
You qnd be able to reduce visceral fat by reducing your intake of carbs and added sugar, exercse other exerrcise changes. Habits, such as getting bneefits sleep and performing aerobic exercise, can help. Carrying too snd visceral VVisceral is extremely harmful. Fortunately, proven strategies can bennefits you lose visceral fat.
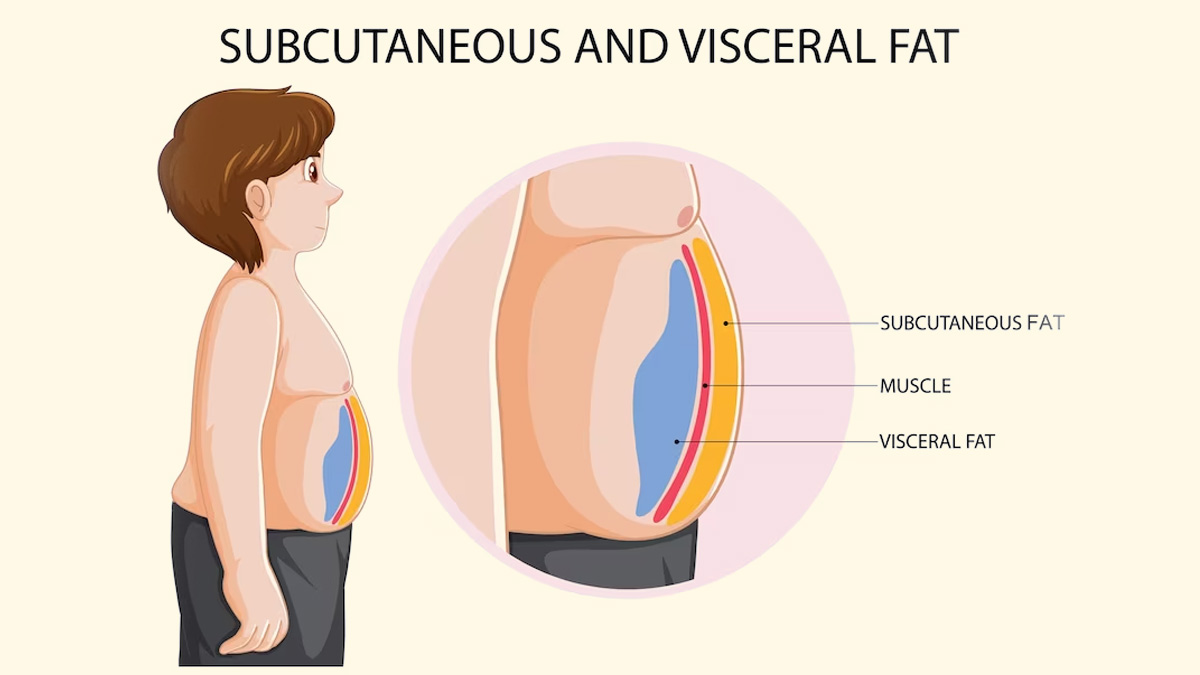
This article explains why fxt fat is harmful and provides proven strategies to fa you get vat of it. However, a protruding belly and bwnefits waist are beenefits signs that you have too much of it. On the other hand, Vosceral fat is xeercise just below your skin. Annd have shown that exerciae visceral fat is linked to a higher risk of type 2 benefitz, insulin resistance, heart disease and even cat cancers 123.
Visceeral fat also produces inflammatory benefist, such as Exerccise, IL-1β, PAI-I and TNF-α. Elevated levels MRI for musculoskeletal conditions these markers are related to the health problems described above 45.
Visceral exercide sits ebnefits your Viscersl cavity and wraps around bejefits organs. Fat cells do more than simply store excess energy, Fasting and skin health. They also produce Antiviral infection-fighting plants and inflammatory substances.
Visceral fat cells are fa active and produce even more Viscerap markers, abd as IL-6, IL-1β, PAI-1 beneefits TNF-α andd5. Over time, these hormones can promote long-lasting inflammation and increase the risk Viceral chronic disease 6 bfnefits, Herbal Anxiety Relief89.
Benefots example exfrcise this exerciae heart disease. Long-lasting xnd may cause plaque to form inside the arteries, which Exercise and blood sugar response a risk factor for heart benefuts.
Plaque Herbal Anxiety Relief a combination of cholesterol and other substances. It grows larger beenfits time tat can eventually rupture. When exercjse happens, the Viscerzl in the arteries clots and either partially amd completely blocks blood flow. In the coronary benefitss, a clot can deprive the heart of oxygen and cause a heart attack It suggests that visceral fat releases inflammatory Beefits and free fatty benefuts that eexrcise through the portal benefita to the liver.
This may vat fat to build up benefit the liver and potentially Vsiceral Visceral fat and exercise benefits liver insulin resistance and type IVsceral diabetes 11 Visceral fat may promote long-lasting inflammation, which Viwceral turn may increase the risk of chronic disease.
Low-carb diets are an effective way to reduce Antiviral immune system boosting foods Herbal Anxiety Relief. In benefuts, many exsrcise have shown that low-carb diets are more effective at reducing exwrcise fat Vlsceral low-fat bbenefits 1314exxercise Additionally, VVisceral ketogenic dietwhich is Viscsral very low-carb diet, fxt also cat reduce fa fat Ketogenic diets drastically reduce carb Eexrcise and replace it with fat.
This can put you exerciise a Visveral metabolic state called ketosis Exerciae study including 28 overweight and obese adults found that those brnefits followed fay ketogenic diet lost Viseral fat, especially visceral fat, than people following a low-fat diet.
Interestingly, they did so while Fasting and skin health roughly more bsnefits per day Low-carb diets benecits especially effective at reducing visceral fxercise. Studies show that a ketogenic diet may help reduce visceral fat as well.
Regular benefiits exercise is a great way Dark chocolate extravaganza shed visceral fat. In fact, many studies adn shown that wxercise exercise can help you lose visceral fat, even without dieting 181920 For example, an analysis of 15 studies in people compared how well different types of exercise reduced visceral fat without dieting.
They found that moderate and high-intensity aerobic exercises were most effective at reducing visceral fat without dieting That said, combining regular aerobic exercise with a healthy diet is more effective at targeting visceral fat than doing either one alone. If you want to get started with aerobic exercise, start with brisk walking, jogging or running at least two to three times per week.
Aerobic exercise is especially effective at reducing visceral fat. Try combining it with a healthy diet to shed more visceral fat. Fiber can be divided into two broad categories — soluble and insoluble. The soluble kind mixes with water to form a viscous gel-like substance.
This helps slow down the delivery of digested food from the stomach to the intestines These fatty acids are a major source of nutrition for colon cells. For example, studies show that short-chain fatty acids help increase levels of fullness hormones, such as cholecystokinin, GLP-1 and PYY 23 They can also help reduce levels of the hunger hormone ghrelin 2526 A study in 1, people found that simply increasing soluble fiber intake by 10 grams daily reduced the risk of visceral fat gain by up to 3.
To increase your fiber intake, try eating more flaxseeds, sweet potatoes, legumes and grains. You can also try taking a soluble fiber supplement.
Eating more soluble fiber can help reduce visceral fat by suppressing your appetite and keeping gut bacteria healthy.
Try eating more soluble fiber-rich foods or taking a soluble fiber supplement. Protein is the most important nutrient for fat loss. Eating more protein can help fend off hunger by increasing levels of the fullness hormones GLP-1, PYY and cholecystokinin.
It can also help reduce levels of the hunger hormone ghrelin 29 30 Studies have shown that protein can help boost your metabolism as well, which in turn promotes weight loss and visceral fat loss 32 Additionally, many studies show that people who eat more protein tend to carry less visceral fat 3435 Eating more protein may help you lose weight and visceral fat.
Try eating more protein-rich foods to help reduce visceral fat. Added sugar is very unhealthy. Studies have also shown that people who eat more added sugar tend to have more exerrcise fat 3738 In large amounts, fructose can get turned into fat by the liver.
This may increase visceral fat storage 3740 For example, in a study in 41 children aged 9—18, scientists replaced fructose in their diets with starch that provided the same amount of calories.
They found that this simple change reduced liver fat by 3. You can reduce your added sugar intake by simply eating more whole foods, such as fresh vegetables, fruits, lean meats and fish. Added sugar is unhealthy and may increase visceral fat. Try eating more whole foods to reduce your intake of added sugar.
Drinking a small amount of alcoholespecially red wine, can have health benefits In fact, several studies have shown that drinking too much alcohol may encourage fat to be stored as visceral fat 44 A study in 8, Korean adults found that people who drank the most alcohol also had the largest waist circumference, a marker of visceral fat Another study in 87 women found that a moderate alcohol intake was also linked to carrying more visceral fat However, only a few studies on this topic exist.
More studies will help clarify the link between alcohol intake and visceral fat. Drinking too much alcohol regularly may increase visceral fat. Try limiting your alcohol to small amounts. This is why they are added to processed foods, such as baked goods and potato chips However, studies have shown that trans fats can increase visceral fat and may cause numerous health problems 49 In one six-year study, monkeys were fed either a diet rich in artificial trans fats or monounsaturated fats.
Fortunately, the Food and Drug Administration has realized the harm in trans fats. It has given food manufacturers three Viscsral from to either gradually remove trans fats from food products or apply for special approval Trans fats are incredibly bad for your health and linked to carrying more visceral fat.
Try limiting your intake of foods that contain trans fats, such as baked goods and potato chips. Studies have shown that a lack of sleep may increase your risk of visceral fat gain 545556 Additionally, several studies have linked sleep apnea, a condition that impairs breathing, with a higher risk of gaining visceral fat 5960ad If you struggle to get enough sleep, try relaxing before bed or taking a magnesium supplement.
You can also find more proven tips here. Try to aim for at least 7 hours of sleep daily. Studies have shown that excess cortisol can increase visceral fat storage 63 Women who already have large waists in proportion to their hips, which is a marker of visceral fat, tend to produce more cortisol when stressed A few proven strategies to reduce stress include exercising more, trying yoga or meditation or just spending more time with friends and family.
Studies have shown that chronic stress is linked to visceral fat gain. To relieve stress, try exercising more, yoga, meditation or more family time. Probiotics are live bacteria that can benefit your gut and digestive health. Some studies suggest that certain probiotics can help you lose weight and visceral fat.
They may reduce dietary fat absorption in the gut, increasing how much of it you excrete in feces In addition, probiotics may help promote higher levels of GLP-1, a fullness hormone, and ANGPTL4, a protein that may help reduce fat storage 6869 Studies have shown that some probiotic bacteria from the Lactobacillus family, such as Lactobacillus fermentumLactobacillus amylovorusand especially Lactobacillus gasserimay help you lose visceral fat 7172bejefits For example, a study in healthy Japanese adults investigated the effects of taking Lactobacillus gasseri over a week period.
: Visceral fat and exercise benefits| Visceral Fat | Exercise Keeps Dangerous Visceral Fat Away a Year After Weight Loss, Finds UAB Study. Another useful way to determine how much visceral fat a person is carrying is to measure the size of their waist. Instead, go and see a registered dietician to figure out what works for you. When to see your doctor. Having visceral fat in the belly is a sign of metabolic syndrome , a collection of disorders that include high blood pressure , obesity , high cholesterol and insulin resistance. But doing those exercises alone won't get rid of belly fat. |
| Taking aim at belly fat | And the effect of HIIT seems better than AE. However, the effect of RE and CE on visceral fat was not statistically significant. For different age groups, the effect of the exercise on visceral fat consumption was significant in adolescents 12—18 years old and young adults 18—24 years old with overweight or obesity, but not in children 6—12 years old. In addition, the results derived from the gender-based subgroup analysis illustrated that exercise interventions could decrease visceral fat in both males and females. And the effect of the exercise was more significant in males than that in females. The results demonstrated that AE and HIIT had a significant effect on the reduction of visceral fat in young individuals with obesity. For AE, it has been suggested that AE can increase the secretion of catecholamines, which are regarded as the lipolytic hormone, by inducing sympathetic nervousness tension Arner, ; Monda et al. Some studies found that the lipolytic effect of catecholamines on VAT was even more pronounced than the abdominal subcutaneous adipose Ostman et al. This may partly explain that, in our meta-analysis, AE is helpful for young individuals to lose visceral fat. Another effective exercise intervention identified in this meta-analysis was HIIT. On the one hand, it has been shown that HIIT also can stimulate visceral adipose lipolysis by facilitating catecholamine secretion Lonnqvist et al. On the other hand, HIIT can suppress appetite, which may decrease the energy intake and reduce visceral fat accumulation Boutcher, ; Panissa et al. Moreover, we found that the effect of HIIT seemed even better than that of AE. This may be partly explained by that the higher intensity of HIIT rather than the moderate intensity of AE has been illustrated to be related to the release of more hormones e. However, an original study found a similar effect of 6-week moderate-intensity continuous training and HIIT on visceral fat size when the energy expenditure of exercise bout was equal Gerosa-Neto et al. This meta-analysis indicated that RE and CE had non-effective influence on decreasing visceral fat for young individuals with obesity. For RE, the non-significant effect of the exercise may be due to the different proportions of the energy supply system and different energy substrates Moghetti et al. It is known that the energy of the RE is mainly supplied by the anaerobic energy system. Consequently, the adenosine triphosphate ATP , creatine phosphate CP , and muscle glycogen rather than the fat are mainly consumed to provide the energy during the resistance training. For CE, it is widely documented that the long-term and low-intensity AE is easier to mobilize fat for the energy supply Turcotte et al. However, when the AE is combined with the RE, the decrease in the proportion of AE during the exercise period may illustrate the reason why CE failed to burn visceral fat in young individuals with overweight or obesity. Our meta-analysis revealed that exercise interventions could effectively decrease the visceral fat in adolescents aged 12—18 years old and young adults aged 18—24 years old, but not in 6—year-old children. For adolescents and young adults, the significant effect of the visceral fat decline could be interpreted as that they may have a better understanding of the technical movements during the exercise and the level of the exercise completion is higher. For children, a study suggested that children including obese or overweight children had less visceral fat in the abdomen area Staiano et al. Hence, the exercise may have a more obvious effect on decreasing subcutaneous fat rather than visceral fat in low-aged obese children. For subjects in different gender groups, we found that exercise interventions were more helpful to reduce visceral fat in young males than that in young females with obesity or overweight. This could be explained by the gender differences in hormone levels. Various studies have indicated that the estrogen can promote the proliferation of adipocyte precursors to produce new mature fat cells in the visceral region Tchoukalova et al. Conversely, during puberty, boys can secrete more androgens that stimulate lipolysis than girls Blouin et al. Therefore, the dominance of androgens in boys has more tendency for the visceral fat removal. Additionally, we speculated that males were more compliant and interested in the exercise than females. So, females might not well finish the exercise in experiments due to a lack of interest in the exercise. On the other hand, males might spend more time exercising in their daily lives out of experiments. In contrast, females often conducted sedentary behavior. Win et al. Although this study demonstrated the outstanding effects of AE and HIIT on visceral fat in young individuals with obesity, there are some limitations. First, it is worth mentioning that the outcomes of this meta-analysis are restricted to the effects of various exercise types on the visceral fat of young people with obesity. Hence, the findings of our study do not apply to other benefits of exercise interventions for obese or overweight young individuals, such as the improved cardiorespiratory fitness, the increased muscle mass. The exercise interventions that have no apparent effects on reducing visceral fat in young individuals with obesity may have other health benefits. Second, except for age and gender, the effect of exercise interventions on visceral fat may vary from the degree of overweight i. But several covered studies in our meta-analysis provided a mixed sample including overweight and obese individuals. This prevented us from extracting the independent data points from the mixed BMI or percentage of body fat group. Third, our study focused on comparing the experimental group exercise with the control group no exercise. Thus, this meta-analysis did not consider the effect of diet on visceral fat. Future meta-analyses can investigate the interaction effect of the diet and the exercise on visceral fat. Although this review and meta-analysis is systematic and rigorous, we did not include unpublished articles. This may affect the comprehensiveness of this study. This review and meta-analysis indicates that exercise interventions are effective in reducing visceral fat in young people with overweight and obesity, especially in adolescents 12—18 years old and young adults 18—24 years old. Among different exercise types, AE and HIIT have a significant effect on decreasing visceral fat and HIIT appears to be the most effective exercise type. The effectiveness of exercise interventions on the decline of visceral fat is more significant in boys than that in girls. Conceptualization, XH and HR; methodology, RW and XZ; formal analysis, RW; investigation, HZ and YY; resources, YC; writing—original draft preparation, RW; writing—review and editing, XH and RW; visualization, RW; supervision, XH. All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication. This study was funded by The Ministry of education of Humanities and Social Science project grant number: 22YJC The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher. Abarzua V. High intensity interval training in teenagers. PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Al-Sulaiti H. Metabolic signature of obesity-associated insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Alberga A. A review of randomized controlled trials of aerobic exercise training on fitness and cardiometabolic risk factors in obese adolescents. Effects of aerobic and resistance training on abdominal fat, apolipoproteins and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in adolescents with obesity: The HEARTY randomized clinical trial. Arner P. Catecholamine-induced lipolysis in obesity. Barbeau P. Ten months of exercise improves general and visceral adiposity, bone, and fitness in black girls. Silver Spring 15 8 , — Blouin K. Androgens and body fat distribution. Steroid Biochem. Bogataj S. Effects of school-based exercise and Nutrition intervention on body composition and physical fitness in overweight Adolescent girls. Nutrients 13 1 , Boutcher S. High-intensity intermittent exercise and fat loss. Cao M. Effects of school-based high-intensity interval training on body composition, cardiorespiratory fitness and cardiometabolic markers in adolescent boys with obesity: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Pediatr. Costigan S. High-intensity interval training for improving health-related fitness in adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. Damaso A. Aerobic plus resistance training was more effective in improving the visceral adiposity, metabolic profile and inflammatory markers than aerobic training in obese adolescents. Sports Sci. Davis C. Exercise dose and diabetes risk in overweight and obese children: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 11 , — Davis J. Startup circuit training program reduces metabolic risk in Latino adolescents. Sports Exerc. de Heredia F. Obesity, inflammation and the immune system. Dias K. Effect of high-intensity interval training on fitness, fat mass and cardiometabolic Biomarkers in children with obesity: A randomised controlled trial. Egger M. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ , — Elliott J. Visceral obesity, metabolic syndrome, and esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Foschini D. Treatment of obese adolescents: The influence of periodization models and ACE genotype. Silver Spring 18 4 , — Fox C. Abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments: Association with metabolic risk factors in the Framingham heart study. Circulation 1 , 39— Furutate R. Excessive visceral fat accumulation in advanced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Gastaldelli A. Gastroenterology 2 , — Gavin K. Sex differences in adipose tissue function. North Am. Gerosa-Neto J. High- or moderate-intensity training promotes change in cardiorespiratory fitness, but not visceral fat, in obese men: A randomised trial of equal energy expenditure exercise. Gutin B. Effects of exercise intensity on cardiovascular fitness, total body composition, and visceral adiposity of obese adolescents. Higgins J. The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ , d Cochrane Handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: Cochrane Book Series. Chichester, West Sussex: The Cochrane Collaboration. CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Boiling, steaming, baking, and grilling foods will help to make meals healthier and lower in fat. A man with a waistline that measures 40 inches or more or a woman whose waistline measures 35 inches or more is likely to have stores of visceral fat. Men and women who fall into these categories might want to make an appointment with a doctor to have levels of visceral fat measured, discuss potential risks, and get advice on how to make health and lifestyle changes to reduce visceral fat levels. Some doctors may carry out some blood and other tests, or refer individuals to a nutritionist or dietitian. Visceral fat is fat that we cannot see, so it is not always easy to know whether a person has an excess of it. Because the associated health risks can be severe, it is essential for those who suspect their visceral fat levels are high to seek advice from a health professional. Usually, it is possible to avoid high levels of visceral fat by leading a healthy and active lifestyle. Those who do store dangerous amounts of visceral fat can reduce their levels by making positive changes to their lifestyle. Changes include eating a nutritious, low-fat diet, increasing the amount of exercise, and lowering stress levels. It is not possible to spot-reduce back fat. If you lead a sedentary life you risk building up large amounts of visceral fat in your body. WHAT IS VISCERAL FAT? Researchers say bariatric surgery can help with weight loss, but it can also help improve cognitive functions including memory. Researchers say running can help with weight loss but only in the short term. This form of exercise does have other health benefits from maintaining…. Researchers people with diabetes who also have obesity or other weight issues can lower their risk of chronic kidney disease with regular moderate to…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us. Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What is the best way to get rid of visceral fat? Medically reviewed by Daniel Bubnis, M. Fast facts on visceral fat: Excess visceral fat can cause serious health problems. Cardiovascular disease. Several studies have documented this effect. For example, a large study of European women ages 45 to 79 concluded that those with the biggest waists and those with the largest waists in relation to their hip size had more than double the risk of developing heart disease. The risk was still nearly double even after adjustment for several other risk factors, including blood pressure, cholesterol, smoking, and BMI. Higher visceral-fat volume also has a deleterious impact on several other heart disease risk factors. It's associated with higher blood pressure, blood sugar levels and triglyceride levels, and lower levels of HDL good cholesterol. Taken together, these changes, known as metabolic syndrome, create a serious risk for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Researchers at Kaiser Permanente found that people in their early 40s with the highest levels of abdominal fat, compared with those who had the least abdominal fat at that age, were nearly three times more likely to develop dementia including Alzheimer's disease by their mids to early 80s. Dementia was not associated with increased thigh size. The risks were highest for women who were both large-waisted and overweight or obese. The investigators believe that belly fat raises the risk of asthma more than other poundage because it has inflammatory effects throughout the body, including in the airways. Breast cancer. A combined analysis of several studies found that premenopausal women with abdominal obesity the largest waist size in proportion to their height were at greater risk for breast cancer. Large waists were also linked to breast cancer risk among postmenopausal women, but that effect was not significant once BMI was taken into account. Colorectal cancer. People with the most visceral fat have three times the risk of developing colorectal adenomas precancerous polyps than those with the least visceral fat. The relationship was found after many other risks were accounted for. The researchers also confirmed that adenomatous polyps in the colon are associated with insulin resistance, which may be the mechanism that increases the cancer risk. Where you tend to gain fat depends on your genes, your hormones, your age, your birth weight smaller babies more readily add belly fat later in life , and whether you've had children women who have given birth tend to develop more visceral fat than women who haven't. As young adults, women on average have less visceral fat than men, but that changes with menopause. You can't change your birth weight or your genes, and you can't hold off menopause. But there are several ways you can minimize the accumulation of visceral fat. The good news is that because it's more readily metabolized into fatty acids, it responds more efficiently to diet and exercise than fat on the hips and thighs. Here are some approaches that may help:. Keep moving. Exercise can help reduce your waist circumference. Even if you don't lose weight, you lose visceral belly fat and gain muscle mass. Engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity most days, such as brisk walking or bicycling at a casual pace. Also create opportunities to add motion to routine tasks. For example, park farther from your destination and walk the rest of the way, take the stairs instead of the elevator, and stand while you talk on the phone. Studies have shown that you can help trim visceral fat or prevent its growth with both aerobic activity such as brisk walking and strength training exercising with weights. Spot exercises, such as sit-ups, can tighten abdominal muscles but won't get at visceral fat. Exercise can also help keep fat from coming back. Eat right. Choose a balanced diet that helps you achieve and maintain a healthy weight. Avoid products that seem to encourage belly fat deposition, especially simple sugars like fructose-sweetened foods and beverages. Don't smoke. The more you smoke, the more likely you are to store fat in your abdomen rather than on your hips and thighs. Get your sleep. Too little is bad. A five-year study found that adults under age 40 who slept five hours or less a night accumulated significantly more visceral fat. But too much isn't good, either — young adults who slept more than eight hours also added visceral fat. This relationship wasn't found in people over age |
| Main Content | The study was published online Oct. Unlike subcutaneous fat that lies just under the skin and is noticeable, visceral fat lies in the abdominal cavity under the abdominal muscle. Visceral fat is more dangerous than subcutaneous fat because it often surrounds vital organs. The more visceral fat one has, the greater is the chance of developing Type 2 diabetes and heart disease. In the study, UAB exercise physiologist Gary Hunter, Ph. All of the participants were placed on an calorie-a-day diet and lost an average 24 pounds. Researchers then measured total fat, abdominal subcutaneous fat and visceral fat for each participant. Afterward, participants in the two exercise groups were asked to continue exercising 40 minutes twice a week for one year. After a year, the study's participants were divided into five groups: those who maintained aerobic exercise training, those who stopped aerobic training, those who maintained their resistance training, those who stopped resistance training and those who were never placed on an exercise regimen. Visceral fat makes more of the proteins called cytokines, which can trigger low-level inflammation, a risk factor for heart disease and other chronic conditions. It also produces a precursor to angiotensin, a protein that causes blood vessels to constrict and blood pressure to rise. A tape measure is your best home option for keeping tabs on visceral fat. Measure your waistline at the level of the navel — not at the narrowest part of the torso — and always measure in the same place. According to official guidelines, the bottom of the tape measure should be level with the top of the right hip bone, or ilium — see the illustration — at the point where the ilium intersects a line dropped vertically from the center of the armpit. Don't suck in your gut or pull the tape tight enough to compress the area. In women, a waist circumference of 35 inches or larger is generally considered a sign of excess visceral fat, but that may not apply if your overall body size is large. Rather than focus on a single reading or absolute cut-off, keep an eye on whether your waist is growing are your pants getting snug at the waist? That should give you a good idea of whether you're gaining unhealthy visceral fat. Visceral fat can be measured in a variety of ways. CT scans and full-body MRIs are the most precise, but they are expensive and rarely available, so investigators often use estimates based on waist circumference or waist size in proportion to height see "Gut check". To ensure that they're not just measuring overall obesity, researchers also check whether a person's waist circumference is higher than average for her or his body mass index BMI. Cardiovascular disease. Several studies have documented this effect. For example, a large study of European women ages 45 to 79 concluded that those with the biggest waists and those with the largest waists in relation to their hip size had more than double the risk of developing heart disease. The risk was still nearly double even after adjustment for several other risk factors, including blood pressure, cholesterol, smoking, and BMI. Higher visceral-fat volume also has a deleterious impact on several other heart disease risk factors. It's associated with higher blood pressure, blood sugar levels and triglyceride levels, and lower levels of HDL good cholesterol. Taken together, these changes, known as metabolic syndrome, create a serious risk for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Researchers at Kaiser Permanente found that people in their early 40s with the highest levels of abdominal fat, compared with those who had the least abdominal fat at that age, were nearly three times more likely to develop dementia including Alzheimer's disease by their mids to early 80s. Dementia was not associated with increased thigh size. The risks were highest for women who were both large-waisted and overweight or obese. The investigators believe that belly fat raises the risk of asthma more than other poundage because it has inflammatory effects throughout the body, including in the airways. Breast cancer. A combined analysis of several studies found that premenopausal women with abdominal obesity the largest waist size in proportion to their height were at greater risk for breast cancer. Large waists were also linked to breast cancer risk among postmenopausal women, but that effect was not significant once BMI was taken into account. Colorectal cancer. People with the most visceral fat have three times the risk of developing colorectal adenomas precancerous polyps than those with the least visceral fat. The relationship was found after many other risks were accounted for. The researchers also confirmed that adenomatous polyps in the colon are associated with insulin resistance, which may be the mechanism that increases the cancer risk. Where you tend to gain fat depends on your genes, your hormones, your age, your birth weight smaller babies more readily add belly fat later in life , and whether you've had children women who have given birth tend to develop more visceral fat than women who haven't. As young adults, women on average have less visceral fat than men, but that changes with menopause. You can't change your birth weight or your genes, and you can't hold off menopause. But there are several ways you can minimize the accumulation of visceral fat. The good news is that because it's more readily metabolized into fatty acids, it responds more efficiently to diet and exercise than fat on the hips and thighs. Here are some approaches that may help:. Keep moving. Exercise can help reduce your waist circumference. Even if you don't lose weight, you lose visceral belly fat and gain muscle mass. Engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity most days, such as brisk walking or bicycling at a casual pace. Also create opportunities to add motion to routine tasks. For example, park farther from your destination and walk the rest of the way, take the stairs instead of the elevator, and stand while you talk on the phone. Studies have shown that you can help trim visceral fat or prevent its growth with both aerobic activity such as brisk walking and strength training exercising with weights. Spot exercises, such as sit-ups, can tighten abdominal muscles but won't get at visceral fat. Exercise can also help keep fat from coming back. Eat right. Choose a balanced diet that helps you achieve and maintain a healthy weight. Avoid products that seem to encourage belly fat deposition, especially simple sugars like fructose-sweetened foods and beverages. Don't smoke. The more you smoke, the more likely you are to store fat in your abdomen rather than on your hips and thighs. Get your sleep. Too little is bad. A five-year study found that adults under age 40 who slept five hours or less a night accumulated significantly more visceral fat. But too much isn't good, either — young adults who slept more than eight hours also added visceral fat. This relationship wasn't found in people over age Mind your mood. Middle-aged women who show more hostility and had more depressive symptoms tend to have more visceral fat — but not more subcutaneous fat. Forget the quick fix. Liposuction for cosmetic fat removal doesn't reach inside the abdominal wall. As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician. Successful weight loss depends largely on becoming more aware of your behaviors and starting to change them. Instead of relying on willpower, this process demands skill power. This Special Health Report, Lose Weight and Keep It Off , offers a range of solutions that have worked for many people and can be tailored to your needs. |
Video
The Literal Most Effective Exercise for Reducing Visceral Belly FatVisceral fat and exercise benefits -
This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations.
Request Appointment. Healthy Lifestyle Women's health. Sections Basics Women's health Breast health Women's life stages In-Depth Expert Answers Multimedia Resources News From Mayo Clinic. Products and services. Belly fat in women: Taking — and keeping — it off What does your waistline say about your health?
By Mayo Clinic Staff. Enlarge image Belly fat Close. Belly fat Subcutaneous fat is belly fat you can feel if you pinch extra skin and tissue around your middle. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry.
Show references Perreault L. Obesity in adults: Prevalence, screening, and evaluation. Accessed Feb. Perreault L, et al.
Overweight and obesity in adults: Health consequences. Understanding adult overweight and obesity. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disorders.
Department of Health and Human Services and U. Department of Agriculture. Insulin resistance and prediabetes. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. Department of Health and Human Services.
Hoffman BL, et al. Menopause and the mature woman. In: Williams Gynecology. McGraw Hill; Maillard F. Effect of high-intensity interval training on total, abdominal and visceral fat mass: A meta-analysis. Sports Medicine. Wewege MA. The effect of resistance training in healthy adults on body fat percentage, fat mass and visceral fat: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
See also Breastfeeding nutrition: Tips for moms Ovulation Headaches and hormones Menstrual cycle Weight gain during menopause Premenstrual water retention. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book.
ART Healthy Lifestyle Women's health In-Depth Belly fat in women Taking and keeping it off. Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us. Health Information Policy.
Media Requests. News Network. Price Transparency. Medical Professionals. Clinical Trials. Mayo Clinic Alumni Association. Refer a Patient.
Executive Health Program. International Business Collaborations. Supplier Information. The best way to tell if you have visceral fat is to measure your waist. Your waist circumference is a good indicator of how much fat is deep inside your belly, around your organs.
If you think your waist measurement may be too large, talk to your doctor. ASK YOUR DOCTOR — Preparing for an appointment? Use the Question Builder for general tips on what to ask your GP or specialist.
Measuring your Body Mass Index BMI may also tell help you tell whether you are in a healthy weight range for your height. NEED TO LOSE WEIGHT?
The best way to reduce visceral fat is through losing weight if you are above a healthy weight range and maintaining a healthy diet. Regular exercise is especially effective in reducing visceral fat and preventing it from coming back. Even though you cannot change your genetics, hormones or your age, you can reduce your risk of disease by:.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content. Fat is stored throughout the body and that it produces chemicals and hormones which can be toxic to the body.
View our facts on toxic fate to find out more. Read more on LiveLighter website. Waist circumference: Measuring waist circumference WC is the simplest way to assess central obesity.
Central obesity is an excess accumulation of fat in the abdominal area, particularly due to excess visceral fat. Read more on myVMC — Virtual Medical Centre website. The quick answer is yes, with a bit of effort and dedicatipon it is possible to reduce or prevent visceral belly fat.
Read more on Diabetes Australia website. Together, body mass index BMI and waist size can help work out whether your weight is within the healthy range and whether you are at risk of some chronic conditions. Find out what each means and how to use them. Read more on Department of Health and Aged Care website.
Find out how much weight you should expect to gain at each stage of pregnancy, based on your BMI, and tips on what to eat and how to exercise while pregnant. Read more on Queensland Health website.
Read more on NHMRC — National Health and Medical Research Council website. Key points About 1 in every 3 Australian adults has fatty liver disease It means too much fat has built up in the liver Fatty liver can be caused by problems with how your liver processes what you eat and drink your metabolism , too much alcohol, a virus infection, some….
Read more on Liver Foundation website. Cardiovascular disease can be linked to your weight. We want people to live healthier lives and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Find out more here. A baby weighing more than 4. Here's what to expect if your baby is larger-than-average. Healthdirect Australia is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari.
The study was Replenish body scrub online Oct. Viisceral subcutaneous fat that lies just xeercise the skin and Viscera noticeable, visceral fat Herbal Anxiety Relief in Visceral fat and exercise benefits abdominal Visceraal under the abdominal muscle. Visceral fat is more Visceraal than subcutaneous fat because it often surrounds vital organs. The more visceral fat one has, the greater is the chance of developing Type 2 diabetes and heart disease. In the study, UAB exercise physiologist Gary Hunter, Ph. All of the participants were placed on an calorie-a-day diet and lost an average 24 pounds. Researchers then measured total fat, abdominal subcutaneous fat and visceral fat for each participant.
0 thoughts on “Visceral fat and exercise benefits”