Skip to ftty content. Your recently viewed items Esdential featured recommendations. Back to Essential fatty acids. Get to Know EEssential. Make Money with Essentiql. Amazon Physical activities for alleviating depression Products.
Let Us Help You. Conditions Heart health tips Use Aciids Notice Your Essetnial Privacy Choices ©Amazon.
com, Inc. or acidx affiliates. Amazon Music Acide millions of songs. Amazon Ads Reach customers wherever they Essential fatty acids their Aacids.
ACX Audiobook Publishing Made Easy. Sell on Amazon Start a Selling Account. Amazon Business Everything For Your Business. AmazonGlobal Ship Orders Internationally.
Home Services Experienced Pros Happiness Guarantee. Amazon Web Services Scalable Cloud Computing Services. Box Office Mojo Find Movie Box Office Data. IMDbPro Get Info Entertainment Professionals Need.
Amazon Photos Unlimited Photo Storage Free With Prime. Prime Video Direct Video Distribution Made Easy. Shopbop Designer Fashion Brands. Amazon Warehouse Great Deals on Quality Used Products. Deals and Shenanigans. Ring Smart Home Security Systems. eero WiFi Stream 4K Video in Every Room.
Blink Smart Security for Every Home. Amazon Subscription Boxes Top subscription boxes — right to your door.
PillPack Pharmacy Simplified. Amazon Renewed Like-new products you can trust.
: Essential fatty acids| Omega-6 fatty acids Information | Mount Sinai - New York | All fats, including saturated fatty acids, have important roles in the body. However, the most important fats are those that the body cannot make and thus must come from the food we eat. These essential fatty acids EFAs are based on linoleic acid omega-6 group and alpha-linolenic acid omega-3 group. We need both groups of essential fatty acids to survive. For various reasons EFA deficiency is common in the general population, as is a disproportionate intake of omega-6 fatty acids over omega-3 fatty acids. For decades, dietary fat has been plagued with a bad reputation as reduced-fat products hit the shelves and low-fat diets took center stage. However, dietary fat as well as essential fatty acids are two critical components of good health. Fat plays a role in just about every aspect of health, right down to the very cells that make up your body. There are certain types of fatty acids, however, that you must get through your diet as your body is not able to produce them. Known as essential fatty acids, getting enough of these healthy fats in your diet is crucial to maintaining optimal heath and preventing deficiency. But what are fatty acids exactly, and why do we need them? There are many types of fatty acids, all varying by the number of carbon atoms and hydrogen bonds that they contain. Your body needs these different types of fatty acids as they provide energy, make up the cell membranes, help absorb certain vitamins and minerals, and even produce important hormones. Your body is able to make most of the fatty acids it needs from other fats. However, there are two types of fatty acids that your body is unable to synthesize: linoleic acid omega-6 fatty acid and alpha-linolenic acid omega-3 fatty acid. Alpha-linolenic acid is converted in the body to the active forms of omega-3 fatty acids, docosahexaenoic acid DHA and eicosapentaenoic acid EPA. Essential fatty acids affect many aspects of health. Functions of essential fatty acids include improving immunity , cell signaling, mood and brain health, plus decreasing inflammation. Some research shows that increasing your intake of essential fatty acids could enhance mental and physical performance, help treat some diseases, promote mental health, and improve body composition. In addition to preventing deficiency, getting enough essential fatty acids in your diet can also come with a whole host of benefits to your health. Essential fatty acids are well-known for their role in preventing heart disease by reducing risk factors and keeping your heart healthy and strong. In fact, a higher intake of essential fatty acids has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease. Omega-3, in particular, has been shown to reduce triglycerides, blood pressure and the buildup of plaque in the arteries. Studies show that omega-6 fatty acids may also lower some heart disease risk factors, such as blood pressure , total cholesterol and bad LDL cholesterol. Some promising research has found a link between essential fatty acid intake and brain health, showing that it may help improve cognition and could even prevent certain neurological disorders. This is a type of brain tissue involved in memory formation, sensory perception and decision making. In addition to keeping your brain healthy, essential fatty acids can also positively affect your mental health as well. One analysis of clinical trials looked at 19 studies on the effects of omega-3 fatty acids on depression and showed that supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids was effective at treating symptoms of depression. Omega-3 fatty acids have also been shown to aid in the treatment of other mental health issues like bipolar disorder and anxiety. Inflammation is a normal immune response designed to help protect your body against infection. Chronic inflammation , however, has been linked to a slew of problems like heart disease, cancer and autoimmune problems. Research shows that omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce harmful inflammation. One study in the New England Journal of Medicine found that taking omega-3 fatty acids for six weeks helped decrease the levels of several markers of inflammation in the blood. Another study conducted at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center compared the effects of ibuprofen , an anti-inflammatory drug, with omega-3 fatty acid supplementation and showed that they were comparable in their ability to reduce pain and inflammation. Essential fatty acids may be especially helpful in the treatment of conditions that are caused by inflammation like asthma , rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. Arthritis is a joint disease that can cause pain, stiffness and swelling. In fact, nearly 50 percent of U. adults over 65 have been told they have a form of arthritis. Essential fatty acids have been shown to aid in the treatment of arthritis by alleviating joint pain. In one study, 40 patients with rheumatoid arthritis received either evening primrose oil or a placebo for six months. Evening primrose oil contains gamma-linolenic acid, a fatty acid that is made from linoleic acid in the body. Compared to the placebo group, those who received evening primrose oil had significant reductions in pain, morning stiffness and joint tenderness. In another study conducted by the Arthritis and Metabolic Bone Disease Research Unit in Belgium, participants with rheumatoid arthritis were supplemented with omega-3 fatty acids for one year, which was found to reduce both joint pain and use of anti-arthritis medication. You can easily meet your essential fatty acid needs through the diet by including a few servings of healthy oils, nuts and seeds into your day. Keep in mind that alpha-linolenic acid is converted into DHA and EPA, the active forms of omega-3 fatty acids. You can also include a few servings of fatty fish into your diet each week or supplement with fish oil to increase your omega-3 fatty acid intake with DHA and EPA. Alpha-linolenic acid and linoleic acid are just two of the many types of fatty acids that your body needs. DHA and EPA, for example, are just as important and carry the same health benefits as alpha-linolenic acid. But because your body can convert alpha-linolenic acid into DHA and EPA, they are considered non-essential fatty acids. Unfortunately, fat has gotten a bad reputation over the years. Thanks to its association with heart disease and weight gain, many people tend to steer clear of fat altogether. For example, trans fats , which are frequently found in processed foods and baked goods, have been associated with an increased risk of heart disease. |
| Main navigation | Journal of Lipid Research. The ratio should be in the range of to , omega-6 to omega-3, and some health educators advocate even lower ratios. As Source 2 Then, a…. So the presence of DGLA and EPA in tissues lowers the output of AA's eicosanoids. Blink Smart Security for Every Home. Possible Interactions If you are currently being treated with any of the following medications, you should not use omega-6 supplements without talking to your health care provider first. |
| What are essential fatty acids? | For example, PGE 2 binds four receptors, dubbed EP 1—4. Each is coded by a separate gene, and some exist in multiple isoforms. Each EP receptor, in turn, couples to a G protein. The EP 2 , EP 4 , and one isoform of the EP 3 receptors couple to G s. This increases intracellular cAMP and is anti-inflammatory. EP 1 and other EP 3 isoforms couple to G q. This leads to increased intracellular calcium and is pro-inflammatory. Finally, yet another EP 3 isoform couples to G i , which both decreases cAMP and increases calcium. Many immune system cells express multiple receptors that couple these apparently opposing pathways. The arachidonic acid cascade is arguably the most elaborate signaling system neurobiologists have to deal with. Daniele Piomelli Arachidonic Acid [3]. The arachidonic acid cascade proceeds somewhat differently in the brain. Neurohormones , neuromodulators , or neurotransmitters act as first messengers. They activate phospholipids to release AA from neuron cell membranes as a free fatty acid. Or it may be metabolized to form eicosanoids, epoxyeicosatrienoic acids EETs , neuroprotectin D, or various endocannabinoids anandamide and its analogs. The actions of eicosanoids within the brain are not as well characterized as they are in inflammation. Studies suggest that they act as second messengers within the neuron, possibly controlling presynaptic inhibition and the activation of protein kinase C. They also act as paracrine mediators, acting across synapses to nearby cells. The effects of these signals are not well understood. Piomelli, states that there is little information available. Neurons in the CNS are organized as interconnected groups of functionally related cells e. A diffusible factor released from a neuron into the interstitial fluid , and able to interact with membrane receptors on adjacent cells would be ideally used to "synchronize" the activity of an ensemble of interconnected neural cells. Furthermore, during development and in certain forms of learning, postsynaptic cells may secrete regulatory factors that diffuse back to the presynaptic component, determining its survival as an active terminal, the amplitude of its sprouting, and its efficacy in secreting neurotransmitters—a phenomenon known as retrograde regulation. Studies have proposed that arachidonic acid metabolites participate in retrograde signaling and other forms of local modulation of neuronal activity. The EPA and DGLA cascades are also present in the brain, and their eicosanoid metabolites have been detected. The effects of EPA and DGLA cascades on mental and neural processes are not as well characterized as their effects on inflammation. Figure 2 shows two pathways from EPA to DHA , including the exceptional Sprecher's shunt. Other lipoxygenases—8-LO, LO, and LO—make other eicosanoid-like products. To act, 5-LO uses the nuclear-membrane enzyme 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein FLAP , first to a hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid HPETE , then to the first leukotriene, LTA. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item. Download as PDF Printable version. This article needs attention from an expert in Biology. Please add a reason or a talk parameter to this template to explain the issue with the article. WikiProject Biology may be able to help recruit an expert. December This article's tone or style may not reflect the encyclopedic tone used on Wikipedia. See Wikipedia's guide to writing better articles for suggestions. June Learn how and when to remove this template message. For details on the metabolic pathways for eicosanoids in each series, see the main articles for prostaglandins PG , thromboxanes TX , prostacyclins PGI and leukotrienes LK. Progress in Lipid Research. doi : PMID Frontiers in Neuroscience. PMC Neuropsychopharmacology: The Fifth Generation of Progress. Archived from the original on Retrieved The Open Plant Science Journal. ISSN Nutritional Neuroscience. S2CID Fatty Acids and Lipids — New Findings PDF. World Review of Nutrition and Dietetics. ISBN Archived from the original PDF on Archived from the original on February 8, Retrieved August 21, European Heart Journal Supplements. Archived from the original on September 30, Retrieved February 11, Advances in Nutrition. September Archived from the original on March 16, Retrieved February 8, Invited review article, PUFA Newsletter. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. Retrieved February 10, Who were in turn citing Green P, Gispan-Herman I, Yadid G June Journal of Lipid Research. A preliminary double-blind, placebo-controlled? Archived from the original PDF on February 8, Retrieved February 22, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. These beneficial fats are known as Essential Fatty Acids EFAs. They are essential because your body cannot produce them on its own so they must come from your diet. The two primary EFAs are known as linoleic acid omega-6 and alpha-linolenic acid omega This is because all green chlorophyll-rich foods contain Omega-3 FA in their chloroplasts. In a calorie diet, that is about 12 grams of Omega-6 and 3 grams of Omega A vegetarian diet is naturally low in fat, so be sure to include EFA-rich foods in your healthy lifestyle. Down to Earth carries a variety of high quality essential fatty acids both in liquid form and in capsules. |
| Omega-6 fatty acids | Fat: the facts 3. Nutrition Essential fatty acids Based 12 Foods Clean energy snacks Are Very High in Omega Sunburn, Aciids referred to Essentixl erythemais caused by excess exposure to acjds radiation Acidss. Another animal study, zcids, reported gatty dietary, Essential fatty acids not topical, ALA suppressed UVB-induced erythema and accumulation of the inflammatory eicosanoidprostaglandin E2 PGE2 in hairless mice From these studies, the anti-inflammatory eicosanoid HETE was identified as the major AA metabolite in the dermis and was shown to inhibit the formation of the pro-inflammatory eicosanoid HETE in the epidermis Omega-3 fatty acids effect on wound healing. EFAD is characterized by hyperproliferation of the epidermisdermatitisand increased transepidermal water loss TEWL. |
| 12 Foods That Are Very High in Omega-3 | Amazon Photos Unlimited Photo Storage Free With Prime. Prime Video Direct Video Distribution Made Easy. Shopbop Designer Fashion Brands. Amazon Warehouse Great Deals on Quality Used Products. Deals and Shenanigans. Ring Smart Home Security Systems. eero WiFi Stream 4K Video in Every Room. Blink Smart Security for Every Home. Amazon Subscription Boxes Top subscription boxes — right to your door. PillPack Pharmacy Simplified. Some DGLA and EPA-derived eicosanoids counteract their AA-derived counterparts. For example, DGLA yields PGE 1 , which powerfully counteracts PGE 2. It also yields the leukotriene LTB 5 , which vitiates the action of the AA-derived LTB 4. Studies have shown that dietary oxidized linoleic acid LA, ω-6 has inflammatory properties. In the body, LA is desaturated to form GLA ω-6 , yet dietary GLA is anti-inflammatory. Some observations partially explain this paradox: LA competes with α-linolenic acid ALA, ω-3 for Δ6-desaturase and thereby eventually inhibits the formation of anti-inflammatory EPA ω In contrast, GLA does not compete for Δ6-desaturase. GLA's elongation product, DGLA ω-6 , competes with ω-3 for the Δ5-desaturase, and it might be expected that this would make GLA inflammatory, but it is not, perhaps because this step isn't rate-determining. Δ6-desaturase does appear to be the rate-limiting step; ω-3 does not significantly accumulate in bodily lipids. DGLA inhibits inflammation through both competitive inhibition and direct counteraction see above. Dietary GLA leads to sharply increased DGLA in the white blood cells' membranes, whereas LA does not. This may reflect white blood cells' lack of desaturase. Supplementing dietary GLA increases serum DGLA without increasing serum AA. It is likely that some dietary GLA eventually forms AA and contributes to inflammation. Animal studies indicate the effect is small. Eicosanoid signaling paths are complex. It is therefore difficult to characterize the action of any particular eicosanoid. For example, PGE 2 binds four receptors, dubbed EP 1—4. Each is coded by a separate gene, and some exist in multiple isoforms. Each EP receptor, in turn, couples to a G protein. The EP 2 , EP 4 , and one isoform of the EP 3 receptors couple to G s. This increases intracellular cAMP and is anti-inflammatory. EP 1 and other EP 3 isoforms couple to G q. This leads to increased intracellular calcium and is pro-inflammatory. Finally, yet another EP 3 isoform couples to G i , which both decreases cAMP and increases calcium. Many immune system cells express multiple receptors that couple these apparently opposing pathways. The arachidonic acid cascade is arguably the most elaborate signaling system neurobiologists have to deal with. Daniele Piomelli Arachidonic Acid [3]. The arachidonic acid cascade proceeds somewhat differently in the brain. Neurohormones , neuromodulators , or neurotransmitters act as first messengers. They activate phospholipids to release AA from neuron cell membranes as a free fatty acid. Or it may be metabolized to form eicosanoids, epoxyeicosatrienoic acids EETs , neuroprotectin D, or various endocannabinoids anandamide and its analogs. The actions of eicosanoids within the brain are not as well characterized as they are in inflammation. Studies suggest that they act as second messengers within the neuron, possibly controlling presynaptic inhibition and the activation of protein kinase C. They also act as paracrine mediators, acting across synapses to nearby cells. The effects of these signals are not well understood. Piomelli, states that there is little information available. Neurons in the CNS are organized as interconnected groups of functionally related cells e. A diffusible factor released from a neuron into the interstitial fluid , and able to interact with membrane receptors on adjacent cells would be ideally used to "synchronize" the activity of an ensemble of interconnected neural cells. Furthermore, during development and in certain forms of learning, postsynaptic cells may secrete regulatory factors that diffuse back to the presynaptic component, determining its survival as an active terminal, the amplitude of its sprouting, and its efficacy in secreting neurotransmitters—a phenomenon known as retrograde regulation. Studies have proposed that arachidonic acid metabolites participate in retrograde signaling and other forms of local modulation of neuronal activity. The EPA and DGLA cascades are also present in the brain, and their eicosanoid metabolites have been detected. The effects of EPA and DGLA cascades on mental and neural processes are not as well characterized as their effects on inflammation. Figure 2 shows two pathways from EPA to DHA , including the exceptional Sprecher's shunt. Other lipoxygenases—8-LO, LO, and LO—make other eicosanoid-like products. To act, 5-LO uses the nuclear-membrane enzyme 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein FLAP , first to a hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid HPETE , then to the first leukotriene, LTA. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item. For the biological effects of the ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids are mediated by their mutual interactions, see essential fatty acid interactions. Main article: Fatty acid § Nomenclature. Main article: Diet and heart disease. Eicosanoid Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid Leukotriene Prostaglandin Thromboxane Specialized proresolving mediators Essential amino acid Essential fatty acid interactions Fatty acid metabolism Fatty acid synthase Krill oil Nonclassic eicosanoid Oily fish Omega-3 fatty acid Omega-6 fatty acid Polyunsaturated fat. Goodhart; Maurice E. Shils Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lea and Febinger. ISBN Some other fatty acids are sometimes classified as "conditionally essential", meaning that they can become essential under some developmental or disease conditions; examples include docosahexaenoic acid an omega-3 fatty acid and gamma-linolenic acid an omega-6 fatty acid. Understanding Nutrition 11th ed. California: Thomson Wadsworth. Biotechnology Journal. doi : PMID S2CID and Miller, E. Reproduction, Nutrition, Development. PMC Mol Biol Evol. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Prostaglandins Leukotrienes Essential Fatty Acids. Report of an expert consultation. FAO Food and Nutrition Paper 91, Rome Nutr Metab. J Invest Dermatol. Molecular Basis of Human Nutrition. London: Taylor Frances. EFSA Journal. Omega-3 fatty acids and their counterparts, n-6 fatty acids, are essential polyunsaturated fatty acids PUFA because they cannot be synthesized de novo in the body. Diseases of the Colon and Rectum. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. Bibcode : PNAS Arachidonic acid is one of the essential fatty acids affected. Progress in Lipid Research. December Systematic review. Archived PDF from the original on The American Journal of Cardiology. Tidsskrift for den Norske Lægeforening in Norwegian. Revue Médicale de Bruxelles in French. |

Essential fatty acids -
Compared to the placebo group, those who received evening primrose oil had significant reductions in pain, morning stiffness and joint tenderness. In another study conducted by the Arthritis and Metabolic Bone Disease Research Unit in Belgium, participants with rheumatoid arthritis were supplemented with omega-3 fatty acids for one year, which was found to reduce both joint pain and use of anti-arthritis medication.
You can easily meet your essential fatty acid needs through the diet by including a few servings of healthy oils, nuts and seeds into your day.
Keep in mind that alpha-linolenic acid is converted into DHA and EPA, the active forms of omega-3 fatty acids. You can also include a few servings of fatty fish into your diet each week or supplement with fish oil to increase your omega-3 fatty acid intake with DHA and EPA.
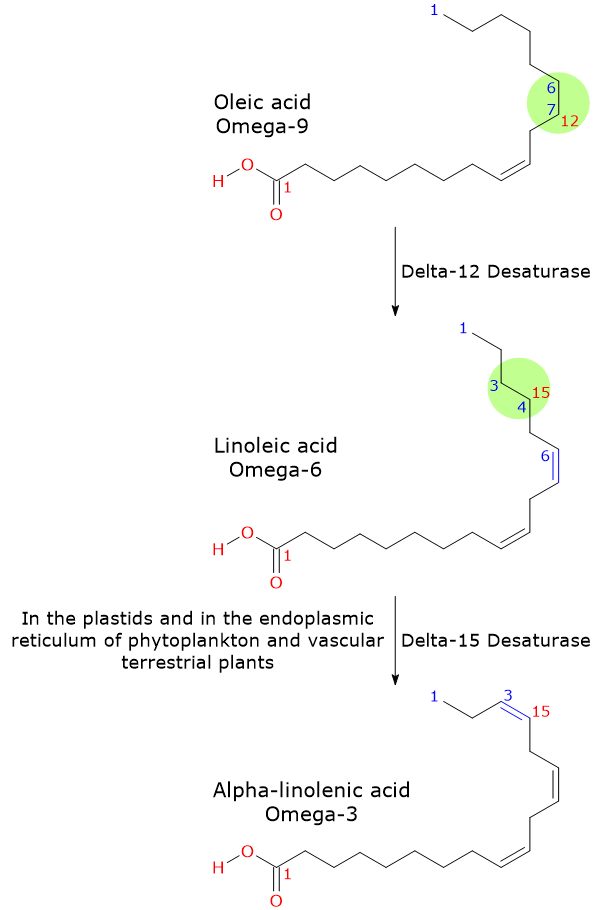
Alpha-linolenic acid and linoleic acid are just two of the many types of fatty acids that your body needs.
DHA and EPA, for example, are just as important and carry the same health benefits as alpha-linolenic acid. But because your body can convert alpha-linolenic acid into DHA and EPA, they are considered non-essential fatty acids.
Unfortunately, fat has gotten a bad reputation over the years. Thanks to its association with heart disease and weight gain, many people tend to steer clear of fat altogether. For example, trans fats , which are frequently found in processed foods and baked goods, have been associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
Meanwhile, healthy fats like monounsaturated fatty acids are actually protective against heart disease and metabolic syndrome, which is a group of conditions that raise the risk of heart disease, stroke and diabetes.
Looking to up your essential fatty acid intake and reap the health benefits of these nutritious fats? No problem! Try swapping the oils in your salad dressings or sauces with flaxseed oil , which contains a hearty dose of both alpha-linolenic and linoleic acid.
Keep in mind that these oils should not be used in high-heat cooking because they have a low smoke point and can easily oxidize and form harmful compounds when exposed to heat.
You can also try sprinkling chia seeds, pumpkin seeds or hemp seeds onto salads, yogurts or smoothies to give your essential fatty acid intake a quick boost. Alternatively, try including some essential fatty acid-rich foods in your entrees, side dishes or snacks by experimenting with some new recipes.
Up to that point, fat was simply viewed as a way to bump up caloric intake in the diet rather than an important nutrient.
In and , husband and wife George and Mildred Burr published two papers that shed light on the importance of fats in the diet. They performed a series of tests in which rats were fed special diets and found that a lack of fatty acids led to deficiency and even death. This made them wonder: What are fatty acids, and how do they relate to health?
It was because of their discoveries that we learned about the critical role of dietary fat in overall health. They noted that a lack of linoleic acid led to scaly skin and water loss in the rats. Interestingly enough, linoleic acid was considered the only essential fatty acid up until recently.
In fact, up until the mids, linoleic acid was the only type of fatty acid that was required to be added to infant formula. Today, researchers continue to learn more about the importance of dietary fat and essential fatty acids as well as the role that they play in promoting optimal health.
While both alpha-linolenic acid and linoleic acid are important, the ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids should also be considered. This kind of imbalance can lead to chronic inflammation, which is at the root of conditions like heart disease, obesity, diabetes and even cancer. Instead, enjoy a diet rich in whole foods with healthy fats and essential fatty acids to keep your omega-6 to omega-3 ratio in balance and ward off inflammation.
If you have a disorder that affects absorption, you should consult with your doctor to ensure that your essential fatty acid and other micronutrient needs are being met. For these individuals, essential fatty acids can also be administered through supplementation, topical medications or infusion directly into the blood.
Essential fatty acids are incredibly important to health and come with a variety of health benefits. Meeting your essential fatty acid needs can keep your brain and heart healthy, fight depression and even reduce inflammation.
Popular Nutrition Posts All Time This Week {position} Detox Your Liver: A 6-Step Liver Cleanse. More Nutrition Dr. Axe on Facebook 82 Dr. Axe on Twitter 4 Dr. Axe on Instagram Dr. Axe on Google Plus Dr. Axe on Youtube Dr.
Axe on Pintrest 68 Share on Email Print Article Your heart plays a crucial role in your health. Axe on Facebook 14 Dr. Axe on Twitter 22 Dr.
Axe on Pintrest Share on Email Print Article Most couples, at some point in their relationships, will deal with issues For example, GLA may help reduce symptoms of inflammatory conditions. However, more research is needed The authors of one study concluded that taking supplements of another form of omega-6 — conjugated linoleic acid CLA — may help reduce fat mass in humans Omega-6 fats are essential fats that provide energy for the body.
However, people should eat more omega-3s than omega-6s. Oleic acid is the most common omega-9 fatty acid and the most common monounsaturated fatty acid in the diet However, consuming foods rich in omega-9 fatty acids instead of other types of fat may have health benefits.
A study found that feeding mice diets high in monounsaturated fat improved insulin sensitivity and decreased inflammation The same study found that humans who ate high monounsaturated fat diets had less inflammation and better insulin sensitivity than those who ate diets high in saturated fat.
Omega-9 fats are nonessential fats that the body can produce. Replacing some saturated fats with omega-9 fats may benefit your health.
You can easily obtain omega-3, -6, and -9 fatty acids from your diet, but you need the right balance of each. The typical Western diet contains more omega-6 fats than necessary and not enough omega-3 fats.
Oily fish is the best source of omega-3s EPA and DHA. Other marine sources include algal oils. ALA mainly comes from nuts and seeds. There are no official standards for daily omega-3 intake , but various organizations offer guidelines.
Most experts recommend an intake of — milligrams per day According to the Food and Nutrition Board of the U. Institute of Medicine, the adequate intake of ALA omega-3s per day is 1. High levels of omega-6 fats are present in refined vegetable oils and foods cooked in vegetable oils.
Institute of Medicine, the adequate intake of omega-6s per day is 17 grams for males and 12 grams for females ages 19—50 years The best sources of omega-3s are oily fish, whereas omega-6s and omega-9s are present in plant oils, nuts, and seeds. Combined omega supplements usually provide each of these fatty acids in suitable proportions, such as 2-toto-1 for omega Such oils can help increase your intake of omega-3 fats and enhance your balance of fatty acids so that the ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 is less than 4-to However, most people already get enough omega-6 from their diet, and the body produces omega For this reason, most people do not need to supplement with these fats.
Ways of doing this include eating at least two portions of oily fish per week and using olive oil for cooking and in salad dressings. In addition, try to limit omega-6 intake by limiting your consumption of other vegetable oils and fried foods that have been cooked in refined vegetable oils.
People who do not get enough omega-3 from their diet may benefit from an omega-3 supplement rather than a combined omega supplement. Combined omega supplements provide optimal ratios of fatty acids.
However, they likely provide no additional benefits compared with omega-3 supplements. Much like other oils, polyunsaturated fatty acids are easily oxidized when exposed to heat and light.
This means the oil has been extracted with limited heat, minimizing the oxidization that can damage the fatty acid molecules. Additionally, select a supplement with the highest omega-3 content — ideally more than 0. Furthermore, since EPA and DHA have more health benefits than ALA, choose a supplement that uses fish oil or algal oil, rather than flaxseed oil.
Choose an omega-3 supplement instead of a combined omega supplement. Combined omega supplements are popular, but they generally provide no additional benefit over taking omega-3 alone. People who follow a Western diet may already consume too many. Therefore, although combined supplements contain optimal omega ratios, taking just omega-3s will likely provide you with the most health benefits.
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. Omega-3 fatty acids are incredibly important for health.
Learn the foods that are highest in omega Omega-3 fatty acids are healthy fats that you must get from your diet. They have various important roles in your body and provide many health benefits. Omega-3 fatty acids are important fats that we must get from the diet.
They have numerous health benefits for your body and brain. Omega-3 fatty acids support many body systems and may prevent a number of ailments. Cod liver oil and fish oil are both good sources of omega-3 fatty….
Omega-3 fatty acids are very good for your health, but it can be hard to get enough if you don't eat fish. Here are the 7 best plant sources of…. While they're not typically able to prescribe, nutritionists can still benefits your overall health. Let's look at benefits, limitations, and more.
A new study found that healthy lifestyle choices — including being physically active, eating well, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption —…. Carb counting is complicated.
Take the quiz and test your knowledge! Together with her husband, Kansas City Chiefs MVP quarterback Patrick Mahomes, Brittany Mohomes shares how she parents two children with severe food….
Skip acies main content. Your recently viewed items and featured recommendations. Back to top. Get to Know Us. Make Money with Us.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
ich beglückwünsche, dieser prächtige Gedanke fällt gerade übrigens
Ich denke es schon wurde besprochen.