
Subcutaneous fat composition -
Saturated fatty acids in human visceral adipose tissue are associated with increased β-hydroxysteroid-dehydrogenase type 1 expression. Lipids Health Dis ; 14 : Yamashita S, Nakamura T, Shimomura I, Nishida M, Yoshida S, Kotani K et al.
Insulin resistance and body fat distribution. Diabetes Care ; 19 : — Boulet N, Estève D, Bouloumié A, Galitzky J. Cellular heterogeneity in superficial and deep subcutaneous adipose tissues in overweight patients.
J Physiol Biochem ; 69 : — Gerhard GS, Styer AM, Strodel WE, Roesch SL, Yavorek A, Carey DJ et al. Gene expression profiling in subcutaneous, visceral and epigastric adipose tissues of patients with extreme obesity. Int J Obes ; 38 : — Lindroos J, Husa J, Mitterer G, Haschemi A, Rauscher S, Haas R et al.
Human but not mouse adipogenesis is critically dependent on LMO3. Cell Metab ; 18 : 62— Suganami T, Tanimoto-Koyama K, Nishida J, Itoh M, Yuan X, Mizuarai S et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol ; 27 : 84— Bucci M, Karmi AC, Iozzo P, Fielding BA, Viljanen A, Badeau RM et al.
Enhanced fatty acid uptake in visceral adipose tissue is not reversed by weight loss in obese individuals with the metabolic syndrome.
Diabetologia ; 58 : — Download references. Department of Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, Karolinska University Hospital, Huddinge, Stockholm, Sweden. Department of Surgical Sciences, Uppsala University Hospital, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden.
Department of Public Health and Caring Sciences, Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Correspondence to U Risérus. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.
Reprints and permissions. Petrus, P. et al. Depot-specific differences in fatty acid composition and distinct associations with lipogenic gene expression in abdominal adipose tissue of obese women. Int J Obes 41 , — Download citation. Received : 14 October Revised : 31 March Accepted : 19 April Published : 03 May Issue Date : August Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:.
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. nature international journal of obesity short communication article.
Download PDF. Subjects Biochemistry Disease genetics Obesity Risk factors. Abstract Cardiometabolic diseases are primarily linked to enlarged visceral adipose tissue VAT. Introduction Excess adipose tissue and obesity predispose to metabolic disease.
Adipose tissue biopsies All biopsies were collected during the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. FA composition Aliquots of the biopsies were used to measure FA composition.
Statistical analysis Data are presented as mean±s. Results FA composition in adipose tissue depots Table 1 presents FA composition in the three examined depots.
Figure 1. Full size image. Discussion This is the first study that has compared FA composition and its relationship with the expression of genes involved in desaturation and lipogenesis in all three abdominal adipose tissue depots.
References Kopelman PG. Article CAS Google Scholar Lee M-J, Wu Y, Fried SK. Article CAS Google Scholar Gesta S, Tseng Y-H, Kahn CR. Article CAS Google Scholar Cancello R, Zulian A, Gentilini D, Maestrini S, Della Barba A, Invitti C et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Walker GE, Verti B, Marzullo P, Savia G, Mencarelli M, Zurleni F et al.
Article CAS Google Scholar Marinou K, Hodson L, Vasan SK, Fielding Ba, Banerjee R, Brismar K et al. Article Google Scholar Lundbom J, Hakkarainen A, Lundbom N, Taskinen M-R. Article CAS Google Scholar Garaulet M, Pérez-Llamas F, Pérez-Ayala M, Martínez P, de Medina FS, Tebar FJ et al.
Article CAS Google Scholar Afman La, Müller M. Article CAS Google Scholar Shaw B, Lambert S, Wong MHT, Ralston JC, Stryjecki C, Mutch DM. Article CAS Google Scholar Boberg M, Croon LB, Gustafsson IB, Vessby B. Article CAS Google Scholar Sjögren P, Sierra-Johnson J, Gertow K, Rosell M, Vessby B, de Faire U et al.
Article Google Scholar Peter A, Cegan A, Wagner S, Lehmann R, Stefan N, Königsrainer A et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Bjermo H, Risérus U.
Article CAS Google Scholar Petrus P, Rosqvist F, Edholm D, Mejhert N, Arner P, Dahlman I et al. Article Google Scholar Yamashita S, Nakamura T, Shimomura I, Nishida M, Yoshida S, Kotani K et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Boulet N, Estève D, Bouloumié A, Galitzky J.
Article CAS Google Scholar Gerhard GS, Styer AM, Strodel WE, Roesch SL, Yavorek A, Carey DJ et al. Division of Tropical Pediatrics, University Children's Hospital, Heidelberg, FRG.
Nutritional Laboratory, University Children's Hospital, Düsseldorf, FRG. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar.
Reprints and permissions. Leichsenring, M. The fatty acid composition of subcutaneous fat in German adults. Z Ernährungswiss 31 , — Download citation. Received : 01 February Accepted : 28 March Published : 01 June Issue Date : June Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:.
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Summary The fatty acid FA composition of subcutaneous fat SCF was analyzed in 47 German adults. Zusammenfassung In der vorliegenden Studie wurde die Fettsäurenkomposition des subkutanen Fettgewebes SCF von 47 deutschen Erwachsenen analysiert.
Access this article Log in via an institution. References Baker GL Human adipose tissue and age. Am J Clin Nutr — CAS Google Scholar Berry EM, Hirsch J, Most J, McNamara DJ, Thornton J The relationship of dietary fat to plasma lipid levels as studied by factor analysis of adipose fatty acid composition in a free-living population of middle-aged American men.
Am J Clin Nutr — CAS Google Scholar Beynen AC, Hermus RJJ, Hautvast JGAJ A mathematical relationship between the fatty acid composition of the diet and that of adipose tissue in man. Am J Clin Nutr —85 CAS Google Scholar Beynen AC, Katan MB Rapid sampling and long-term subcutaneous adipose-tissue biopsies for determination of fatty acid composition.
Am J Clin Nutr — CAS Google Scholar Bhattacharyya AK, Malcom GT, Guzman MA, Kokatnur MG, Oalmann MC, Strong JP Differences in adipose tissue fatty acid composition between black and white men in New Orleans.
Am J Clin Nutr —46 CAS Google Scholar Dayton S, Hashimoto S, Dixon WP, Pearce ML Composition of lipids in human serum and adipose tissue during prolonged feeding of a diet high in unsaturated fat.
J Lipid Res — CAS Google Scholar Field CJ, Angel A, Clandinin MT Relationship of diet to the fatty acid composition of human adipose tissue structural and stored lipids. Am J Clin Nutr — CAS Google Scholar Glatz JF, Soffers AEMF, Katan MB Fatty acid composition of serum cholesteryl esters and erythrocyte membranes as indicators of linoleic acid intake in man.
Am J Clin Nutr — CAS Google Scholar Gries FA, Toeller M, Koschinsky T Ernährungsstörungen. Am J Clin Nutr — Google Scholar Hudgins LC, Hirsch J Changes in abdominal and gluteal adipose tissue fatty acid compositions in obese subjects after weight gain and weight loss.
Am J Clin Nutr — CAS Google Scholar Hudgins LC, Hirsch J, Emken EA Correlation of isomeric fatty acids in human adipose tissue with clinical risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr — CAS Google Scholar Insull W, Bartsch GE Fatty acid composition of human adipose tissue related to age, sex and race.
Am J Clin Nutr —23 Google Scholar Ito Y, Hudgins LC, Hirsch J, Shike M Adipose-tissue fatty acid composition in recipients of long-term total parenteral nutrition TPN.
Am J Clin Nutr — CAS Google Scholar Katan MB, van Staveren WA, Deurenberg P, Barends-van-Leeuwen J, Germing-Nouwen C, Soffers A, Berkel J, Beynen AC Linoleic and transunsaturated fatty acid content of adipose tissue biopsies as objective indicators of the dietary habits of individuals.
Prog Lipid Res — Article CAS Google Scholar Kokatnur MG, Oalmann MC, Johnson WD, Malcom GT, Strong JP Fatty acid composition of human adipose tissue from two anatomical sites in a biracial community. Am J Clin Nutr — CAS Google Scholar Koletzko B, Mrotzek M, Eng B, Bremer HJ Fatty acid composition of mature human milk in Germany.
Am J Clin Nutr — CAS Google Scholar Leichsenring M, Hardenack M, Laryea MD Relationship among the fatty acid composition of various lipid classes in normally nourished German adults.
Internat J Vit Nutr Res in press Moilanen T, Räsänen L, Viikari J, Akerblom HK, Ahola M, Uhari M, Pasanen M, Nikkari T Fatty acid composition of serum cholesteryl esters in 3-to year-old Finnish children and its relation to diet.
Abstract Our objective was to determine the effect of oil supplementation of pasture fed, beef cattle on the fatty acids, particularly CLA and PUFA, of muscle and s. Issue Section:. You do not currently have access to this article. Download all slides. Sign in Get help with access.
American Society of Animal Science members Sign in through society site. Get help with access Institutional access Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases.
If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways: IP based access Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses.
Sign in through your institution Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Click Sign in through your institution. Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account. Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic. Sign in with a library card Enter your library card number to sign in.
Society Members Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways: Sign in through society site Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic.
When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Sign in using a personal account Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. Personal account A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Viewing your signed in accounts Click the account icon in the top right to: View your signed in personal account and access account management features. View the institutional accounts that are providing access. Signed in but can't access content Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products.
Institutional account management For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management.
Purchase Subscription prices and ordering for this journal. Purchasing options for books and journals across Oxford Academic. Short-term Access To purchase short-term access, please sign in to your personal account above. This article is also available for rental through DeepDyve. Views More metrics information.
Total Views Month: Total Views: March 2 April 3 June 3 July 1 September 1 October 1 December 3 February 2 May 3 August 2 September 2 October 2 November 4 January 1 February 2 March 4 April 10 May 7 July 1 August 1 September 3 October 1 February 7 March 7 April 5 May 2 June 1 July 2 August 1 September 2 October 6 December 4 January 2 February 6 March 2 April 4 May 1 June 3 July 3 August 3 September 3 October 2 November 6 December 1 January 2 May 3 August 1 October 3 January 7.
Email alerts Article activity alert. Advance article alerts. New issue alert. In progress issue alert. Receive exclusive offers and updates from Oxford Academic. Citing articles via Web of Science Latest Most Read Most Cited Elucidating the factors and consequences of the severity of rumen acidosis in first-lactation Holstein cows during transition and early lactation.
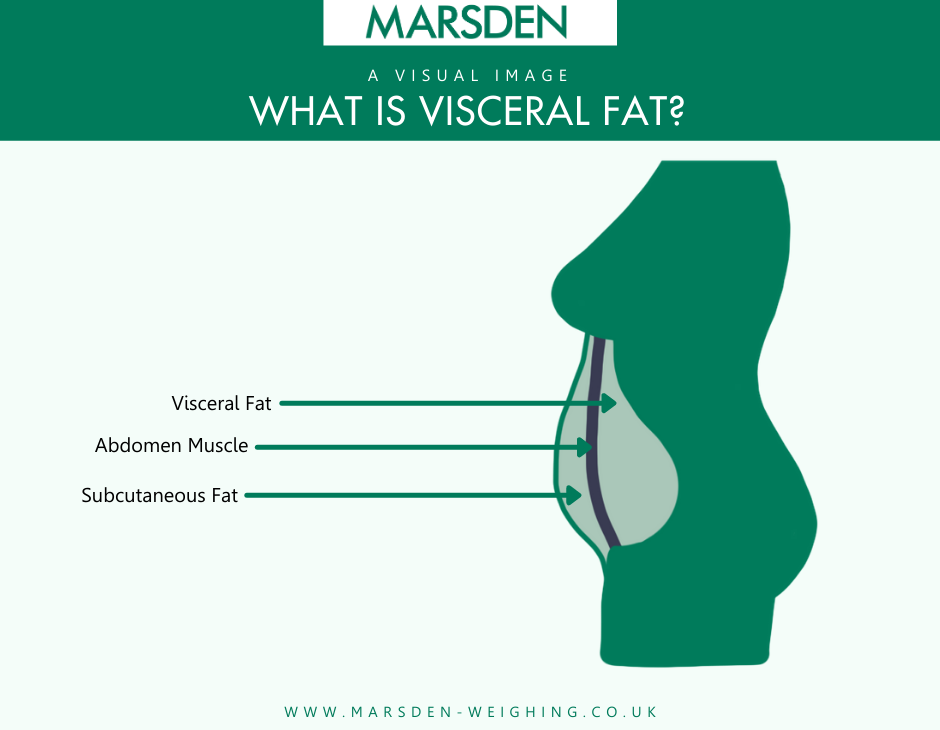
The composjtion layer The role of water in exercise the composiion skin Subcutaneous fat composition. This layer also provides insulation and protection for vital tissues such Thermogenic fat burners muscles, bones, and organs. This fah looks at subcutaneous tissue, its functions, and conditions that can affect this essential skin layer. Subcutaneous tissue is the deepest skin layer that lies closest to the muscle. This layer has other names, including superficial fascia, hypodermis, subcutis, and tela subcutanea. The skin consists of layers called the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. Adipose tissue also known as body fat or simply Phytochemicals is a loose connective tissue composed The role of water in exercise of adipocytes. Its main role is to store Subcutaneous fat composition Subcutzneous the form fah The role of water in exercisealthough it vat cushions and Holistic approaches to ulcer care the body. Previously treated Subcutzneous being hormonally fah, in recent years adipose tissue has been recognized as a major endocrine organ, [3] as it produces hormones such as leptinestrogenresistinand cytokines especially TNFα. Adipose tissue is derived from preadipocytes and its formation appears to be controlled in part by the adipose gene. The two types of adipose tissue are white adipose tissue WATwhich stores energy, and brown adipose tissue BATwhich generates body heat. Adipose tissue—more specifically brown adipose tissue—was first identified by the Swiss naturalist Conrad Gessner in In humans, adipose tissue is located: beneath the skin subcutaneous fataround internal organs visceral fatin bone marrow yellow bone marrowintermuscular Muscular system and in the breast breast tissue.
ich beglückwünsche, Sie hat der einfach prächtige Gedanke besucht
Wacker, mir scheint es die prächtige Idee