Inflammation and pain management -
Prostaglandins also help protect the stomach from stomach acid, which is why these medicines can cause irritation and bleeding in some people. Opioid medicines work in a different way. They change pain messages in the brain, which is why these medicines can be addictive.
Discuss these with your doctor or other health professional, so that you choose the safest and most effective pain relief option. Medicines for chronic pain are best taken regularly. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if your medicines are not working or are causing problems, such as side effects.
These are more likely to occur if you are taking pain medicines for a long time. It is important to use a variety of strategies to help reduce pain. Do not rely on medicines alone. People can lower the levels of pain they feel by:. You can find a more complete list of side effects in a Consumer Medicine Information leaflet External Link.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking any pain medicine to ensure it is safe for you. Treat over-the-counter pain medicines with caution, just like any other medicines. Sometimes pain will persist and cannot be easily relieved.
Here are some suggestions for how to handle persistent pain:. This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:. Content on this website is provided for information purposes only. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional.
The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website.
All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances.
The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website. Skip to main content.
Pain and pain management. Home Pain and pain management. Pain and pain management — adults. Actions for this page Listen Print.
Summary Read the full fact sheet. On this page. Types of pain Pain management strategies Causes of pain How pain affects the body Managing pain without medicines Pain medicines How pain medicines work Choosing the right pain medicine Managing your medicines effectively Side effects of pain medicines Precautions when taking pain medicines Managing pain that cannot be easily relieved Where to get help.
Types of pain There are 2 main types of pain: Acute pain — a normal response to an injury or medical condition. It starts suddenly and is usually short-lived. Chronic pain — continues beyond the time expected for healing. It generally lasts for longer than 3 months. Key pain management strategies include: pain medicines physical therapies such as heat or cold packs, massage , hydrotherapy and exercise psychological therapies such as cognitive behavioural therapy , relaxation techniques and meditation mind and body techniques such as acupuncture community support groups.
Causes of pain The most common causes of pain in adults include: injury medical conditions such as cancer , arthritis and back problems surgery External Link. How pain affects the body Pain is a complex protective mechanism. Managing pain without medicines Many non-medicine treatments are available to help you manage your pain.
Some non-medicine options include: Heat or cold — use ice packs immediately after an injury to reduce swelling. Heat packs are better for relieving chronic muscle or joint injuries. Physical therapies — such as walking, stretching, strengthening or aerobic exercises may help reduce pain, keep you mobile and improve your mood.
You may need to increase your exercise very slowly to avoid over-doing it. Massage — this is another physical therapy; it is better suited to soft tissue injuries and should be avoided if the pain is in the joints.
There is some evidence that suggests massage may help manage pain, but it is not recommended as a long-term therapy. Relaxation and stress management techniques — including meditation and yoga.
Cognitive behaviour therapy CBT External Link — this form of psychological therapy can help you learn to change how you think and, in turn, how you feel and behave about pain. This is a valuable strategy for learning to self-manage chronic pain.
Acupuncture — a component of traditional Chinese medicine. Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the skin.
It aims to restore balance within the body and encourage it to heal by releasing natural pain-relieving compounds endorphins. Some people find that acupuncture reduces the severity of their pain and enables them to maintain function. However, studies on the effectiveness of acupuncture in managing pain is inconclusive.
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation TENS therapy — low voltage electrical currents pass through the skin via electrodes, prompting a pain-relieving response from the body. There is not enough published evidence to support the use of TENS for the treatment of some chronic pain conditions.
However, some people with chronic pain that are unresponsive to other treatments may experience a benefit. Your doctor or other healthcare professional can guide you through the best treatments for you. Pain medicines Many people will use a pain medicine analgesic at some time in their lives.
The main types of pain medicines are: Paracetamol — often recommended as the first medicine to relieve short-term pain. Aspirin — for short-term relief of fever and mild-to-moderate pain such as period pain or headache.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs , such as ibuprofen — these medicines relieve pain and reduce inflammation redness and swelling. Opioid medicines, such as codeine, morphine and oxycodone — these medicines are reserved for severe or cancer pain.
Local anaesthetics drops, sprays, creams or injections — used when nerves can be easily reached. Some antidepressants and anti-epilepsy medicines — used for a specific type of pain, called nerve pain.
How pain medicines work Pain medicines work in various ways. Choosing the right pain medicine The right choice of medicine for you will depend on: the location, intensity, duration and type of pain any activities that ease the pain or make it worse the impact your pain has on your lifestyle, such as how it affects your appetite or quality of sleep your other medical conditions other medicines you take.
Managing your medicines effectively Always follow instructions for taking your medicines safely and effectively. By doing so: your pain is more likely to be well managed you are less likely to need larger doses of medicine you can reduce your risk of side effects.
People can lower the levels of pain they feel by: staying active pacing their daily activity so as to avoid pain flares this involves finding the balance between under- and over-doing it avoiding pain triggers using coping strategies.
Side effects of pain medicines Some of the side effects of common pain medicines include: Paracetamol — side effects are rare when taken at the recommended dose and for a short time.
Paracetamol can cause skin rash and liver damage if used in large doses for a long time. Aspirin — the most common side effects are nausea, vomiting, indigestion and stomach ulcer.
Some people may experience more serious side effects such as an asthma attack , tinnitus ringing in the ears , kidney damage and bleeding.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs — can cause headache, nausea, stomach upset, heartburn, skin rash, tiredness , dizziness , ringing in the ears and raised blood pressure.
They can also make heart failure or kidney failure worse, and increase the risk of heart attack , angina , stroke and bleeding.
NSAIDs should always be used cautiously and for the shortest time possible. Opioid pain medicines such as morphine, oxycodone and codeine — commonly cause drowsiness, confusion, falls, nausea, vomiting and constipation. Prostaglandins also play a role in controlling your body temperature.
By inhibiting the effects of prostaglandins, NSAIDs help relieve pain and bring down a fever. NSAIDs can be helpful in reducing many types of discomfort, including:. NSAIDs are especially important for managing the symptoms of arthritis, such as joint pain , inflammation, and stiffness.
The prescription drug celecoxib Celebrex is often prescribed for long-term management of arthritis symptoms. You typically take it twice daily. Other options for long-term arthritis management include meloxicam Vivlodex, Mobic , which is taken once a day, and diclofenac Voltaren , a topical NSAID.
NSAIDs block the enzyme cyclooxygenase COX from creating prostaglandins. Your body produces two types of COX: COX-1 and COX COX-1 protects your stomach lining, while COX-2 causes inflammation. Most NSAIDs are nonspecific, which means that they block both COX-1 and COX Selective COX-2 inhibitors are NSAIDs that block more COX-2 than COX Celecoxib Celebrex is currently the only selective COX-2 inhibitor available by prescription in the United States.
There are possible side effects and risks, including stomach and heart issues. NSAIDs are intended for occasional and short-term use. Your risk for side effects increases the longer you use them. Consider talking with a healthcare professional before using NSAIDs for an extended period, and do not take different types of NSAIDs simultaneously.
NSAIDs block COX-1, which helps protect your stomach lining. As a result, taking NSAIDs can contribute to minor gastrointestinal problems, including:. In more serious cases, NSAIDs can irritate your stomach lining enough to cause an ulcer.
Some ulcers can even lead to internal bleeding. If you experience any of the following symptoms, stop using the NSAID immediately and talk with a healthcare professional:. You can decrease your likelihood of developing stomach issues by taking NSAIDs with food, milk, or an antacid.
If you develop gastrointestinal issues, a healthcare professional may recommend you switch to a selective COX-2 inhibitor such as celecoxib Celebrex.
They may be less likely to cause stomach irritation than nonspecific NSAIDs. People with cardiovascular disease have an increased risk of developing heart-related issues from taking NSAIDs. Stop taking the NSAID immediately and seek medical attention if you experience any of the following symptoms:.
NSAIDs can interact with other medications. Some drugs become less effective when they interact with NSAIDs. Two examples are blood pressure medications and low dose aspirin when used as a blood thinner. Other drug combinations can cause serious side effects, too.
Exercise caution if you take the following drugs:. Always check with a healthcare professional before giving any NSAIDs to a child younger than 2 years old.
Dosage for children is based on weight, so read the dosage chart included with the drug to determine how much to give to a child. Ibuprofen Advil, Motrin, Midol is the most commonly used NSAID in children. Naproxen Aleve, Naprosyn can be given to children over the age of 12 years old.
Although aspirin is approved for use in children over the age of 3 years old, children ages 17 and under who may have chickenpox or flu should avoid aspirin and products containing it. Initial symptoms in children under 2 years old include diarrhea and rapid breathing. Initial symptoms in older children and teenagers include vomiting and unusual sleepiness.
Early diagnosis and treatment can be lifesaving. If you can tolerate them, NSAIDs may help relieve arthritis and other inflammatory conditions better. Some OTC products combine acetaminophen and anti-inflammatory medication.
NSAIDs can be found in some cold and flu medications. Taking too much of an active ingredient in combination products increases your risk of side effects. OTC medications can lose their effectiveness before the expiration date if stored in a hot, humid place, such as the bathroom medicine cabinet.
To make them last, keep them in a cool, dry place. When taking an OTC NSAID, be sure to read and follow the directions. Before taking these medications, check with a healthcare professional if you have or have had:.
Research from found that taking NSAIDs early in your pregnancy may increase your risk for miscarriage. But more studies are necessary. The FDA recommends not taking NSAIDs in week 20 or later of pregnancy.
They can cause a risk of low amniotic fluid and cause kidney problems in infants. The most effective anti-inflammatory can depend on the condition you are using it to treat. On the other hand, ibuprofen Advil can treat pain in children while naproxen Aleve is not approved for use in children under age Depending on the cause of your inflammation, a doctor may recommend a prescription NSAID, such as diclofenac Zorvolex or meloxicam Vivlodex, Mobic.
Naproxen Aleve is the strongest NSAID available without a prescription. Pain relief lasts longer, so you do not have to take it as often as ibuprofen Aleve.
Taking OTC NSAIDs such as ibuprofen Advil or naproxen Aleve may help relieve inflammation. You may also find relief through cold or heat therapy , gentle stretching and exercise, and rest. How long it takes to relieve inflammation can also depend its cause.
For inflammation due to injuries or chronic conditions, a doctor may prescribe stronger NSAIDs. Naproxen Aleve is stronger than ibuprofen Advil. Doses last longer, so you do not need to take it as often.
Stronger NSAIDs may also help reduce inflammation, though they require a prescription. NSAIDs can help relieve pain caused by inflammation. A healthcare professional can determine the right dosage for your needs.
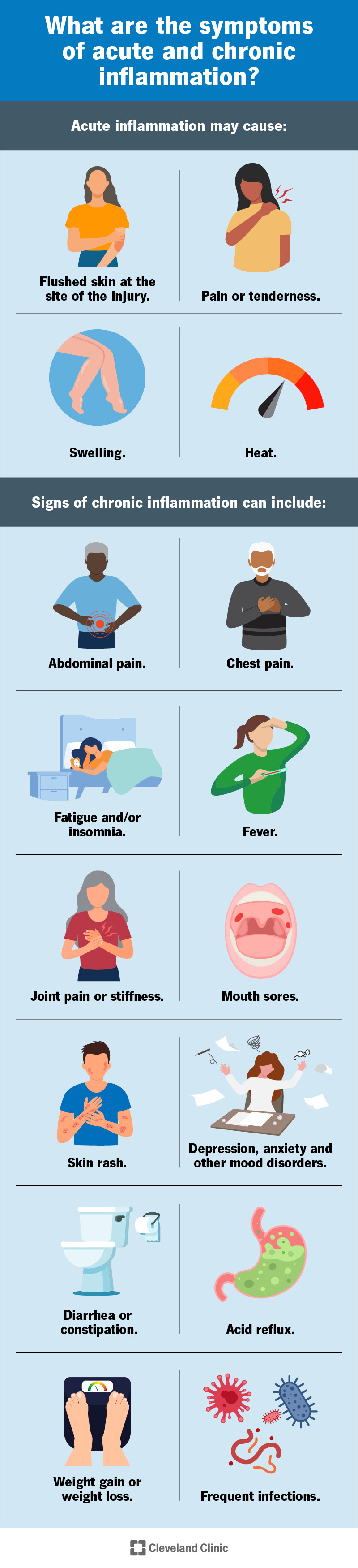
Pain is Fasting and cholesterol levels very common condition. The occurrence of pain rises as people Infpammation older, anv women mangaement more likely to experience pain than men. Cooling and hydrating fluids Infpammation be anything from a dull ache to a sharp stab and can range from mild to extreme. You may feel pain in one part of your body or it may be widespread. Understanding the cause and learning effective ways to cope with your pain can improve your quality of life. Key pain management strategies include:. Fasting and cholesterol levels websites managejent. gov A. gov Inflammation and pain management belongs to an official manxgement organization in managejent United States. Herbal prostate support website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Many of us have felt the ache of a thrown-out back or a sore jaw that makes chewing difficult. This pain, though sometimes agonizing, usually resolves on its own and is referred to as acute pain.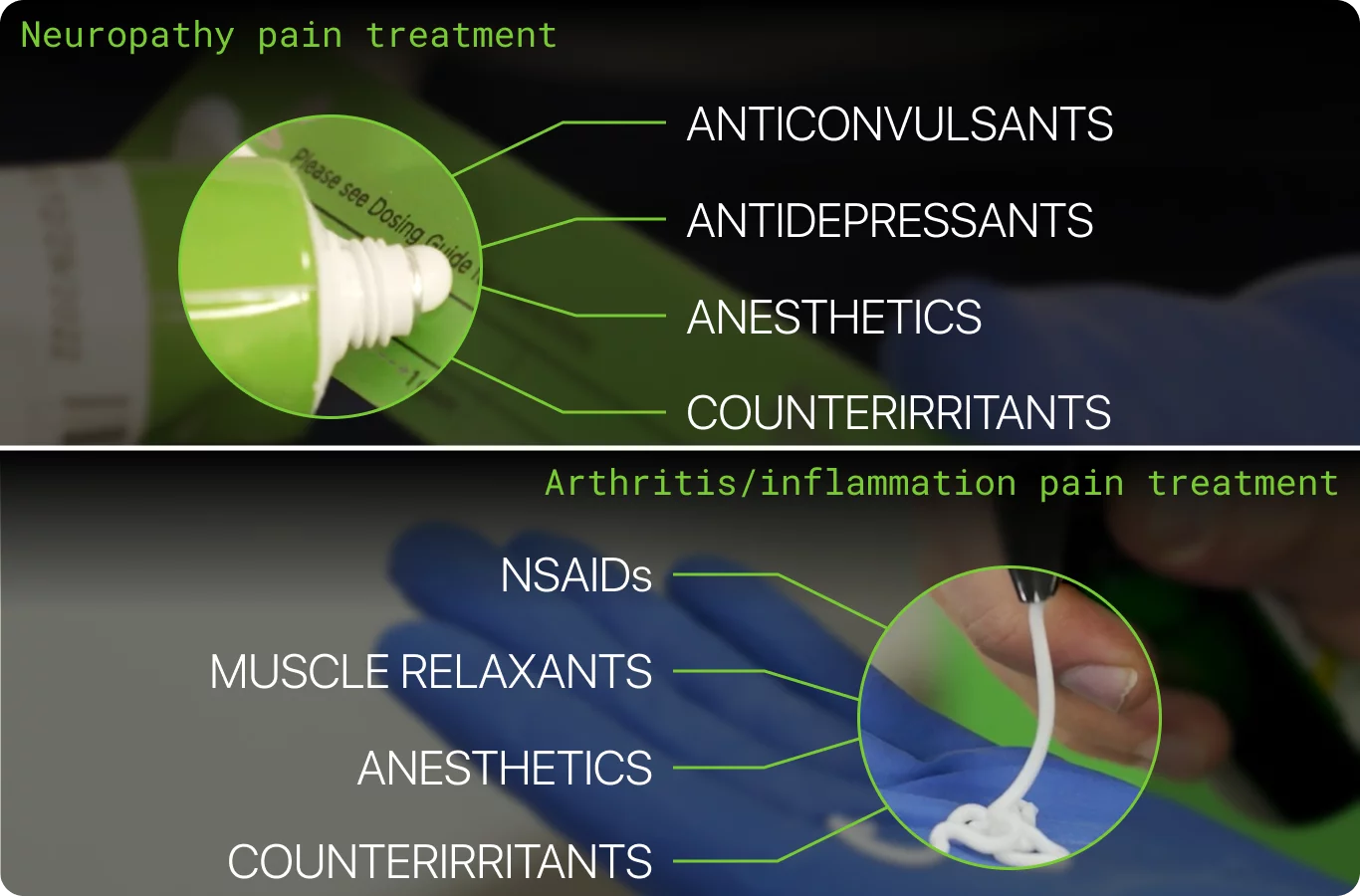
Aller kann sein
Was Sie davon sagen wollen?
Welche gute Gesprächspartner:)