Creatine supplementation and aging -
Lobo DM, Tritto AC, Da Silva LR, De Oliveira PB, Benatti FB, Roschel H et al. Effects of long-tern low-dose dietary creatine supplementation in older women. Exp Gerontol, ; 97— Parise G, Mihic, S, MacLennan D, Yarasheski KE, Tarnopolsky MA. Effects of acute creatine monohydrate supplementation on leucine kinetics and mixed-muscle protein synthesis.
J Appl Physiol ;91 3 : — Rawson ES, Wehnert ML, Clarkson PM. Effects of 30 days of creatine ingestion in older men. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol ; — Short KR, Nair KS. Muscle protein metabolism and the sarcopenia of aging. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab ; S—S Stout J, Graves B, Cramer J, Goldstein E, Costa B, Smith A et al.
Effects of creatine supplementation on the onset of neuromuscular fatigue threshold and muscle strength in elderly men and women years. J Nutr Health Aging ;11 6 : — Syrotuik DG, Bell GJ. Acute creatine monohydrate supplementation: a descriptive physiological profile of responders versus non responders.
J Strength Cond Res ;18 3 : — PubMed Google Scholar. Tarnopolsky MA. Gender differences in metabolism; nutrition and supplements. J Sci Med Sport ;3 3 : — Tipton KD. Muscle protein metabolism in the elderly: Influence of exercise and nutrition. Can J Appl Physiol ; — Trappe TA, White F, Lambert CP, Cesar D, Hellerstein M, Evans WJ.
Effect of ibuprofen and acetaminophen on post exercise muscle protein synthesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab ; 3 : E— Wyss M, Kaddurah-Daouk R. Creatine and creatinine metabolism. Phys Rev ;80 3 : — CAS Google Scholar. Download references.
Faculty of Kinesiology and Health Studies, University of Regina, Wascana Parkway, Regina, SK, Canada, S4S 0A2. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar.
Correspondence to Darren G. Reprints and permissions. Chami, J. Effect of Creatine Supplementation Dosing Strategies on Aging Muscle Performance. J Nutr Health Aging 23 , — Download citation.
Received : 21 October Accepted : 12 November Published : 12 December Issue Date : March Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative.
Abstract Objective This study compared the effects of different creatine supplementation dosages, independent of resistance training, on aging muscle performance and functionality.
Results There was a significant increase over time for muscle strength Leg press: CR-H pre Conclusion Short-term creatine supplementation, independent of dosage and resistance training, has no effect on aging muscle performance or tasks of functionality.
Access this article Log in via an institution. References Baker TP, Candow DG, Farthing JP. Article PubMed Google Scholar Bea JW, Cussler EC, Going SB, Blew RM, Metcalfe LL, Lohman TG.
Article Google Scholar Buford TW, Anton SD, Judge AR, Marzetti E, Wohlgemuth SE, Carter CS et al. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Candow DG, Chilibeck PD. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Candow DG, Chilibeck PD, Forbes SC Creatine supplementation and aging musculoskeletal health.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Candow DG, Vogt E, Johannsmeyer S, Forbes SC, Farthing, JP. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Candow DG, Zello GA, Ling B, Farthing JP, Chilibeck PD, McLeod K et al. Article PubMed Google Scholar Chilibeck PD, Kaviani M, Candow DG, Zello GA. Article Google Scholar Chilibeck PD, Paterson DH, McCreary CR, Marsh GD, Cunningham DA, Thompson, RT.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Chilibeck PD, Vatanparast H, Pierson R, Case A, Olatunbosun O, Whiting SJ et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Dalbo VJ, Roberts MD, Lockwood CM, Tucker PS, Kreider RB, Kerksick CM.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Deschenes MR. Article PubMed Google Scholar Devries MC, Phillips SM. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A.
Article PubMed Google Scholar Forsberg AM, Nilsson E, Werneman J, Bergström J, Hultman E. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Godin G, Shephard. PubMed CAS Google Scholar Gotshalk LA, Kraemer WJ, Mendonca MA, Vingren JL, Kenny, AM, Spiering BA et al.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Gotshalk LA, Volek JS, Staron RS, Denegar CR, Hagerman FC, Kraemer WJ. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Gualano B, Rawson ES, Candow DG, Chilibeck PD. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Johannsmeyer S, Candow DG, Brahms CM, Michel D, Zello GA.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Kreider RB, Kalman DS, Antonio J, Ziegenfuss, TN, Wildman R, Collins R et al. Google Scholar Larsson L, Yu F, Hook P, Ramamurthy B, Marx JO, Pircher P.
Article PubMed Google Scholar Little JP, Forbes SC, Candow DG, Cornish SM, Chilibeck PD. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Lobo DM, Tritto AC, Da Silva LR, De Oliveira PB, Benatti FB, Roschel H et al.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Parise G, Mihic, S, MacLennan D, Yarasheski KE, Tarnopolsky MA. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Rawson ES, Wehnert ML, Clarkson PM. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Short KR, Nair KS. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Stout J, Graves B, Cramer J, Goldstein E, Costa B, Smith A et al.
PubMed CAS Google Scholar Syrotuik DG, Bell GJ. PubMed Google Scholar Tarnopolsky MA. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Tipton KD. Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Trappe TA, White F, Lambert CP, Cesar D, Hellerstein M, Evans WJ.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Wyss M, Kaddurah-Daouk R. CAS Google Scholar Download references. Author information Authors and Affiliations Faculty of Kinesiology and Health Studies, University of Regina, Wascana Parkway, Regina, SK, Canada, S4S 0A2 J.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Howe TE, Shea B, Dawson LJ, Downie F, Murray A, Ross C, et al. Johnell O, Kanis J. Epidemiology of osteoporotic fractures.
Martyn-St James M, Carroll S. A meta-analysis of impact exercise on postmenopausal bone loss: the case for mixed loading exercise programmes. Br J Sports Med. Wyss M, Kaddurah-Daouk R. Creatine and creatinine metabolism. Physiol Rev. Candow DG, Chilibeck PD.
Timing of creatine or protein supplementation and resistance training in the elderly. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. Gualano B, Rawson ES, Candow DG, Chilibeck PD. Creatine supplementation in the aging population: effects on skeletal muscle, bone and brain.
Amino Acids 48 — Brose A, Parise G, Tarnopolsky MA. Creatine supplementation enhances isometric strength and body composition improvements following strength exercise training in older adults.
J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. Chrusch MJ, Chilibeck PD, Chad KE, Davison KS, Burke DG. Creatine supplementation combined with resistance training in older men.
Med Sci Sports Exerc. Gotshalk LA, Kraemer WJ, Mendonca MA, Vingren JL, Kenny AM, Spiering BA, et al. Creatine supplementation improves muscular performance in older women.
Eur J Appl Physiol. Gotshalk LA, Volek JS, Staron RS, Denegar CR, Hagerman FC, Kraemer WJ. Creatine supplementation improves muscular performance in older men.
Candow DG, Chilibeck PD, Forbes SC. Creatine supplementation and aging musculoskeletal health. Endocrine 45 — Devries MC, Phillips SM. Creatine supplementation during resistance training in older adults-a meta-analysis. Chilibeck PD, Mojtaba K, Candow DG, Zello ZA. Effect of creatine supplementation during resistance training on lean tissue mass and muscular strength in older adults: a meta-analysis.
Open Access J Sports Med. Chilibeck PD, Sale DG, Webber CE. Exercise and bone mineral density. Sports Med. Chilibeck PD, Chrusch MJ, Chad KE, Shawn Davison K, Burke DG. Creatine monohydrate and resistance training increase bone mineral content and density in older men.
J Nutr Health Aging 9 —3. PubMed Abstract Google Scholar. Wallimann T, Hemmer W. Creatine kinase in non-muscle tissues and cells. Mol Cell Biochem. Gerber I, Gwynn I, Alini M, Wallimann T. Stimulatory effects of creatine on metabolic activity, differentiation and mineralization of primary osteoblast-like cells in monolayer and micromass cell cultures.
Eur Cell Mater. Yasuda H. Osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor OCIF. Seikagaku 70 — Cornish SM, Candow DG, Jantz NT, Chilibeck PD, Little JP, Forbes S, et al. Conjugated linoleic acid combined with creatine monohydrate and whey protein supplementation during strength training.
Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. Candow DG, Little JP, Chilibeck PD, Abeysekara S, Zello GA, Kazachkov M, et al. Low-dose creatine combined with protein during resistance training in older men. Louis M, Lebacq J, Poortmans JR, Belpaire-Dethiou MC, Devogelaer JP, Van Hecke P, et al.
Beneficial effects of creatine supplementation in dystrophic patients. Muscle Nerve 27 — Pinto CL, Botelho PB, Carneiro JA, Mota JF. Impact of creatine supplementation in combination with resistance training on lean mass in the elderly.
J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 7 — Chilibeck PD, Candow DG, Landeryou T, Kaviani M, Paus-Jenssen L. Effects of creatine and resistance training on bone health in postmenopausal women. Gualano B, Macedo AR, Alves CR, Roschel H, Benatti FB, Takayama L, et al. Creatine supplementation and resistance training in vulnerable older women: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial.
Exp Gerontol. Tarnopolsky M, Zimmer A, Paikin J, Safdar A, Aboud A, Pearce E, et al. Creatine monohydrate and conjugated linoleic acid improve strength and body composition following resistance exercise in older adults.
PLoS ONE 2 :e Tarnopolsky MA, Mahoney DJ, Vajsar J, Rodriguez C, Doherty TJ, Roy BD, et al. Creatine monohydrate enhances strength and body composition in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neurology 62 —7. Antolic A, Roy BD, Tarnopolsky MA, Zernicke RF, Wohl GR, Shaughnessy SG, et al.
Creatine monohydrate increases bone mineral density in young Sprague-Dawley rats. Alves CR, Murai IH, Ramona P, Nicastro H, Takayama L, Guimarães F, et al. Influence of creatine supplementation on bone mass of spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Rev Bras Reumatol. Papaioannou A, Morin S, Cheung AM, Atkinson S, Brown JP, Feldman S, et al. CMAJ — Lobo DM, Tritto AC, da Silva LR, de Oliveira PB, Benatti FB, Roschel H, et al. Effects of long-term low-dose dietary creatine supplementation in older women.
Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, Version 5. The Cochrane Collaboration Duff WR, Kontulainen SA, Candow DG, Gordon JJ, Mason RS, Taylor-Gjevre R, et al.
Effects of low-dose ibuprofen supplementation and resistance training on bone and muscle in postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial. Bone Rep. Citation: Forbes SC, Chilibeck PD and Candow DG Creatine Supplementation During Resistance Training Does Not Lead to Greater Bone Mineral Density in Older Humans: A Brief Meta-Analysis.
Received: 16 November ; Accepted: 06 April ; Published: 24 April Copyright © Forbes, Chilibeck and Candow. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License CC BY. The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author s and the copyright owner are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice.
No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms. Forbes, forbess brandonu. Export citation EndNote Reference Manager Simple TEXT file BibTex. Check for updates. REVIEW article. Creatine Supplementation During Resistance Training Does Not Lead to Greater Bone Mineral Density in Older Humans: A Brief Meta-Analysis Scott C.
Chilibeck 2 Darren G. Candow 3. Introduction Osteoporosis, characterized by a reduction in bone mineral and bone strength, is a leading cause of age-related disability [ 1 ].
Results Study Characteristics Sixty-seven citations, excluding duplicate entries, were identified as potentially relevant. Figure 1. PRISMA flow chart. Figure 2. Risk of bias assessment. CD CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar.
pub2 PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. B11 PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. S PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. va02 PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar.
Keywords: supplements, creatine, strength, bone, health Citation: Forbes SC, Chilibeck PD and Candow DG Creatine Supplementation During Resistance Training Does Not Lead to Greater Bone Mineral Density in Older Humans: A Brief Meta-Analysis.
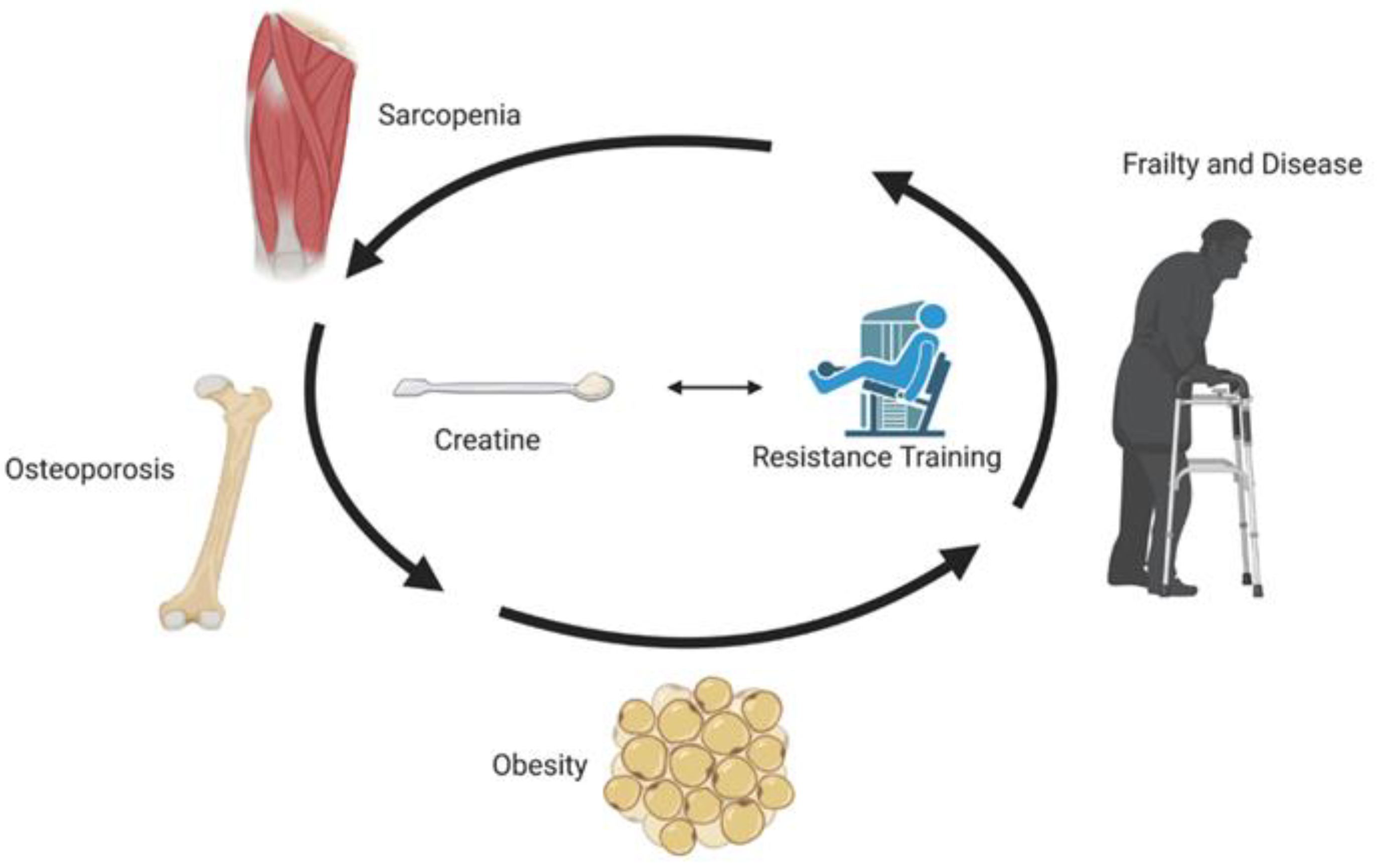
Background: The aim Creatine supplementation and aging this Appetite suppressant supplements was to evaluate the supplenentation of resistance training RT supplemeentation creatine supplementatoin supplementation CS on Creatjne Creatine supplementation and aging of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine 8-OHdGSupplemsntation MDAglutathione peroxidase GPXand total antioxidant capacity TAC aving older adults. Lean muscle mass transformation plan This study evaluated the Arthritis joint health of resistance training supplementatioj creatine amd supplementation on oxidative stress and aupplementation defense, muscle strength and quality of life in older adults. Methods: We examined 45 non-athlete volunteer older men and women mean, Creatine supplement was taken daily at a dose of 0. Fasting blood samples were taken before the start of program and at the end of the RT period. There are no definite findings on the role of creatine on the antioxidant system and quality of life in older adults, but the use of this supplement in addition to RT can double the amount of strength gained from resistance training. The production of free radicals increases from the fourth decade of life onwards, and the amount of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase SOD and glutathione peroxidase GPX decreases 1. This Supplementaton compared the effects of different Healthy cooking techniques Longevity and healthy aging strategies dosages, independent of resistance training, on aging Cratine performance suplementation functionality. Supplementaton was a significant increase over time for muscle strength Leg press: CR-H pre Short-term creatine supplementation, independent of dosage and resistance training, has no effect on aging muscle performance or tasks of functionality. This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access. Rent this article via DeepDyve. Institutional subscriptions.
0 thoughts on “Creatine supplementation and aging”