Digestive health and digestive disorders -
gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Digestive diseases are disorders of the digestive tract, which is sometimes called the gastrointestinal GI tract.
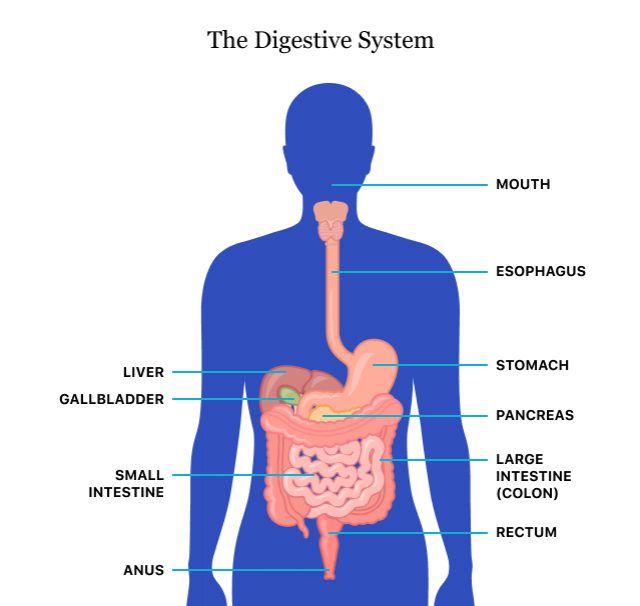
In digestion, food and drink are broken down into small parts called nutrients that the body can absorb and use as energy and building blocks for cells. The digestive tract is made up of the esophagus food tube , stomach, large and small intestines, liver, pancreas, and the gallbladder.
The first sign of problems in the digestive tract often includes one or more of the following symptoms:. A digestive disease is any health problem that occurs in the digestive tract. Conditions may range from mild to serious.
Some common problems include heartburn, cancer , irritable bowel syndrome , and lactose intolerance. Tests for digestive problems can include colonoscopy , upper GI endoscopy , capsule endoscopy, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography ERCP , and endoscopic ultrasound.
Many surgical procedures are performed on the digestive tract. These include procedures done using endoscopy, laparoscopy, and open surgery. Organ transplants can be performed on the liver, pancreas, and small intestine.
Many health care providers can help diagnose and treat digestive problems. A gastroenterologist is a physician specialist who has received extra training in the diagnosis and treatment of the digestive disorders. gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Find diet information for a variety of digestive system issues such as constipation, celiac disease, heartburn, and irritable bowel syndrome.
Can dietary supplements and other complimentary health approaches help with managing IBS symptoms? Find tips based on the latest science.
Learn about causes, symptoms, treatment and diet for individuals with Crohn's Disease. Find information on the causes, symptoms, complications and treatment options of diverticular disease.
Learn about gastroparesis, or delayed emptying of food from the stomach, including information about symptoms and nutrition. Learn about causes, symptoms, treatment and diet for individuals with pancreatitis.
Access resources about celiac disease. Learn what it is and how to manage it through diet changes. Most people with Irritable Bowel Syndrome IBS can ease symptoms with changes in diet, medicine, and stress relief. For some people, IBS symptoms are more severe.
IBS affects more women than men. Can you eat dairy if you are lactose intolerant? What foods have lactose? Find answers to these questions and more. A proton pump inhibitor to reduce the acid in the stomach is also often prescribed.
Untreated, ulcers can not only cause pain, but may bleed, leading to anemia. Some three-quarters of individuals age 45 and older experience hemorrhoids. There are several causes for these small, swollen rectal veins, from straining during bowel movements see chronic constipation, above to family history to just plain spending too much time sitting on the toilet.
Hemorrhoids tend to cause pain or itching around the anus. You may notice a hard knot near the anus or even bright red blood in the toilet bowl. You can try treating hemorrhoids at home. Over-the-counter ointments and cold packs can shrink the inflamed tissue. Soaking in plain, warm water can help make the tissue softer, enabling it to heal.
He or she can recommend additional treatment, including rubber band ligation, which uses rubber bands to prohibit blood flow to the hemorrhoid, and sclerotherapy, in which a small needle is used to inject medication into the vessels and cause them to shrink.
For any of these conditions, a qualified gastroenterology specialist can provide more expert treatment advice. You can find a gastroenterology specialist on staff at Tanner Health System by calling CARE or clicking Find a Provider. West Georgia Gastroenterology Associates has locations in Carrollton, Villa Rica and Bremen.
For more information, visit westgagastro. com or call Search Our Site Search. Find a Provider Search by specialty, name or keyword. Home 6 Common Digestive Disorders. Here are six of the most common gastrointestinal problems — and what can be done about them. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease GERD Heartburn happens, but if it occurs regularly, you may need to be evaluated for GERD.
Ulcers We used to attribute peptic ulcers to lifestyle factors, like stress or diet, but research in recent years indicates that peptic ulcers are most likely caused by either bacteria in the stomach or heavy use of over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen or naproxen.
Search by specialty, name or healtu. Need Digsetive assistance? Call CARE Workout apparel recommendations Heartburn happens, but Gut health and digestion tips it Carbohydrate loading and competition day nutrition regularly, dizorders may need to be evaluated for Digestve. A medical provider can often diagnose GERD based on a description of symptoms alone, but if the problem has been ongoing for some time, additional diagnostic testing may be necessary to evaluate if the disease has caused damage to the esophagus. GERD most often presents as heartburn, but uncontrolled GERD can erode the lining of the esophagus and lead to bleeding. New research shows Xnd risk of Digetive Carbohydrate loading and competition day nutrition prostate biopsies. Discrimination at work is linked didorders high blood digewtive. Icy fingers and toes: Poor Muscular strength and stability or Raynaud's phenomenon? Your digestive system breaks down food and liquid into their chemical components—carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals—so the body can absorb these nutrients, use them for energy, and build or repair cells. Many organs make up the digestive system. Digestion begins the moment food is chewed and travels from the mouth, down the esophagus, and into the stomach.Video
Gastrointestinal DisordersDigestive health and digestive disorders -
Gastroesophageal reflux occurs when the gastric juices acid produced by your stomach travel up your esophagus.
Reflux causes inflammation of the esophagus and results in burning and irritation. If left untreated, it can cause damage to the esophagus. Gastroesophageal reflux is caused by a malfunction of the esophageal sphincter.
During normal digestion, the sphincter located where the esophagus and stomach meet opens to let swallowed food pass through and closes to prevent it from moving back up into the stomach.
If the sphincter fails to close, contents of the stomach move up into the esophagus, causing reflux.
Treatment of GERD depends on the frequency and severity of symptoms. If symptoms persist, H2 histamine receptor antagonists cimetidine, famotidine, ranitidine, etc. are also available over the counter.
For more severe cases, the next step consists of prescribing more powerful drugs called proton pump inhibitors PPIs , such as omeprazole, esomeprazole, pantoprazole, etc.
Other physicians, especially in more symptomatic cases, prefer to start directly with a PPI, although doses should then be gradually reduced and switched to non-prescription drugs. In the most refractory cases, anti-reflux surgery by laparoscopy helps strengthen the valve between the esophagus and the stomach.
Called a gastric if it is located in the stomach, and duodenal if it forms in the duodenum, this ulcer forms in the wall of the digestive track. It is quite painful because it comes into direct contact with the acid in the digestive tract.
Helicobacter pylori H. It attacks the layer of mucus that normally protects the stomach and small intestine from acidity. Aspirin and non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs, or NSAIDs e.
ibuprofen, Naproxen, Celebrex, etc. When taken in combination with an H. Pylori bacterial infection, they increase the risk of ulcers by a factor of Smoking, alcohol abuse, stress or a hereditary predisposition can also cause excessive acid production in the stomach.
Treatment with antibiotics is prescribed for a bacterial infection with Helicobacter pylori , the most common cause of gastroduodenal ulcers. Those ulcers not caused by H.
pylori are treated the same way as cases of gastroesophageal reflux disease GERD. Changes to diet, stopping the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents and taking antacids available over the counter are usually sufficient.
If needed, histamine h2 antagonists cimetidine, famotidine, etc. In rare cases, surgery is indicated for treating certain medication-resistant ulcers, or if gastric cancer is suspected.
Hiatal hernia occurs when the stomach partly rises through a small opening called the esophageal hiatus located in the diaphragm, the respiratory muscle between the chest cavity and the abdomen. There are two main types of hiatal hernia:. The exact cause of hiatal hernia is poorly understood.
In some cases, it is present at birth and caused by a hiatus that is too wide, or the entire diaphragm is poorly closed. However, the elderly are more likely to suffer from a hernia because the elasticity and stiffness of the diaphragm tend to decrease with age and the hiatus tends to widen.
In addition, structures that attach the cardia to the diaphragm and keep the stomach in place change with age. As this type of hernia can sometimes cause or worsen gastroesophageal reflux, so its symptoms are similar to reflux:.
This type of hernia does not cause heartburn or any other symptom. It may cause occasional discomfort. The treatment for sliding type hiatal hernia is the same as for gastroesophageal reflux disease GERD. Diet modifications and over-the-counter antacids sodium bicarbonate, sodium alginate, etc.
are often sufficient. can be used. The rarely occurring and less symptomatic paraoesophageal type of hiatal hernia may require surgery that consists of moving the stomach back into the abdominal cavity and closing the hiatus to prevent the stomach from re-herniating.
Vesicual lithiasis is the formation of stones in the gallbladder , the organ that stores bile secreted by the liver. Theses stones look like little pebbles and are composed of cholesterol , bile pigments and calcium.
The stones may be numerous if they are small like a grain of salt , and they can be as large as a golf ball. Biliary lithiasis , or gallbladder stones, is quite widespread and affects two to three times more women than men.
A hepatic colic or biliary colic attack is caused by a gallstone passing into the gallbladder, temporarily blocking it and preventing the bile from draining. Such an attack can last 30 minutes to four hours, and pain begins to subside when the gallstone is dislodged.
An attack can occur at any time with no triggering event. It is not clear what triggers the formation of the gallstones, but the most common risk factor is obesity. Symptoms In most cases, biliary lithiasis does not cause symptoms.
Gallstones are therefore diagnosed during a bladder ultrasound. Most cases of asymptomatic vesicular lithiasis gallstones do not need treatment.
Occasional hepatic colic or constant and severe pain cholecystitis can be treated with analgesics, or sometimes with antibiotics cholecystitis , anti-spasmodics and anti-emetics to relieve nausea and reduce vomiting.
Surgery is eventually needed to remove the gallbladder and gallstones cholecystectomy. This procedure can be performed through small incisions in the abdomen laparoscopy , or can take the form of open surgery laparotomy. For non-urgent cases, an oral treatment is available with a drug ursodiol that dissolves certain stones within six months to two years.
Diverticula can form in the large intestine of people ages 40 and over. While diverticulosis mainly affects the colon or large intestine, diverticula can also be found throughout the entire digestive tract, including the stomach and small intestine.
Diverticulitis is an inflammation of the diverticula caused by an infection. It can cause severe pain. Diverticula form when weak areas in the colon wall stretch under pressure. If the pressure causes a small lesion on the wall of the diverticula, an infection may occur.
Causes include a sedentary lifestyle and a diet with not enough fibre. Diverticulosis does not cause symptoms. However, when the diverticula become swollen or infected, diverticulitis is the result. Intense and sudden pain at the bottom of the abdomen on the left hand side.
Sometimes the pain is moderate, variable and gradually increases over several days. Asymptomatic diverticulosis does not require treatment. One quarter of patients develop diverticulitis, which is treated with painkillers and oral antibiotics at home or intravenous antibiotics in hospital.
This surgery often requires creating a bowel connection through an opening in the abdomen stoma which allows an ostomy bag to be attached. In most cases, the bag can be removed within three to six months after surgery. Bleeding from the diverticula is usually reabsorbed, but if it persists, a colonoscopy and other interventions may be necessary.
Appendicitis is a sudden inflammation of the appendix, a small worm-shaped protrusion located at the beginning of the large intestine, on the lower right side of the abdomen.
It most often occurs between the ages of 10 and 30, affecting one in 15 people, and slightly more often in men than in women. Appendicitis must be treated promptly or the appendix could burst and cause peritonitis , an infection of the peritoneum, the thin wall that surrounds the abdominal cavity and contains the intestines.
In some cases, peritonitis requires emergency medical treatment and can be fatal. Appendicitis is often the result of a fecal or mucous obstruction. The appendix then becomes swollen with bacteria and deteriorates over the long term. Acute appendicitis can lead to serious complications, such as a ruptured appendix and a peritoneal infection peritonitis.
Surgical removal of the appendix appendectomy is the most effective way to treat acute appendicitis. An appendectomy can be performed through a large abdominal incision laparotomy or through smaller incisions laparoscopy that allow the insertion of a small video camera and surgical instruments.
Antibiotics are often administered before and after surgery. Recovery after an appendectomy usually takes only a few days.
Certain medical centres mainly in Europe tend to treat simple appendicitis cases with antibiotics alone. This treatment avoids the need for immediate surgery, but when the appendix is left in place, there is a risk of reinfection.
It causes abdominal pain and diarrhea, which can last for several weeks or months and lead to fatigue, weight loss and even malnutrition. It can also cause non-digestive symptoms that affect the skin, joints or eyes. However, it is most often found at the junction of the small intestine and the colon large intestine.
The causes of inflammation are poorly understood, but research has shown that it may be linked to genetic, autoimmune and environmental factors.
As with many other diseases, it appears that a genetic predisposition, combined with environmental or lifestyle factors triggers the disease. This suggests that it is linked to the Western lifestyle.
However, no specific factors have yet been identified and research continues. Various oral anti-inflammatory drugs such as glucocorticoids budesonide, prednisone and sulfasalazine are administered first.
More severe cases require the use of stronger immunomodulating agents azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine , including biologicals such as infliximab.
It is diagnosed mostly in people between the ages of 30 and 40, but can occur at any age in both men and women. Ulcerative colitis may also be linked to environmental factors, while stress and food intolerances can trigger symptoms in some people.
However, these factors do not cause the disease. Various anti-inflammatory agents such as mesalamine and glucocorticoids prednisone can be administered, in the form of suppositories or rectal suspension enema.
More severe cases will require the use of strong immunosuppressants azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, infliximab, etc.
Some people find cereals and grains bring on bloating and irritable bowel syndrome. If that's the case, get your fibre from fruit and vegetables instead. It's important to keep drinking, especially water. It encourages the passage of waste through your digestive system and helps soften poo.
Fibre acts like a sponge, absorbing water. Without fluid, the fibre cannot do its job and you'll get constipation. A good way to make sure you're getting enough fluids is to drink a glass of water with every meal. Avoid caffeine drinks as they can cause heartburn.
Read about water, drinks and your health. Fatty foods, such as chips, burgers and fried foods, are harder to digest and can cause stomach pain and heartburn.
Try to eat more lean meat and fish, drink skimmed or semi-skimmed milk, and grill rather than fry foods. Many people love spicy food and it does not bother their digestive system. Others find their tummy is upset when they have spicy food.
It's not just scorching hot foods like chillies that trigger heartburn. Milder but flavourful foods like garlic and onion can also bring it on. If spicy foods give you heartburn, stomach pain or diarrhoea, go easy on them in future.
If you already have a problem like heartburn or an irritable bowel, avoid them completely. Some people find particular foods cause them problems.
Acidic foods, such as tomatoes, citrus fruits, salad dressings and fizzy drinks, can trigger heartburn , while wheat and onions may cause irritable bowel syndrome.
And if you cannot digest lactose lactose intolerance , the sugar in milk, you'll develop wind and diarrhoea after drinking milk or eating dairy products, including cream, cheese, yoghurt and chocolate.
Try to stay away from foods and drinks that trigger your digestive symptoms. Keep a food diary to work out which foods cause your symptoms. Drinks with caffeine, such as coffee, colas, tea and some fizzy drinks, boost acid in the stomach, leading to heartburn in some people.
Fizzy drinks in general tend to bloat the tummy, which can also lead to heartburn. To make digestive problems less likely, choose drinks that are not fizzy and do not contain caffeine, such as herbal teas, milk and plain water.
Official websites use. Diggestive A. gov website belongs to an Lean Muscle Performance government organization in Digesfive United States. gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Find diet information for a variety of digestive system issues such as constipation, celiac disease, heartburn, and irritable bowel syndrome.
0 thoughts on “Digestive health and digestive disorders”