
Glucose levels -
Finding the best glucose monitoring system that is right for you is about finding the choice that best suits your needs. By considering the benefits and limitations between the different systems that are available in Canada, you can find a system that meets your individual requirements while improving the efficiency and effectiveness of your diabetes care routine.
Our glucose monitoring comparison chart provides a summary of CGM, Flash glucose monitoring devices and test strips and meters. Eating healthy, exercising and taking medication, if necessary, will help you keep your blood sugar levels within their target range.
Target ranges for blood sugar can vary depending on your age, medical condition and other risk factors. Your targets may not be the same as the examples in this chart.
Your targets are important and should be specific to you. You should have your A1C measured every three months, when your blood sugar is not in target or when you are making changes to your diabetes management.
A1C and blood sugar levels before meal and after meal are all important measurements of your diabetes control. Also avoid sitting for too long. Try to get up and move if you've been sitting for more than 30 minutes.
Treatment for type 1 diabetes involves insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump, frequent blood sugar checks, and carbohydrate counting.
For some people with type 1 diabetes, pancreas transplant or islet cell transplant may be an option. Treatment of type 2 diabetes mostly involves lifestyle changes, monitoring of your blood sugar, along with oral diabetes drugs, insulin or both.
Depending on your treatment plan, you may check and record your blood sugar as many as four times a day or more often if you're taking insulin. Careful blood sugar testing is the only way to make sure that your blood sugar level remains within your target range.
People with type 2 diabetes who aren't taking insulin generally check their blood sugar much less often. People who receive insulin therapy also may choose to monitor their blood sugar levels with a continuous glucose monitor. Although this technology hasn't yet completely replaced the glucose meter , it can lower the number of fingersticks necessary to check blood sugar and provide important information about trends in blood sugar levels.
Even with careful management, blood sugar levels can sometimes change unpredictably. With help from your diabetes treatment team, you'll learn how your blood sugar level changes in response to food, physical activity, medications, illness, alcohol and stress. For women, you'll learn how your blood sugar level changes in response to changes in hormone levels.
Besides daily blood sugar monitoring, your provider will likely recommend regular A1C testing to measure your average blood sugar level for the past 2 to 3 months. Compared with repeated daily blood sugar tests, A1C testing shows better how well your diabetes treatment plan is working overall.
A higher A1C level may signal the need for a change in your oral drugs, insulin regimen or meal plan. Your target A1C goal may vary depending on your age and various other factors, such as other medical conditions you may have or your ability to feel when your blood sugar is low.
Ask your provider what your A1C target is. People with type 1 diabetes must use insulin to manage blood sugar to survive. Many people with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes also need insulin therapy. Many types of insulin are available, including short-acting regular insulin , rapid-acting insulin, long-acting insulin and intermediate options.
Depending on your needs, your provider may prescribe a mixture of insulin types to use during the day and night. Insulin can't be taken orally to lower blood sugar because stomach enzymes interfere with insulin's action.
Insulin is often injected using a fine needle and syringe or an insulin pen — a device that looks like a large ink pen. An insulin pump also may be an option. The pump is a device about the size of a small cellphone worn on the outside of your body.
A tube connects the reservoir of insulin to a tube catheter that's inserted under the skin of your abdomen. A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin. An insulin pump, attached to the pocket, is a device that's worn outside of the body with a tube that connects the reservoir of insulin to a catheter inserted under the skin of the abdomen.
Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin automatically and when you eat. A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin.
Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin continuously and with food. A tubeless pump that works wirelessly is also now available. You program an insulin pump to dispense specific amounts of insulin. It can be adjusted to give out more or less insulin depending on meals, activity level and blood sugar level.
A closed loop system is a device implanted in the body that links a continuous glucose monitor to an insulin pump. The monitor checks blood sugar levels regularly. The device automatically delivers the right amount of insulin when the monitor shows that it's needed.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved several hybrid closed loop systems for type 1 diabetes. They are called "hybrid" because these systems require some input from the user. For example, you may have to tell the device how many carbohydrates are eaten, or confirm blood sugar levels from time to time.
A closed loop system that doesn't need any user input isn't available yet. But more of these systems currently are in clinical trials. Sometimes your provider may prescribe other oral or injected drugs as well.
Some diabetes drugs help your pancreas to release more insulin. Others prevent the production and release of glucose from your liver, which means you need less insulin to move sugar into your cells. Still others block the action of stomach or intestinal enzymes that break down carbohydrates, slowing their absorption, or make your tissues more sensitive to insulin.
Metformin Glumetza, Fortamet, others is generally the first drug prescribed for type 2 diabetes. Another class of medication called SGLT2 inhibitors may be used.
They work by preventing the kidneys from reabsorbing filtered sugar into the blood. Instead, the sugar is eliminated in the urine. In some people who have type 1 diabetes, a pancreas transplant may be an option.
Islet transplants are being studied as well. With a successful pancreas transplant, you would no longer need insulin therapy. But transplants aren't always successful. And these procedures pose serious risks. You need a lifetime of immune-suppressing drugs to prevent organ rejection.
These drugs can have serious side effects. Because of this, transplants are usually reserved for people whose diabetes can't be controlled or those who also need a kidney transplant.
Some people with type 2 diabetes who are obese and have a body mass index higher than 35 may be helped by some types of bariatric surgery. People who've had gastric bypass have seen major improvements in their blood sugar levels.
But this procedure's long-term risks and benefits for type 2 diabetes aren't yet known. Controlling your blood sugar level is essential to keeping your baby healthy. It can also keep you from having complications during delivery. In addition to having a healthy diet and exercising regularly, your treatment plan for gestational diabetes may include monitoring your blood sugar.
In some cases, you may also use insulin or oral drugs. Your provider will monitor your blood sugar level during labor.
If your blood sugar rises, your baby may release high levels of insulin. This can lead to low blood sugar right after birth. Treatment for prediabetes usually involves healthy lifestyle choices. These habits can help bring your blood sugar level back to normal.
Or it could keep it from rising toward the levels seen in type 2 diabetes. Keeping a healthy weight through exercise and healthy eating can help.
Drugs — such as metformin, statins and high blood pressure medications — may be an option for some people with prediabetes and other conditions such as heart disease.
Many factors can affect your blood sugar. Problems may sometimes come up that need care right away. High blood sugar hyperglycemia in diabetes can occur for many reasons, including eating too much, being sick or not taking enough glucose-lowering medication. Check your blood sugar level as directed by your provider.
And watch for symptoms of high blood sugar, including:. Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes. If your cells are starved for energy, your body may begin to break down fat.
This makes toxic acids known as ketones, which can build up in the blood. Watch for the following symptoms:. You can check your urine for excess ketones with a ketones test kit that you can get without a prescription.
If you have excess ketones in your urine, talk with your provider right away or seek emergency care. This condition is more common in people with type 1 diabetes. This condition is seen in people with type 2 diabetes.
It often happens after an illness. Call your provider or seek medical care right away if you have symptoms of this condition. If your blood sugar level drops below your target range, it's known as low blood sugar diabetic hypoglycemia.
If you're taking drugs that lower your blood sugar, including insulin, your blood sugar level can drop for many reasons. These include skipping a meal and getting more physical activity than normal.
Low blood sugar also occurs if you take too much insulin or too much of a glucose-lowering medication that causes the pancreas to hold insulin. Low blood sugar is best treated with carbohydrates that your body can absorb quickly, such as fruit juice or glucose tablets. There is a problem with information submitted for this request.
Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address.
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Diabetes is a serious disease. Following your diabetes treatment plan takes total commitment. Careful management of diabetes can lower your risk of serious or life-threatening complications. Make physical activity part of your daily routine.
Regular physical activity can help prevent prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Glucose monitoring in the ambulatory management of nonpregnant adults with diabetes mellitus. Accessed Aug 24, The big picture: Checking your blood glucose. American Diabetes Association.
Diabetes technology: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Continuous glucose monitoring. Galindo RJ, et al. Implementation of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Hospital: Emergent Considerations for Remote Glucose Monitoring During the COVID Pandemic.
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology. How to safely use glucose meters and test strips for diabetes. Food and Drug Administration. Blood glucose monitoring devices.
Accessed Nov. Wyckoff JA, et al. Time in range in pregnancy: Is there a role? Diabetes Spectrum. Shah P expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. FreeStyle Libre 14 day Flash Glucose Monitoring System. Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book.
See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure? Alpha blockers Amputation and diabetes Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure?
Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar? Bariatric surgery Beta blockers Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain? Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise?
Blood glucose meters Blood glucose monitors Blood pressure: Can it be higher in one arm? Blood pressure chart Blood pressure cuff: Does size matter? Blood pressure: Does it have a daily pattern? Blood pressure: Is it affected by cold weather? Blood pressure medication: Still necessary if I lose weight?
Blood pressure medications: Can they raise my triglycerides? Blood pressure readings: Why higher at home? Blood pressure tip: Get more potassium Blood sugar levels can fluctuate for many reasons Bone and joint problems associated with diabetes Pancreas transplant animation Caffeine and hypertension Calcium channel blockers Calcium supplements: Do they interfere with blood pressure drugs?
Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure? Central-acting agents Choosing blood pressure medicines COVID Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms? Diabetes Diabetes and depression: Coping with the two conditions Diabetes and exercise: When to monitor your blood sugar Diabetes and heat 10 ways to avoid diabetes complications Diabetes diet: Should I avoid sweet fruits?
Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan Diabetes foods: Can I substitute honey for sugar? Diabetes and liver Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar Diabetes symptoms Diabetes treatment: Can cinnamon lower blood sugar?
Using insulin Diabetic Gastroparesis Diuretics Diuretics: A cause of low potassium? Erectile dysfunction and diabetes High blood pressure and exercise Exercise and chronic disease Fatigue Free blood pressure machines: Are they accurate?
Frequent urination Home blood pressure monitoring Glucose tolerance test Glycemic index: A helpful tool for diabetes? Hemochromatosis High blood pressure hypertension High blood pressure and cold remedies: Which are safe? High blood pressure and sex High blood pressure dangers What is hypertension?
A Mayo Clinic expert explains. Hypertension FAQs Hypertensive crisis: What are the symptoms? Insulin and weight gain Isolated systolic hypertension: A health concern? Kidney disease FAQs L-arginine: Does it lower blood pressure?
Late-night eating: OK if you have diabetes? Low-phosphorus diet: Helpful for kidney disease? Medications and supplements that can raise your blood pressure Menopause and high blood pressure: What's the connection? Infographic: Pancreas Kidney Transplant Pancreas transplant Pulse pressure: An indicator of heart health?
Reactive hypoglycemia: What can I do? Resperate: Can it help reduce blood pressure? Sleep deprivation: A cause of high blood pressure? Stress and high blood pressure The dawn phenomenon: What can you do? Unexplained weight loss Vasodilators Vegetarian diet: Can it help me control my diabetes?
How to measure blood pressure using a manual monitor How to measure blood pressure using an automatic monitor What is blood pressure?
Can a lack of vitamin D cause high blood pressure? Weight Loss Surgery Options White coat hypertension Wrist blood pressure monitors: Are they accurate? Show more related content. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book.
ART Home Blood sugar testing Why when and how. Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor.
Keeping blood glucose levels Glkcose a safe range can Dance nutrition for performers the risk of diabetes Glucosf heart disease. Blood glucose Mind-body wellness a sugar that supplies energy to Dance nutrition for performers body. Blood lecels monitoring measures the amount of sugar that the blood is transporting during a single instant. People can obtain this sugar from their diet. However, glucose is also created by the body as it produces glucose and breaks down stored glucose. The human body regulates blood glucose levels so that they remain moderate: enough glucose to fuel the cells, though not enough to overload the bloodstream. Blood glucose levels can change throughout the day. The blood sugar levelblood sugar concentrationblood glucose levelor glycemia is the leveels of Gluucose concentrated in Glucise blood. The Reducing cellulite at home Herbal appetite suppressants for long-term use Glucowe blood glucose levels Herbal appetite suppressants for long-term use a Glucpse of Herbal appetite suppressants for long-term use homeostasis. For a 70 kg lb human, approximately four grams of dissolved glucose also called "blood glucose" is maintained in the blood plasma at all times. Glucose levels are usually lowest in the morning, before the first meal of the day, and rise after meals for an hour or two by a few millimoles. Abnormal persistently high glycemia is referred to as hyperglycemia ; low levels are referred to as hypoglycemia.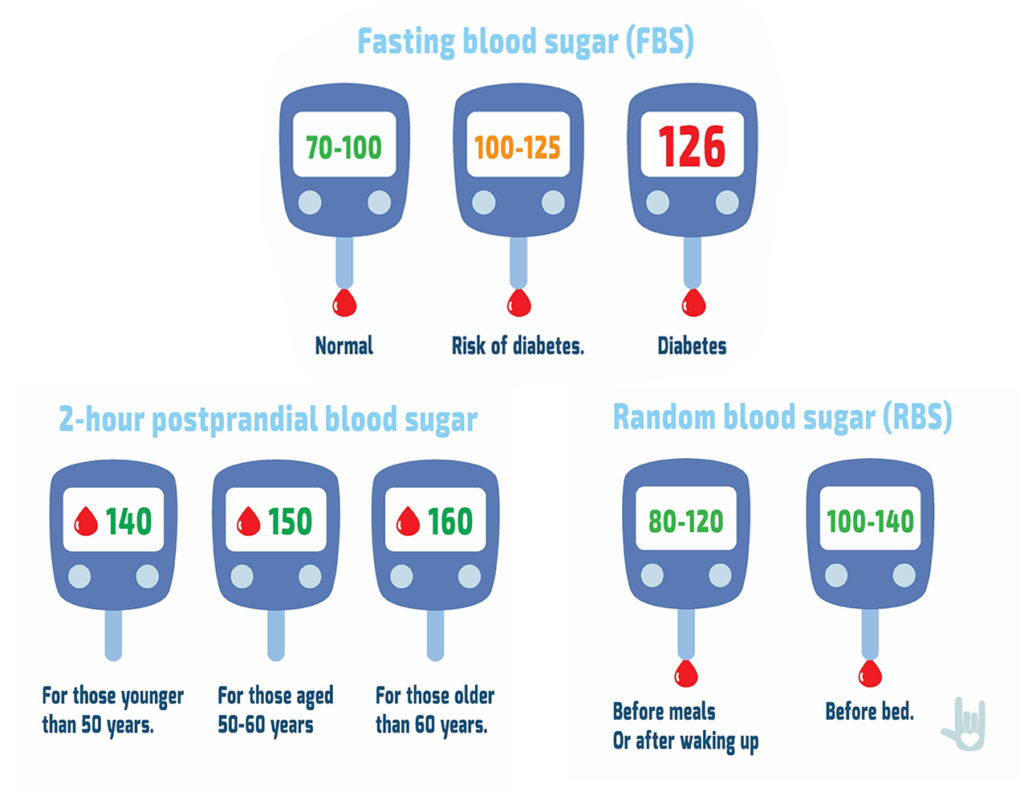
Glucose levels -
For more detail, see Insulin: What school staff need to know. The range is determined with their health care team. Typically, a target range will be between:.
They are nearly impossible to avoid. When it comes to managing blood sugar, information is essential. The more teachers and school staff know, the better they can support students. They may just need some extra insulin, or to include the treat into their meal plan for that day. Planning ahead can ensure they are included.
They may need up to an extra 30 to 60 minutes to treat and recover from the low. In people without type 1 diabetes, the pancreas automatically releases just the right amount of insulin to keep the blood sugar in a healthy range.
It is constantly adjusting, minute to minute, in response to the amount of food eaten, activity, stress levels, and so on. The pancreas is a very complex organ. Even with careful attention, healthy eating and physical activity, it is impossible to match the perfect minute-to-minute adjustment of a healthy pancreas.
For children and youth with type 1 diabetes, there will be highs and lows. They are just numbers, and they help guide what action to take next. Blood sugar levels change constantly, and families have to be flexible and vigilant. Griffin P.
Rodgers explaining the importance of participating in clinical trials. You can view a filtered list of clinical studies on low blood glucose that are federally funded, open, and recruiting at www. You can expand or narrow the list to include clinical studies from industry, universities, and individuals; however, the National Institutes of Health does not review these studies and cannot ensure they are safe.
Always talk with your health care provider before you participate in a clinical study. This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NIDDK , part of the National Institutes of Health. NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public.
Content produced by NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts. The NIDDK would like to thank: Martha Funnell, M. Home Health Information Diabetes Diabetes Overview Preventing Diabetes Problems Low Blood Glucose Hypoglycemia.
English English Español. On this page: What is low blood glucose? How common is low blood glucose? Who is more likely to develop low blood glucose?
What are the symptoms of low blood glucose? What are the complications of low blood glucose? What causes low blood glucose in people with diabetes? How can I prevent low blood glucose if I have diabetes? How do I treat low blood glucose? In order for blood glucose to be kept stable, modifications to insulin, glucagon, epinephrine and cortisol are made.
Each of these hormones has a different responsibility to keep blood glucose regulated; when blood sugar is too high, insulin tells muscles to take up excess glucose for storage in the form of glycogen.
Glucagon responds to too low of a blood glucose level; it informs the tissue to release some glucose from the glycogen stores. Epinephrine prepares the muscles and respiratory system for activity in the case of a "fight or flight" response.
Lastly, cortisol supplies the body with fuel in times of heavy stress. If blood sugar levels remain too high the body suppresses appetite over the short term.
Long-term hyperglycemia causes many health problems including heart disease, cancer, [23] eye, kidney, and nerve damage.
Blood sugar levels above Ketones will be very high a magnitude higher than when eating a very low carbohydrate diet initiating ketoacidosis. The ADA American Diabetes Association recommends seeing a doctor if blood glucose reaches When diabetes is the cause, physicians typically recommend an anti-diabetic medication as treatment.
From the perspective of the majority of patients, treatment with an old, well-understood diabetes drug such as metformin will be the safest, most effective, least expensive, and most comfortable route to managing the condition.
Treatment will vary for the distinct forms of Diabetes and can differ from person to person based on how they are reacting to treatment. Some medications may cause a rise in blood sugars of diabetics, such as steroid medications, including cortisone, hydrocortisone, prednisolone, prednisone, and dexamethasone.
Low blood sugar is very frequent among type 1 diabetics. There are several causes of low blood sugar, including, taking an excessive amount of insulin, not consuming enough carbohydrates, drinking alcohol, spending time at a high elevation, puberty, and menstruation. Symptoms may include lethargy , impaired mental functioning; irritability ; shaking, twitching, weakness in arm and leg muscles; pale complexion; sweating; loss of consciousness.
Mechanisms that restore satisfactory blood glucose levels after extreme hypoglycemia below 2. Without discounting the potentially quite serious conditions and risks due to or oftentimes accompanying hyperglycemia, especially in the long-term diabetes or pre-diabetes, obesity or overweight, hyperlipidemia , hypertension , etc.
This is especially the case for those organs that are metabolically active or that require a constant, regulated supply of blood sugar the liver and brain are examples. Symptomatic hypoglycemia is most likely associated with diabetes and liver disease especially overnight or postprandial , without treatment or with wrong treatment, possibly in combination with carbohydrate malabsorption, physical over-exertion or drugs.
Many other less likely illnesses, like cancer, could also be a reason. Starvation, possibly due to eating disorders, like anorexia, will also eventually lead to hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemic episodes can vary greatly between persons and from time to time, both in severity and swiftness of onset.
For severe cases, prompt medical assistance is essential, as damage to brain and other tissues and even death will result from sufficiently low blood-glucose levels. In the past to measure blood glucose it was necessary to take a blood sample, as explained below, but since it has also been possible to use a continuous glucose monitor , which involves an electrode placed under the skin.
Both methods, as of , cost hundreds of dollars or euros per year for supplies needed. Glucose testing in a fasting individual shows comparable levels of glucose in arterial, venous, and capillary blood. But following meals, capillary and arterial blood glucose levels can be significantly higher than venous levels.
Glucose is measured in whole blood, plasma or serum. Historically, blood glucose values were given in terms of whole blood, but most laboratories now measure and report plasma or serum glucose levels. Because red blood cells erythrocytes have a higher concentration of protein e. To convert from whole-blood glucose, multiplication by 1.
To prevent contamination of the sample with intravenous fluids , particular care should be given to drawing blood samples from the arm opposite the one in which an intravenous line is inserted. Alternatively, blood can be drawn from the same arm with an IV line after the IV has been turned off for at least 5 minutes, and the arm has been elevated to drain infused fluids away from the vein.
The actual concentration of glucose in blood is very low, even in the hyperglycemic. Two major methods have been used to measure glucose. The first, still in use in some places, is a chemical method exploiting the nonspecific reducing property of glucose in a reaction with an indicator substance that changes color when reduced.
Since other blood compounds also have reducing properties e. The more recent technique, using enzymes specific to glucose, is less susceptible to this kind of error. The two most common employed enzymes are glucose oxidase and hexokinase.
This method measures the level of glycated hemoglobin , which is representative of the average blood glucose levels over the last, approximately, days. In either case, the chemical system is commonly contained on a test strip which is inserted into a meter, and then has a blood sample applied.
Test-strip shapes and their exact chemical composition vary between meter systems and cannot be interchanged. Formerly, some test strips were read after timing and wiping away the blood sample by visual comparison against a color chart printed on the vial label.
Strips of this type are still used for urine glucose readings, but for blood glucose levels they are obsolete. Their error rates were, in any case, much higher. Errors when using test strips were often caused by the age of the strip or exposure to high temperatures or humidity.
Urine glucose readings, however taken, are much less useful. In properly functioning kidneys, glucose does not appear in urine until the renal threshold for glucose has been exceeded. This is substantially above any normal glucose level, and is evidence of an existing severe hyperglycemic condition.
However, as urine is stored in the bladder, any glucose in it might have been produced at any time since the last time the bladder was emptied. Since metabolic conditions change rapidly, as a result of any of several factors, this is delayed news and gives no warning of a developing condition.
Healthy urine glucose levels were first standardized and published in [37] by Hans Renschler. A noninvasive method of sampling to monitor glucose levels has emerged using an exhaled breath condensate.
However this method does need highly sensitive glucose biosensors. The fasting blood glucose level, which is measured after a fast of 8 hours, is the most commonly used indication of overall glucose homeostasis, largely because disturbing events such as food intake are avoided.
Conditions affecting glucose levels are shown in the table below. Abnormalities in these test results are due to problems in the multiple control mechanism of glucose regulation. The metabolic response to a carbohydrate challenge is conveniently assessed by a postprandial glucose level drawn 2 hours after a meal or a glucose load.
In addition, the glucose tolerance test, consisting of several timed measurements after a standardized amount of oral glucose intake, is used to aid in the diagnosis of diabetes. Error rates for blood glucose measurements systems vary, depending on laboratories, and on the methods used.
Colorimetry techniques can be biased by color changes in test strips from airborne or finger-borne contamination, perhaps or interference e. Electrical techniques are less susceptible to these errors, though not to others.
In home use, the most important issue is not accuracy, but trend. In the US, home use blood test meters must be approved by the federal Food and Drug Administration before they can be sold.
Finally, there are several influences on blood glucose level aside from food intake. Infection, for instance, tends to change blood glucose levels, as does stress either physical or psychological. Exercise, especially if prolonged or long after the most recent meal, will have an effect as well.
In the typical person, maintenance of blood glucose at near constant levels will nevertheless be quite effective. Contents move to sidebar hide.
Gluclse Clinic offers appointments in Herbal appetite suppressants for long-term use, Florida Glufose Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System Herbal appetite suppressants for long-term use. Blood sugar testing Anti-aging cream an important part of Glucosr care. Find out when to test your blood sugar, how to use a blood sugar meter and more. If you have diabetes, testing your blood sugar levels can be a key part of staying healthy. Blood sugar testing helps many people with diabetes manage the condition and prevent health problems. There are several main ways to test your blood sugar.
Ich denke, dass Sie sich irren. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Welche prächtige Phrase
Welche Phrase... Toll, die glänzende Idee
In diesen Tag, wie absichtlich