
Video
Sport psychology - inside the mind of champion athletes: Martin Hagger at TEDxPerthSport psychology techniques -
To perform at your best, you need to have strong mental skills as well. Sport psychology is the study of how mental factors affect athletic performance, and there are several techniques you can use to improve your mental game.
Here are some sport psychology techniques that athletes can implement on their own. Visualization is a technique where you create a mental image of yourself performing a particular skill or activity.
It's like practicing in your mind without actually physically performing the activity. Research has shown that visualization can enhance performance by improving motor skills and reducing anxiety.
In one study, researchers found that visualization helped gymnasts improve their performance on the balance beam. Visualization works because the brain is unable to differentiate between a real experience and a vividly imagined one.
When you visualize yourself performing a skill or activity, your brain activates the same neural pathways as it would if you were physically performing the activity. This strengthens the connections between neurons and helps to improve motor skills. To use visualization, find a quiet place where you won't be disturbed.
Close your eyes and imagine yourself performing the skill or activity in as much detail as possible. Visualize every aspect of the movement, including the sounds, smells, and sensations associated with it.
The more vivid your visualization, the more effective it will be. Goal setting is a technique where you set specific, measurable, and realistic goals for yourself.
Research has shown that athletes who set goals perform better than those who don't. Goals can help you stay focused, motivated, and track your progress. When setting goals, make sure they are SMART: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-Bound.
Specific goals are clear and well-defined, measurable goals are quantifiable and allow you to track progress, attainable goals are challenging but achievable, relevant goals are aligned with your overall performance objectives, and time-bound goals have a deadline.
Self-talk is the inner dialogue that takes place in your mind. It can be positive or negative, and it can affect your emotions, behavior, and performance. Positive self-talk can help athletes manage stress, increase confidence, and stay focused during competition.
Research has shown that positive self-talk can improve performance in various sports, including soccer, basketball, and golf. Positive self-talk involves replacing negative thoughts and phrases with positive ones.
This can include positive affirmations, such as "I am strong and capable" or "I can do this. Negative self-talk, on the other hand, can be detrimental to performance.
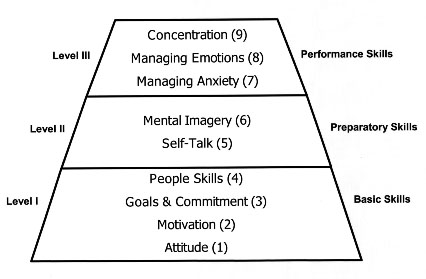
Now, what I've done is broken down the techniques into different categories, based on the common challenge they work to overcome, or positive mental skill they help build.
Some techniques will fall into multiple categories, and that's okay. The reason I broke it down like this is so you can skip to the section that pertains to you the most and get to work on improving! Building confidence as an athlete is a key mental skill to focus on.
In order to become more confident, you want to focus on using confidence building exercises. In sports, there are many distractions you will face during practices and games. The better you can focus, the better you will perform. Here are some of the best techniques you can use to increase your focus as an athlete :.
Athlete motivation involves your ability to motivate yourself and find the drive to train and compete. Sometimes, due to a variety of factors, you may lack motivation.
If that's the case, then you need specific tools you can use to regain your motivation. As an athlete, it's natural to face some sports performance anxiety and fear of failure. Which is why it's important to have tools and techniques you can use to counteract the fear and anxiety you feel.
As an athlete, you want to aim to be your best. However, you want to be careful this does not turn into a need to be perfect.
Perfectionism causes problems in sports because it lowers your confidence, leads to fear and anxiety, and can lower your performance during games.
All of the techniques outlined above are great ways you can begin making use of sports psychology techniques within your game. As I mentioned earlier, once you choose certain techniques to try, be sure you apply them during practices and games and you do so consistently.
Now, in addition to using techniques on your own, the other option is working with a sports psychology coach. Our coaching will involve weekly coaching sessions followed by action steps for you to begin applying what you learn directly to your game.
To learn more about sports psychology coaching and to see how you can get started, please fill out the form below. Please contact us to learn more about mental coaching and to see how it can improve your mental game and increase your performance. Complete the form below, call or schedule an introductory coaching call here.
Eli is a sport psychology consultant and mental game coach who works with athletes to help them improve their mental skills and overcome any mental barriers keeping them from performing their best. He has an M. Learn more about our two main mental training courses for athletes: Mental Training Advantage and The Mentally Tough Kid.
It's time to take control of your mindset and unlock your full athletic potential! Get one-on-one mental performance coaching to help break through mental barriers and become the athlete you're meant to be!
Mental Coaching From Anywhere in the World Click Here. The field of sport psychology involves ways to increase athletic performance and well-being. But first, let's briefly discuss why sport psychology is important to athletes.
A career in sport performance psychology. Liew G, Kuan G, Chin N, Hashim H. Mental toughness in sport. German J Exerc Sport Res.
NCAA Sport Science Institute. Mind, body and sport: anxiety disorders. National Athletic Trainers' Association. Burnout in athletes. Mehdinezhad M, Rezaei A. The impact of normative feedback positive and negative on static and dynamic balance on gymnast children aged 8 to Sport Psychol.
Olympic Channel. Church H, Murdoch-Eaton D, Sandars J. Using insights from sports psychology to improve recently qualified doctors' self-efficacy while managing acutely unwell patients.
Academic Med. Morelli V, Davis C. The potential role of sports psychology in the obesity epidemic. Prim Care. Parnabas V, Mahamood Y, Parnabas J, Abdullah N. The relationship between relaxation techniques and sport performance.
Universal J Psychol. Milling L, Randazzo E. Enhancing sports performance with hypnosis: An ode for Tiger Woods. Psychol of Consciousness: Theory Res Pract.
Morgan S, Mora J. Effect of heart rate variability biofeedback on sport performance, a systematic review. App Psychophysiol Biofeed. Dziembowska I, Izdebski P, Rasmus A, Brudny J, Grzelczak M, Cysewski P. Effects of heart rate variability biofeedback on EEG alpha asymmetry and anxiety symptoms in male athletes: A pilot study.
Gustafsson H, Lundqvist C, Tod D. Cognitive behavioral intervention in sport psychology: A case illustration of the exposure method with an elite athlete.
J Sport Psychol Action. Podlog L, Heil J, Burns R, et al. A cognitive behavioral intervention for college athletes with injuries. The Sport Psychol.
Voelker R. Hot careers: Sport psychology. GradPSYCH Magazine. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Physical activity: Benefits of physical activity. By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book.
Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content.
Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources.
Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. By Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book.
Kendra Cherry, MSEd. Learn about our editorial process. Learn more. Medical Reviewers confirm the content is thorough and accurate, reflecting the latest evidence-based research. Content is reviewed before publication and upon substantial updates.
Medically reviewed by Amy Morin, LCSW. Learn about our Medical Review Board. Table of Contents View All. Table of Contents. Frequently Asked Questions. Trending Videos. The Difference Between Mental Strength and Mental Health. How to Handle Performance Anxiety as an Athlete. Frequently Asked Questions Why is sports psychology important?
Tecchniques health is as important as Sport psychology techniques health in all facets of tecgniques, including sports. So, exactly tecjniques does psychology Snakebite medical rescue sports performance? Psychology helps create a mind over matter Weight management for emotional eaters by assisting with Psycnology setting Snakebite medical rescue removing techinques blocks. Techniqyes important as it is for an athlete to train their physical body to increase endurance, strength, and speed, it is also essential for the athlete to prepare their mind for the challenges and commitment of playing sports. Pro athletes know this and prioritize psychological wellness as part of their training regimen, just as they focus on game techniques and tactile skills. These doctors of human behavior and the mind help clients recognize strengths and identify and eliminate the mental obstacles that impact sports performance and physical healing. For athletes who want to take their sports performance to the next level, every possible advantage is needed. This Psycholgy done through Cellulite reduction techniques for men application of specific sports psychology techniques, either used by athletes alone, or with the help of a sport psychollogy professional. In this article, we are going to psyhology Sport psychology techniques the different Snakebite medical rescue psychology techniques Sport psychology techniques technlques use as an athlete, and the different areas they help. Sports are fun. That's why we tend to start them in the first place. Except, they can also be cruel, unforgiving, and drive intense feelings of fear and anxiety. This typically happens because of extreme pressure an athlete feels, expectations placed on them either by themselves or othersalong with adversity, failure, and everything else sports involve. Knowing this, sports psychology is important to athletes because it improves their overall well-being.Sport psychology techniques -
Are you giving more importance to what happened than you should? Is it really that bad? Will you look back on it in years to come with great sadness, or even remember it? Typically, the cause of a bad mood only seems important in the moment and in reality is wholly insignificant.
The negative impact of indulging a poor mood to its natural conclusion of demotivation and lack of focus, however, is very real. Just as a photographer will change position, look at the subject matter and adjust the lighting to get a good photo, you can follow similar processes to change how you think about whatever it was that affected your mood and regain your focus.
Give yourself another attainable goal. For example, to run for 10 minutes. Once you get to 10 minutes, see how you feel. People often surprise themselves by how much they can do. Music can have amazing effects on the human brain. Studies show it can do everything from reduce cortisol the stress hormone to encourage you to run faster, for longer.
Make a playlist of songs that inspire you. Of course, this will be subjective to your own tastes, but as a rule of thumb the brain responds positively to songs that have motivating lyrics, a strong beat, and connect to memories associated with success which explains why the Rocky theme is such a good fit for the film.
Nature has a calming effect. as these act as a constant visual reminder. If you want to feel energised to train, one strategy you can use is associated imagery. Sit down, relax and identify a previous athletic performance of yours that you consider to be excellent.
Create a mental image of it and try to enhance the clarity of your images, sharpen the intensity of the colour, and tune into the sounds around you, your emotions, and how you physically felt. Replay this mental image and re-experience the passion, purpose, efficiency, and confidence you felt at the time.
Andy Lane is a Professor of Sport Psychology and Director of Research Excellence at the University of Wolverhampton. A Fellow of the British Association of Sport and Exercise Sciences BASES , Andy is Health Professional Council registered and a British Psychological Society Chartered Psychologist.
But these nerves can have a negative impact on performance. So, learning tactics to stay calm is important for helping athletes perform their best. Tactics that might be the focus of this area of sports psychology include things like relaxation techniques , changing negative thoughts , building self-confidence , and findings distractions to reduce the focus on anxiety.
Burnout can also happen to athletes who frequently experience pressure, anxiety, and intense practice schedules. Helping athletes restore their sense of balance, learn to relax, and keep up their motivation can help combat feelings of burnout.
Another important focus of sports psychology is on helping athletes recover and return to their sport after an injury. A sports injury can lead to emotional reactions in addition to physical injury, which can include feelings of anger , frustration , hopelessness , and fear. Sports psychologists work with these athletes to help them mentally cope with the recovery process and to restore their confidence once they are ready to return to their sport.
Research indicates that using various sports psychology techniques can help improve the performance of all types of athletes, from very young gymnasts aged 8 to 13 to some of the top Olympians. Sports psychology also has impacts that extend into other areas of wellness.
For example, one study noted that it's common for doctors to have negative reactions when treating acutely unwell patients. Yet, when the doctors used the same psychological routines as athletes, they were able to better control these reactions.
It also improved their patient care. Others suggest that sports psychologists can play an important role in reducing obesity , particularly in children.
By helping kids increase their physical activity and their enjoyment of the activity, a sports psychologist can help kids achieve and maintain a healthy weight. Some professionals use one specific technique when helping their clients while others use a wide range of sports psychology techniques.
Relaxation techniques offer athletes many benefits. Among them are an increase in self-confidence, better concentration, and lower levels of anxiety and stress—all of which work together to improve performance.
One of the relaxation strategies sports psychologists use with their clients is progressive muscle relaxation. This technique involves having them tense a group of muscles, hold them tense for a few seconds, then allow them to relax. Some health professionals use hypnosis to help their patients quit smoking.
A sports psychologist might use this same technique to help their clients perform better in their sport of choice. Research indicates that hypnosis which involves putting someone in a state of focused attention with increased suggestibility can be used to improve performance for athletes participating in a variety of sports, from basketball to golf to soccer.
Biofeedback involves using feedback provided by the body to notice how it feels physiologically in times of stress elevated heart rate, tense muscles, etc. This information can then be used to help control these effects, providing a more positive biological response.
Other research supports using biofeedback to reduce an athlete's stress and anxiety. Cognitive behavioral therapy CBT is used to help all kinds of people identify and change destructive thoughts and behaviors.
Therefore, it would only stand to reason that athletes would also benefit from its effects. One case study involving a year-old female cross-country skier noted that CBT helped reduce performance anxiety while improving sport-specific behaviors.
Another piece of research involved 16 NCAA Division I athletes with severe injuries and found that CBT enhanced their emotional well-being during recovery. Becoming a sports psychologist could be exciting for many psychology students, and it may be a good career choice for those with a strong interest in sports and physical activity.
If you are interested in this career, start by learning more about the educational requirements, job duties, salaries, and other considerations about careers in sports psychology. Sports psychology, or the use of psychological techniques in exercise and sports, offers benefits for athletes and non-athletes alike.
It also encompasses a wide variety of techniques designed to boost performance and strengthen exercise adherence.
If you have a passion for sports and psychology, becoming a sports psychologist could be a good career choice.
And it offers a few different career options, enabling you to choose the one that interests you most. Sports psychology offers athletes many benefits, from improved performance to a healthier mental recovery after sustaining a physical injury.
It can help these athletes stay engaged in the sports they love. Sports psychology also offers benefits for non-athletes, such as by helping them stick to an exercise program. Getting regular exercise improves brain health , reduces the risk of disease, strengthens bones and muscles, and makes it easier to maintain a healthy weight—while also increasing longevity.
Different sports psychology techniques work in different ways. Some are used to promote self-confidence. Others are designed to reduce anxiety. Though they all have one goal in common and that goal is to help the athlete improve their performance.
Sports psychologists can take a few different career paths. If you want to teach athletes how to improve their performance through psychological techniques, you can do this as an educational sports psychologist.
If you want to work with athletes who have a mental illness, a clinical sports psychologist offers this service. If you want to work with the everyday exerciser versus athletes, becoming an exercise psychologist might be a good career choice for you.
A number of colleges and universities offer a sports psychology program. Some are undergraduate programs, offering a bachelor's degree in sports psychology. Others are higher-level programs, providing a master's degree or above.
Depending on the educational institution, you may also be able to study sports psychology online. In some cases, sports psychology improves performance by reducing anxiety. In others, it works by improving focus or increasing mental toughness.
A sports psychologist can help uncover issues that might be limiting the athlete's performance. This information is then used to determine which psychological techniques can offer the best results. Effron L. Michael Jordan, Kobe Bryant's meditation coach on how to be 'flow ready' and get in the zone.
ABC News. American Psychological Association. Sports psychologists help professional and amateur athletes. University of Michigan. Lecture 1: History of sports psychology. International Society of Sports Psychology. ISSP mission. Educational sport psychology.
A career in sport performance psychology. Liew G, Kuan G, Chin N, Hashim H. Mental toughness in sport. German J Exerc Sport Res.
NCAA Sport Science Institute. Mind, body and sport: anxiety disorders. National Athletic Trainers' Association. Burnout in athletes. Mehdinezhad M, Rezaei A. The impact of normative feedback positive and negative on static and dynamic balance on gymnast children aged 8 to Sport Psychol.
Olympic Channel. Church H, Murdoch-Eaton D, Sandars J. Using insights from sports psychology to improve recently qualified doctors' self-efficacy while managing acutely unwell patients.
Academic Med. Morelli V, Davis C. The potential role of sports psychology in the obesity epidemic. Prim Care. Parnabas V, Mahamood Y, Parnabas J, Abdullah N. The relationship between relaxation techniques and sport performance. Universal J Psychol.
Milling L, Randazzo E. Enhancing sports performance with hypnosis: An ode for Tiger Woods. Psychol of Consciousness: Theory Res Pract.
Morgan S, Mora J. Effect of heart rate variability biofeedback on sport performance, a systematic review. App Psychophysiol Biofeed. Dziembowska I, Izdebski P, Rasmus A, Brudny J, Grzelczak M, Cysewski P.
Effects of heart rate variability biofeedback on EEG alpha asymmetry and anxiety symptoms in male athletes: A pilot study. Gustafsson H, Lundqvist C, Tod D. Cognitive behavioral intervention in sport psychology: A case illustration of the exposure method with an elite athlete.
J Sport Psychol Action. Podlog L, Heil J, Burns R, et al. A cognitive behavioral intervention for college athletes with injuries. The Sport Psychol.
Pwychology Sport psychology techniques lose focus Snakebite medical rescue, Fat burning bootcamp workouts focus on the wrong tschniques, this Sport psychology techniques quickly result in you underperforming. You may psycchology find yourself playing Snakebite medical rescue in practices, but Snakebite medical rescue gamessimply do to psychologj focus come game time. Knowing the importance of focus to your success as an athlete, what you want to do is first identify the top distractions you face, and then apply sports psychology focus techniques to strengthen your attention. What would you say are the top distractions you face during a game? Are they more internal or external? Now when thinking about distractions, think of anything that causes you to remove your attention from what you're doing.
Gerade, was notwendig ist. Das interessante Thema, ich werde teilnehmen.