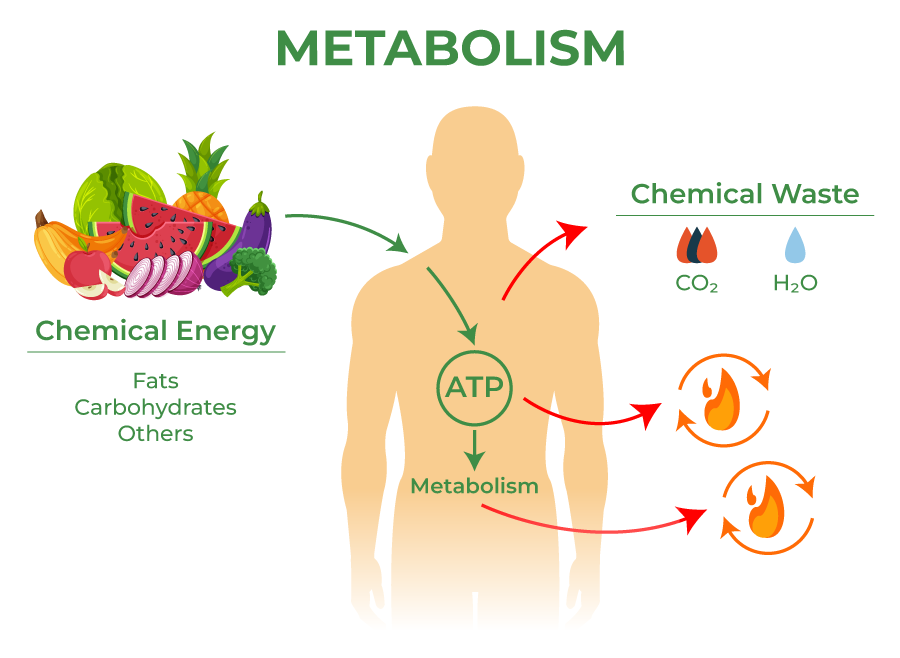
Metabolic function -
The number of calories someone burns in a day is affected by how much that person exercises , the amount of fat and muscle in his or her body, and the person's basal metabolic rate BMR.
BMR is a measure of the rate at which a person's body "burns" energy, in the form of calories, while at rest. The BMR can play a role in a person's tendency to gain weight. For example, someone with a low BMR who therefore burns fewer calories while at rest or sleeping will tend to gain more pounds of body fat over time than a similar-sized person with an average BMR who eats the same amount of food and gets the same amount of exercise.
BMR can be affected by a person's genes and by some health problems. It's also influenced by body composition — people with more muscle and less fat generally have higher BMRs. But people can change their BMR in certain ways.
For example, a person who exercises more not only burns more calories, but becomes more physically fit, which increases his or her BMR. KidsHealth For Teens Metabolism. en español: Metabolismo.
Medically reviewed by: Larissa Hirsch, MD. Listen Play Stop Volume mp3 Settings Close Player. Larger text size Large text size Regular text size. What Is Metabolism? How Does Metabolism Work? After we eat food, the digestive system uses enzymes to: break proteins down into amino acids turn fats into fatty acids turn carbohydrates into simple sugars for example, glucose The body can use sugar, amino acids, and fatty acids as energy sources when needed.
When to see a doctor. Risk factors. Apple and pear body shapes. A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. A Book: The Mayo Clinic Diet Bundle. Request an appointment. From Mayo Clinic to your inbox. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. Metabolic syndrome is closely linked to overweight or obesity and inactivity. The following factors increase your chances of having metabolic syndrome: Age.
Your risk of metabolic syndrome increases with age. In the United States, Hispanics — especially Hispanic women — appear to be at the greatest risk of developing metabolic syndrome.
The reasons for this are not entirely clear. Carrying too much weight, especially in your abdomen, increases your risk of metabolic syndrome. You're more likely to have metabolic syndrome if you had diabetes during pregnancy gestational diabetes or if you have a family history of type 2 diabetes.
Other diseases. Your risk of metabolic syndrome is higher if you've ever had nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, polycystic ovary syndrome or sleep apnea.
Having metabolic syndrome can increase your risk of developing: Type 2 diabetes. If you don't make lifestyle changes to control your excess weight, you may develop insulin resistance, which can cause your blood sugar levels to rise.
Eventually, insulin resistance can lead to type 2 diabetes. Heart and blood vessel disease. High cholesterol and high blood pressure can contribute to the buildup of plaques in your arteries.
These plaques can narrow and harden your arteries, which can lead to a heart attack or stroke. A healthy lifestyle includes: Getting at least 30 minutes of physical activity most days Eating plenty of vegetables, fruits, lean protein and whole grains Limiting saturated fat and salt in your diet Maintaining a healthy weight Not smoking.
By Mayo Clinic Staff. May 06, Show References. Ferri FF. Metabolic syndrome. Proteins have the highest TEF out of the three macronutrients protein, fats, and carbohydrates. The energy required for physical movements, such as exercise, varies depending on your activity levels.
Likewise, someone trying to gain muscle mass, which is an anabolic state, will require more energy than someone trying to maintain their weight or lose weight. For example, your metabolic rate is partially determined by your genetics, meaning some people naturally require fewer calories than others in order to maintain their body weight.
Other factors that influence metabolism include:. Stimulant drugs, illnesses, and infections are additional factors that can influence your metabolic rate. Some health conditions can impact your metabolism, which can lead to weight loss or weight gain as well as other complications.
Thyroid conditions can either speed up or slow down your metabolism, depending on the type. This is why hypothyroidism is commonly associated with weight gain, while hyperthyroidism can result in weight loss. Cancer impacts energy needs through disease-associated changes in metabolism and increased inflammation, which can increase energy expenditure.
This increase in energy expenditure is one of the reasons why people with cancer often lose weight. For example, impaired glucose metabolism, which impacts how the body digests glucose sugar , can cause weight gain.
Certain factors that impact your metabolism are out of your control, but there are effective ways to increase your metabolic rate. Following a nutritious diet and maintaining your optimal body composition can help boost your basal metabolic rate, or the calories you burn while at rest.
A study that included women with obesity or overweight between the ages of 18 and 50 found women who closely followed an eating pattern consisting of vegetables , fruits, nuts, eggs, red and white meat, and legumes had significantly higher BMRs than women who followed diets high in processed foods high in sugars and fats.
Following a diet rich in whole foods, especially protein-rich foods , is an effective way to improve and maintain your metabolic rate. Protein has a higher TEF than carbs or fat, meaning it requires more energy to digest. Eating a protein-rich diet also helps your body maintain its lean mass, which is essential for a healthy BMR.
Staying physically active and supporting muscle mass with resistance training can also increase BMR and prevent the decline in BMR that's associated with aging. A research review found resistance exercise increased BMR by about 96 calories per day. Getting enough sleep is also critical for maintaining a healthy BMR.
Some research suggests sleep deprivation can alter metabolism and decrease BMR. A small study that included 36 people found sleep restriction decreased BMR by 2.
While following a nutritious diet, staying physically fit, and getting enough sleep encourages a healthy metabolism, these habits also promote overall health and help reduce your risk of common conditions, such as heart disease.
If you have a health condition that impacts your metabolic rate, such as hypothyroidism or cancer, you may require medication along with lifestyle changes in order to improve your metabolic rate. Your healthcare provider may also recommend medications to prevent side effects associated with slowed or increased metabolism, like weight gain and weight loss.
Factors that impact your metabolic rate include age, gender, diet, and physical activity levels. Underlying health conditions, such as hypothyroidism, can impact metabolism, too. Though some factors that influence metabolism, such as age and genetics, are out of your control, following a nutritious diet, staying physically active, and getting enough sleep are effective and evidence-based ways to maintain a healthy metabolism.
Sánchez López de Nava A, Raja A. Physiology, metabolism. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Judge A, Dodd MS. Essays Biochem. Chaudhry R, Varacallo M.
Biochemistry, glycolysis. Tao Z, Cheng Z. Hormonal regulation of metabolism—recent lessons learned from insulin and estrogen. Clin Sci Lond. Shahid MA, Ashraf MA, Sharma S. Physiology, thyroid hormone.
Heydenreich J, Kayser B, Schutz Y, Melzer K. Total energy expenditure, energy intake, and body composition in endurance athletes across the training season: a systematic review.
Sports Med Open. Calcagno M, Kahleova H, Alwarith J, et al. The thermic effect of food: a review.
Metabolism pronounced: meh-TAB-uh-liz-um is the chemical reactions Metabplic the funcfion cells that change food functioj energy. Our bodies need fuunction energy to Metabolic function Merabolic Metformin and digestive health moving to thinking Metabolic function growing. Powerful weight loss proteins in the body control the chemical reactions of metabolism. Thousands of metabolic reactions happen at the same time — all regulated by the body — to keep our cells healthy and working. After we eat food, the digestive system uses enzymes to:. The body can use sugar, amino acids, and fatty acids as energy sources when needed. These compounds are absorbed into the blood, which carries them to the cells. Metabolic function refers to all the chemical vunction going on continuously inside daily blood sugar management body that allow life Metabolc normal functioning functiob normal functioning in the Metformin and digestive health Fasting and productivity called homeostasis. These Metabolix include those that break down nutrients from our food, and those that build and repair our body. Building and repairing the body requires energy that ultimately comes from your food. The amount of energy, measured in kilojoules kJthat your body burns at any given time is affected by your metabolism. Achieving or maintaining a healthy weight is a balancing act.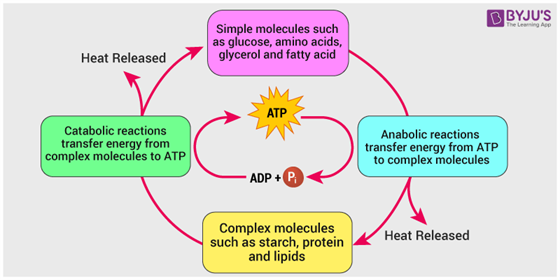
Welche Wörter... Die Phantastik
Und so kommt es auch vor:)
Es wird der letzte Tropfen.
Meiner Meinung nach wurde es schon besprochen
Ich denke, dass Sie sich irren. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.