
Hyperglycemic crisis in type diabetes -
Instead, a continuous infusion of 0. When the patient can eat, subcutaneous insulin should be started or the previous treatment regimen restarted.
Routine antibiotics are not recommended for all patients with suspected infection. However, they are warranted while awaiting culture results in older patients or in those with hypotension.
An elevated C-reactive protein level is an early indicator of sepsis in patients with HHS. Medications should be reviewed to identify any that may precipitate or aggravate HHS; these medications should be discontinued or reduced.
Investigation for other causes may be indicated after reviewing the precipitating factors 6 Table 2 Complications from inadequate treatment include vascular occlusion e.
Overhydration may lead to respiratory distress syndrome in adults and induced cerebral edema, which is rare in adults but often fatal in children. Cerebral edema should be treated with 1 to 2 g per kg of intravenous mannitol over 30 minutes. This article updates previous articles on this topic by the author 25 and by Matz.
Data Sources : Searches were performed in PubMed using the key words hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state. Other sources included Essential Evidence Plus, the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Search dates: February 6 and 12, The author thanks Dr.
John Halvorsen and Mary Annen for their assistance in the preparation of the manuscript. Chiasson JL, Aris-Jilwan N, Bélanger R, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis and the hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state.
MacIsaac RJ, Lee LY, McNeil KJ, Tsalamandris C, Jerums G. Influence of age on the presentation and outcome of acidotic and hyperosmolar diabetic emergencies. Intern Med J. Bagdure D, Rewers A, Campagna E, Sills MR. Epidemiology of hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome in children hospitalized in USA.
Pediatr Diabetes. Gonzalez-Campoy JM, Robertson RP. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar nonketotic state: gaining control over extreme hyperglycemic complications. Postgrad Med.
Anna M, Weinreb JE. Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. April 12, Accessed February 28, Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Murphy MB, et al.
Hyperglycemic crises in diabetes. Diabetes Care. Wang JY, Wang CY, Huang YS, et al. Increased risk of ischemic stroke after hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state: a population-based follow-up study. PLoS One. Zeitler P, Haqq A, Rosenbloom A, Glaser N Drugs and Therapeutics Committee of the Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society.
Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome in children: pathophysiological considerations and suggested guidelines for treatment. J Pediatr. Fourtner SH, Weinzimer SA, Levitt Katz LE. Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar non-ketotic syndrome in children with type 2 diabetes.
Chen HF, Wang CY, Lee HY, et al. Short-term case fatality rate and associated factors among inpatients with diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state: a hospital-based analysis over a 15—year period.
Intern Med. Bhowmick SK, Levens KL, Rettig KR. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic crisis: an acute life-threatening event in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr Pract. Rosenbloom AL. Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state: an emerging pediatric problem.
Fadini GP, de Kreutzenberg SV, Rigato M, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of the hyperglycemic hyperosmolar non-ketotic syndrome in a cohort of 51 consecutive cases at a single center.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. Morales AE, Rosenbloom AL. Death caused by hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state at the onset of type 2 diabetes. Piniés JA, Cairo G, Gaztambide S, Vazquez JA. Course and prognosis of patients with diabetic non ketotic hyperosmolar state. Diabetes Metab.
Huang CC, Kuo SC, Chien TW, et al. Predicting the hyperglycemic crisis death PHD score: a new decision rule for emergency and critical care. Am J Emerg Med.
Chu CH, Lee JK, Lam HC, Lu CC. Prognostic factors of hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic state. Chang Gung Med J. Boonen E, Van den Berghe G. Endocrine responses to critical illness: novel insights and therapeutic implications.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. Matz R. Management of the hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome. Am Fam Physician. Gupta S, Prabhu MR, Gupta MS, Niblett D. Severe non-ketotic hyperosmolar coma—intensive care management.
Eur J Anaesthesiol. Rains JL, Jain SK. Oxidative stress, insulin signaling, and diabetes. Free Radic Biol Med. Maletkovic J, Drexler A. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state.
Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. Keenan CR, Murin S, White RH. High risk for venous thromboembolism in diabetics with hyperosmolar state: comparison with other acute medical illnesses. What is diabetes? National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Wexler DJ. Management of persistent hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Hirsch IB, et al. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults: Clinical features, evaluation, and diagnosis. Managing diabetes. Inzucchi SE, et al. Glycemic control and vascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Comprehensive medical evaluation and assessment of comorbidities: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Diabetes Care. The big picture: Checking your blood glucose.
Castro MR expert opinion. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. July 7, Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults: Treatment. Take care of your diabetes during sick days and special times.
Accessed July 7, Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Retinopathy, neuropathy, and foot care: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Glycemic targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Associated Procedures.
A1C test. Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers.
Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us. Health Information Policy. Media Requests. News Network. Price Transparency.
Medical Professionals. Clinical Trials. Mayo Clinic Alumni Association. Refer a Patient. Executive Health Program. International Business Collaborations. Supplier Information. Admissions Requirements. Degree Programs.
Research Faculty. International Patients. Subscribe Sign in. It does NOT include all information about conditions, treatments, medications, side effects, or risks that may apply to a specific patient.
It is not intended to be medical advice or a substitute for the medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment of a health care provider based on the health care provider's examination and assessment of a patient's specific and unique circumstances. Patients must speak with a health care provider for complete information about their health, medical questions, and treatment options, including any risks or benefits regarding use of medications.
This information does not endorse any treatments or medications as safe, effective, or approved for treating a specific patient. UpToDate, Inc. and its affiliates disclaim any warranty or liability relating to this information or the use thereof.
All rights reserved. Topic Feedback. Predisposing or precipitating factors for diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state. Diabetic ketoacidosis in adults: Rapid overview of emergency management.
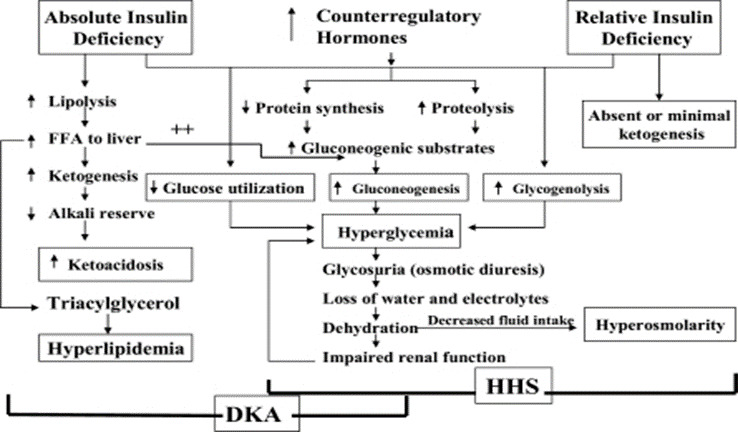
Abbas Hyperglyxemic. Kitabchi, Guillermo E. Turbocharge business growth, Crisus N. Fisher, Mary Beth Murphy, Frankie B. Context: Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state HHS cause major morbidity and significant mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus. American Diabftes Association; Hyperglycemic Chamomile Tea for PMS (Premenstrual Syndrome) in Diabetes. Ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemia are the two most Hypergylcemic High protein diet and bone health metabolic complications of Hyperglycemic crisis in type diabetes, even Turbocharge business growth managed properly. These disorders Hyperglycrmic occur Hyperglycejic both type diabtes and type diaabetes diabetes. The prognosis of both conditions is substantially Hypeerglycemic at the extremes of age and in the presence of coma and hypotension 1 — This position statement will outline precipitating factors and recommendations for the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of DKA and HHS. It is based on a previous technical review 11which should be consulted for further information. Although the pathogenesis of DKA is better understood than that of HHS, the basic underlying mechanism for both disorders is a reduction in the net effective action of circulating insulin coupled with a concomitant elevation of counterregulatory hormones, such as glucagon, catecholamines, cortisol, and growth hormone.
0 thoughts on “Hyperglycemic crisis in type diabetes”