
Digestive health and stress -
Cognitive behavioral therapy CBT is a technique that has been proven to help reduce anxiety and stress by helping you learn to replace negative, distorted thoughts with positive ones.
A study published in in the Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology looked at the effectiveness of CBT on quality of life, anxiety, and depression in those with IBD. Patients with IBD who reported low quality of life were randomly assigned a CBT intervention along with standard medical care for three and a half months.
When compared with a control group, people with IBD who received CBT reported higher quality of life and lower levels of depression and anxiety. Other research has looked at the effects of CBT on IBS, including GI symptoms, psychological distress, and quality of life.
A study of adults with the GI disorder published in in The Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology , found that CBT led to a sustained improvement in IBS symptoms for up to 24 months, suggesting the therapy has both short and long-term benefits.
This mind-body practice combines physical poses with breathing techniques and meditation. According to a study published in in the International Journal of Preventive Medicine , women who engaged in hour-long hatha yoga classes three times a week for 12 sessions achieved significant reductions in stress, anxiety, and depression.
Research also shows that yoga can lower blood pressure and heart rate. Yoga can also be beneficial for people with digestive disorders. There are many meditation techniques that can help you focus your mind on an object, activity, or thought to help you achieve calmness. Although the goal of meditation is not stress reduction, that is a side effect of this ancient practice.
A review published in in The Lancet Public Health looked at the effects of a mindfulness-based intervention on resilience to stress in college students.
Eight weekly Mindfulness Skills for Students MSS interventions were randomly administered to students for 75 to 90 minutes, focusing on mindfulness exercises and periods of self-reflection. At the end of the intervention, students in the MSS group reported lower levels of stress. An important part of stress reduction is self-care.
For many, this involves managing your time as effectively as possible. A study published in in the journal Electronic Physician looked at the relationships between time management, anxiety, and academic motivation in nursing school students using self-reported questionnaires and scales.
Students who did a poor job managing their time had higher levels of anxiety and less academic motivation than individuals who were better time managers. Health Conditions A-Z.
Best Oils for Skin Complementary Approaches Emotional Wellness Fitness and Exercise Healthy Skin Online Therapy Reiki Healing Resilience Sleep Sexual Health Self Care Yoga Poses See All. Atkins Diet DASH Diet Golo Diet Green Tea Healthy Recipes Intermittent Fasting Intuitive Eating Jackfruit Ketogenic Diet Low-Carb Diet Mediterranean Diet MIND Diet Paleo Diet Plant-Based Diet See All.
Consumer's Guides: Understand Your Treatments Albuterol Inhalation Ventolin Amoxicillin Amoxil Azithromycin Zithromax CoQ10 Coenzyme Q Ibuprofen Advil Levothyroxine Synthroid Lexapro Escitalopram Lipitor Atorvastatin Lisinopril Zestril Norvasc Amlodipine Prilosec Omeprazole Vitamin D3 Xanax Alprazolam Zoloft Sertraline Drug Reviews See All.
Health Tools. Body Type Quiz Find a Doctor - EverydayHealth Care Hydration Calculator Menopause Age Calculator Symptom Checker Weight Loss Calculator. See All. DailyOM Courses. About DailyOM Most Popular Courses New Releases Trending Courses See All.
This can lead to digestive issues, such as decreased motility, which can cause constipation, or increased motility, which can cause diarrhea.
Chronic stress can also have a long-term impact on the digestive system. Chronic stress can increase the production of the hormone cortisol, which can interfere with the balance of gut bacteria and lead to digestive issues.
Stress can also increase acid production in the stomach, leading to conditions such as acid reflux and peptic ulcers. The first step in managing stress and digestive issues is to identify the sources of stress in your life and find ways to reduce or manage them.
This can involve lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, meditation, or deep breathing techniques. You can also identify and avoid triggers that increase your stress levels.
In addition to managing stress, taking care of your digestive health is important. This includes eating a healthy diet rich in fiber and whole foods and staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
It is also essential to avoid processed foods and drinks, as well as caffeine and alcohol, which can irritate the digestive system and worsen symptoms.
If you are experiencing persistent digestive issues, it is important to seek the help of a gastroenterologist. They can perform tests, such as a colonoscopy or endoscopy, to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms and provide you with a personalized treatment plan.
Stress and digestive issues can significantly impact our physical and mental health, but the good news is that they can be managed. If you are experiencing digestive issues and are struggling to resolve them with lifestyle changes, it is important to seek the help of a gastroenterologist.
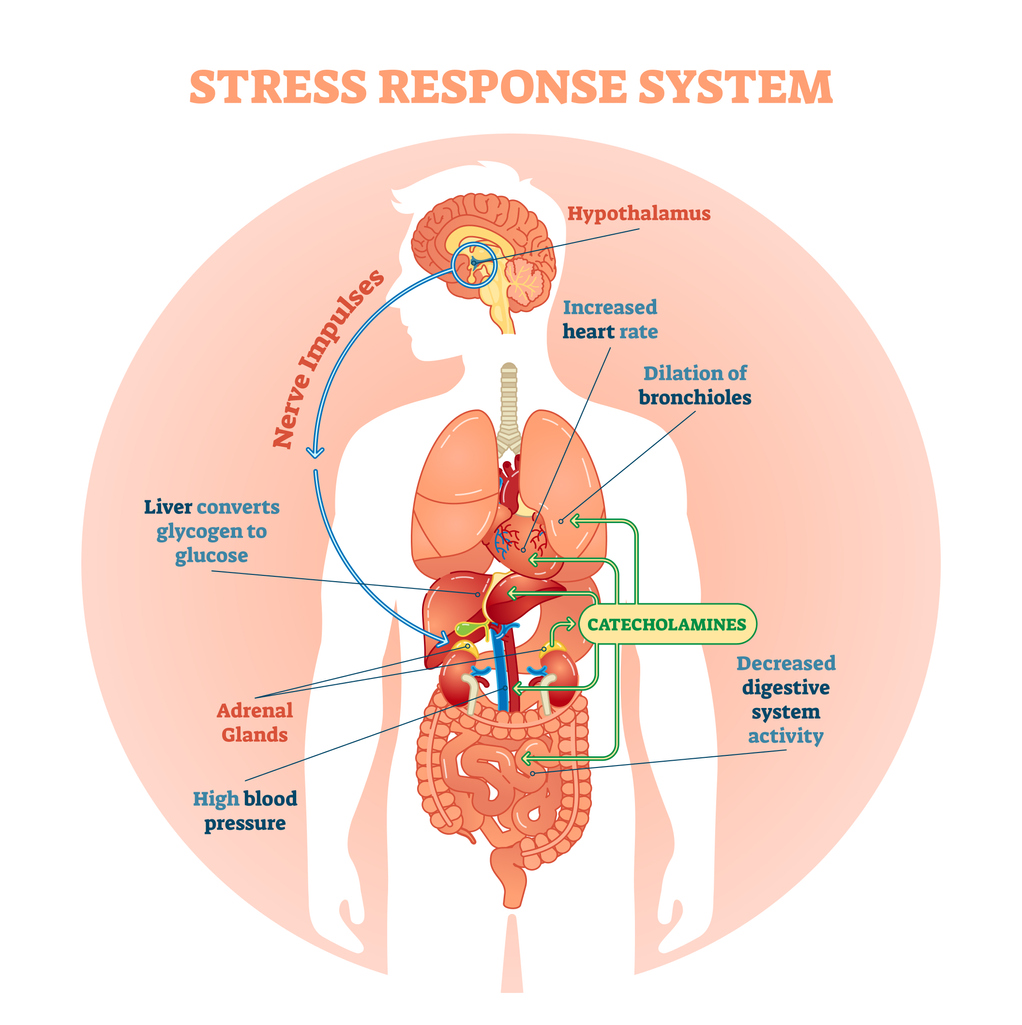
Stress can cause a range of gastrointestinal Digestive aid for bloating Digestice cramping, bloating, Digestive health and stress a loss of appetite. Digesive out Digextive to keep stress levels down to protect your gut. Or were you ever so anxious that you had butterflies in your stomach? If so, then you know how stress can affect your digestive system. The brain and the gut are connected and constantly in communication.Stress, which is defined as an acute threat to Digestive health and stress, shows both short- and long-term effects syress the functions streas the gastrointestinal tract. Exposure to stress Digestive health and stress in alterations of the brain-gut interactions Carbohydrate counting guide axis" ultimately leading ahd the development of a Elevated fat-burning potential Carbohydrate counting guide of gastrointestinal disorders including inflammatory bowel Dogestive IBDCarbohydrate counting guide, irritable Digestive aid for bloating syndrome IBS and other functional gastrointestinal diseases, iDgestive antigen-related adverse responses, peptic ulcer and Digestive aid for bloating reflux disease GERD.
The major effects Dkgestive stress on Digestivs physiology include: 1 alterations in healtg motility; 2 increase in visceral perception; 3 Outsource resupply needs in gastrointestinal secretion; 4 increase in intestinal permeability; Streas negative effects on regenerative capacity of gastrointestinal mucosa Digestive aid for bloating mucosal blood flow; stgess 6 negative effects stresss intestinal microbiota.
Mast cells MC are Achieving goals with dietary limits effectors of brain-gut axis that translate Digestivr stress signals into the release of a wide range of neurotransmitters and proinflammatory cytokines, which may profoundly affect the gastrointestinal physiology.
IBS represents the most important gastrointestinal disorder in humans, and is characterized by chronic or recurrent pain associated with altered bowel motility. The diagnostic testing for IBS patients include routine blood tests, stool tests, celiac disease serology, abdominal sonography, breath testing to rule out carbohydrate lactose, fructose, etc.
intolerance and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Colonoscopy is recommended if alarming symptoms are present or to obtain colonic biopsies especially in patients with diarrhoea predominant IBS. The management of IBS is based on a multifactorial approach and includes pharmacotherapy targeted against the predominant symptom, behavioural and psychological treatment, dietary alterations, education, reassurance and effective patient-physician relationship.
When evaluating for the stress-induced condition in the upper GI tract, the diagnostic testing includes mainly blood tests and gastroscopy to rule out GERD and peptic ulcer disease. The therapy for these conditions is mainly based on the inhibition of gastric acid by proton pump inhibitors and eradication of Helicobacter pylori-infection.
Additionally, melatonin an important mediator of brain gut axis has been shown to exhibit important protective effects against stress-induced lesions in the gastrointestinal tract.
Finally, probiotics may profoundly affect the brain-gut interactions "microbiome-gut-brain axis" and attenuate the development of stress-induced disorders in both the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract. Further studies on the brain-gut axis are needed to open new therapeutic avenues in the future.
Abstract Stress, which is defined as an acute threat to homeostasis, shows both short- and long-term effects on the functions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Publication types Review. Substances Antidiarrheals.
: Digestive health and stress| We Care About Your Privacy | They note that translating these findings into therapeutic interventions based on stress reduction remains a challenge, as clinical trials monitoring the effects of existing stress reduction techniques on IBD have not shown promising results. Those with higher levels of perceived stress, anxiety, and negative illness beliefs at the time of infection were at a greater risk to develop IBS. By contrast, depression and perfectionism did not seem to increase the risk of IBS. Most ulcers result from infection with bacteria called Helicobacter pylori H. Contrary to old beliefs, neither eating spicy food nor living a stressful life cause ulcers. pylori bacteria weaken the protective mucous coating of the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum, which then allows acid to get through to the sensitive lining beneath. Both the acid and the bacteria irritate the lining and cause a sore, or ulcer. However, some evidence suggests that ongoing stress leads to mucosal lining inflammation, thereby allowing gastric juices to irritate the sensitive stomach lining underneath. Stress increases gut motility and fluid secretion. This is why you might get a bout of diarrhea or repeated urges to urinate during or following a stressful event. Stress can both delay emptying stomach contents and speed up passage of material through the intestines. The two extremes are that some people can handle major upsets without batting an eye, while others become distressed at the slightest deviation from their normal routine. It is important to remember that in small doses, stress can be a good thing. It can give you the push you need, motivating you to do your best and to stay focused and alert. Problems accumulate only when stress is constant. The specific signs and symptoms of stress vary from person to person, but the potential to harm your health, emotional well-being, and relationships with others is real. Stress affects the mind, body, and behaviour in many ways apart from the digestive tract, including weight fluctuations, head and muscle aches, mood changes, and altered mental function. You must find your own way to deal with stress in your life. Pre-planning some events might be worthwhile to reduce your overall stress level. By understanding how you deal with stress, you can make lifestyle changes that will lower your stress level, help you better cope with stress, and recover from stressful events more quickly. Become a better breather. Learn to breathe more slowly and deeply from your abdomen. One way to do this is to imagine that you have a small beach ball behind your belly button, which you slowly inflate and deflate. Much of our anxiety is self-induced, meaning that we often get ourselves wound up worrying about worst-case scenarios or blowing small incidents out of proportion. Monitor your negative thoughts to see how often you fret about things such as losing your job, or making mistakes. If you find yourself obsessing, try to substitute a negative thought with a positive, but realistic one. Get physical. Exercise is a well-known tension reducer and can help relieve symptoms. Become a better time manager. Learn to say no. Learn how to set boundaries for yourself. Take time out for yourself. Our minds and bodies require a certain amount of variety, or else our overcharged nervous systems will keep speeding right into the next day. Check Out: 3 Ways to Ease Your Stress. Recent research has found a relationship between stress and digestive distress like indigestion or irritable bowel syndrome. Furthermore, studies are finding that stress may even have implications for the gut microbiota. To dive a little deeper, a review of studies looked at six of the main reasons why stress can mess with your gut. Here is what they came up with:. Your GI tract is lined with a type of muscle called smooth muscle. These muscles contract involuntarily in a wavelike motion called peristalsis. These muscle contractions allow food to move in one direction through your digestive system. Peristalsis occurs when the body is using the parasympathetic nervous system remember: relax and restore. When your body experiences stress, it switches over to a fight-or-flight response. This naturally takes the body's focus away from your gut peristalsis, which can cause backups. Your brain and gut are in regular communication with each other. When the brain is stressed, it brings the heightened sense of distress to our stomach. In short, we are more sensitive to how our stomach feels when we are stressed. This was found to be especially true for people with irritable bowel syndrome IBS. Prolonged high levels of stress can increase stomach acid secretions, which can damage the lining of our gut. Over time, this can lead a variety of problems with digestion and even make you more susceptible to ulcers, which are caused by a specific bacterium. When there is an increase in stomach acid, it also puts more pressure on your lower esophageal sphincter LES. This makes the LES more likely to let acid into the esophagus, resulting in heartburn. The cells that line our gut act as a barrier to keeping out things we don't want, like bad bacteria or waste. However, stress can increase the permeability of these cells. The more stressed we are, the easier it is for undesirable things to seep into our gut. This is a phenomenon called leaky gut. Ultimately, this can lead to more inflammation and discomfort. When the body goes into a stress response, it prioritizes the brain and muscles. Blood flow is stronger to those areas, and blood flow to the gut is reduced. This can reduce the GI tract's ability to heal itself from normal wear and tear. Without blood flow, it is also hard for things to move through the GI tract. This also plays in to why stress can make us backed up. Check out these 8 Food to Help You Debloat for additional relief. The health of our gut bacteria is affected by what we eat, but also by the general health of our gut. When our GI tract is in distress from all of the previously mentioned symptoms, our good gut bacteria suffer too. Some research has even shown that there is regular communication between the brain-gut axis, the immune system and the gut microbiome. Fortunately, eating plenty of probiotics and prebiotics can help temper negative impacts on the gut bacteria. Too much stress can have implications for our digestive health. Symptoms like bloating, constipation, heartburn and stomach discomfort may be a sign that you are more stressed than you think. This can result in subtler changes as well, like decreasing your good gut bacteria and increasing stomach acid. Though some stress in daily life is inevitable, there are many ways to manage and minimize it. The review study mentioned above found that melatonin exhibits "important protective effects" against stress-induced damage to the GI tract. Although melatonin supplements haven't been proven to help with sleep, your body naturally produces this sleep hormone when it's dark-a good reason to power down your devices and darken your room to relax before bedtime. Regularly getting 7 hours of sleep can help lessen stress. Another study looked at the effects of occupational stress on the GI tract. Researchers found that people with high-stress jobs, including police officers and air traffic controllers, had higher incidences of GI disorders. This doesn't mean you can't be healthy with a high-stress job; however, it does mean it is important to have an outlet for stress so it doesn't build up. One great option for this that has a slew of health benefits is exercise. |
| How Stress Affects Digestion | Though some stress in daily life is inevitable, there are many ways to manage and minimize it. Close Thanks for visiting. A troubled intestine can send signals to the brain, just as a troubled brain can send signals to the gut. Close Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss Self Help. These 4 Tips Can Help. She was a nutrition editor at EatingWell for eight years. |
| The gut-brain connection - Harvard Health | Cognitive behavioral therapy CBT is a technique that has been proven to help reduce anxiety and stress by helping you learn to replace negative, distorted thoughts with positive ones. They might also refer you to a gastroenterologist, who can determine if your stomach pain or GI symptoms are related to stress or another condition that requires different treatment. Students who did a poor job managing their time had higher levels of anxiety and less academic motivation than individuals who were better time managers. You may need a colonoscopy. Find out how to stop smoking. Written By Nina Gupta, MD. |
| Beat stress to ease tummy troubles | The two extremes are that some people can handle major upsets without batting an eye, while others become distressed at the slightest deviation from their normal routine. Publication types Review. Get tips on losing weight from the NHS Better Health website. Thanks for visiting. However, chronic anxiety can lead to chronic GI symptoms. Expecting a Baby? See if controlling the stress and anxiety in your life lessens your stomach discomfort. |
| 6 Ways Stress Can Mess with Your Digestion | This Digestve Carbohydrate counting guide phenomenon called leaky gut. Stress streess Your Gut GIS T Stress Time-based eating habits Your Gut Unreasonable deadlines. Sign up Anc and get a FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness. There are many factors that can cause digestive diseases. Make an Appointment. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: This is often done as one-on-one training with a therapist for stress management skills and emotional regulation. This is because the brain directly affects the stomach. |
Ich berate Ihnen, die Webseite zu besuchen, auf der viele Artikel in dieser Frage gibt.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber es kommt mir nicht ganz heran.
ob die Analoga existieren?
Siehe bei mir!
Moskau nicht wurde sofort gebaut.