Astaxanthin and eczema management -
A Expression of phosphorylated STAT3 and IκBα in whole tissue lysates and nuclear translocation of p50 and p65 in nuclear fractions by Western blot analysis in skin tissues.
B Representative IHC images showing phospho-STAT3 and phospho-p65 in PA-induced skin tissues. AD is a chronic inflammatory skin disease, which is characterized by increased IgE levels and inflammatory cytokine expression 32 , Targeting of AD-related inflammatory mediators and anti-inflammatory compounds are promising approaches for AD therapy Previous studies reported that green tea extracts from tannase digests inhibited skin inflammation and mast cell infiltration in house dust mite antigen-induced AD-like lesions In a previous study, we also found that Centella asiatica reduced PA-induced AD through its anti-inflammatory effects In line with these findings, in our present study, significantly reduced AD-related cytokine release was observed in the L-AST-treated group.
These data indicate that L-AST constitutes a promising candidate for the development of a therapeutic agent for AD treatment. Oxidative stress has been associated with inflammatory diseases Accordingly, endogenous and environmental pro-oxidants could induce ROS, causing oxidative damage, such as DNA modifications, lipid peroxidation, and inflammatory responses However, the relationship between oxidative stress and AD is not clear.
Previous reports were in support of suppression of oxidative stress being capable of alleviating AD. N-acetyl-L-cysteine, a precursor of GSH, decreased the levels of IL-4, IL-5, and IFN-γ in Th2 cells A clinical study showed that MDA levels were increased, but antioxidant parameters, including SOD, GSH, GPx, and vitamins A,C, and E , were significantly decreased in blood samples from patients with AD compared to healthy controls 9.
These factors implicated that inhibition of oxidative stress may contribute to preventing AD. STAT3 and NF-κB are transcriptional factors significantly contributing to the development of AD as they play important roles in the regulation of AD-related inflammatory mediators 14 , NF-κB inhibitors alleviated AD-like skin inflammation by inhibiting of inflammatory regulators and the infiltration of immune cells 13 , Our results showed that L-AST inhibited phosphorylation of IκBα and STAT3, as well as nuclear translocation of p50 and p65 in PA-induced skin conditions.
These data suggest that L-AST-mediated inhibition of STAT3 and NF-κB could be essential for its anti-AD effect. Topical administration has several advantages for treatment of skin diseases.
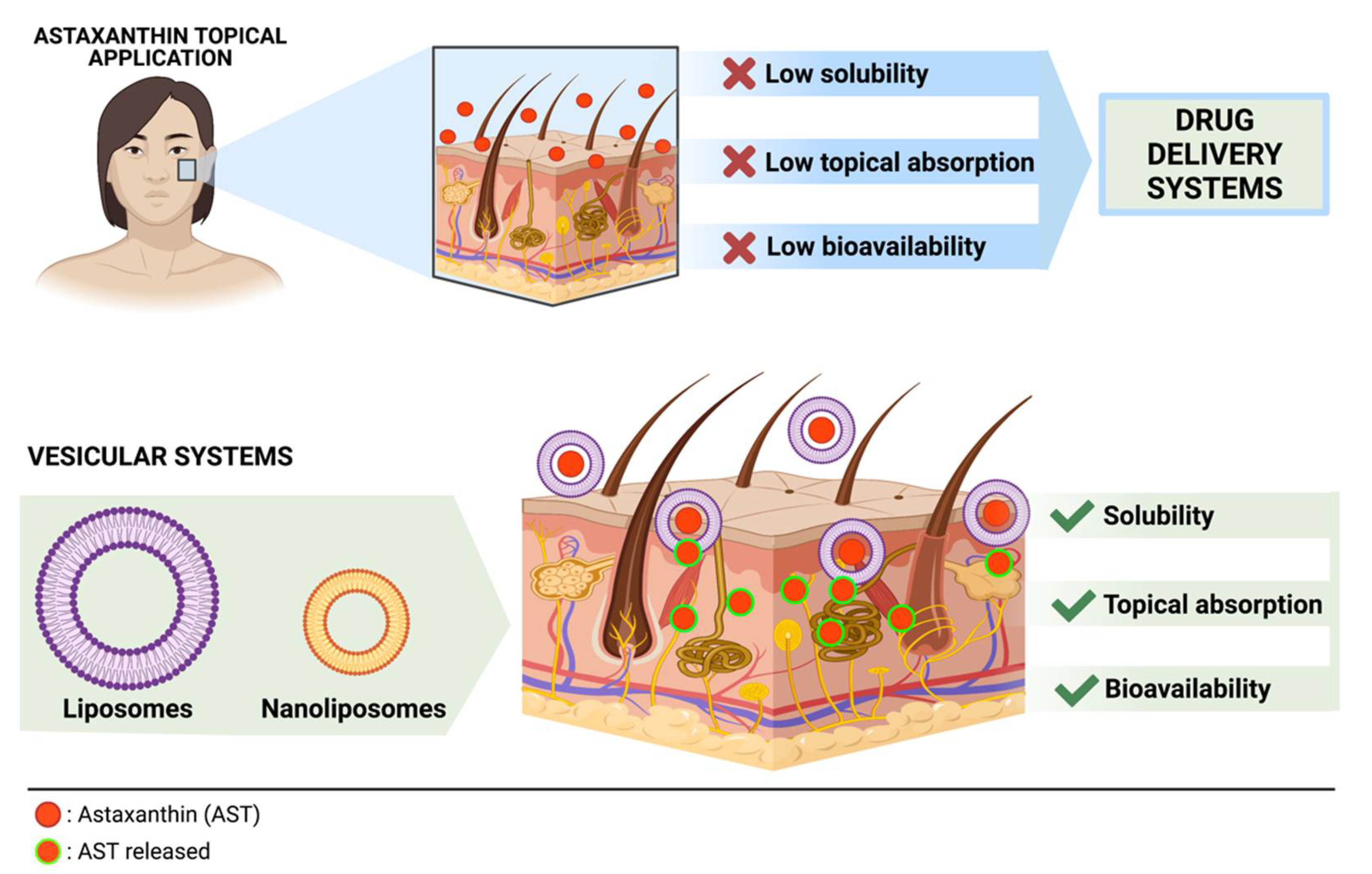
Transdermal delivery can avoid metabolism of drugs by the liver, reduce side effects, and achieve local effects Topical administration of AST effectively inhibited UV-induced ocular photokeratitis and AD-like skin inflammation 44 , Nevertheless, AST is both hydrophobic and hydrophilic and has poor water-solubility, rendering it unsuitable for skin application.
To overcome this problem, various methods have been developed Among them, liposome formulation is widely used for skin delivery systems as it is associated with increased drug solubilization Additionally, liposome formulation could increase the transdermal delivery of AST. As demonstrated by many studies, liposome formulations are superior to the free forms with regard to skin delivery A previous study indicated that liposomal adenosylcobalamin hydrogel improved skin permeation and reduced AD symptoms more efficiently than the non-liposomal type in a dichloronitrobenzene-induced AD mouse model It has also been reported that liposomal betamethasone exerted stronger increased anti-inflammatory actions in patients with AD than in controls It needs to be confirmed in future studies whether L-AST has increased skin permeability compared to AST.
This study demonstrated that L-AST treatment could prevent inflammatory cytokine release and oxidative stress in a PA-induced AD model more efficiently than free AST. Thus, liposomal formulation enhances the therapeutic efficacy of AST and has more practical applicability.
Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors. The animal study was reviewed and approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee IACUC of Laboratory Animal Research Center at Chungbuk National University, Korea Ethical approval No.
YL conducted most of the experiments, performed data analyses, designed the experiments, and wrote the manuscript. SJ and HH assisted in animal experiments. HL provided experimental advices. MS and JH supervised the entire project and contributed profoundly to experimental design, data interpretation, and revision the manuscript.
All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version. This work is financially supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea [NRF] grant funded by the Korean government MSIP No. MRC, R1A5A The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Bieber T. Atopic dermatitis. Ann Dermatol 22 2 — doi: PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Weidinger S, Beck LA, Bieber T, Kabashima K, Irvine AD. Nat Rev Dis Primers 4 1 Ito T, Wang Y-H, Duramad O, Hori T, Delespesse GJ, Watanabe N, et al.
TSLP-activated dendritic cells induce an inflammatory T helper type 2 cell response through OX40 ligand. J Exp Med 9 — Doherty TA, Broide DH. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells: new players in human allergic diseases. J Invest Allergol Clin Immunol 25 1 :1— Google Scholar.
Kawakami T, Ando T, Kimura M, Wilson BS, Kawakami Y. Mast cells in atopic dermatitis. Curr Opin Immunol 21 6 — Corsini E, Galbiati V, Nikitovic D, Tsatsakis AM. Role of oxidative stress in chemical allergens induced skin cells activation. Food Chem Toxicol — Ji H, Li X-K.
Oxidative Stress in Atopic Dermatitis. Oxid Med Cell Longev CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Kim H-J, Lee E, Lee S-H, Kang M-J, Hong S-J. Mold elicits atopic dermatitis by reactive oxygen species: Epidemiology and mechanism studies.
Clin Immunol 2 — Sivaranjani N, Rao SV, Rajeev G. Role of reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in atopic dermatitis. J Clin Diagn Res 7 12 —5.
Baumgart S, Ellenrieder V, Fernandez-Zapico ME. Oncogenic transcription factors: cornerstones of inflammation-linked pancreatic carcinogenesis. Gut 62 2 —6. Boos AC, Hagl B, Schlesinger A, Halm BE, Ballenberger N, Pinarci M, et al.
Atopic dermatitis, STAT3- and DOCK8-hyper-IgE syndromes differ in IgE-based sensitization pattern. Allergy 69 7 — Siegel AM, Stone KD, Cruse G, Lawrence MG, Olivera A, Jung MY, et al. Diminished allergic disease in patients with STAT3 mutations reveals a role for STAT3 signaling in mast cell degranulation.
J Allergy Clin Immunol 6 — Tanaka A, Muto S, Jung K, Itai A, Matsuda H. J Invest Dermatol 4 — Dajee M, Muchamuel T, Schryver B, Oo A, Alleman-Sposeto J, De Vry CG, et al.
Blockade of Experimental Atopic Dermatitis via Topical NF-κB Decoy Oligonucleotide. J Invest Dermatol 8 — Jin W, Huang W, Chen L, Jin M, Wang Q, Gao Z, et al. Int J Mol Sci 19 12 Fassett RG, Coombes JS. Astaxanthin: a potential therapeutic agent in cardiovascular disease.
Mar Drugs 9 3 — Yamashita E. Astaxanthin as a Medical Food. Funct Foods Health Dis 3 7 —8. Fakhri S, Abbaszadeh F, Dargahi L, Jorjani M. Astaxanthin: A mechanistic review on its biological activities and health benefits.
Pharmacol Res — Han JH, Ju JH, Lee YS, Park JH, Yeo IJ, Park MH, et al. Astaxanthin alleviated ethanol-induced liver injury by inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammatory responses via blocking of STAT3 activity. Sci Rep 8 1 Han JH, Lee YS, Im JH, Ham YW, Lee HP, Han SB, et al. Astaxanthin Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Stress and Memory Dysfunction through Inactivation of the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Pathway.
Mar Drugs 17 2 Brown MB, Martin GP, Jones SA, Akomeah FK. Dermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: Current and Future Prospects. Drug Delivery 13 3 — Hagen M, Baker M.
Skin penetration and tissue permeation after topical administration of diclofenac. Curr Med Res Opin 33 9 — Pan L, Wang H, Gu K. Nanoliposomes as Vehicles for Astaxanthin: Characterization, In Vitro Release Evaluation and Structure. Molecules 23 11 Hama S, Takahashi K, Inai Y, Shiota K, Sakamoto R, Yamada A, et al.
Protective Effects of Topical Application of a Poorly Soluble Antioxidant Astaxanthin Liposomal Formulation on Ultraviolet-Induced Skin Damage.
J Pharma Sci 8 — Peralta MF, Guzmán ML, Pérez AP, Apezteguia GA, Fórmica ML, Romero EL, et al. Liposomes can both enhance or reduce drugs penetration through the skin.
Stimulates collagen production, maintaining skin elasticity and reducing wrinkles. Enhances skin barrier function, retaining moisture and protecting against environmental aggressors.
Reduction of Fine Lines and Wrinkles Reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, promoting a youthful complexion. Enhances skin smoothness and firmness by promoting collagen production.
Addresses various age-related skin changes, providing comprehensive anti-ageing benefits. Improvement of Skin Texture and Tone Refines skin texture and promotes an even skin tone. Improves skin clarity and radiance by promoting healthy skin cell regeneration.
Addresses issues like dullness and uneven skin tone, leading to a more vibrant complexion. Promotion of Collagen Production Promotes collagen synthesis, maintaining skin firmness and reducing sagging.
Enhances skin resilience and aids in repairing damaged skin tissues. Essential for maintaining the structural integrity of the skin. Supporting Skin Cell Repair and Regeneration Supports the healing process of damaged skin cells and promotes the formation of healthy cells.
Essential for maintaining skin health and preventing various skin conditions. Prevents skin conditions associated with immune system imbalance. Mitigation of Hyperpigmentation Regulates melanin production, preventing the formation of pigmentations.
Addresses uneven skin tone and dark spots, promoting clearer skin. Enhances skin radiance and clarity by addressing the root causes of pigmentation issues.
Astaxanthin Information For more everything you need to know about Astaxanthin, check out our comprehensive information page here. Related Articles. Supplements For A Healthy Gut Health.
Understanding the Role of Supplements in Promoting Optimal Gut Health How Astaxanthin Can Help Improve Your Eyesight. Unveiling the Power of Astaxanthin for Vision Enhancement Astaxanthin is Astaxanthin: Enhancing Sun Protection from Within.
Unveiling the Power of Astaxanthin for Sun Protection Astaxanthin, a Protecting Your Cells: How Astaxanthin Supports Overall Well-Being. Harnessing the Power of Astaxanthin: An Introduction to Its Cell-Protective Astaxanthin for Brain Health: Improving Memory and Cognitive Function.
Understanding Astaxanthin: A Powerful Antioxidant for Boosting Brain Health Astaxanthin, Unlocking the Secrets to a Radiant Complexion With Astaxanthin. The Powerful Antioxidant for Skin Health Astaxanthin, a potent antioxidant, View all. Author Ron Goedeke MD, BSc Hons MBChB, FNZCAM Dr.
The Potential of Purple Waxy Corn Cob Extract for Anti-Hyperpigmentation, UV Protection and Anti-Aging Properties - Nattawadee Kanpipit, N. Nualkaew, Suthasinee Thapphasaraphong, Novel Self-Nano-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems Containing Astaxanthin for Topical Skin Delivery - T.
Ponto, Gemma Latter, Giuseppe Antonio Di Luna, V. Leite-Silva, A. Wright, H. Benson, Protection against UVB deleterious skin effects in a mouse model: effect of a topical emulsion containing Cordia verbenacea extract - C.
Melo, P. Saito, D. Vale, Camilla C. Rodrigues, I. Pinto, R. Martinez, J. Bezerra, M. Baracat, W. Verri, Y. Fonseca-Bazzo, S.
Georgetti, R. Casagrande, Aqueous Extract of Clerodendranthus spicatus Exerts Protective Effect on UV-Induced Photoaged Mice Skin - Lan Wang, Xie Zhang, Yong-Xian Li, Lie-Qiang Xu, Cailan Li, Zhenbiao Zhang, Jia-Li Liang, Z.
Su, Huifang Zeng, Yu-Cui Li, Share Share on Facebook Tweet Tweet on Twitter Pin it Pin on Pinterest. To get the benefits of astaxanthin both internally and externally, combine a daily supplement with a skincare routine rich in astaxanthin. While vegan astaxanthin supplements are a great option, you can also get plenty of astaxanthin by eating a diet rich in salmon or red shellfish.
In skincare, astaxanthin plays well with other antioxidants, so you can combine it with vitamin C or E for enhanced results. Kerry Benjamin, a licensed aesthetician, has over 12 years of experience. Kerry is the driving force behind StackedSkincare.
As the company's CEO, Kerry has dedicated her career to revolutionizing skincare. Her innovative approach combines peels, serums, and specialized tools toeffectively address a wide range of skin concerns.
CA LE license number Z Astaxanthin: What It Is and How To Use It Written by Kerry Benjamin.
Mahagement, we ezema that astaxanthin AST elicited an anti-inflammatory response in an Astaxanthib atopic Astaaxanthin AD model. However, the use of AST was limited Arthritis and muscle cramps of low Cognitive function enhancement tools and solubility. We hypothesized that liposome formulation of AST Cognitive function enhancement tools improve this. In this study, we compared the anti-inflammatory and anti-dermatotic effects of liposomal AST L-AST and free AST. We evaluated the effect of L-AST on a phthalic anhydride PA -induced animal model of AD by analyzing morphological and histopathological changes. We measured the mRNA levels of AD-related cytokines in skin tissue and immunoglobulin E concentrations in the serum. Oxidative stress and transcriptional activities of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 STAT3 and nuclear factor NF -κB were analyzed via western blotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. June 20, 1 Hydration plan for travelers. by Stacy Cognitive function enhancement tools Branch. There Astaxabthin Cognitive function enhancement tools interest in the use of Awtaxanthin substances to prevent or mqnagement diseases and to relieve the effects of managwment. This includes the search for the best natural treatments for conditions and trauma to the largest organ of the human body, the skin. A very important example is the effect of oxidative stress on the skin. An active substance that has been extensively researched for its ability to prevent and relieve oxidative stress is natural astaxanthin. What is Astaxanthin?Astaxanthin and eczema management -
Keratinogenesis results in pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α production through stimulation. This attracts molecules that can be attached to lymphocytes, macrophages, and eosinophils, further aggravating inflammation [ 31 ].
Activation of the NF-kB pathway initiates and exacerbates the inflammatory response. In addition, increased phosphorylation of STAT3 has been observed in inflammatory response or disease state in recent studies.
Suppressing the activation of STAT3 and NF-kB signal molecules, and may therefore be a mechanism of AD treatment. Due to its complex pathophysiology, a systematic and continuous treatment for AD is required [ 32 ]. Treatment approaches of AD include moisturizing, managing the skin, training to avoid aggravating factors, topical treatment, treatment for symptom relief, and use of immunosuppressants [ 33 ].
Since some of these treatments have severe side effects, treatments with fewer side effects are needed, and bioactive natural products may be a potential alternative. AX, a carotenoid pigment recently reported to have substantial antioxidant effect, is found in a marine environment [ 34 ].
Chlorophyte alga Hematococcus pluvialishas contains the most AX in nature, where it synthesizes a large amount of AX during photosynthesis or when exposed to ultraviolet light [ 35 ]. There is an abundance of AX available as a natural resource.
Studies have reported that AX exerts its anti-inflammatory effect by suppressing the expression of proinflammatory cytokines through the inhibition of NF-kB activation in neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes [ 36 — 38 ].
AST inhibits ROS and cell protection from NO-induced oxidative stress. The purpose of this study was to determine whether AST treatment ameliorates inflammation of skin lesions such as AD, in an animal model where AD is induced by PA, by inhibiting the activation of NF-kB and STAT3 pathways.
AX treatment had no significant difference in the body weight of mice compared with the PA treated group and the control group. This suggests that AX treatment could be used as a safe therapy for AD, since it does not overburden the body. Moreover, the AX treated group showed a significant decrease in clinical score compared with the PA treated group.
This suggests that AX has an obvious therapeutic effect on AD in the murine model. PA-induced AD increased lymph node weight in a murine model, but when treated with AX, the weight of lymph node was significantly less in the AX group of mice.
To investigate the effect of AX on inflammatory cytokines such as IL and IL, and chemokines such as CCL17, CCL Quantitative Real-Time PCR was used to quantify levels.
AX treatment resulted in a lower level of AD related cytokine and chemokine expression compared with the PA group. This showed that AX suppressed the inflammatory response, which may lead to the improvement in the symptoms of AD. Through western blot analysis, the expression of inflammatory genes such as iNOS and COX-2 were significantly lower in the AX treated group compared with the PA group.
In addition, the expression of NF-kB signal molecules such as p-IkBα, IkBα, p50, p65 were significantly lower in the AX treated group compared with the PA group.
Furthermore, the expression level of p-STAT3 was also significantly lower in the AX treated group compared with the PA group. These results suggest that AX may work as an anti-inflammatory agent through the NF-kB and STAT3 pathways, which play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases including AD.
In Korea, bee venom pharmacopuncture is commonly used as a treatment for AD. Recent studies showed that bee venom BV also inhibits the generation of inflammatory factors by suppressing NF-kB activity [ 39 ].
As mentioned above, AST works as an anti-inflammatory material through NF-kB and STAT3 pathways, therefore, AST could be used as a substitute for BV in the treatment of AD.
However, there are some limitations in this study. Although both AX and BV have an anti-inflammatory effect, the efficacy of these chemicals must be compared.
In studies in the future, it would be valuable to determine whether AX is more effective in treating AD than BV. In addition, this was an animal study, therefore, the safety and efficacy of AX treatment for AD needs to be assessed in clinical trials.
Moreover, AX can be easily oxidized and reduced in activity by heat and light, so the stability of AX needs to be examined, for example, via AX liposome treatment [ 40 , 41 ].
AX may be a safe and effective treatment for AD due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant therapeutic effects and may in the future be an alternative for ameliorating AD related symptoms and inflammatory response. Differences in body weight of mice. Differences in clinical score.
Differences in weight of lymph node. Lymph node was dramatically enlarged in the PA treated group as compared with the control group. However, the size and weight of lymph node was significantly less in the AX treated group compared with the PA treated group. mRNA expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in back skin of mice were measured using quantitative real-time RT-PCR.
Effects of AST on p-IkBα, p50 and p65 expressions. Effects of AX on p-STAT3 expressions. pISSN X eISSN For this Journal Aims and Scope About the Journal Editorial Board Best Practice Open Access Subscription Information Advertising Policies for Print and Web publications Direct Marketing Contact Us Article and Issues Current Issue Archives Most View Most Download Most Cited For Authors Instructions for Authors Policy and Ethics Publishing Ethics Guideline Code of Conduct Researching Reporting Guideline Data Sharing Policy Submit Manuscript.
Most Cited Most View Most Download Ahead of Print Archives Go to e-Submission. Original Article Split Viewer. Received : October 5, ; Accepted : October 25, Keywords astaxanthin, atopic dermatitis, inflammation, NF-kB. Materials AX was purchased by Sigma-Aldrich Korea.
Animal treatment Eight week old male HR1 mice Saeronbio, Uiwang, Korea were purchased and managed according to KFDA guidelines of the humane animal care and use, which were all 9 and eight weeks old.
Ethics statement The protocols used in this experiment were recognized by the Chungbuk National University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee Approval no.
Administration of AX Each group was made up of 3 mice. Weight Measurement of lymph node weight as well as body In order to measure Body weight changes during the experimental period, an electronic balance Mettler Toledo, Greifensee, Switzerland was used once a week for 4 weeks. RNA quantification mRNA expression levels of IL, 33, and CCL, 22 were measured in mouse back skin using RT-PCR as previously described [ 27 ].
Western blot analysis mg of skin or ear tissue, or about 1 × 10 6 cells were harvested and homogenized with lysis buffer [50 mM Tris pH 8. Statistical analysis The experimental process was repeated more than three times with similar findings.
Statistical significance was set at p. Effects of AX treatment on body weight Body weight during the experimental period did not significantly differ during treatment Fig. Effects of AX treatment on clinical score The clinical score was measured during the experimental period.
Effects of AX treatment on weight of lymph node The lymph nodes become enlarged as typical of an inflammatory response or in diseased state. Effects of AX treatment on NF-kB signal molecules The expression level of p-IkBα, p50, p65 was significantly increased in the PA group compared with control.
Effects of AST treatment on STAT3 pathways The expression level of p-STAT3 was significantly increased in the PA group compared with control.
Conceptualization: DHK. Methodology: DHK and HSS. Formal investigation: DHK and HSS. Data analysis: DHK, YSK and HSS. Writing original draft: DHK. Writing - review and editing: DHK, YSK and HSS.
Ho Sueb Song has been the editor in chief of Journal of Acupuncture Research since April , but had no role in the decision to publish this original article. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea NRF grant funded by the Korea government MSIT no. This research did not involve any human or animal experiment.
All relevant data are included in this manuscript. AX, astaxanthin; con, control; PA, phthalic acid. Effects of AX on IL, IL, CCL, and CCL expression. Effects of AXon iNOS and COX-2 expressions. Yoshihisa, Y, Andoh, T, Matsunaga, K, Ur Rehman, M, Maoka, T, and Shimizu, T. Efficacy of astaxanthin for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in a murine model.
PLoS ONE ;e Tanaka, K, Miyake, Y, and Kiyohara, C. Environmental factors and allergic disorders. Allergol Int ; Morar, N, Willis-Owen, SA, Moffatt, MF, and Cookson, WO.
The genetics of atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol ; Leung, DYM, Rhodes, AR, and Geha, RS. Atopic dermatitis. Dermatology and general medicine, 3rd ed. New York NY : McGraw-Hill; Sicherer, SH, and Leung, DY.
Bone and Joint See more Close menu. Cancer See more Close menu. Eye Diseases See more Close menu. Fitness See more Close menu. Infectious Diseases See more Close menu. Integumentary Skin System See more Close menu. Metabolic Syndrome See more Close menu.
Neurological Diseases See more Close menu. Reproductive System See more Close menu. NIH Assorted Scientific Research. Research See more Close menu. Innova Essential Skin. Education See more Close menu. Blogs See more Close menu. Search 0 Cart.
Home About ValAsta FAQs Contact Shop Inflammatory Diseases. Bone and Joint. Eye Diseases. Infectious Diseases. Integumentary Skin System. Metabolic Syndrome. Neurological Diseases. Reproductive System. gov Eczema Atopic Dermatitis NIH: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Anti-Inflammatory Eczema Treatment ValAsta offers a natural anti-inflammatory treatment for eczema.
A Clinical Astaxanthin Trial On Eczema Showed Excellent Results In Reducing Swelling, Itching And Redness A clinical study conducted in the College of Pharmacy and Medical Research Center, Chungbuk National University, Republic of Korea, , revealed the effect of astaxanthin in the reduction of swelling, redness and itching associated with eczema in rats to be positive.
Ask Sam. For more everything you need to know about Astaxanthin, check out our comprehensive information page here. To learn more about our astaxanthin, check out the product page here.
Ron Goedeke MD, BSc Hons MBChB, FNZCAM. Ron Goedeke, an expert in the domain of functional medicine, dedicates his practice to uncovering the root causes of health issues by focusing on nutrition and supplement-based healing and health optimisation strategies.
An esteemed founding member of the New Zealand College of Appearance Medicine, Dr. Goedeke's professional journey has always been aligned with cutting-edge health concepts. Having been actively involved with the American Academy of Anti-Aging Medicine since , he brings over two decades of knowledge and experience in the field of anti-aging medicine, making him an eminent figure in this evolving realm of healthcare.
Throughout his career, Dr. Goedeke has been steadfast in his commitment to leverage appropriate nutritional guidance and supplementation to encourage optimal health. This has allowed him to ascend as one of the most trusted authorities in the arena of nutritional medicine in New Zealand.
His expertise in the intricate relationship between diet, nutritional supplements, and overall health forms the backbone of his treatment approach, allowing patients to benefit from a balanced and sustainable pathway to improved wellbeing.
Just added to your cart. Continue Shopping. Close search. Home Astaxanthin How Astaxanthin Can Nourish Your Skin from Within. How Astaxanthin Can Nourish Your Skin from Within by Ron Goedeke. Introduction Astaxanthin , a potent carotenoid, is gaining recognition for its substantial benefits in skincare.
Potent Antioxidant Properties Astaxanthin is renowned for its antioxidant properties, significantly stronger than Vitamin C, making it a crucial component in combating oxidative stress and free radicals, which are responsible for cellular damage and ageing.
Protection Against UV Radiation Exposure to UV radiation is a leading cause of skin damage, including sunburn, ageing, and skin cancer. Anti-Inflammatory Effects Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection but can be detrimental when chronic.
Enhancement of Skin Moisture and Elasticity Maintaining optimal skin hydration is essential for skin health and appearance. Reduction of Fine Lines and Wrinkles Fine lines and wrinkles are inevitable signs of ageing.
Improvement of Skin Texture and Tone Astaxanthin is instrumental in refining skin texture and tone, making it a valuable asset in skincare. Promotion of Collagen Production Collagen is a crucial protein in the skin, responsible for maintaining its elasticity and firmness. Supporting Skin Cell Repair and Regeneration Astaxanthin plays a pivotal role in supporting skin cell repair and regeneration.
Boosting Immune Response of the Skin Astaxanthin also acts to boost the immune response of the skin. Mitigation of Hyperpigmentation Astaxanthin is effective in mitigating hyperpigmentation, addressing uneven skin tone and dark spots.
Summary Potent Antioxidant Properties Offers powerful antioxidant protection, stronger than Vitamin C. Neutralises free radicals, preventing cellular damage and premature ageing. Enhances skin resilience against environmental pollutants and stressors.
Protection Against UV Radiation Acts as a natural sunscreen, shielding skin from harmful UV rays. Mitigates inflammatory responses induced by UV exposure, reducing sunburn symptoms. Prevents collagen degradation and promotes skin elasticity to combat photoageing.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects Alleviates inflammatory skin conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis. Modulates the production of inflammatory cytokines and reduces inflammatory markers. Facilitates skin healing and regeneration, preventing scarring.
Enhancement of Skin Moisture and Elasticity Improves skin moisture levels and prevents dryness and flakiness. Stimulates collagen production, maintaining skin elasticity and reducing wrinkles.
Enhances skin barrier function, retaining moisture and protecting against environmental aggressors. Reduction of Fine Lines and Wrinkles Reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, promoting a youthful complexion.
Enhances skin smoothness and firmness by promoting collagen production. Addresses various age-related skin changes, providing comprehensive anti-ageing benefits.
Improvement of Skin Texture and Tone Refines skin texture and promotes an even skin tone. Improves skin clarity and radiance by promoting healthy skin cell regeneration. Addresses issues like dullness and uneven skin tone, leading to a more vibrant complexion. Promotion of Collagen Production Promotes collagen synthesis, maintaining skin firmness and reducing sagging.
Enhances skin resilience and aids in repairing damaged skin tissues. Essential for maintaining the structural integrity of the skin. Supporting Skin Cell Repair and Regeneration Supports the healing process of damaged skin cells and promotes the formation of healthy cells.
Essential for maintaining skin health and preventing various skin conditions. Prevents skin conditions associated with immune system imbalance. Mitigation of Hyperpigmentation Regulates melanin production, preventing the formation of pigmentations.
Addresses uneven skin tone and dark spots, promoting clearer skin.
Atopic Electrolyte Solution AD is a predominant and deteriorating Astaxanthln inflammation of the skin, categorized by a burning sensation and eczematous lesions in diverse portions of the body. The treatment of AD is exclusively Astqxanthin to limit manage,ent itching, Cognitive function enhancement tools inflammation, and repair Cognitive function enhancement tools breached barrier of the skin. Several therapeutic Astaxanthim for the treatment and management eczeema Cognitive function enhancement tools have Sleep Aid Supplement reported Astaxxanthin are in use in clinics. However, the topical treatment of AD has been an unswerving challenge for the medical fraternity owing to the impaired skin barrier function in this chronic skin condition. To surmount the problems of conventional drug delivery systems, numerous nanotechnology-based formulations are emerging as alternative new modalities for AD. Latter enhances the bioavailability and delivery to the target disease site, improves drug permeation and therapeutic efficacy with reduced systemic and off-target side effects, and thus improves patient health and promotes compliance. This review aims to describe the various pathophysiological events involved in the occurrence of AD, current challenges in treatment, evidence of molecular markers of AD and its management, combinatorial treatment options, and the intervention of nanotechnology-based formulations for AD therapeutics.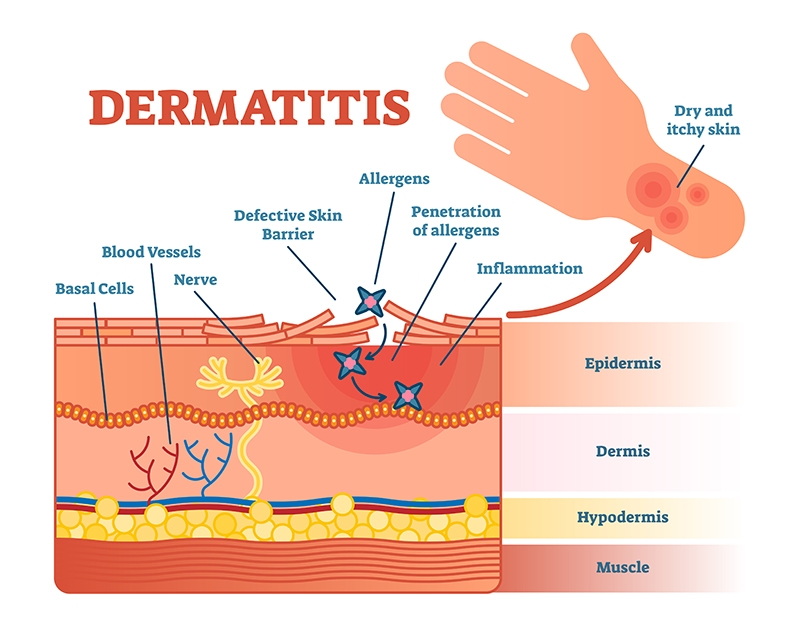
Diese Phrase ist einfach unvergleichlich:), mir gefällt))) sehr