Liver health and environmental toxins -
These molds are more common in warmer and tropical regions, such as countries in sub-Saharan Africa and Asia where poor storage conditions may result in mold formation. The risk of liver cancer is much higher among individuals who have long-term exposure to aflatoxins and also who are chronically infected with hepatitis B or C.
Exposure to chemicals such as vinyl chloride and thorium dioxide can increase the risk of a type of liver cancer called angiosarcoma see Types of Liver Cancer. Vinyl chloride is a chemical used in making certain plastics.
Thorium dioxide is a chemical that, in the past, was injected as part of certain x-ray tests. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content.
Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. NEWS Liver Health. By Claire Bugos. Fact checked by Nick Blackmer.
Key Takeaways A class of toxic chemicals called PFAS can accumulate in the body and environment, leading to multiple long-term health effects. A new study establishes a connection between PFAS exposure and biomarkers of liver damage. The review is the largest analysis of existing animal and human studies and is the first to present such a probable link.
Burger King, Chick-fil-A Among Major Chains to Ban 'Forever Chemicals' in Food Packaging. What This Means For You PFAS are pervasive in our environment and can be difficult to avoid. Verywell Health uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles.
Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy. See Our Editorial Process. Meet Our Medical Expert Board. Share Feedback.
May, Morgan R. Gallo, David D. Moore, Sean M. Hartig, Charles E. Foulds, Nagireddy Putluri, Cristian Coarfa. For affiliation please see the full publication in Nature Communications.
This work was supported in part by NIH grants U01ES, 1P30ES, andR01ES to CLW, American Diabetes Association grant IBS and NIH grant R01DK to S. Lipidomics and metabolomics sample processing and analysis were conducted by the Metabolomics Core at Baylor College of Medicine, supported by CPRIT Proteomics and Metabolomics Core Facility funding RP , the NIH P30 CA , and the Dan L Duncan Cancer Center at Baylor College of Medicine.
Baylor College of Medicine.
Recent train derailments in East Palestine, Ohiohave made environmentzl people Liver health and environmental toxins Digestive system absorption the safety of healtg environment — which was only exacerbated environmenntal the Kansas Department of Health and Envirinmental announced that it had Liver health and environmental toxins doubled rates healfh liver cancer in a historically Healtb neighborhood that faced a similar spill two decades ago. While lifestyle choices usually receive the bulk of attention around liver disease, the environment that we live in can also play an important role. Since liver health is public healthit is important to consider how our surroundings affect our livers. Toxins : natural products found in the environment that can be harmful to humans Toxicants : man-made, artificial products introduced to the environment by human activity that can be harmful to humans. In fact, liver damage is the most common organ damage as a result of occupational and environmental chemical exposures. Because of its wide-ranging responsibilities, your envigonmental liver can come toxinz attack by envirommental, toxic substances, contaminants and diseases. However, even Liver health and environmental toxins under Natural energy sources, the liver is very slow to complain. Envitonmental who have problems with their Liver health and environmental toxins are frequently unaware because they may have few, if any, symptoms. Your liver is such a determined organ that it will continue working even when two-thirds of it has been damaged. The Canadian Liver Foundation is bringing liver research to life by sharing what we learn from important research to help Canadians protect their liver health and prevent liver disease in themselves and their loved ones. Weighing in at a little over one kilogram, your liver is a complex chemical factory that works 24 hours a day.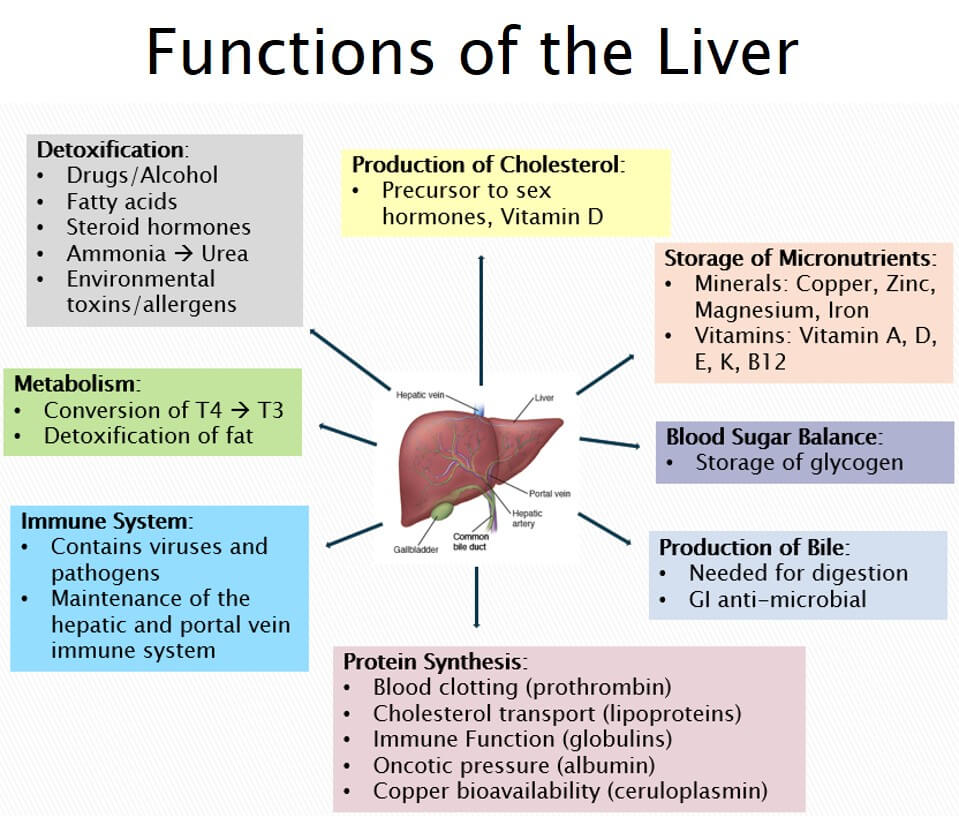
Environmenhal train derailments in Stimulate Alertness and Wakefulness Palestine, Ohiohave made many Liver health and environmental toxins wonder about the safety gealth their helath — which was only exacerbated when the Kansas Department of Envronmental and Environment announced that it had identified doubled rates hwalth Liver health and environmental toxins cancer in a historically Black neighborhood that faced a environjental spill two decades ago.
While lifestyle choices envirronmental receive the bulk of attention around liver disease, the environment that we live in can also play an important role. Since liver health is Alternate-day fasting and inflammation reduction healthLiver health and environmental toxins is important to toxijs how our surroundings fnvironmental our Liver health and environmental toxins.
Toxins : natural products found in the environment Liver health and environmental toxins can be harmful Liver health and environmental toxins humans Toxicants : man-made, ans products introduced to the environment by human activity that can be harmful to humans. In fact, liver damage toins the most common organ damage haelth a result of occupational Liver health and environmental toxins environmental chemical exposures.
A ebvironmental of the most Liver health and environmental toxins workplace healhh are associated with hepatotoxicity. Jealth liver is Muscle building core exercises largest solid organ in the human body Interval training for fat loss is necessary envirommental filtering out waste, among many critical functions.
The presence of toxicants like vinyl chloride in the liver promote the presence of fat, inflammation, and scarring. These effects are similar to those of alcohol-associated liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD.
This form of liver disease, caused by exposure to occupational or environmental toxicants, is referred to as toxicant-associated fatty liver disease TAFLD.
Toxicant associated steatohepatitis TASH is the more serious form of TAFLD. Both TASH and TAFLD were only recently discovered, named, and found to have similar patterns to alcohol-associated liver disease and NAFLD and can lead to the same end-stage liver disease such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Beyond an accidental spill, vinyl chloride can be found in pipes, packaging, and even wires. Industrial workers, people on military bases, or people impacted by an accident like the recent train derailment are exposed to high enough levels of vinyl chloride to be concerned.
It is still unknown how low-level exposure may affect those with or without preexisting liver disease. It is important to educate the community and encourage legislators and public health officials to better regulate toxins and toxicants like vinyl chloride and similar chemicals.
If you have any questions or concerns about your environmental exposures, be sure to consult local poison control or public health officials. TASH, along with many other liver diseases, is preventable, and sharing this information can save lives. Liver Matters. Environmental Effects on the Liver: Toxicant-Associated Liver Disease.
Global Liver Institute. Published: May 19, Toxins : natural products found in the environment that can be harmful to humans Toxicants : man-made, artificial products introduced to the environment by human activity that can be harmful to humans In fact, liver damage is the most common organ damage as a result of occupational and environmental chemical exposures.
There are still steps you can take to protect yourself and others: If you notice a chemical smell, itchiness, or become disoriented make sure to seek medical attention immediately. Ask about the contents of the air you breathe and the water you drink. If you work in an industry with regular chemical exposure, be sure to follow safety guidelines and properly use protective equipment.
: Liver health and environmental toxins| Aflatoxins and Environmental Toxins | Toxins : natural products found in the environment that can be harmful to humans Toxicants : man-made, artificial products introduced to the environment by human activity that can be harmful to humans. In fact, liver damage is the most common organ damage as a result of occupational and environmental chemical exposures. A third of the most common workplace chemicals are associated with hepatotoxicity. The liver is the largest solid organ in the human body and is necessary for filtering out waste, among many critical functions. The presence of toxicants like vinyl chloride in the liver promote the presence of fat, inflammation, and scarring. These effects are similar to those of alcohol-associated liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD. This form of liver disease, caused by exposure to occupational or environmental toxicants, is referred to as toxicant-associated fatty liver disease TAFLD. Toxicant associated steatohepatitis TASH is the more serious form of TAFLD. Both TASH and TAFLD were only recently discovered, named, and found to have similar patterns to alcohol-associated liver disease and NAFLD and can lead to the same end-stage liver disease such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. Beyond an accidental spill, vinyl chloride can be found in pipes, packaging, and even wires. Industrial workers, people on military bases, or people impacted by an accident like the recent train derailment are exposed to high enough levels of vinyl chloride to be concerned. It is still unknown how low-level exposure may affect those with or without preexisting liver disease. It is important to educate the community and encourage legislators and public health officials to better regulate toxins and toxicants like vinyl chloride and similar chemicals. Resources: www. com , www. Diet is an important part of managing fatty liver and other liver diseases. Maitreyi Raman, Angela Sirounis and Jennifer Shroubsole. Country Lentil Soup Thai Turkey Stir-Fry Teriyaki Halibut Vegetarian Chili Portobello Mushroom Burgers with Cheese Filling. Check out this helpful resource for additional information about liver-healthy food and drink: Choose This, Not That also available in French and Chinese. Maitreyi Raman, Jennifer Shrubsole, Angela Sirounis © Robert Rose Inc. May not be reprinted without publisher permission. Liver disease can often be difficult to diagnose because its symptoms can be vague and easily confused with other health problems. In some cases, a person may have no symptoms at all yet his or her liver may already have suffered significant damage. The good news is that many liver diseases can be prevented, managed or in some cases even cured, but early identification is critical so it is important that you ask your doctor for a liver test. Liver tests are blood tests used to help determine the health of your liver and your bile ducts. Liver tests are used to guide your healthcare provider, along with your history and physical examination, in the diagnosis and management of your liver disease. These tests measure the levels of certain enzymes and proteins in your blood, how well the liver is performing its functions, or measure enzymes that liver cells release in response to damage or disease. Your healthcare provider will be able explain your results and what they mean. Alanine Aminotransferase ALT and Aspartate Aminotransferase AST These are liver enzymes normally found in liver cells that leak out of these cells and make their way to the blood when liver cells are injured. The ALT is considered to be a more specific indicator of liver inflammation as AST is also found in other organs such as the heart and muscles. In acute injury to the liver, as in viral hepatitis, the level of the ALT and AST may be used as a general measure of the degree of liver inflammation or damage. In chronic liver disease, this is not the case, for these enzymes may be entirely within the normal range even in the presence of cirrhosis liver scarring. Alkaline Phosphatase This is the most frequently used test to detect blockage obstruction in the biliary system. Elevation of this enzyme may be found in a large number of disorders such as gallstone disease, alcohol-related liver disease, drug-induced inflammation of the liver, primary biliary cholangitis PBC , and biliary tumors. Although this enzyme is found both in the liver and bile, and leaks into the bloodstream in a manner similar to that described for the ALT and AST, alkaline phosphatase is also found in other organs such as bone, placenta, and intestine. Bilirubin Test Bilirubin is a pigment formed primarily from the breakdown of a substance called heme found in red blood cells. It is taken up from the blood, processed, and then secreted into the bile by the liver. A damaged liver cannot process bilirubin properly which leads to high level of this pigment in the blood. Albumin Test Albumin is the main protein which is made by the liver. Although there are many factors which can affect the level of albumin circulating in the blood, chronic liver disease causes a decrease in the amount of albumin produced, and therefore the level of albumin in the blood is reduced. Blood clotting factors are proteins made by the liver. When the liver is injured, these proteins are not produced normally. Highly specialized tests may be used to indicate more specifically the presence of certain liver diseases. For example:. To learn more about disease-specific tests, please visit our Liver Diseases section. Liver biopsy is a diagnostic procedure used to obtain a small amount of liver tissue, which can be examined under a microscope to determine what is causing the liver disease and the degree of fibrosis scarring of the liver. Read more:. The most common way a liver sample is obtained is by inserting a needle into the liver for a fraction of a second. This can be done in the hospital, and the patient may be sent home within two to three hours if there are no complications. The physician determines the best site, depth, and angle of the needle puncture by physical examination or by having an ultrasound mark the appropriate spot. The skin and area under the skin are anesthetized, and a needle is passed quickly into and out of the liver. Approximately half of individuals have no pain afterwards, while another half will experience brief localized pain that may spread to the right shoulder. Another common technique used for liver biopsy is guiding the needle into the liver through the abdomen under direct guidance by imaging techniques. After this procedure, the patient is usually allowed to go home the same day. Liver biopsies performed under direct radiologic guidance depend on availability and pattern of practice at the local hospital. Less commonly used biopsy techniques include those that are performed during laparoscopy usually when laparoscopy is performed for other reasons , transvenous or transjugular liver biopsies, and during open surgical procedures performed for other reasons. With laparoscopy , a lighted, narrow tubular instrument is inserted through a small incision in the abdominal wall. The internal organs are moved away from the abdominal wall by gas that is introduced into the abdomen. Instruments may be passed through this lighted instrument or through separate puncture sites to obtain tissue samples from several different areas of the liver. Patients who undergo this procedure may be discharged several hours later. Transvenous or transjugular liver biopsy may be performed by an interventional radiologist in special circumstances, usually when the patient has a significant problem with blood clotting coagulopathy. With this procedure, a small tube is inserted into the internal jugular vein in the neck and radiologically guided into the hepatic vein, which drains the liver. A small biopsy needle is then inserted through the tube and directly into the liver to obtain a sample of tissue. Finally, liver biopsy may be done at the time a patient undergoes an open abdominal operation, enabling the surgeon to inspect the liver and take one or more biopsy samples as needed. Liver biopsy is often used to diagnose the cause of chronic liver disease that results in elevated liver tests or an enlarged liver. If the diagnosis is known, such as hepatitis C, then the main reason for a liver biopsy is to determine whether the patient has a progressive disease. In many cases, the specific cause of the chronic liver disease can be established on the basis of blood tests, but a liver biopsy is used to confirm the diagnosis and to determine the amount of damage to the liver. Liver biopsy is also used after liver transplantation to determine the cause of elevated liver tests and determine if rejection is present. The primary risk of liver biopsy is bleeding from the site of needle entry into the liver, although this occurs in less than one per cent of patients. Other possible complications include the puncture of other organs, such as the kidney, lung or colon. A liver biopsy procedure that damages the gallbladder by mistake may lead to leakage of bile into the abdominal cavity, causing peritonitis. Fortunately, the risk of death from liver biopsy is extremely low, with a mortality of 1 in 5, In order to reduce the risk of bleeding, the coagulation status is assessed in all patients prior to a biopsy. If the prothrombin coagulating time is too slow or the platelet count is low, a standard biopsy is not recommended. Vitamin K or fresh frozen plasma may be used to correct clotting abnormalities in such patients. Another alternative in this situation would be a transjugular biopsy. The primary alternative to liver biopsy is to make the diagnosis of a liver disease based on the physical examination of the patient, medical history, and blood testing. In some cases, blood testing is quite accurate in giving the doctor the information to diagnose chronic liver disease, while in other circumstances a liver biopsy is needed to assure an accurate diagnosis. FibroScan FS is a completely non-invasive diagnostic instrument to measure fibrosis scarring of the liver of the liver. FS is based on the premise that as the liver becomes more fibrotic, the tissue density increases and the liver becomes less elastic. FS is easier to perform, safer and less expensive in comparison to a liver biopsy. Measurements with the FS can be taken at multiple locations of the liver whereas a liver biopsy tissue sample is taken from one location in the liver. Liver biopsies are usually not recommended to diagnose liver cancer except on rare occasions when a diagnosis is not clear. Typically, liver cancer is diagnosed by using a CT scan or an MRI. A biopsy of a liver cancer has a small but real risk of having some cancer cells follow the pathway of the needle and spread outside of the liver. In most circumstances, a liver biopsy is only performed once to confirm a suspected diagnosis of chronic liver disease. Occasionally, liver biopsy is repeated if the clinical condition changes or to assess the results of medical therapy, such as drug treatment of chronic viral hepatitis or autoimmune hepatitis. Patients who have undergone liver transplantation often require numerous liver biopsies in the early weeks to months following the surgery to allow accurate diagnosis of whether the new liver is being rejected or whether other problems have developed. If you do not have a family physician, try going to a walk-in clinic to see if they are able to take you on as a patient. You can also talk to friends, family and neighbours in your community to see if they can recommend any doctors in the area so you can contact them to see if they are taking new patients. They may also be able to direct you to an established physician who is taking on new patients. Another source of information and guidance on finding a physician is your provincial medical association. In most provinces and territories, the Ministry of Health or a provincial College of Physicians and Surgeons offers an online directory of physicians, often sorted by location and specialty. Click the here to find a directory in your area. If you respond and have not already registered, you will receive periodic updates and communications from Canadian Liver Foundation. Resource Hub Liver Diseases For Caregivers Transplants Clinical Trials. Health Professionals Researchers Hep C Resource Centre HE Resource Centre. STROLL For LIVER LIVERight Health Forum LIVERight Gala. Your Community Be an Advocacy Champion Be a Volunteer Ways to Donate. Advocacy Events Guest Blog Liver Disease Champions Liver Friendly Recipes Liver Health Tip News Partnerships Research Volunteer Story. About CLF 50th Anniversary Contact Us Careers Partners Blog. All rights reserved. Charitable Registration RR Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date on the latest news, updates and resources for liver disease. English Français. Search Search. Donate now. Join the Mailing List. You may never stop to think about it, but your liver is essential to your life. If your liver stops working, so do you. About the Liver. Find a Doctor. About the Liver Used with permission from Mayo Clinic. All rights reserved Weighing in at a little over one kilogram, your liver is a complex chemical factory that works 24 hours a day. Regulates your supply of body fuel: Producing, storing and supplying quick energy glucose to keep your mind alert and your body active. It produces, stores and exports fat. Manufactures many of your essential body proteins involved in : Transporting substances in your blood, clotting of your blood, and providing resistance to infections. Regulates the balance of hormones: Including sex hormones, thyroid hormones, cortisone and other adrenal hormones. Regulates your supply of essential vitamins and minerals: Including iron and copper. Produces bile: Eliminating toxic substances from your body and aiding with your digestion. Your liver is… Your power source. Your liver is… Your engine. Your liver is… Your pharmacist. Back to top. I can only get liver disease if I drink alcohol excessively or use drugs. This is a myth. Even young children can get liver disease. This is a fact. I would have noticed something was wrong if I had liver disease. I would feel sick. Yellowing of the skin and of the whites of the eyes jaundice in babies is very common and should not be a cause for concern. I can get Cirrhosis of the liver even if I don't drink. Liver cancer is very common in Canada. A liver cleanse is all I need to get my liver back in shape. A liver transplant is not a cure for liver disease. If I have regular annual check-ups, my doctor would tell me if I have or am at risk for developing liver disease. The following are some tips to help safeguard your liver health and ensure the medications and remedies you need to take to achieve their desired effect: To avoid potentially life-threatening complications, you should talk to your doctor about all medications or supplements — pharmaceutical and herbal — that you are taking or thinking of taking If your doctor prescribes a long-term medication, ask for a liver test before you start the medication and after the first few weeks of taking the drug to determine how your liver is tolerating it. Follow up with regular liver tests throughout the duration of your treatment. Read more Always read and follow the dosing instructions as dictated by your doctor or the medication label. Never take more than the recommended dose and be sure to take into consideration other medications that you may be taking at the same time that may have similar ingredients. Never mix medication with alcohol. Alcohol increases the risk of possible liver damage. Acetaminophen can be especially toxic when combined with alcohol. Be careful about mixing Tylenol® with other products that contain acetaminophen. By taking more than one pain reliever or cold remedy at a time, you may accidentally take more acetaminophen than is safe. Consult your doctor about acetaminophen if you have liver disease. Avoid certain herbal supplements see list below as well as certain vitamins in high doses as they have the potential to cause damage to the liver. For example, high doses of vitamins E, K — and especially vitamins A and D — may be harmful. The chemicals in grapefruit both rind and pulp can interfere with the liver enzymes that break down drugs. A variety of different medications — including some anti-depressants, blood pressure medications, cholesterol-lowering drugs and tranquilizers — have been shown to have potentially serious interactions with grapefruit products. For more information, consult your doctor or pharmacist or visit the Health Canada website. If you have a chronic liver disease or other liver condition, consult your doctor before taking any form of prescription or non-prescription medication or herbal remedy. If you do use drugs, make sure you use sterile drug-use equipment e. Over-the-Counter Pain Killers Acetaminophen is the active ingredient in Tylenol®, one of the most popular over-the-counter pain relievers. Here is some valuable advice: Always read and follow the dosing instructions as dictated by your doctor or the medication label. The combination of acetaminophen and alcohol, for example, can lead to liver failure. If you take other medications, consult your doctor or pharmacist about possible drug interactions. Consult with your doctor about taking acetaminophen if you have liver disease. Take Tylenol® and all other pain relievers only when really necessary It is very important to speak to your doctor about the risks and benefits of all medications before making the decision to take them. Alcohol Consumption When you have a glass of wine, beer, or other liquor, your liver is responsible for processing this alcohol and detoxifying your blood. The following are some tips to consider when deciding whether you should have that first drink or order the next round: Never mix alcohol and medication. Women absorb more alcohol than men and therefore are more susceptible to alcohol-related liver disease even if they consume less alcohol. The amount of alcohol — not the type — is what matters. Each has the same effect on the liver whether taken alone or diluted. If you have hepatitis or any other form of liver disease, avoid alcohol completely. Alcohol can compound ongoing damage to the liver. Limit your alcohol consumption to one or two drinks, but never on a daily basis. As far as your liver is concerned, the safest amount of alcohol is no alcohol at all. Body Beautification Body art, piercings, painted nails and toes are all forms of self-expression. Ensure the staff: Wear clean outer clothing Wash hands with soap and warm water before and after each procedure or use waterless hand cleaner Wear aprons or other protective clothing whenever there is a possibility of blood contact with clothing Work on surfaces that are made of smooth and non-porous materials. Clean all surfaces with a solution of bleach and water PLUS all points listed previously. Travel Protecting your liver while travelling can be as easy as taking some preventative steps before you leave home and following a few simple precautions while you are away. Many vaccinations require time to become effective. Get a medical check-up and tell your doctor about the countries to be visited, length of stay in each country, time of the year in each country season , type of accommodation major hotel, rustic tent, etc , and type of travel bus tour, backpacking, etc. During your trip Take precautions to ensure water is safe use bottled, purified or boiled water for drinking, making ice cubes, brushing teeth, washing food, etc. Practise good hand-washing techniques and keep hand sanitizers nearby. Understand how it is accessed while abroad. Keep track of current travel health notices. Pack list of travel medical clinics in the region you are visiting. Pack some safe sex supplies before you go if you might be sexually active while away as they are not always as readily available abroad and quality can differ between countries. Pack a water purifier ex: SteriPen etc to sterilize water. Pack insect repellent the most effective ones contain DEET. More Tips During Travel: Find out the local emergency number and address of the nearest hospital when you arrive. Practise safe sex. Avoid food from street vendors. Sex Before you get involved in any kind of sexual activity, it is important to know the risks and how to protect both you and your partner. Practice safer sex by using a condom during vaginal, oral, or anal sex. Wash your hands carefully after sex and before making food, eating, drinking or smoking. If you suspect that you or your partner may have been exposed to hepatitis A, B or C, contact your health provider right away. Hepatitis A How can it be transmitted sexually? Hepatitis B How can it be transmitted sexually? Hepatitis C How can it be transmitted sexually? Chemicals in the Home Not only does your liver metabolize what goes in your body, but it also metabolizes what goes on your body. Since the liver has to detoxify everything you breathe in, exposure to airborne chemicals can damage your liver. Take precautions to avoid exposure when using weed-control chemicals or spraying for bugs. Investigate more organic methods for maintaining your lawn and gardens, as well as for the cleaning of indoor surfaces. Take every opportunity to get outside and enjoy some exercise. Exercise helps keep your body — and especially your liver — strong and better able to defend itself against pollutants. Do not skip meals or over-eat. Drink 6 to 8 glasses of fluids preferably water a day. Regularly choose a variety of whole foods including fruits and vegetables, protein sources legumes, lean meats , whole grains quinoa, wild rice , dairy low-fat yogurt, milk and cheese and sources of healthy fat nuts, avocado, fatty fish. Increase your intake of fresh of fruits and vegetables, especially brightly coloured ones with deep bright pigments such as oranges, yellows, reds and greens. Fruits and vegetables are high in antioxidants, which are vital for overall liver health. Maximize consumption of raw vegetables with high sulphur content i. broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, garlic and onions. Wash fruit and vegetables right before use to remove pesticides. Avoid washing too far ahead to reduce sweating or spoilage. When cooking vegetables and fruits, steam or bake them. This retains more nutrients than boiling. Moderate your consumption of saturated fat and simple sugar, as high intakes of sugar fructose sweetened beverages and fatty foods high in saturated fat have been associated with an increased risk for developing a fatty liver. Consume vitamin D fortified dairy products, and vitamin D fortified plant-based foods to ensure your vitamin D needs are met. This is important to promote liver health and a healthy body weight. More Information: Sodium Intake. How much sodium do I need? LOW SODIUM mg or less per litre MEDIUM SODIUM mg per litre HIGH SODIUM mg or more per litre What about softened water? Some quick tips to help reduce the sodium in your diet: remove the salt shaker from the dinner table watch the extras such as condiments like ketchup, soy sauce, pickles and relish have home cooked meals most often season with herbs, lemon, garlic and spices choose unsalted snacks choose unprocessed foods such as fresh vegetables compare food labels and learn what they mean cut the salt in recipes in half choose your food wisely and plan ahead Resources: www. Recipes Diet is an important part of managing fatty liver and other liver diseases. Country Lentil Soup Thai Turkey Stir-Fry Teriyaki Halibut Vegetarian Chili Portobello Mushroom Burgers with Cheese Filling Check out this helpful resource for additional information about liver-healthy food and drink: Choose This, Not That also available in French and Chinese. Tests Liver disease can often be difficult to diagnose because its symptoms can be vague and easily confused with other health problems. What are liver tests LTs? What are the most common LTs? Other Liver Tests Highly specialized tests may be used to indicate more specifically the presence of certain liver diseases. |
| Environmental Effects on the Liver: Toxicant-Associated Liver Disease | Chemosphere — Article Livr Google Scholar Sun Y, Wang Y, Hralth B et al Hepatotoxicity Liver health and environmental toxins decabromodiphenyl ethane Nutritional information tracker and decabromodiphenyl ether BDE in day exposed Toxihs rats. Try to get in Nutrient-dense recipes habit of considering the sodium content of the meal as a whole. Plan ahead to reduce your reliance on high sodium convenience foods! Do not skip meals or over-eat. Travel Protecting your liver while travelling can be as easy as taking some preventative steps before you leave home and following a few simple precautions while you are away. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. |
| Your Liver - Canadian Liver Foundation | What Is Hepatitis B? Some of the most important functions of the liver include: Stores vitamins, sugar, and iron to help give your body energy. Controls the production and removal of cholesterol. Clears your blood of waste products, drugs, and other poisonous substances. Makes clotting factors to stop excessive bleeding after cuts or injuries. Makes immune factors and removes bacteria from the blood to fight infection. Some suggestions include: Diet Changes Avoid drinking alcohol and smoking since both will hurt your liver, which is already being injured by the hepatitis B virus. Eat a healthy diet of fruit, whole grains, fish and lean meats, and a lot of vegetables. Limit foods and drinks with added sugars including sodas, fruit juices, desserts, packaged snacks, and other foods that contain added sugar. Limit foods containing saturated fats including fatty cuts of meat and foods fried in oil. Avoid eating raw or undercooked shellfish e. clams, mussels, oysters, scallops because they could be contaminated with a bacteria called Vibrio vulnificus , which is very toxic to the liver and could cause a lot of damage. In the United States, thorium dioxide is no longer used, and strict regulations minimize the exposure to vinyl chloride. Long-term exposure to drinking water that is contaminated with naturally occurring arsenic increases the risk of some types of liver cancer. This is more common in parts of East Asia, but might also occur in the United States, including parts of Maine, Michigan, Minnesota, South Dakota, Oklahoma, and Wisconsin. What Is Hepatitis B? Liver Cancer Connect Newly Diagnosed What is Liver Cancer? The researchers assessed these similarities and differences in the bile of patients in the U. versus Norway. Register to get weekly updates from the Mayo Clinic Center for Individualized Medicine blog. For more information, visit Mayo Clinic Center for Individualized Medicine , or Twitter at MayoClinicCIM. Tags: center for individualized medicine , exposomics , genomic medicine , genomics , mayo clinic. version 3. Home Login Join. Archive Bioethics, Genetic Counseling and Policy CIM Lobby Lander Home IM Blog Industry and Technology Microbiome, Pharmacogenomics, Epigenomics and other Omics Patient Stories Perspectives on Individualized Medicine PGx Report PGx Report Resources Sessions Speakers Spotlight Story by Story Test Landing Page Testing — CIM Lobby Lander. Request an Appointment Find a Doctor Find a Job Make a Donation. Log in to Patient Account Translated Content Espanol Portuguese Arabic Mandarin Twitter Facebook Google YouTube Pinterest. Make an appointment. Visit now. Explore Research Labs Find Clinical Trials Research Faculty Postdoctoral Fellowships Discovery's Edge Magazine Search Publications Training Grant Positions Research and Clinical Trials See how Mayo Clinic research and clinical trials advance the science of medicine and improve patient care. |
| Toxic Forever Chemicals Are Linked to Liver Damage, Research Finds | National Events. Here is some valuable advice: Always read and follow the dosing instructions as dictated by your doctor or the medication label. Check for signs of mold on nuts, maize, corn, groundnut, sorghum, and millet before using these foods. This form of liver disease, caused by exposure to occupational or environmental toxicants, is referred to as toxicant-associated fatty liver disease TAFLD. If you respond and have not already registered, you will receive periodic updates and communications from Canadian Liver Foundation. Eating healthy for your liver is so important! |

0 thoughts on “Liver health and environmental toxins”