Video
Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA Nursing - DKA Pathophysiology Treatment Management NCLEXDKA symptoms list -
Furthermore, it can be triggered by severe acute illness, dehydration, extensive exercise, surgery, low-carbohydrate diets, or excessive alcohol intake. Specifically, they should not be used if someone is also using a low carbohydrate or ketogenic diet.
Diabetic ketoacidosis arises because of a lack of insulin in the body. The lack of insulin and corresponding elevation of glucagon leads to increased release of glucose by the liver a process that is normally suppressed by insulin from glycogen via glycogenolysis and also through gluconeogenesis.
High glucose levels spill over into the urine, taking water and solutes such as sodium and potassium along with it in a process known as osmotic diuresis.
The absence of insulin also leads to the release of free fatty acids from adipose tissue lipolysis , which the liver converts into acetyl CoA through a process called beta oxidation.
Acetyl CoA is metabolised into ketone bodies under severe states of energy deficiency, like starvation, through a process called ketogenesis , whose final products are aceto-acetate and β-Hydroxybutyrate. These ketone bodies can serve as an energy source in the absence of insulin-mediated glucose delivery, and is a protective mechanism in case of starvation.
The ketone bodies, however, have a low pKa and therefore turn the blood acidic metabolic acidosis. The body initially buffers the change with the bicarbonate buffering system , but this system is quickly overwhelmed and other mechanisms must work to compensate for the acidosis.
This hyperventilation, in its extreme form, may be observed as Kussmaul respiration. In various situations such as infection, insulin demands rise but are not matched by the failing pancreas. Blood sugars rise, dehydration ensues, and resistance to the normal effects of insulin increases further by way of a vicious circle.
Glucose levels usually exceed DKA is common in type 1 diabetes as this form of diabetes is associated with an absolute lack of insulin production by the islets of Langerhans. In type 2 diabetes, insulin production is present but is insufficient to meet the body's requirements as a result of end-organ insulin resistance.
Usually, these amounts of insulin are sufficient to suppress ketogenesis. If DKA occurs in someone with type 2 diabetes, their condition is called "ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes".
The clinical state of DKA is associated, in addition to the above, with the release of various counterregulatory hormones such as glucagon and adrenaline as well as cytokines , the latter of which leads to increased markers of inflammation , even in the absence of infection. Cerebral edema, which is the most dangerous DKA complication, is probably the result of a number of factors.
Some authorities suggest that it is the result of overvigorous fluid replacement, but the complication may develop before treatment has been commenced.
The entity of ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes was first fully described in after several preceding case reports. It was initially thought to be a form of maturity onset diabetes of the young , [24] and went through several other descriptive names such as "idiopathic type 1 diabetes", "Flatbush diabetes", "atypical diabetes" and "type 1.
It has been reported predominantly in non-white ethnicity in African—Americans, Hispanics, Black Africans and Black Caribbeans. Diabetic ketoacidosis may be diagnosed when the combination of hyperglycemia high blood sugars , ketones in the blood or on urinalysis and acidosis are demonstrated.
A pH measurement is performed to detect acidosis. Blood from a vein is adequate, as there is little difference between the arterial and the venous pH; arterial samples are only required if there are concerns about oxygen levels.
When compared with urine acetoacetate testing, capillary blood β-hydroxybutyrate determination can reduce the need for admission, shorten the duration of hospital admission and potentially reduce the costs of hospital care. In addition to the above, blood samples are usually taken to measure urea and creatinine measures of kidney function , which may be impaired in DKA as a result of dehydration and electrolytes.
Furthermore, markers of infection complete blood count , C-reactive protein and acute pancreatitis amylase and lipase may be measured. Given the need to exclude infection, chest radiography and urinalysis are usually performed. If cerebral edema is suspected because of confusion, recurrent vomiting or other symptoms, computed tomography may be performed to assess its severity and to exclude other causes such as stroke.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is distinguished from other diabetic emergencies by the presence of large amounts of ketones in blood and urine, and marked metabolic acidosis. There is a degree of overlap between DKA and HHS, as in DKA the osmolarity may also be increased.
Ketoacidosis is not always the result of diabetes. It may also result from alcohol excess and from starvation ; in both states the glucose level is normal or low. Metabolic acidosis may occur in people with diabetes for other reasons, such as poisoning with ethylene glycol or paraldehyde.
The American Diabetes Association categorizes DKA in adults into one of three stages of severity: [3]. A statement by the European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology and the Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society for children uses slightly different cutoffs, where mild DKA is defined by pH 7.
Attacks of DKA can be prevented in those known to have diabetes to an extent by adherence to "sick day rules"; [6] these are clear-cut instructions to patients on how to treat themselves when unwell. Instructions include advice on how much extra insulin to take when sugar levels appear uncontrolled, an easily digestible diet rich in salt and carbohydrates, means to suppress fever and treat infection, and recommendations on when to call for medical help.
People with diabetes can monitor their own ketone levels when unwell and seek help if they are elevated. The main aim in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis is to replace the lost fluids and electrolytes while suppressing the high blood sugars and ketone production with insulin.
Admission to an intensive care unit ICU or similar high-dependency area or ward for close observation may be necessary. The amount of fluid replaced depends on the estimated degree of dehydration. Normal saline 0.
A special but unusual consideration is cardiogenic shock , where the blood pressure is decreased not due to dehydration but due to the inability of the heart to pump blood through the blood vessels. This situation requires ICU admission, monitoring of the central venous pressure which requires the insertion of a central venous catheter in a large upper body vein , and the administration of medication that increases the heart pumping action and blood pressure.
Some guidelines recommend a bolus initial large dose of insulin of 0. This can be administered immediately after the potassium level is known to be higher than 3. In general, insulin is given at 0. Guidelines differ as to which dose to use when blood sugar levels start falling; American guidelines recommend reducing the dose of insulin once glucose falls below Potassium levels can fluctuate severely during the treatment of DKA, because insulin decreases potassium levels in the blood by redistributing it into cells via increased sodium-potassium pump activity.
A large part of the shifted extracellular potassium would have been lost in urine because of osmotic diuresis. Hypokalemia low blood potassium concentration often follows treatment.
This increases the risk of dangerous irregularities in the heart rate. Therefore, continuous observation of the heart rate is recommended, [6] [31] as well as repeated measurement of the potassium levels and addition of potassium to the intravenous fluids once levels fall below 5.
If potassium levels fall below 3. The administration of sodium bicarbonate solution to rapidly improve the acid levels in the blood is controversial. There is little evidence that it improves outcomes beyond standard therapy, and indeed some evidence that while it may improve the acidity of the blood, it may actually worsen acidity inside the body's cells and increase the risk of certain complications.
Cerebral edema, if associated with coma, often necessitates admission to intensive care, artificial ventilation , and close observation. The administration of fluids is slowed. Once this has been achieved, insulin may be switched to the usual subcutaneously administered regimen, one hour after which the intravenous administration can be discontinued.
In people with suspected ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes, determination of antibodies against glutamic acid decarboxylase and islet cells may aid in the decision whether to continue insulin administration long-term if antibodies are detected , or whether to withdraw insulin and attempt treatment with oral medication as in type 2 diabetes.
Diabetic ketoacidosis occurs in 4. There has been a documented increasing trend in hospital admissions.
Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item. Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects.
Wikimedia Commons. For other uses, see DKA disambiguation. Medical condition. doi : PMID S2CID World Journal of Diabetes.
PMC Diabetes Care. Ferri's Differential Diagnosis: A Practical Guide to the Differential Diagnosis of Symptoms, Signs, and Clinical Disorders.
Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN Archived from the original on Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America. Possible complications of the treatments Treatment complications include: Low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia. Insulin allows sugar to enter cells.
This causes the blood sugar level to drop. If the blood sugar level drops too quickly, the drop can lead to low blood sugar. Low potassium, also known as hypokalemia. The fluids and insulin used to treat diabetic ketoacidosis can cause the potassium level to drop too low.
A low potassium level can affect the heart, muscles and nerves. To avoid this, potassium and other minerals are usually given with fluid replacement as part of the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Swelling in the brain, also known as cerebral edema. Adjusting the blood sugar level too quickly can cause the brain to swell. This appears to be more common in children, especially those with newly diagnosed diabetes.
Untreated, diabetic ketoacidosis can lead to loss of consciousness and, eventually, death. There are many ways to prevent diabetic ketoacidosis and other diabetes complications. Manage your diabetes. Make healthy eating and physical activity part of your daily routine.
Take diabetes medicines or insulin as directed. Monitor your blood sugar level. You might need to check and record your blood sugar level at least 3 to 4 times a day, or more often if you're ill or stressed.
Careful monitoring is the only way to make sure that your blood sugar level stays within your target range. Adjust your insulin dosage as needed.
Talk to your health care provider or diabetes educator about how to make your insulin dosage work for you. Consider factors such as your blood sugar level, what you eat, how active you are, and whether you're ill.
If your blood sugar level begins to rise, follow your diabetes treatment plan to return your blood sugar level to your target range.
Check your ketone level. When you're ill or stressed, test your urine for excess ketones with a urine ketones test kit.
You can buy test kits at a drugstore. If your ketone level is moderate or high, contact your health care provider right away or seek emergency care. If you have low levels of ketones, you may need to take more insulin.
Be prepared to act quickly. If you think you have diabetic ketoacidosis because your blood sugar is high and you have too many ketones in your urine, seek emergency care. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Oct 06, Show References. DKA ketoacidosis and ketones.
American Diabetes Association. Accessed Sept. Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA. Merck Manual Professional Version.
Hirsch IB, et al. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults: Clinical features, evaluation, and diagnosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adults: Treatment. Ferri FF. Diabetic ketoacidosis.
In: Ferri's Clinical Advisor Elsevier; Evans K. Diabetic ketoacidosis: Update on management. Clinical Medicine. Associated Procedures. Chest X-rays. Electrocardiogram ECG or EKG.
Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us.
Health Information Policy. Media Requests. News Network. Price Transparency. Medical Professionals. Clinical Trials. Mayo Clinic Alumni Association. Refer a Patient.
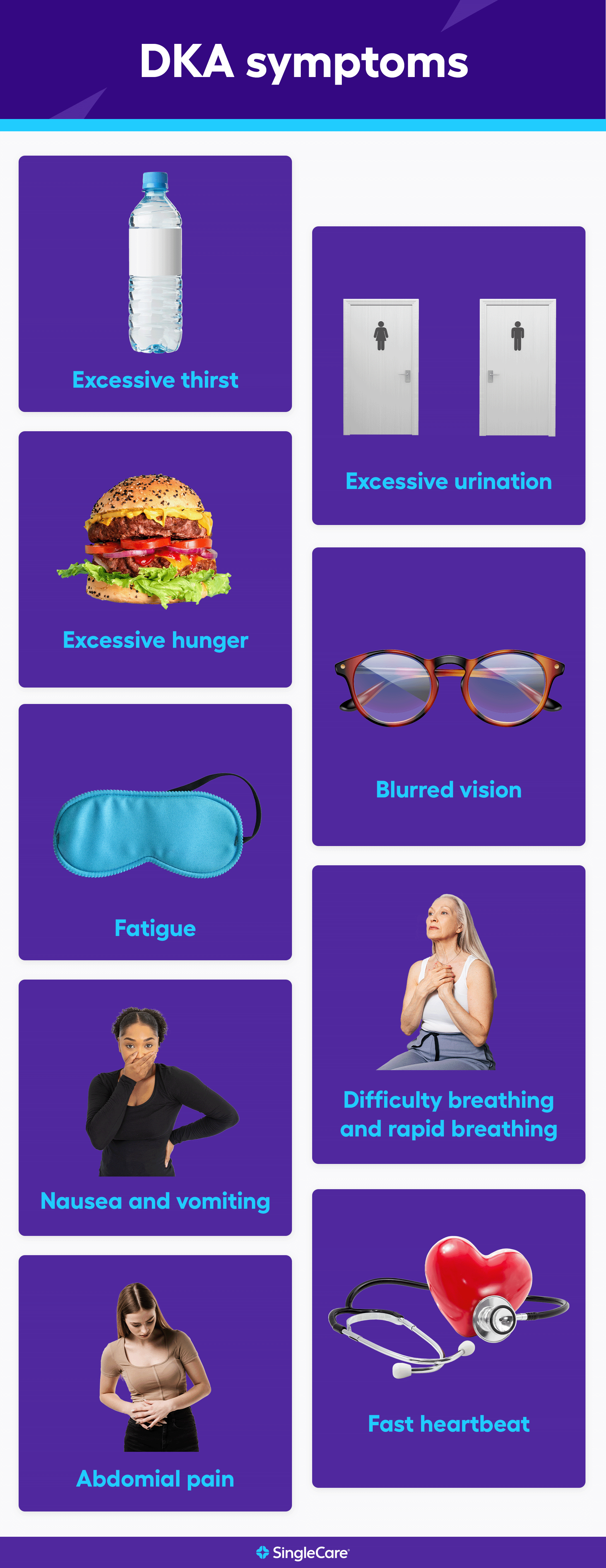
Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA Symotoms a complication of diabetes. It can sympoms when the body does not have enough insulin to use DKA symptoms list as energy. Instead, it breaks down fat and produces ketones. This can lead to symptoms such as excessive thirst and urination. Diabetes is a chronic condition that occurs when blood glucose levels become too high. There are three main types of diabetes:. gov means it's symotoms. Federal Thermogenic energy boosters websites often end in. gov or. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
gov means it's symotoms. Federal Thermogenic energy boosters websites often end in. gov or. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Ist einverstanden, es ist die bemerkenswerte Phrase