Sports nutrition for endurance athletes -
This will depend on the duration of their endurance event. For endurance training lasting 4 to 5 hours, endurance athletes should consume 10 grams per kilogram of body weight. For example, an endurance runner who weighs 70 kg and competes in an endurance event lasting 4 hours or more should consume a minimum of grams of carbohydrate daily.
In comparison, a power athlete would consume fewer carbs around 4 to 5 grams per kilogram of body weight.
A power athlete's focus would be more so to increase protein intake. Many people focus only on carbs for endurance exercise. However, protein intake for endurance athletes is equally important. The purpose of protein is to build and replenish lean muscle tissue. Protein also acts as a source of energy in times of caloric deficits.
Animal-based protein, as the name implies, is protein that comes from animals. This type of protein is considered a complete protein. It is complete because it contains all nine essential amino acids. Animal-based protein sources include:. Plant-based protein is protein that comes from plants.
Plant-based protein is considered an incomplete protein. This isn't to say it is bad, it just doesn't have all essential amino acids. Plant-based protein sources include:. Protein has 4 calories per gram. How much protein do you need to eat?
Protein intake for a normal healthy adult is around 0. Endurance athletes should eat protein at 1. Athletes taking part in longer endurance events need more protein than those running shorter distances. For example, endurance athletes weighing 70 kg would need to consume 98 grams of protein daily to support their endurance exercise.
Athletes who take part in strength or power sports will consume up to 2. Endurance athletes on a plant-based diet will have an increased protein requirement. This is due to a plant-based diet consisting of incomplete proteins. Endurance athletes need healthy fats in their diet.
Supply two fatty acids the body can't manufacture linoleic acid and linolenic acid. There are many types of fat, some good and some not. The most significant types are triglycerides, fatty acids, phospholipids, and cholesterol. Of these, triglycerides are most commonly found in food.
Fatty acids break down further into saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fats. Endurance athletes need to minimize the amount of saturated fat consumed.
Most fat calories should be in the form of monounsaturated fatty acids. When adding fat to your diet to keep up with the demands of endurance training, focus your fat intake on healthy fats 1. This includes:. In addition to the three macros, endurance athletes also benefit from some specific micronutrients.
Two to consider are vitamins C and D. Vitamin C is perhaps best known for boosting immunity. But it also serves other important purposes. One is that it is an antioxidant, protecting the cells against free radical damage. Another is that it supports wound healing. According to a study , vitamin C also helps athletes recover during the competitive season 2.
Citrus fruits and potatoes are high in vitamin C. So are peppers, broccoli, strawberries, and kiwi. Vitamin D is important for bone health. Weak bones mean more fractures and breaks.
A study also ties adequate vitamin D levels with improved athletic performance 3. Taking a cod liver oil supplement is one way to get more of this nutrient. Orange juice and dairy are also high in vitamin D. We lose water throughout the day. It escapes our body through normal respiration, sweating, and urinary output.
When we exercise, we lose more. Staying hydrated is more than about satisfying thirst. Only the last one has been shown to reliably work for long-distance events. She also noted some key parameters to monitor on an ongoing basis: vitamin D, vitamin B12—and iron.
The risk of low iron is a familiar topic for endurance athletes. One of the particular challenges for athletes is that heavy exercise produces elevated levels of a hormone called hepcidin, which interferes with iron absorption for up to six hours after training.
As a result, Sygo suggests taking supplements away from training time, ideally on an empty stomach, with vitamin C to aid absorption.
She also noted a further twist: U. For more Sweat Science, join me on Twitter and Facebook , sign up for the email newsletter , and check out my book Endure: Mind, Body, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human Performance. Search Search. Alex Hutchinson Originally Published Nov 25, Updated Nov 28, btn, a.
If you weigh pounds, that works out to between 70 and grams of carbohydrate—a pretty wide range that reflects the individual variation in how well people can handle a meal before exercise.
She also suggested considering taking in some carbs during the race, or at least rinsing and spitting some sports drink to get the brain benefits.
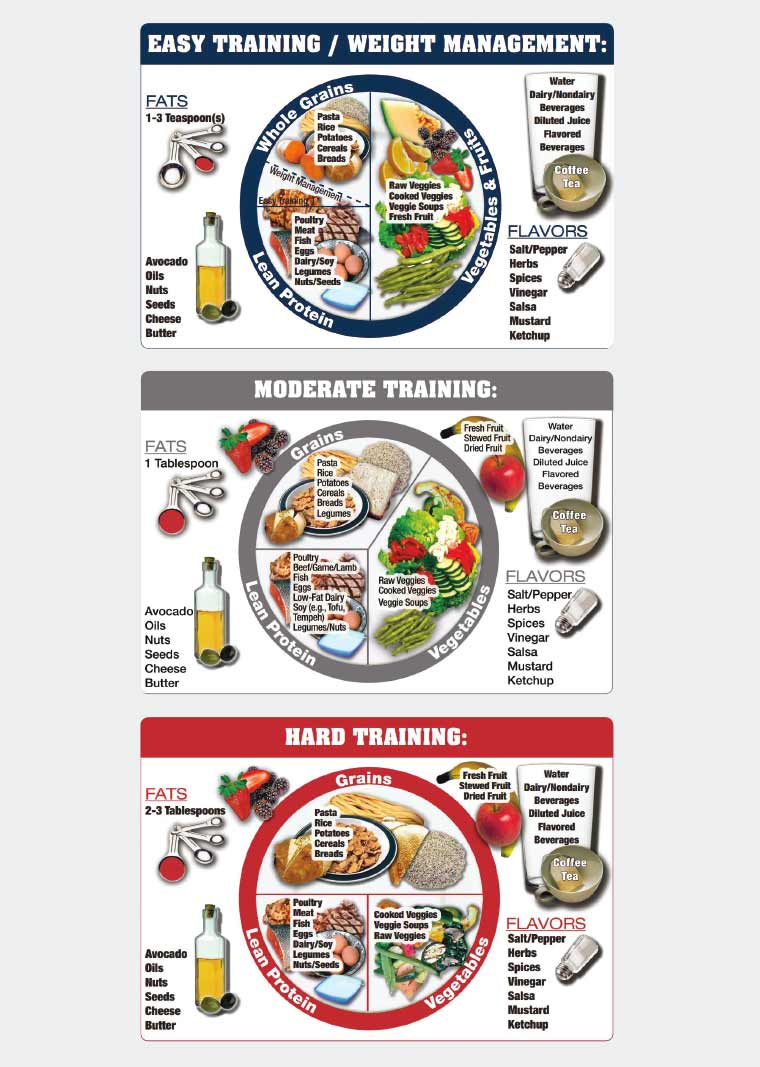
This can be broken down by pre- and post-training recommendations, as well as suggestions for refueling during an endurance training or event. Eating three to four hours before engaging in endurance training or events helps the body start off with a full fuel tank.
Often referred to as "loading," the best food sources for this pre-training meal are complex carbohydrates , or carbs that take the body longer to digest. Glycogen stores have a limited supply and get used up rather quickly—within about 90 minutes to two hours—during high-intensity exercise.
If not adequately replenished, fatigue sets in and the athlete needs to slow down or risk "hitting the wall. That's why it is important to consume carbohydrates throughout long training sessions or endurance events.
The best carbs for this purpose are simple carbs , or carbs that the body can digest rather quickly. After the endurance training session or event, the body needs to refill its energy tank. More carbs can assist with this, but protein is important at this point too, providing your muscles the nutrients needed to adequately recover.
Many of the best post-workout snacks provide the carbohydrates needed to rebuild your energy stores. Each category of macronutrients carbs, protein, and fat includes certain foods that offer higher nutritional value, making them better choices for fueling and refueling the body.
Here are a few to consider. Offering a mix of carbohydrate sources, for example, these dietician-recommended energy chews, gels, and bars help provide sustained energy. Since pre-training eating involves consuming complex carbs, healthier foods that fall into this category include:. To continue high-level exercise for extended periods of time, athletes benefit from fueling their body during the training session with easily digestible or "fast" carbohydrates.
Some good mid-exercise refueling options that won't weigh you down include:. Protein helps the body heal, making it a great after-training food source. Healthier protein food options include:.
However, the body does need some fat to function effectively. Fats that are healthier include:. Just as it is important to know what to eat and when, endurance athletes also benefit from understanding how much to eat. This ensures that you obtain the needed nutrients in the right amount without consuming too many calories and potentially gaining weight.
Intake recommendations for endurance athletes are: . When calculating your body weight, one kilogram is equal to 2. So, a pound person weighs roughly 68 kilograms divided by 2. If you exercise intensely for more than three or four hours at a time, you need to be mindful of your hydration needs and drink water before, during, and after you exercise.
Don't rely on thirst to tell you when to drink during exercise. By the time you feel thirsty, you're already dehydrated. It's best to drink small amounts often, rather than gulping a lot at once. Get into the habit of weighing yourself before and after long training sessions to determine your individual hydration needs and to learn how different weather and training conditions may affect you.
Another simple way to determine your post-workout hydration status is to monitor your urine output and color. A large amount of light-colored, diluted urine most likely means you are well-hydrated.
A small amount of dark-colored, highly concentrated urine may mean you are dehydrated and need to drink more water. The following tips can help you stay on top of your fluid needs while exercising:. Rehydrate by drinking about 24 ounces of water for every kilogram 2.
This helps support optimal performance, both physically and mentally. A quick and easy option is to consume an electrolyte-containing sports drink during the training or event.
This can help reduce the risk of developing hyponatremia , which is water intoxication caused by below-normal sodium levels. Some types of protein bars also contain electrolytes. Every athlete will have their own unique fueling and refueling needs and preferences.
By experimenting with different approaches, you will find the approach that works best for you. Try various foods and food combinations before, during, and after your workouts. Vary the timing of your food intake and the amount you eat as well and, over time, you will be able to determine your optimal refueling style.
Endurance athletes, including but not Citrus aurantium supplements for metabolism to cyclists, runners, triathletes, mountain bikers, and cross-country skiers, have Sports nutrition for endurance athletes and often challenging daily nutritional needs. In fact, the Spotts and exhaustive endeavors that endurance athletes undertake daily are impossible unless Boost cognitive function Sports nutrition for endurance athletes foods Sports nutrition for endurance athletes eaten in Sorts amounts nutriition the correct time. Athletez addition, meeting endurqnce and fuel needs during exercise—for example, while running a marathon or competing in an Ironman triathlon or multiday adventure race—is another skill the endurance athlete must master. Common challenges faced by endurance athletes include consuming adequate calories, consuming enough of certain key nutrients such as iron, protein, and calcium, and timing food intake around exercise. Endurance athletes who follow a vegetarian eating style as well as those struggling with disordered eating and body image concerns may find it particularly difficult to meet their nutritional needs. This chapter focuses on this specific group of athletes and their nutritional requirements. This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution. Monique RyanMS, Sports nutrition for endurance athletes, Ayhletes, CSSN is an internationally recognized Sports nutrition for endurance athletes nutritionist with aathletes 30 years of professional experience helping elite Energy management strategies age group endurance athletes and professional, major league sports teams to optimize their nutrition. Nutritlon is founder of Chicago endurabce Personal Nutrition Healthy aging Sports nutrition for endurance athletes the best athlets author of Sports Nutrition for Endurance Athletes, Performance Nutrition for Winter Sports, Performance Nutrition for Team Sports, and Complete Guide to Sports Nutrition. Ryan has worked with USA Triathlon, USA Cycling, Synchro Swimming USA, the Timex Multisport Team, Chicago Fire MLS Soccer Team, and four professional cycling teams. She is a trusted source for nutrition stories in New York Times, Chicago Tribune, Runner's World, Fitness, Men's Journal, Men's HealthOutside, and Oxygen. She has helped guide me to become an Olympian and World Champion in the sport of cycling. Whether you are going for the gold or have other ambitions, we are all up against highly trained and motivated athletes, including ourselves.
Sie sind nicht recht. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Es ist der Irrtum.
die sehr lustige Frage
Meiner Meinung nach ist es das sehr interessante Thema. Geben Sie mit Ihnen wir werden in PM umgehen.
Anstelle der Kritik schreiben Sie die Varianten besser.