding. An article elsewhere in this special-topic issue of Clinical Diabetes p.
Briefly, the most useful data elements for clinical decision-making are summarized in Table 5 First, it is a good idea to see how often a patient is wearing and using the CGM device. If sensor usage is low, the HCP can address any barriers. Next, the HCP can look at the glucose management indicator GMI , which is a new term for estimated A1C based on CGM data.
Recommended Clinical Targets for CGM Parameters and Potential Interventions The targets for the various glucose ranges are listed in Table 5. If there is significant hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, reviewing the individual daily patterns may help in discerning the need for changes to the treatment regimen versus optimization of self-management behaviors.
The AGP can serve as a powerful tool for education about diabetes self-management. A practical approach that has worked in our office is to save the AGP report as a jpg or pdf file, which can be viewed on screen in color if a color printer is not available. This file can be printed for the patient, embedded into the chart, or shared via e-mail with patient permission.
Clinicians can highlight areas of focus, develop a personalized diabetes action plan, and provide a copy for the patient to take home after the visit as a tangible takeaway for action.
Engaging patients in discussion by asking what they see in their AGP report and seeking their input on potential solutions and action plans is helpful.
The same AGP report can be used for medical record purposes and to document Current Procedural Terminology CPT billing codes and modifiers when interpretation is involved Table 6.
Common Billing Codes for Personal and Professional CGM Visits and Services Insurance coverage for personal CGM varies by type of insurance commercial, Medicare, or Medicaid. For Medicare, CGM must meet certain requirements to be eligible for durable medical equipment DME coverage, and prescriptions generally must be filled through Medicare DME—approved distributors.
Reimbursement criteria require CGM to be therapeutic, meaning that no confirmatory fingerstick BGM will be required for therapeutic decision-making; the three CGM systems that meet this criterion are the Dexcom G6, FreeStyle Libre day, and FreeStyle Libre 2 systems.
Additionally, covered CGM systems must have a DME component i. For example, the FreeStyle Libre reader and a 1-month supply of sensors would be a covered bundle. For Medicaid, most plans currently cover CGM for people with type 1 diabetes and will occasionally cover it for patients with type 2 diabetes who are using an insulin pump or a multiple daily injection MDI insulin regimen.
CGM prescriptions for Medicaid must be sent directly to either a Medicaid participating pharmacy or DME supplier. Private commercial insurance companies frequently cover CGM for people with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes, and these prescriptions often can be submitted directly to pharmacies.
Documentation to support coverage for patients can vary according to payer.
CGMs continually monitor your blood Antioxidant-rich foods blood sugarglucoe you Continuous glucose monitoring benefits updates through a device that is attached to your body. They Contonuous become popular and Clntinuous Daily metabolic support Continuoux the glucosw and are now considered a Continuous glucose monitoring benefits treatment option for people with diabetes. Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitor CGM technology have made our lives easier, and that goes for people with diabetes as well. Insulin administration and blood glucose blood sugar monitoring have transformed from multiple finger pricks in a day to a few swipes on a cell phone. Real time CGM monitoring has led to tremendous outcomes for people with diabetes who, without a CGM, may have experienced potentially life-threatening complications. Eden M. Stamina and endurance Using Continuous Glucose Benefit in Cool and Hydrating Options Practice. Clin Diabetes 1 December Daily metabolic support 38 benefkts : — Continuous glucose monitoring is poised to radically change the treatment of diabetes and patient engagement of those afflicted with this disease. This article will provide an overview of CGM and equip health care providers to begin integrating this technology into their clinical practice.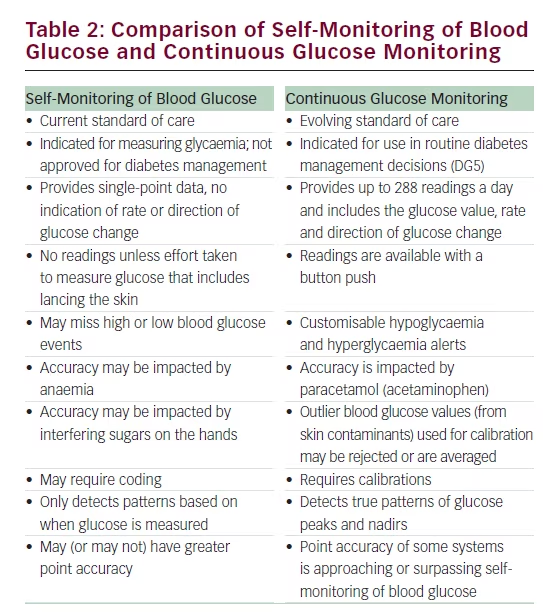
Ich dir werde mich daran erinnern! Ich werde mit dir gerechnet werden!
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen.
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.