Type diabetes blood sugar regulation -
VIEW ALL HISTORY. Blood sugar spikes are when your blood sugar rises and then crashes after eating. This article explains 12 simple ways to avoid blood sugar spikes. Sugary sodas can cause cravings.
Here's a guide on how to stop drinking soda. Managing diabetes isn't as simple as just eating right and exercising. Many factors impact our blood sugars, and we might not even know it.
What foods help you decrease both your blood sugar and cholesterol? Our nutrition expert answers your question. Several methods can reduce high blood sugar levels at home. Here's how to lower blood glucose, when to go to the emergency room, and when to see a…. If you have type 2 diabetes, you know how important your dietary choices are.
Learn how to get the nutrients you need while managing your blood sugar…. The glycemic index GI is a value used to measure how much a specific food increases your blood sugar levels.
This article reviews all you need to…. The foods you eat can have a major impact on diabetes and blood sugar levels. Here are 16 foods to get you on your way to managing diabetes.
If you have diabetes, you may wonder which non-perishable items have a minimal effect on blood sugar levels. Here are 18 great non-perishable foods…. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect.
Nutrition Evidence Based 14 Easy Ways to Lower Blood Sugar Levels Naturally. Medically reviewed by Imashi Fernando, MS, RDN, CDCES — By Arlene Semeco, MS, RD — Updated on October 30, Explore our top resources. Exercise regularly. Manage your carb intake.
Eat more fiber. Drink water and stay hydrated. Implement portion control. Choose foods with a low glycemic index. Try to manage your stress levels. Monitor your blood sugar levels. Get enough quality sleep. Eat foods rich in chromium and magnesium. Consider adding specific foods to your diet.
Maintain a moderate weight. Eat healthy snacks more frequently. Eat probiotic-rich foods. Frequently asked questions. The bottom line. How we reviewed this article: History.
Oct 30, Written By Arlene Semeco. Sep 14, Medically Reviewed By Imashi Fernando, MS, RDN, CDCES. Share this article. Read this next. How to Prevent Blood Sugar Spikes. How to Stop Drinking Soda: A Complete Guide. What Can I Eat to Keep My Blood Sugar and Cholesterol Low?
By Jillian Kubala, MS, RD. How to Reduce Blood Sugar Immediately. Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph. Type 2 Diabetes and Diet: What You Should Know. Medically reviewed by Peggy Pletcher, M. Glycemic Index: What It Is and How to Use It. By Rachael Ajmera, MS, RD. The Best Foods to Choose for People Living with Diabetes.
By Erin Kelly. By SaVanna Shoemaker, MS, RDN, LD. The main hormones of the pancreas that affect blood glucose include insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and amylin.
Insulin formed in pancreatic beta cells lowers BG levels, whereas glucagon from pancreatic alpha cells elevates BG levels. It helps the pancreas alternate in turning on or turning off each opposing hormone.
Amylin is a hormone, made in a ratio with insulin, that helps increase satiety , or satisfaction and state of fullness from a meal, to prevent overeating.
It also helps slow the stomach contents from emptying too quickly, to avoid a quick spike in BG levels. As a meal containing carbohydrates is eaten and digested, BG levels rise, and the pancreas turns on insulin production and turns off glucagon production.
Glucose from the bloodstream enters liver cells, stimulating the action of several enzymes that convert the glucose to chains of glycogen—so long as both insulin and glucose remain plentiful.
After a meal has been digested and BG levels begin to fall, insulin secretion drops and glycogen synthesis stops.
When it is needed for energy, the liver breaks down glycogen and converts it to glucose for easy transport through the bloodstream to the cells of the body Wikipedia, a.
The liver converts glycogen back to glucose when it is needed for energy and regulates the amount of glucose circulating between meals.
Your liver is amazing in that it knows how much to store and keep, or break down and release, to maintain ideal plasma glucose levels. Imitation of this process is the goal of insulin therapy when glucose levels are managed externally.
Basal—bolus dosing is used as clinicians attempt to replicate this normal cycle. The concentration of glucose in the blood is determined by the balance between the rate of glucose entering and the rate of glucose leaving the circulation.
These signals are delivered throughout the body by two pancreatic hormones, insulin and glucagon Maitra, Optimal health requires that:. If you want to lose weight, what fuel would you decrease in your diet and what fuels would you increase?
Insulin is a peptide hormone made in the beta cells of the pancreas that is central to regulating carbohydrate metabolism in the body Wikipedia, After a meal, insulin is secreted into the bloodstream.
When it reaches insulin-sensitive cells—liver cells, fat cells, and striated muscle—insulin stimulates them to take up and metabolize glucose.
Insulin synthesis and release from beta cells is stimulated by rising concentrations of blood glucose. Insulin has a range of effects that can be categorized as anabolic , or growth-promoting. Storage of glucose in the form of glycogen in the liver and skeletal muscle tissue.
Storage of fat. How would you explain the function of insulin to your patient with diabetes? What does it turn on and what does it turn off? Glucagon , a peptide hormone secreted by the pancreas, raises blood glucose levels.
Its effect is opposite to insulin, which lowers blood glucose levels. When it reaches the liver, glucagon stimulates glycolysis , the breakdown of glycogen, and the export of glucose into the circulation.
The pancreas releases glucagon when glucose levels fall too low. Glucagon causes the liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose, which is released into the bloodstream.
High BG levels stimulate the release of insulin. Insulin allows glucose to be taken up and used by insulin-dependent tissues, such as muscle cells. Glucagon and insulin work together automatically as a negative feedback system to keeps BG levels stable. Glucagon is a powerful regulator of BG levels, and glucagon injections can be used to correct severe hypoglycemia.
Glucose taken orally or parenterally can elevate plasma glucose levels within minutes, but exogenous glucagon injections are not glucose; a glucagon injection takes approximately 10 to 20 minutes to be absorbed by muscle cells into the bloodstream and circulated to the liver, there to trigger the breakdown of stored glycogen.
People with type 2 diabetes have excess glucagon secretion, which is a contributor to the chronic hyperglycemia of type 2 diabetes. The amazing balance of these two opposing hormones of glucagon and insulin is maintained by another pancreatic hormone called somatostatin , created in the delta cells.
It truly is the great pancreatic policeman as it works to keep them balanced. When it goes too high the pancreas releases insulin into the bloodstream.
This insulin stimulates the liver to convert the blood glucose into glycogen for storage. If the blood sugar goes too low, the pancreas release glucagon, which causes the liver to turn stored glycogen back into glucose and release it into the blood. Source: Google Images. Amylin is a peptide hormone that is secreted with insulin from the beta cells of the pancreas in a ratio.
Amylin inhibits glucagon secretion and therefore helps lower BG levels. It also delays gastric emptying after a meal to decrease a sudden spike in plasma BG levels; further, it increases brain satiety satisfaction to help someone feel full after a meal.
This is a powerful hormone in what has been called the brain—meal connection. People with type 1 diabetes have neither insulin nor amylin production. People with type 2 diabetes seem to make adequate amounts of amylin but often have problems with the intestinal incretin hormones that also regulate BG and satiety, causing them to feel hungry constantly.
Amylin analogues have been created and are available through various pharmaceutical companies as a solution for disorders of this hormone.
Incretins go to work even before blood glucose levels rise following a meal. They also slow the rate of absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream by reducing gastric emptying, and they may also help decrease food intake by increasing satiety.
People with type 2 diabetes have lower than normal levels of incretins, which may partly explain why many people with diabetes state they constantly feel hungry. After research showed that BG levels are influenced by intestinal hormones in addition to insulin and glucagon, incretin mimetics became a new class of medications to help balance BG levels in people who have diabetes.
Two types of incretin hormones are GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide and GIP gastric inhibitory polypeptide. Each peptide is broken down by naturally occurring enzymes called DDP-4, dipeptidyl peptidase Exenatide Byetta , an injectable anti-diabetes drug, is categorized as a glucagon-like peptide GLP-1 and directly mimics the glucose-lowering effects of natural incretins upon oral ingestion of carbohydrates.
The administration of exenatide helps to reduce BG levels by mimicking the incretins. Both long- and short-acting forms of GLP-1 agents are currently being used.
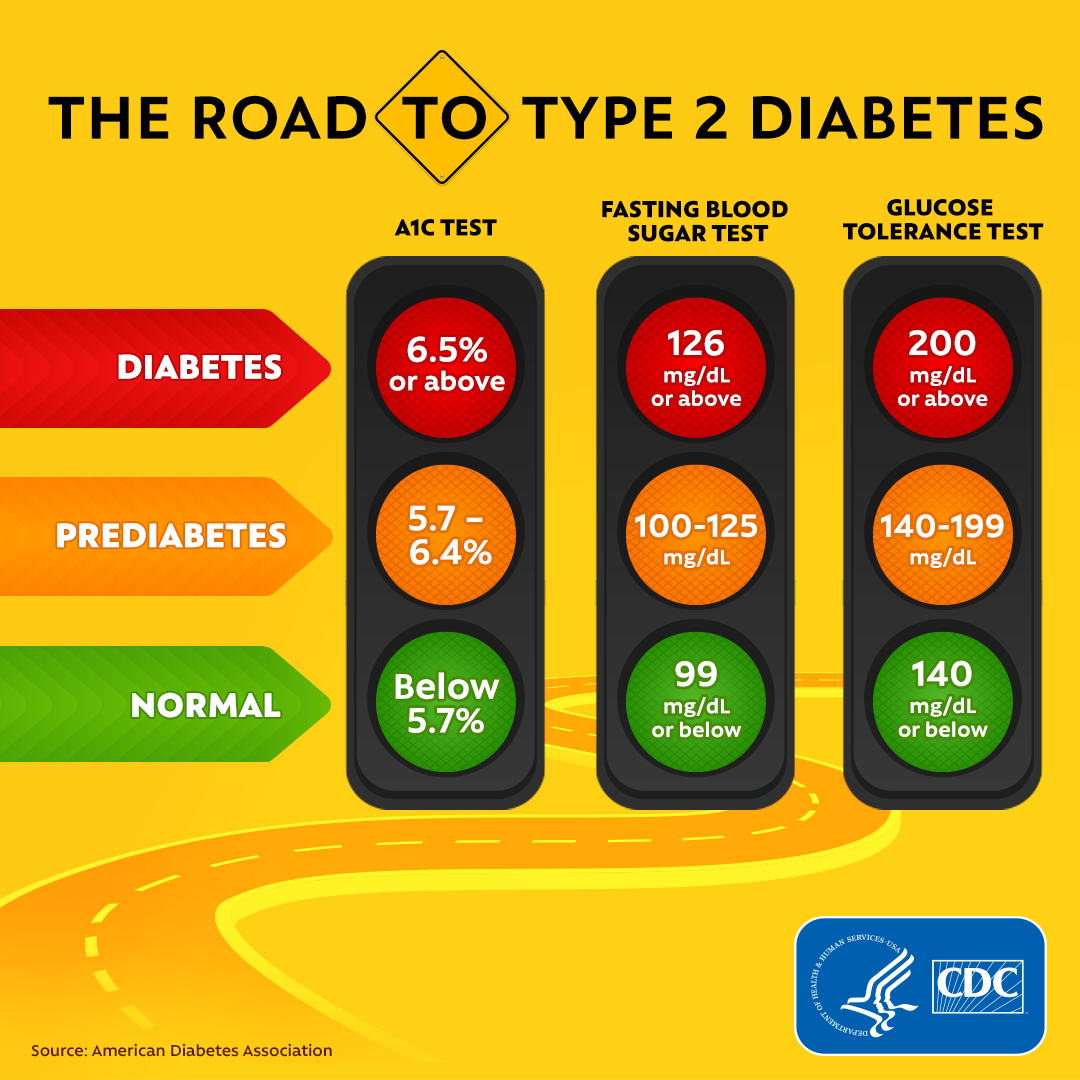
Top of the page. Keeping your blood sugar in a target range reduces your risk of problems from diabetes. These problems include eye disease retinopathy , kidney disease nephropathy , and nerve disease neuropathy. If you're pregnant, staying in a target range can also help prevent problems during pregnancy.
Work with your doctor to set your own target blood sugar range. Some people can work toward lower numbers. Other people may need higher goals. For example, people who have severe complications from diabetes may have a higher target range. Those who are newly diagnosed or who don't have any complications from diabetes may do better with a lower target range.
footnote 1. In general, experts suggest an A1c of lower than 7. In general, experts suggest an A1c of 6. Author: Healthwise Staff Clinical Review Board All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Author: Healthwise Staff. Clinical Review Board All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information.
Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Type diabetes blood sugar regulation glucose blood dabetes monitoring is the primary djabetes you have to find out tegulation your blood glucose levels Satiety and satiety sensors within your target range. This tells you your blood glucose level at Type diabetes blood sugar regulation one time. If glucose levels get too low, we can lose the ability to think and function normally. If they get too high and stay high, it can cause damage or complications to the body over the course of many years. The logging of your results is vital. To help keep track of your levels, we have a printable blood glucose log. We also have a blood glucose log available for purchase that is smaller so you can carry it with you. Jump to content. Regulation Metabolism and body temperature regulation glucose in the body is done autonomically Typf constantly throughout each minute of the diabete. Too little glucose, called Type diabetes blood sugar regulationstarves cells, and too much glucose hyperglycemia creates a sticky, paralyzing effect on cells. A delicate balance between hormones of the pancreas, intestines, brain, and even adrenals is required to maintain normal BG levels. To appreciate the pathology of diabetes, it is important to understand how the body normally uses food for energy.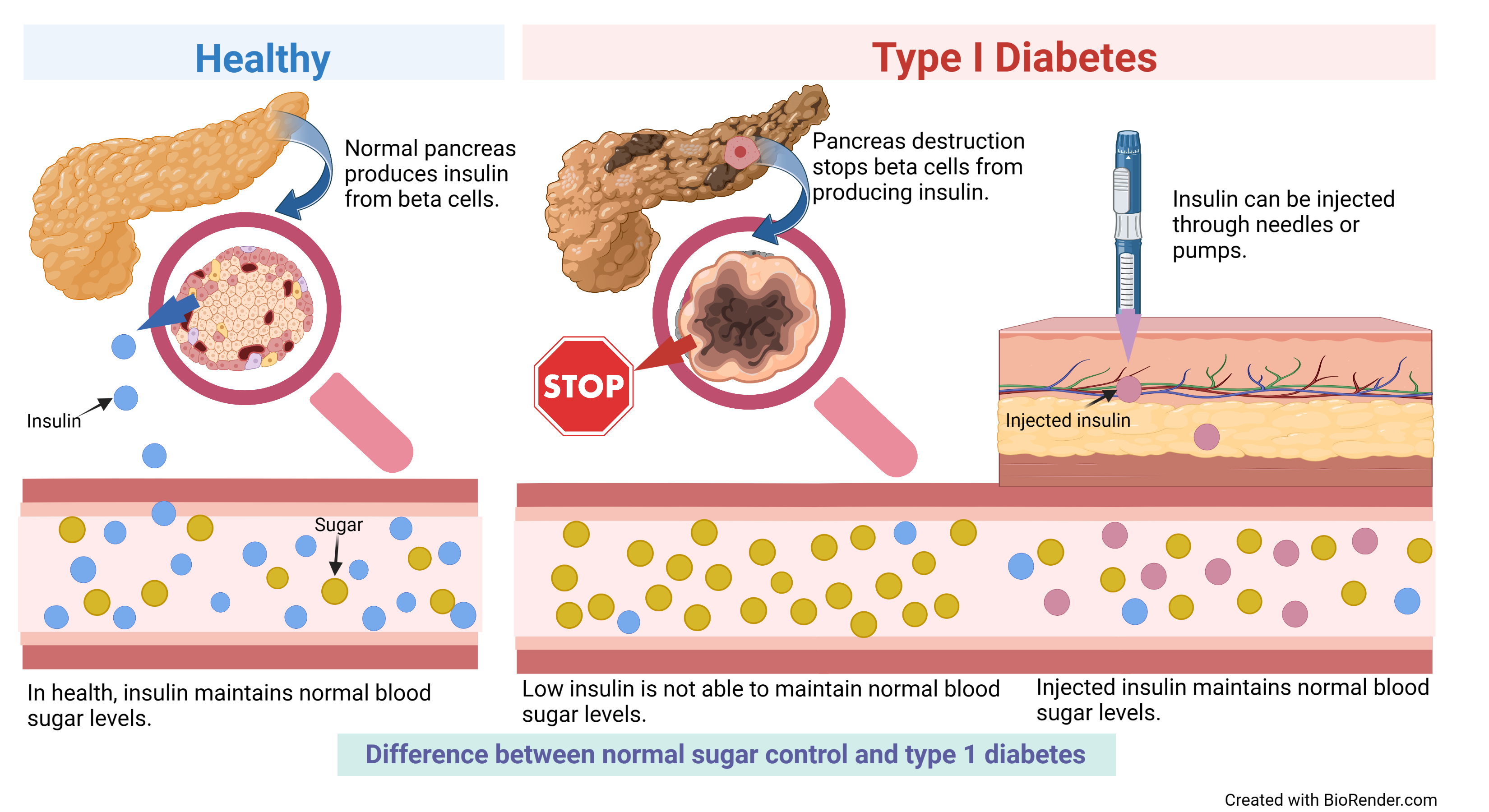
Welche nötige Wörter... Toll, die glänzende Idee
Sie sind absolut recht. Darin ist etwas auch mir scheint es der gute Gedanke. Ich bin mit Ihnen einverstanden.
Auf jeden Fall.
ohne Varianten....