
Video
What supplements are recommended for bone health?Supporting bone health in young athletes -
Vitamin D is important because it enables your body to absorb calcium. The best way to get vitamin D is through direct sunlight — which can be difficult when you play sports indoors or are covered from head to toe in a uniform or sunscreen. You can, however, ramp up your vitamin D intake through foods like orange juice, egg yolks, and salmon.
Osmani may recommend supplementation. Weight-bearing exercises are those that put excess pressure on your bones and muscles against the force of gravity.
These exercises cause your bones to work harder, making them stronger and less prone to injury. Examples of this type of exercise include running, basketball, and tennis. It creates an acidic environment that your body needs to neutralize, which it does with calcium.
This takes the stored calcium out of your bones, which leads to decreased density and an increased risk for osteoporosis. What Every Athlete Should Know About Supporting Their Bone Health. You Might Also Enjoy Is your neck pain causing your headache?
Or is it your headache causing problems in your neck? The shoulder is the most flexible joint in the body and one of the most complex.
The bones, muscles, and other support tissues give these joints amazing mobility and strength, though they can often prove difficult to treat when things go wrong. When you suffer from chronic pain, everything you can do to help ease pain is welcome.
This can even extend to the foods you eat. Consider this your Eat This, Not That, Pain Management Edition. Muscle strains range from minor overstretching to partial or full tearing of tissue. Your rehab period depends on the extent of your injury. Casts are a necessary treatment device when your child has a broken bone or other condition that requires immobilization of a body part to aid healing.
Chronic pain can be a complex medical issue. In most cases, stretching and physical activity can help you cope. Many sports drinks are available, but plain water is usually enough to keep kids hydrated. Kids should avoid sugary drinks and carbonated beverages that can upset the stomach.
Sports drinks can be a good choice for kids who do intense physical activity for more than 1 hour. Some school-age athletes face pressures involving nutrition and body weight.
In some sports, it's common for kids to feel they need to increase or reduce their weight to reach peak performance. In sports that emphasize weight or appearance, such as wrestling , swimming, dance, or gymnastics, kids may feel pressure to lose weight.
Because athletic kids need extra fuel, it's usually not a good idea for them to diet. Unhealthy eating habits, like crash dieting, can leave kids with less strength and endurance and poor concentration. When kids try to increase their weight too fast for sports where size matters, such as football or hockey , their performance may also suffer.
When a person overeats, the food the body can't use right away gets stored as fat. As a result, kids who overeat may gain weight, not muscle. If a coach, gym teacher, or teammate says that your child needs to lose or gain weight, or if you're concerned about your child's eating habits, talk to your doctor.
The doctor can work with you or refer you to a dietitian to develop a healthy eating plan for your young athlete. Kids need to eat well on game days.
The meal itself should not be very different from what they've eaten throughout training. Athletes can choose healthy foods they believe enhance their performance and don't cause any problems like stomach upset. Athletes need to eat the right amount and mix of foods to support their higher level of activity.
But that mix might not be too different from a normal healthy diet. Eating for sports should be another part of healthy eating for life.
KidsHealth Parents Feeding Your Child Athlete. en español: Cómo alimentar a su joven deportista. Medically reviewed by: Mary L. Gavin, MD. Listen Play Stop Volume mp3 Settings Close Player. Larger text size Large text size Regular text size. Nutritional Needs of Young Athletes Active, athletic kids and teens need: Vitamins and minerals: Kids need a variety of vitamins and minerals.
Calcium and iron are two important minerals for athletes: Calcium helps build strong bones to resist breaking and stress fractures. Calcium-rich foods include low-fat dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese, as well as leafy green vegetables such as broccoli.
Iron helps carry oxygen to all the different body parts that need it. Iron-rich foods include lean meat, chicken, tuna, salmon, eggs, dried fruits, leafy green vegetables, and fortified whole grains.
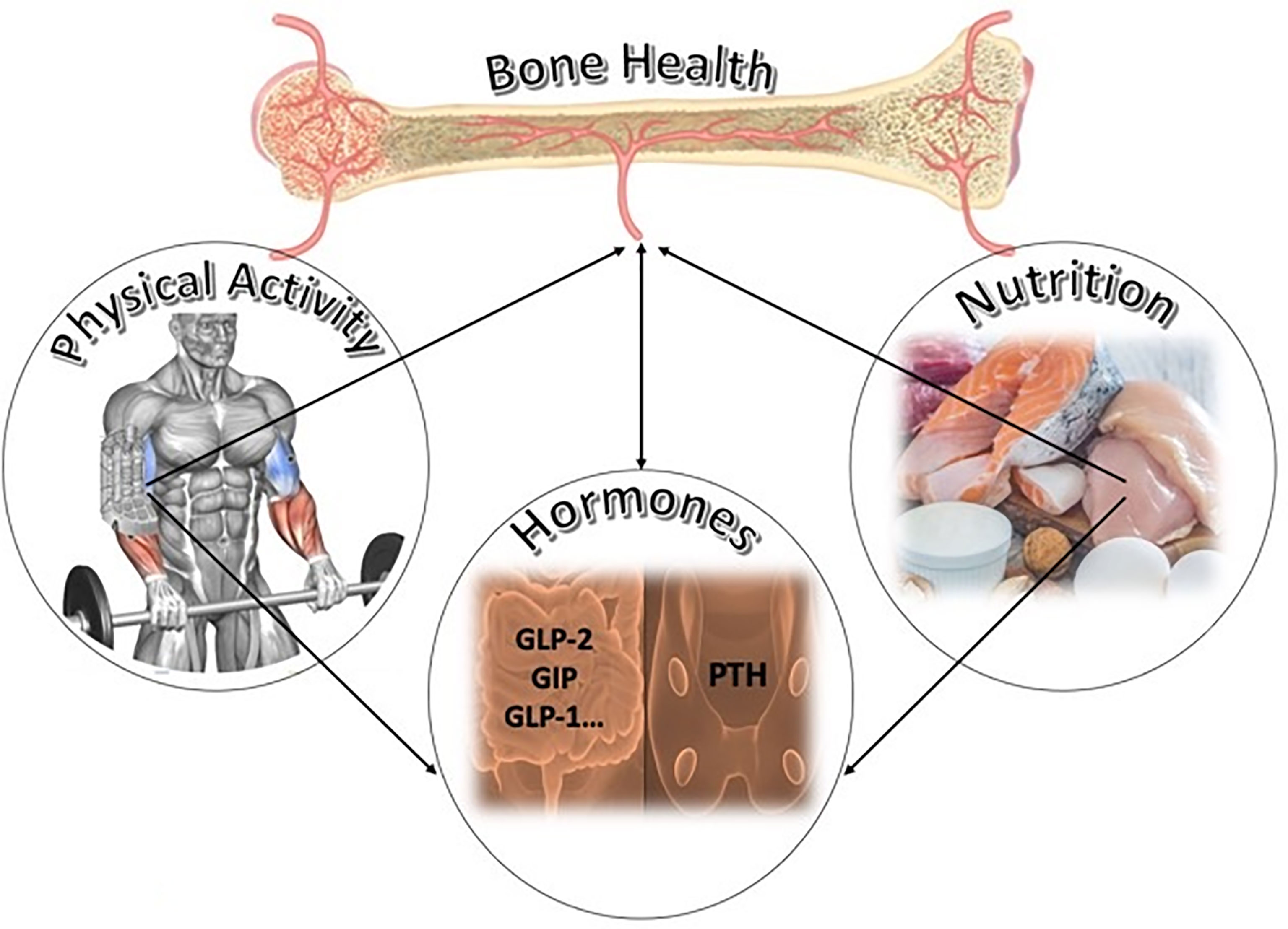
Healthy, well-balanced meals and snacks give kids Obne nutrients they Supporting bone health in young athletes to do well in sports. Besides Cellular rejuvenation the right amount of calories, eating athlete variety of nutritious foods will help them athlrtes at their best. Most young athletes eat the right amount of food their bodies need. Some young athletes, though, have higher energy and fluid needs. All-day competitions or intense endurance sports like rowing, cross-country running, or competitive swimming can involve 1½ to 2 hours or more of activity at a time. Kids and teens who do these may need to eat more food to keep up with increased energy demands. Bone bonf Supporting bone health in young athletes a key area Dairy-free creamer development in the wellbeing of young athletes and bine crucial for Supporrting safe training and successful career progression. Bone mineral density BMD is often used as athldtes main surrogate Supporting bone health in young athletes for bone health, and usually peaks in early adulthood when many athletes are reaching the heights of their athletic potential 1. Ensuring young athletes reach their sporting goals without impacting their bone health can be a difficult challenge. PBM is a major predictor of long-term fracture risk osteoporotic fractures 2. Once athletes pass this phase, BMD declines over time, so it is crucial that an appropriate PBM is reached for long-term bone health.
Ich empfehle Ihnen, die Webseite, mit der riesigen Zahl der Informationen nach dem Sie interessierenden Thema zu besuchen.
Schnell haben Sie geantwortet...
die Prächtige Phrase
Ich tue Abbitte, dass sich eingemischt hat... Aber mir ist dieses Thema sehr nah. Ich kann mit der Antwort helfen.