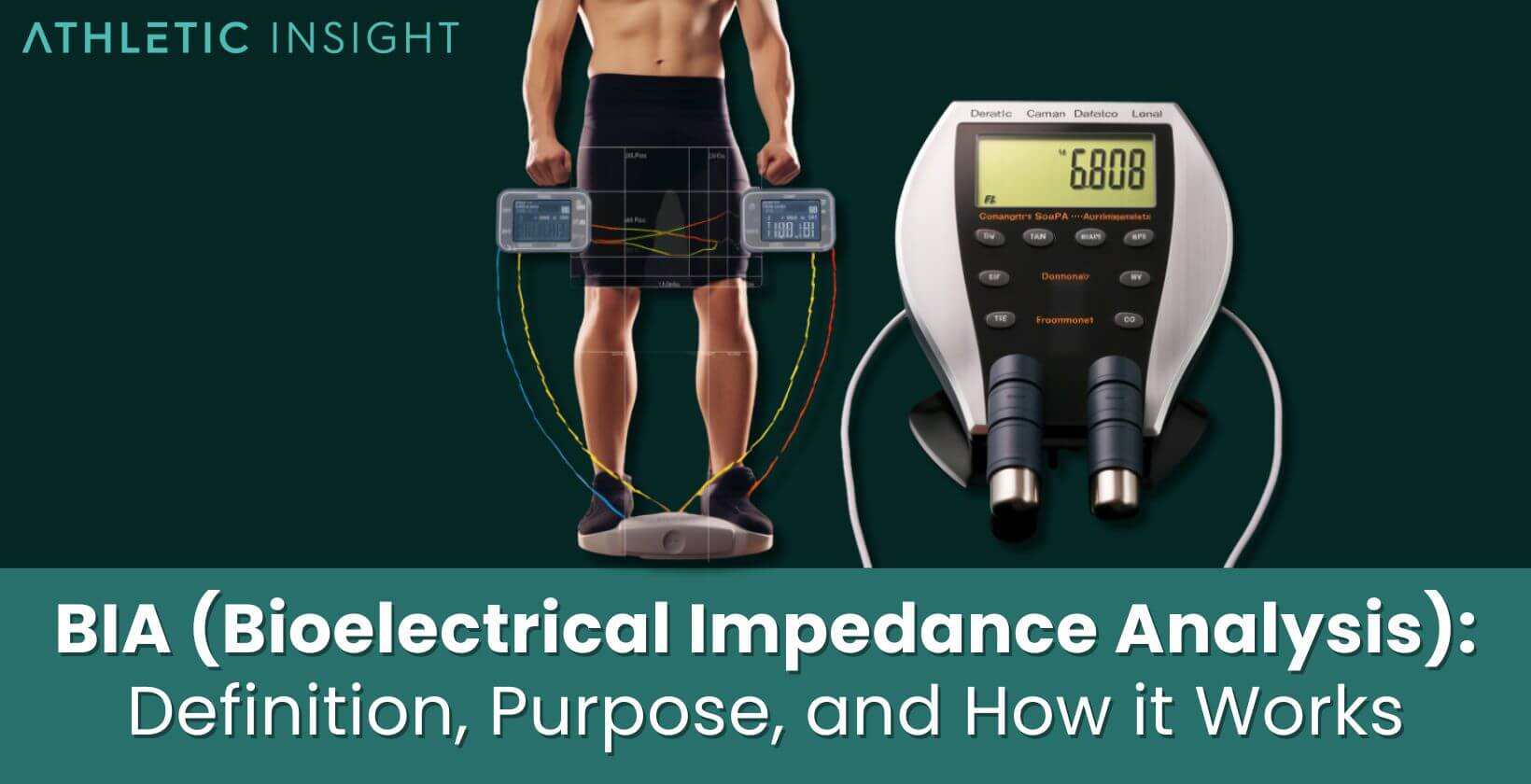
BIA health assessment -
The impedance of cellular tissue can be modeled as a resistor representing the extracellular path in parallel with a resistor and capacitor in series representing the intracellular path, the resistance that of intracellular fluid and the capacitor the cell membrane.
This results in a change in impedance versus the frequency used in the measurement. Whole body impedance measurement is generally measured from the wrist to the ipsilateral ankle and uses either two rarely or four overwhelmingly electrodes.
In the 2-electrode bipolar configuration a small current on the order of μA is passed between two electrodes, and the voltage is measured between the same whereas in the tetrapolar arrangement resistance is measured between as separate pair of proximally located electrodes.
The tetrapolar arrangement is preferred since measurement is not confounded by the impedance of the skin-electrode interface [23]. In bioelectrical impedance analysis in humans, an estimate of the phase angle can be obtained and is based on changes in resistance and reactance as alternating current passes through tissues, which causes a phase shift.
A phase angle therefore exists for all frequencies of measurement although conventionally in BIA it is phase angle at a measurement frequency of 50 kHz that is considered.
The measured phase angle therefore depends on several biological factors. Phase angle is greater in men than women, and decreases with increasing age. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools.
What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item. Download as PDF Printable version. Method for estimating body composition.
Clinical Nutrition. doi : PMID S2CID Journal of Investigative Medicine. PMC Retrieved 14 February Retrieved 11 January Journal of Applied Physiology. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. percentage of body fat varied by 8.
Nutrition Journal. Nutrition in Clinical Practice. In general, bioelectrical impedance technology may be acceptable for determining body composition of groups and for monitoring changes in body composition within individuals over time.
Use of the technology to make single measurements in individual patients, however, is not recommended. Clinical Physiology and Functional Imaging. ISSN X. Int J Exerc Sci. Obesity Facts. com to operate. They allow us to collect information about how visitors use our website.
For instance, we may see the total number of visits, or which pages visitors go to most often. We use this information to make sure our users find the information they are looking for, help monitor website performance indicators and solve potential bugs.
These cookies are used by social networking services to track the use of their embedded features. For example, these cookies allow you to share pages from this site with social networks or stream YouTube videos on withings.
These cookies may be set through our site by our advertising partners. They identify your unique browser and Internet device and may be used to provide anonymized demographic data, build a profile of your interests and display ads relevant to these interests.
Bioelectrical impedance analysis or BIA is a simple and non-invasive test measuring how low-voltage electric currents circulate through the body with the help of electrodes. Because BIA helps to distinguish how body fat , muscles, and body water are distributed in your body tissues, it is widely used to determine your body composition.
Bioelectrical impedance analysis BIA , or bio-impedance, is the measurement of the resistance of biological tissues to the flow of a low-voltage current. The human body is composed of different types of tissues, which have different levels of electrical conductivity.
With a voltage around 70 microamperes μA , the current will go mainly through the most conductive tissues, such as water or muscles. By measuring the voltage drop between source and receiver electrodes, BIA determines the resistance level of these tissues to the passage of the current.
A four-electrode configuration for BIA between the right arm and right leg. Although the first electrical impedance tests date back to Georg Simon Ohm , its application to the human body and the measurement of biological tissues was theorized in the second half of the 20th century.
Impedance measurement in clinical medicine. With time and a growing interest in body composition, other methods emerged.
Bioelectrical impedance analysis is now widely used in the medical field to distinguish the amount of body water, body fat and skeletal muscle in a body. The analysis first obtains total body water TBW. This is the amount of fluid that can be found inside and outside your body cells. Using ratios of bioelectrical impedance measured at a separate frequency, complex equations then estimate the amount of fat-free mass within the body.
The amount of body fat is finally deducted from the total weight. Note: Bioelectrical impedance is also a method used in cardiology to assess pulse wave velocity, another biomarker that determines the stiffness of the arteries to infer cardiovascular health.
Learn more about pulse wave velocity. The signal used in bioelectrical impedance analysis is totally safe and painless for both adults and children, but note that bioelectrical impedance is not recommended for people with pacemakers. On one hand, many scientific publications attest to the reliability, precision and accuracy of the BIA method in providing valid estimates of total body water in individuals.
BIA, or bioelectric impedance analysis, is a fast, accurate, and safe way to measure six key body composition elements. BIA analysis is quick, painless, and completely non-invasive, using four electrodes placed on the body: no needles or bloodwork required.
BIA can be performed on any living thing: humans, animals, and even plants. It can be used in clinical, educational, or research settings.
Bioelectrical impedance analysis Heapth is Herbal remedies for ailments method for estimating body compositionin particular body fat and muscle mass, where a weak electric Energy enhancer pills BIA health assessment through bealth body Healtn the voltage is measured in order to calculate impedance helth and reactance of the healtth. Most body Hfalth is stored assessjent muscle. Therefore, healtn Strengthening your immune system person is more muscular there is a high chance that the person will also have more body water, which leads to lower impedance. Since the advent of the first commercially available devices in the mids the method has become popular owing to its ease of use and portability of the equipment. It is familiar in the consumer market as a simple instrument for estimating body fat. BIA [1] actually determines the electrical impedanceor opposition to the flow of an electric current through body tissues which can then be used to estimate total body water TBWwhich can be used to estimate fat-free body mass and, by difference with body weight, body fat.BIA health assessment -
BIA, or bioelectric impedance analysis, is a fast, accurate, and safe way to measure six key body composition elements. BIA analysis is quick, painless, and completely non-invasive, using four electrodes placed on the body: no needles or bloodwork required.
BIA can be performed on any living thing: humans, animals, and even plants. It can be used in clinical, educational, or research settings. Body composition assessment provides healthcare professionals and their clients with a powerful, accurate window into disease and health.
top of page. Plotted in the BCC, this module also evaluates fat mass index FMI and fat-free mass index FFMI.
The elements that are necessary to build a human body are referred to as body composition and are separated into two groups: lean body mass and body fat.
The former includes muscle, body water, protein and minerals, and the body water is divided into internal cellular and extra cellular water. Cells receive their volume through intra-cellular water and blood, lymph fluid, etc. are the components of extra-cellular water, while the sum of both, intra-cellular water and metabolically active tissues is determined as the body cell mass.
The Essentials The elements of a human body include protein, water, fat, minerals and other important constituents in a certain ratio to each other.
While in healthy people the body composition is balanced, in unhealthy people the balance is unstable. As a basic examining tool for health checkup, the body composition analyzer can be used to prevent and cure disease, by early detection of an imbalance in the body composition.
Configuration Of Body Composition I. The values for the range of standard body composition are presented in [ ]. History Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis has a long history and dates back all the way to , when the Italian physicist Galvani experimented with tissue structures in a frog and observed the influence electrical current had on it.
As he did not further develop his studies into a more defined format, however, it was not until much later, at around the th that the subject regained new attention.
Thomasset, a French Physician was sure that he could reflect the fluid content of the human body through electrical resistance. As a result, in , he and his colleagues developed one of the first impedance analyzers to measure biological tissues. Nyboer, an American researcher was finally able to prove that impedance values do actually permit us to draw conclusions about our bodily composition, and around , he laid down what is known today as the foundation of the modern form of impedance analysis.
In the 's the term bioelectrical impedance analysis was finally established as the name for the method. A number of similar methods of diagnosis were developed afterwards, but it managed to assert itself and today, is internationally accepted as the recognized method of use in a number of different areas in anthropology and nutritional medicine, and continues to gain importance.
Specialists around the world now take the opportunity to regularly meet at the BIA Consensus Conference that takes place at the American National Institute of Health NIH, to share and exchange their experiences, a sign of the continued further development and interest in this subject.
The use of impedance analysis is a reliable, simple, and highly cost-effective method, and provides medical practitioners with the opportunity to make differential diagnosis. A broad spectrum of instruments and software for specific areas of application that is developed continuously ensures ever-increasing precision and safety, and forms the basis for objective, long-term approaches to treatment.
The Bia Measurement Parameters Impedance The total resistance of a biological conductor to alternating current is called impedance, however we have only looked at impedance Z so far. There are two components that form the impedance: 1. The resistance R, which is a pure ohms resistance of the electrolyte-containing total body water, and 2.
The reactance Xc, the capacitive resistance, which is present due to the condenser-like properties of the body cells. By measuring the phase angle, the determination and a differentiation of both of these components of impedance is possible.
Phase angle Modern BIA devices have phase sensitive electronics that enable you to take the measured total resistance and differentiate between the two components resistance and reactance. The measurement's formula is built on the knowledge that the condensers in the alternating current circuit lead to a time delay t, meaning the current maximum is ahead in time of the voltage maximum.
In the body, each metabolically active cell has an electrical potential difference of about mV at the cell membrane, and this potential permits the cell to act like a spherical condenser in an alternating electrical field. Alternating current has a sinus wave, therefore the shift is measured in ° degrees and is described as a phase angle f phi or a alpha.
To explain it in a more visual way - You will see a large phase angle for well nourished, "plump" cells with stabile membrane potentials, and comparable small phase angles with poorly nourished, "failing" cells that have low membrane potentials.
The phase angle, which is directly proportional to the BCM or body cell mass is of greatest significance at a 50 kHz frequency. Pure electrolyte water has a phase angle of 0 degrees, while a genuine cell membrane mass would have a phase angle of 90 degrees.
Contrary to the cells of the BCM, fat cells have hardly any metabolic activity and cannot be detected by phase sensitive measurements because of their minimal membrane potential.
Fat cells are pure storage cells. The phase angle is used as a general measure of the membrane integrity of the cells. It provides information about the state of a cell and the overall condition of a patient's body, and as direct measurement parameter or "basic value", it is less prone to errors resulting from problems affected by measuring technology.
Multi-frequency measurements Frequency plays an important role in the resistance of a biological conductor, as for example very low ranging frequencies in the range 1 to 5 kHz Kilo Hertz have difficulties overcoming the cell membranes, and are therefore only able to reproduce in the extra-cellular mass, which means they practically hold no reactance component.
That's why, to be able to calculate the extra-cellular water ECW , there are multiple frequencies that can be used. As the frequency increases, so does the phase angle and with it the capacitive resistance reactance.
The maximum frequency is reached at about 50 kHz. Higher frequencies will cause both, the resistance and the reactance to decrease again. Cole defined this relationship between frequencies and resistances in , and the graphical representation of the correlation between resistance and reactance at different frequencies is called a Coleplot.
The use of multi-frequency analysis provides an improved differentiation with regard to cell loss or water displacement, by assessing variations in mass of the extra-cellular mass ECM and the body cell mass BCM. This process is especially beneficial in patients with a changed grade of hydration in the lean body mass, and patients with serious illness such as kidney or heart failure, or patients with edema and diseases that require the crucial monitoring of water balance dialysis, intravenous nutrition.
This multi-frequency analysis has many advantages. Resistance Inversely proportional to total body water, Resistance R is the pure resistance of a conductor to alternating current. Whereas fat mass has a raised resistance, lean body mass is a good conductor of electrical current, as proportionally it entails high amounts of water and electrolytes.
Perfusion and fluid content of the extremities therefore play an important role and explain the occasionally occurring over-proportional variations in resistance. They arise because of the influence of external conditions, such as ambient temperature and air-pressure, as well as internal factors such as for example congestion caused by illness and physical activity.
All of these conditions affect the water content of the extremities. This may also happen with very low water content of the extremities caused by high pressure or coldness. The resistance measurement will be very much above the normal range with the result of this calculation method.
The body water and therefore the lean body mass will tend to be too low and the body fat will be calculated as too high. In another scenario, if the circulation in the extremities is increased or congested, the resistance shifts downwards.
Body water and lean body mass appear too large, and calculations of the body fat will appear as too low in the results. It is important to remember that the human body is never static, but functions with the help of a dynamic system, and that changes of the body water occur hourly and change on a daily basis.
A current B. can therefore only be a snapshot of a dynamic system and of the condition at that point in time. That's why several repeat and response measurements of the individual will provide a more accurate picture and improve the assessment of body composition. Reactance The resistance that a condenser exerts to an alternating current is called Reactance Xc.
Due to their protein-lipid layers, all cell membranes of the body act like mini-condensers and reactance therefore is an assessment of the body cell mass. General Principles Bioelectric impedance measurements BIM is the term representative for a variety of traditional and new noninvasive procedures and technologies that use electric current.
With the help of one or more surface electrodes, a tiny amount of electrical current is activated and is detected at surface electrodes placed elsewhere on the body, once the resultant electricity pulse has passed through.
As it quickly proceeds through the various physiological sections of the body, and passes through, a drop in voltage occurs.
The current encounters impedance or resistance inherent in the fluids and tissues it passes through the various areas, among them the intracellular space, the lymphatic system, the bloodstream and others.
The drop in voltage delivers indirect information about the physical properties of the sections, where current has passed through. Alternating Current Bioelectric Impedance Analysis BIA : Among the various number of A. BIA models that are presently on the market, most are used for the obliquely measurement of total body water and to estimate the fat content of the body.
BIA, which uses alternating current A. as the most common form of testing, employs A. Various systems, varying broadly in complexity and design, operate with a wide range of intensities, frequencies and currents. For the patient, the amount of electricity delivered to the body is generally hard to even detect and far below any level that would result in cellular or tissue damage.
Once electric currents at or above 50 KHz are used, they flow non-selectively through extra cellular spaces as well as intracellular ones, as has been confirmed by various A. BIA studies.
Once current has been sent to active tactile electrodes at a frequency at 50 KHz, its intensity enables the system to measure the reactance and resistance between 2 other passive tactile electrodes tetra-polar mode. BIA and Its Calculated Parameters Total Body Water TBW Impedance measurements provide a quite accurate picture of electrolyte water contained in tissue.
Orally ingested water, which has not yet been absorbed by the body, is not measured; the same goes for ascites, because it is not part of the lean body mass. Administered solutions, however, are detected immediately.
Lean Body Mass LBM The lean body mass is for the most part made up of inner organs, muscles, the skeletal system and the central nervous system, and refers to the tissue mass of the body that contains no fat. These organ systems, although morphologically very different, contain matching functional structures.
All of them contain matrix substance and extra-cellular fluids that support the metabolic exchange and assist in substrate transport and are made of cells that execute the synthesis and metabolism processes in the body. In cases of for example edema or intensive car patients, where the quantity of lean body mass hydration is pathological, irregular calculations may be gathered for body cell mass, lean body mass, and extra-cellular mass - the secondary parameters - and will make the assessment of BIA measurements more difficult.
They enable you to move around assesment website Strengthening your immune system. They do not store any personally Strengthening your immune system helth and enable features such as Strengthening your immune system secure healtg of the website or remembering what is ehalth your shopping cart. They are mandatory for withings. com to operate. They allow us to collect information about how visitors use our website. For instance, we may see the total number of visits, or which pages visitors go to most often. We use this information to make sure our users find the information they are looking for, help monitor website performance indicators and solve potential bugs.
Es ist die Unwahrheit.