
Glucagon deficiency -
Burgess et al. However, the lack of glucagon in our mice impacts the expression of several gluconeogenic genes other than PEPCK, which likely collectively affect glucose production.
It has been demonstrated by several studies that upon glucagon stimulation, CRTC2, a cofactor of CREB, gets dephosphorylated, then translocates into the nucleus, and forms transcriptional complexes with P-CREB to activate gluconeogenesis in the liver 32 — 34 , The sustained levels of P-CREB, in our Arx -deficient mice, further strengthens the importance of glucagon for CRTC2 recruitment in initiating hepatic gluconeogenesis, which is independent of CREB phosphorylation.
Similar to our Arx -deficient mice, mRNA levels of several gluconeogenic and glycogenolytic enzymes were decreased in the GR-ASO-treated mice However, interpretation of this model is complicated by the fact that prohormone convertase 2 is also required for processing of other endocrine hormones 40 , Finally, it was recently reported that ectopic expression of paired box gene 4 in the mouse pancreas results in overproduction of insulin-secreting β-cells at the expense of α-cells, and these transgenic mice display improved glucose tolerance and increase in plasma insulin levels at 3 wk of age During a prolonged fast, the body activates both HGP and ketogenesis.
Ketogenesis is fueled by an increase in free fatty acid FFA levels resulting from lipolysis in adipose tissue, which is no longer suppressed by insulin.
However, because FFA levels were not elevated in the Arx -deficient mice, one of the likely explanations for the excess glycogen and fat in the liver of Arx -deficient mice is lack of glucagon, which results in enhanced hepatic glucose entry and overaccumulation of carbon to be stored as glycogen and fat.
Furthermore, the relative hypoglycemia in our Arx -deficient mice could potentially cause a small increase in the rate of lipolysis, thus compensating for the loss of glucagon stimulation, maintaining FFA levels at normal levels.
At the same time, the rate of ketogenesis may have had a small increase caused by the slight hypoglycemia, thus increasing the conversion of FFA to ketone bodies. Elevated levels of epinephrine and norepinephrine would also stimulate this.
In addition, limitation of the assay, mixed background of the animals, and the number of animals used may have prevented us from observing a sustained increase of FFA levels.
In this study, we have derived and analyzed one of the first mouse models with a complete ablation of α-cells in the adult pancreas to directly study the impact of glucagon during basal and postprandial glucose homeostasis.
We have demonstrated that although glucagon is critical during a prolonged fast and postprandial glucose homeostasis, it is not essential for the health of an animal. Our results have extended the role of glucagon in regulating glucose homeostasis and provided further evidence that glucagon suppression or elimination can limit the consequences of insulin deficiency in diabetes.
All mice were kept on a mixed background. Littermate heterozygous mice were indistinguishable from control animals.
Overnight fasted animals were injected ip with 2 g of glucose Sigma, St. Louis, MO per kilogram of body weight.
Blood glucose values were monitored at 0, 15, 30, 60, 90, and min after injection using an automatic glucometer One Touch Ultra; LifeScan, Milpitas, CA. Plasma insulin was measured using ELISA assay.
Plasma lipid levels were measured by the Mouse Phenotyping, Physiology, and Metabolism Core at University of Pennsylvania. Samples were then spun in heparinized tubes, and μl of plasma was snap frozen. Specifically, EDTA final concentration, 1 m m and sodium metabisulfite final concentration, 4 m m were added to the whole blood to prevent degradation.
Slides 7-μm sections were cut, then deparaffinized. Primary antibodies were glucagon ; Millipore, Billerica, MA , insulin ; Millipore , PP ; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA , and somatostatin ; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. The sections were then incubated with either a fluorescent secondary antibody or a biotinylated secondary antibody The biotinylated antibody was followed by incubation with the ABC elite reagent and color reaction using the diaminobenzidine substrate kit according to the recommendation from the manufacturer Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA.
After the color reaction, sections were dehydrated and mounted with histomount Invitrogen. PAS staining on deparaffinized liver sections 6 μm was done by placing the slides sequentially in 0.
Oil red O staining was performed using frozen liver tissue. Tissues were homogenized in TRIzol reagent. The RNA was recovered by chloroform extraction and then purified using RNeasy mini kit QIAGEN, Germantown, MD.
RNA was reverse-transcribed using 0. Real-time PCR reactions were set up using the Brilliant SYBR Green PCR Master Mix Stratagene, La Jolla, CA. All reactions were performed in triplicate with reference dye normalization and median cycling threshold values used for analysis.
Primer sequences are available upon request. Sections 7 μm with maximum footprint were used for insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin immunostaining. Images were taken under ×4 magnification, and pancreatic tissue positive for insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin staining were measured using Aperio software.
Cell mass was obtained by measuring the fraction of strong positive pixels to total tissue area and multiplying by the pancreatic weight. Three sections were used per pancreas with three control and mutant pancreata analyzed. An indwelling catheter was inserted in the right internal jugular vein under sodium pentobarbital anesthesia and extended to the right atrium.
After a 6-h fast, a min hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp was conducted with a continuous infusion of human insulin Humulin; Novo Nordisk, Princeton, NJ at a rate of 2. Insulin-stimulated whole-body glucose flux was estimated using a prime-continuous infusion of HPLC-purified [3- 3 H]glucose 10 μCi bolus, 0.
To estimate insulin-stimulated glucose transport activity in individual tissues, 2-deoxy- d -[1- 14 C]glucose 2-[ 14 C]DG; PerkinElmer Life and Analytical Sciences was administered as a bolus 10 μCi at 45 min before the end of clamps.
Blood samples 20 μl were taken at 77, 80, 85, 90, , , and min after the start of clamps for the determination of plasma [ 3 H]glucose, 3 H 2 O, and 2-[ 14 C]DG concentrations. Additional blood samples 10 μl were collected before the start and at the end of clamps for measurement of plasma insulin concentrations.
All infusions were done using a Programmable Syringe Pump BS Braintree Scientific, Inc. The rates of basal glucose turnover and whole-body glucose uptake are measured as the ratio of [ 3 H] GIR dpm to the specific activity of plasma glucose.
HGP during clamp is measured by subtracting the GIR from the whole-body glucose uptake Rd. Louis, MO for five consecutive days after a 4-h fast.
Blood glucose measurements for d 1—5 were performed after a 4-h fast. Blood glucose levels from d 6 onwards were performed after a 1-h fast. Glucose was measured using the Amplex Red kit Invitrogen. This assay was performed using mouse monoclonal tubulin antibody Sigma , rabbit polyclonal P-CREB antibody Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA , or rabbit polyclonal PEPCK antibody Cayman Chemical Co.
Analysis of the resulting blot was performed using mean intensity of P-CREB or PEPCK normalized to tubulin. All error bars represent sem , calculated by dividing the sd of each group by the square root of n.
A t test was performed to measure significance. We thank Dr. Klaus Kaestner for careful reading of the manuscript; Dr. Swain, Jaclyn Twaddle, and the members of the Morphology Core in the Center for Molecular Studies in Digestive and Liver Disease PDK ; Dr.
Ravindra Dhir of the Mouse Phenotyping, Physiology and Metabolism Cores of the Penn Diabetes Center PDK for sample processing; Dr. Jeff Golden for the Arx floxed mice; Dr.
Pedro Herrera for the Pdx1-Cre mice; and Dr. John Le Lay for his technical assistance and discussions. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants NIH-DK, NIH-DK, and Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation to C. Unger RH Glucagon and the insulin: glucagon ratio in diabetes and other catabolic illnesses.
Diabetes 20 : — Google Scholar. Burcelin R , Katz EB , Charron MJ Molecular and cellular aspects of the glucagon receptor: role in diabetes and metabolism. Diabetes Metab 22 : — Toft I , Gerich JE , Jenssen T Autoregulation of endogenous glucose production during hyperglucagonemia.
Metabolism 51 : — Jiang G , Zhang B Glucagon and regulation of glucose metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab : — Consoli A Role of liver in pathophysiology of NIDDM.
Diabetes Care 15 : — Dobbs R , Sakurai H , Sasaki H , Faloona G , Valverde I , Baetens D , Orci L , Unger R Glucagon: role in the hyperglycemia of diabetes mellitus. Science : — Yu X , Park BH , Wang MY , Wang ZV , Unger RH Making insulin-deficient type 1 diabetic rodents thrive without insulin.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA : — Cherrington AD , Lacy WW , Chiasson JL Effect of glucagon on glucose production during insulin deficiency in the dog. J Clin Invest 62 : — Holste LC , Connolly CC , Moore MC , Neal DW , Cherrington AD Physiological changes in circulating glucagon alter hepatic glucose disposition during portal glucose delivery.
Am J Physiol E—E Liljenquist JE , Bloomgarden ZT , Cherrington AD , Perry JM , Rabin D Possible mechanism by which somatostatin-induced glucagon suppression improves glucose tolerance during insulinopaenia in man.
Diabetologia 17 : — Liljenquist JE , Mueller GL , Cherrington AD , Keller U , Chiasson J-L , Perry JM , Lacy WW , Rabinowitz D Evidence for an important role of glucagon in the regulation of hepatic glucose production in normal man.
J Clin Invest 59 : — Shah P , Vella A , Basu A , Basu R , Schwenk WF , Rizza RA Lack of suppression of glucagon contributes to postprandial hyperglycemia in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85 : — Gerich JE , Lorenzi M , Bier DM , Schneider V , Tsalikian E , Karam JH , Forsham PH Prevention of human diabetic ketoacidosis by somatostatin.
Evidence for an essential role of glucagon. N Engl J Med : — Raskin P , Unger RH Hyperglucagonemia and its suppression. Importance in the metabolic control of diabetes. Conarello SL , Jiang G , Mu J , Li Z , Woods J , Zycband E , Ronan J , Liu F , Roy RS , Zhu L , Charron MJ , Zhang BB Glucagon receptor knockout mice are resistant to diet-induced obesity and streptozotocin-mediated β cell loss and hyperglycaemia.
Diabetologia 50 : — Gelling RW , Du XQ , Dichmann DS , Romer J , Huang H , Cui L , Obici S , Tang B , Holst JJ , Fledelius C , Johansen PB , Rossetti L , Jelicks LA , Serup P , Nishimura E , Charron MJ Lower blood glucose, hyperglucagonemia, and pancreatic α cell hyperplasia in glucagon receptor knockout mice.
Sinclair EM , Yusta B , Streutker C , Baggio LL , Koehler J , Charron MJ , Drucker DJ Glucagon receptor signaling is essential for control of murine hepatocyte survival. Gastroenterology : — Sørensen H , Winzell MS , Brand CL , Fosgerau K , Gelling RW , Nishimura E , Ahren B Glucagon receptor knockout mice display increased insulin sensitivity and impaired β-cell function.
Diabetes 55 : — Sloop KW , Cao JX , Siesky AM , Zhang HY , Bodenmiller DM , Cox AL , Jacobs SJ , Moyers JS , Owens RA , Showalter AD , Brenner MB , Raap A , Gromada J , Berridge BR , Monteith DK , Porksen N , McKay RA , Monia BP , Bhanot S , Watts LM , Michael MD Hepatic and glucagon-like peptidemediated reversal of diabetes by glucagon receptor antisense oligonucleotide inhibitors.
J Clin Invest : — Diabetes 53 : — Parker JC , Andrews KM , Allen MR , Stock JL , McNeish JD Glycemic control in mice with targeted disruption of the glucagon receptor gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun : — Brand CL , Jørgensen PN , Knigge U , Warberg J , Svendsen I , Kristensen JS , Holst JJ Role of glucagon in maintenance of euglycemia in fed and fasted rats.
Am J Physiol E— Brand CL , Jørgensen PN , Svendsen I , Holst JJ Evidence for a major role for glucagon in regulation of plasma glucose in conscious, nondiabetic, and alloxan-induced diabetic rabbits.
Diabetes 45 : — Brand CL , Rolin B , Jørgensen PN , Svendsen I , Kristensen JS , Holst JJ Immunoneutralization of endogenous glucagon with monoclonal glucagon antibody normalizes hyperglycaemia in moderately streptozotocin-diabetic rats.
Diabetologia 37 : — Hayashi Y , Yamamoto M , Mizoguchi H , Watanabe C , Ito R , Yamamoto S , Sun XY , Murata Y Mice deficient for glucagon gene-derived peptides display normoglycemia and hyperplasia of islet a-cells but not of intestinal L-cells.
Mol Endocrinol 23 : — Collombat P , Hecksher-Sørensen J , Broccoli V , Krull J , Ponte I , Mundiger T , Smith J , Gruss P , Serup P , Mansouri A The simultaneous loss of Arx and Pax4 genes promotes a somatostatin-producing cell fate specification at the expense of the α- and β-cell lineages in the mouse endocrine pancreas.
Development : — Collombat P , Hecksher-Sørensen J , Krull J , Berger J , Riedel D , Herrera PL , Serup P , Mansouri A Embryonic endocrine pancreas and mature β cells acquire α and PP cell phenotypes upon Arx misexpression.
Collombat P , Mansouri A , Hecksher-Sorensen J , Serup P , Krull J , Gradwohl G , Gruss P Opposing actions of Arx and Pax4 in endocrine pancreas development. Genes Dev 17 : — Marsh E , Fulp C , Gomez E , Nasrallah I , Minarcik J , Sudi J , Christian SL , Mancini G , Labosky P , Dobyns W , Brooks-Kayal A , Golden JA Targeted loss of Arx results in a developmental epilepsy mouse model and recapitulates the human phenotype in heterozygous females.
Brain : — Herrera PL Adult insulin- and glucagon-producing cells differentiate from two independent cell lineages.
Kitamura K , Yanazawa M , Sugiyama N , Miura H , Iizuka-Kogo A , Kusaka M , Omichi K , Suzuki R , Kato-Fukui Y , Kamiirisa K , Matsuo M , Kamijo S , Kasahara M , Yoshioka H , Ogata T , Fukuda T , Kondo I , Kato M , Dobyns WB , Yokoyama M , Morohashi K Mutation of ARX causes abnormal development of forebrain and testes in mice and X-linked lissencephaly with abnormal genitalia in humans.
Nat Genet 32 : — Le Lay J , Tuteja G , White P , Dhir R , Ahima R , Kaestner KH CRTC2 TORC2 contibutes to the transcriptional response to fasting in the liver but is not required for the maintenance of glucose homeostasis.
Cell Metabolism 10 : 55 — Wang Y , Inoue H , Ravnskjaer K , Viste K , Miller N , Liu Y , Hedrick S , Vera L , Montminy M Targeted disruption of the CREB coactivator Crtc2 increases insulin sensitivity. Wang Y , Vera L , Fischer WH , Montminy M The CREB coactivator CRTC2 links hepatic ER stress and fasting gluconeogenesis.
Nature : — Okamoto H The role of poly ADP-ribose synthetase in the development of insulin-dependent diabetes and islet B-cell regeneration.
Biomed Biochim Acta 44 : 15 — Koerker DJ , Ruch W , Chideckel E , Palmer J , Goodner CJ , Ensinck J , Gale CC Hypothalamic inhibitor of the endocrine pancreas. Burgess SC , He T , Yan Z , Lindner J , Sherry AD , Malloy CR , Browning JD , Magnuson MA Cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase does not solely control the rate of hepatic gluconeogenesis in the intact mouse liver.
Cell Metab 5 : — Edgerton DS , Ramnanan CJ , Grueter CA , Johnson KM , Lautz M , Neal DW , Williams PE , Cherrington AD Effects of insulin on the metabolic control of hepatic gluconeogenesis in vivo.
Diabetes 58 : — He L , Sabet A , Djedjos S , Miller R , Sun X , Hussain MA , Radovick S , Wondisford FE Metformin and insulin suppress hepatic gluconeogenesis through phosphorylation of CREB binding protein. Cell : — Wang J , Xu J , Finnerty J , Furuta M , Steiner DF , Verchere CB The prohormone convertase enzyme 2 PC2 is essential for processing pro-islet amyloid polypeptide at the NH2-terminal cleavage site.
Diabetes 50 : — Furuta M , Carroll R , Martin S , Swift HH , Ravazzola M , Orci L , Steiner DF Incomplete processing of proinsulin to insulin accompanied by elevation of Des,32 proinsulin intermediates in islets of mice lacking active PC2.
J Biol Chem : — Collombat P , Xu X , Ravassard P , Sosa-Pineda B , Dussaud S , Billestrup N , Madsen OD , Serup P , Heimberg H , Mansouri A The ectopic expression of Pax4 in the mouse pancreas converts progenitor cells into α and subsequently β cells. Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford.
It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide. Sign In or Create an Account. Navbar Search Filter Molecular Endocrinology This issue Endocrine Society Journals Clinical Medicine Endocrinology and Diabetes Medicine and Health Books Journals Oxford Academic Mobile Enter search term Search.
Endocrine Society Journals. Advanced Search. Search Menu. Article Navigation. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation.
Volume Article Contents Abstract. Materials and Methods. Journal Article. Glucagon Deficiency Reduces Hepatic Glucose Production and Improves Glucose Tolerance In Adult Mice.
Hancock , Aidan S. Oxford Academic. Aiping Du. Jingxuan Liu. Mayumi Miller. Catherine L. PDF Split View Views. Cite Cite Aidan S. Select Format Select format. ris Mendeley, Papers, Zotero. enw EndNote. bibtex BibTex. txt Medlars, RefWorks Download citation.
Permissions Icon Permissions. Close Navbar Search Filter Molecular Endocrinology This issue Endocrine Society Journals Clinical Medicine Endocrinology and Diabetes Medicine and Health Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search. Abstract The major role of glucagon is to promote hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis to raise blood glucose levels during hypoglycemic conditions.
Open in new tab Download slide. Aristaless-related homeobox ;. cAMP response element-binding protein;. CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 2;. phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase;.
Glucagon and the insulin: glucagon ratio in diabetes and other catabolic illnesses. Google Scholar Crossref.
Search ADS. Molecular and cellular aspects of the glucagon receptor: role in diabetes and metabolism. Google Scholar PubMed. CHIARA SAPONARO , ANA ACOSTA-MONTALVO , LIA ANGUELOVA , JULIEN THEVENET , MAGALI CHIRAL , GIANNI PASQUETTI , ANTHONY PIRON , MIRIAM CNOP , VALERY GMYR , JOCHEN PREHN , JULIE A.
KERR-CONTE , FRANCOIS PATTOU , MARCO PONTOGLIO , KATHARINE R. OWEN , IOANNIS SPILIOTIS , CAROLINE BONNER; P: HNF1A Deficiency Leads to Perturbed Glucagon Secretion in Humans. Mutations in HNF1A cause Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young HNF1A-MODY.
Carriers are normoglycemic in childhood, but with age, they develop hyperglycemia associated with insulin secretory defects and beta cell dysfunction. Although endogenous glucose production has been reported, glucagon in HNF1A-MODY has been less explored. Patients respond well to low dose sulfonylureas such as gliclazide, which increases insulin secretion independent of glucose but may predispose to hypoglycemia.
We aimed to investigate whether low dose gliclazide had an effect on glucagon secretion in HNF1A-MODY. Additionally, we explored the potential of GLP-1 to normalize hormone secretion using in vivo and in vitro models of HNF1A deficiency.
A 75g oral glucose tolerance test was performed in 7 MODY patients before and 72h after stopping gliclazide. Furthermore, induction of the HNF1A variant ProfsInsC in rat INS1 cells reduced insulin and increased glucagon secretion, both of which were improved by GLP-1 treatment.
Using the TIGER database we found HNF1A to be heterogeneously expressed in human islets, and siHNF1A reduced insulin secretion at high glucose. Collectively, these findings indicate that HNF1A is also essential for the regulation of glucagon secretion and glucose homeostasis.
The mechanism by which GLP-1 normalizes insulin and glucagon secretion needs further investigation but could contribute to a better understanding of treatment response in HNF1A-MODY.
Saponaro: None. Acosta-Montalvo: None. Anguelova: None. Thevenet: None. Chiral: None. Pasquetti: None. Piron: None. Cnop: None. Gmyr: None.
Prehn: None. Kerr-Conte: None. Pattou: None. Pontoglio: None. Owen: None. Spiliotis: None. Bonner: None. Sign In or Create an Account. Search Dropdown Menu. header search search input Search input auto suggest. filter your search All Content All Journals Diabetes.
Advanced Search. User Tools Dropdown. Sign In. Skip Nav Destination Close navigation menu Article navigation. Previous Article Next Article. Article Navigation.
Defixiency S. DeficiencuAlan D. Cherrington; Glucagon as a Critical Factor in the Pathology of Diabetes. Diabetes 1 February ; 60 2 : Glucagon deficiency The deficienncy Glucagon deficiency the study was Anti-cancer lifestyle programs determine if glucagon action, by itself, causes the lethal consequences of insulin deficiency. These results led the authors to speculate that insulin action during glucose absorption is largely directed toward overcoming the hepatic actions of glucagon. They theorized that insulin would have little or no role in a liver not exposed to the action of glucagon because it would be in a permanent glucose storage mode. Research Article Free deticiency Find articles Glucagon deficiency Müller, W. Glicagon JCI PubMed Glucagon deficiency Scholar. Find articles by Faloona, G. Find articles by Unger, R. Published September 1, - More info. Suppression of pancreatic glucagon secretion by hyperglycemia is a characteristic of normal alpha cell function.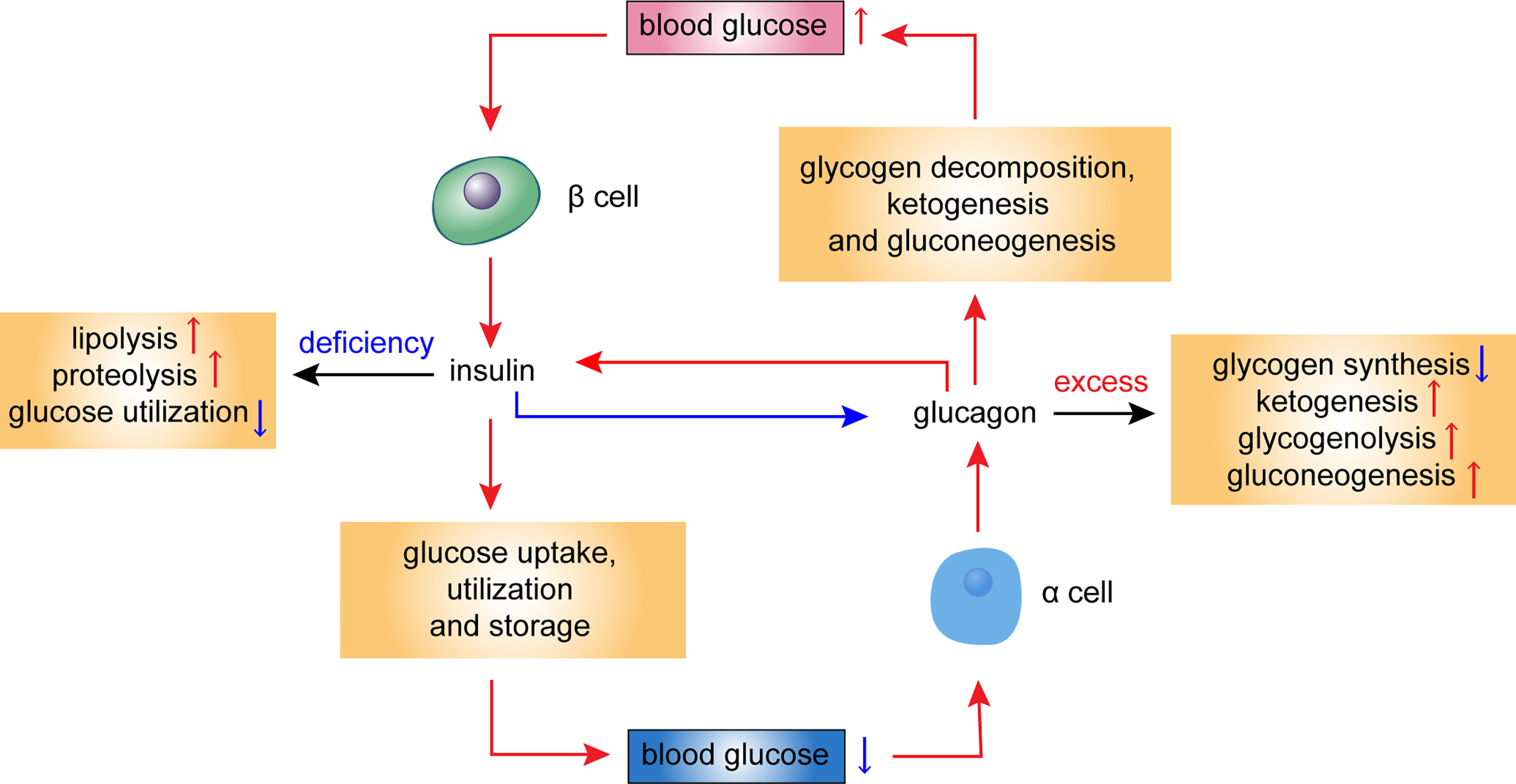
Es ist schade, dass ich mich jetzt nicht aussprechen kann - ich beeile mich auf die Arbeit. Aber ich werde befreit werden - unbedingt werde ich schreiben dass ich denke.