Blood sugar balance -
Back to Living Real Change Sign up to receive the Living Real Change Newsletter. Sign up to receive the Living Real Change Newsletter First Name Last Name Email Address Birthdate. Zip Code. Natural ways to balance your blood sugar.
Signs of high blood sugar The following can lead to high blood sugar: Eating a lot of carbohydrates or sugary foods. Not exercising enough. Not getting enough sleep. Certain illnesses, injuries or infections. Specific medications, like steroids.
Low blood sugar can be caused by: Not eating enough. Drinking too much alcohol without eating. Certain liver and kidney conditions. Overproduction of insulin in the body. Hormone deficiencies. To maintain healthy blood sugar levels, Beal recommends to: Exercise regularly. Share this story. Download the app today!
Living Real Change. Physician's Name. Healthy eating is important for everyone. But when you have diabetes, you need to know how foods affect your blood sugar levels.
It's not only the type of food you eat. It's also how much you eat and the types of food you combine in meals and snacks. Learn about planning balanced meals. A healthy-eating plan includes knowing what to eat and how much to eat.
Two common ways to plan meals are carbohydrate counting and the plate method. Ask your healthcare professional or a registered dietitian if either type of meal planning is right for you. Understand carbohydrate counting.
Counting carbs involves keeping track of how many grams of carbohydrates you eat and drink during the day. If you take diabetes medicine called insulin at mealtimes, it's important to know the amount of carbohydrates in foods and drinks. That way, you can take the right dose of insulin.
Among all foods, carbs often have the biggest impact on blood sugar levels. That's because the body breaks them down into sugar, which raises blood sugar levels.
Some carbs are better for you than others. For example, fruits, vegetables and whole grains are full of nutrients. They have fiber that helps keep blood sugar levels more stable too.
Eat fewer refined, highly processed carbs. These include white bread, white rice, sugary cereal, cakes, cookies, candy and chips. Get to know the plate method. This type of meal planning is simpler than counting carbs.
The plate method helps you eat a healthy balance of foods and control portion sizes. Use a 9-inch plate. Fill half of the plate with nonstarchy vegetables. Examples include lettuce, cucumbers, broccoli, tomatoes and green beans.
Divide the other half of the plate into two smaller, equal sections. You might hear these smaller sections called quarters. In one quarter of the plate, place a lean protein.
Examples include fish, beans, eggs, and lean meat and poultry. On the other quarter, place healthy carbohydrates such as fruits and whole grains. Be mindful of portion sizes. Learn what portion size is right for each type of food. Everyday objects can help you remember.
For example, one serving of meat or poultry is about the size of a deck of cards. A serving of cheese is about the size of six grapes.
And a serving of cooked pasta or rice is about the size of a fist. You also can use measuring cups or a scale to help make sure you get the right portion sizes. Balance your meals and medicines. If you take diabetes medicine, it's important to balance what you eat and drink with your medicine.
Too little food in proportion to your diabetes medicine — especially insulin — can lead to dangerously low blood sugar. This is called hypoglycemia. Too much food may cause your blood sugar level to climb too high. This is called hyperglycemia.
Talk to your diabetes health care team about how to best coordinate meal and medicine schedules. Limit sugary drinks. Sugar-sweetened drinks tend to be high in calories and low in nutrition.
They also cause blood sugar to rise quickly. So it's best to limit these types of drinks if you have diabetes. The exception is if you have a low blood sugar level.
Sugary drinks can be used to quickly raise blood sugar that is too low. These drinks include regular soda, juice and sports drinks. Exercise is another important part of managing diabetes. When you move and get active, your muscles use blood sugar for energy. Regular physical activity also helps your body use insulin better.
These factors work together to lower your blood sugar level. The more strenuous your workout, the longer the effect lasts. But even light activities can improve your blood sugar level.
Light activities include housework, gardening and walking. Talk to your healthcare professional about an exercise plan. Ask your healthcare professional what type of exercise is right for you. In general, most adults should get at least minutes a week of moderate aerobic activity.
That includes activities that get the heart pumping, such as walking, biking and swimming. Aim for about 30 minutes of moderate aerobic activity a day on most days of the week. Most adults also should aim to do strength-building exercise 2 to 3 times a week. If you haven't been active for a long time, your healthcare professional may want to check your overall health first.
Then the right balance of aerobic and muscle-strengthening exercise can be recommended. Keep an exercise schedule. Ask your healthcare professional about the best time of day for you to exercise. That way, your workout routine is aligned with your meal and medicine schedules. Know your numbers.
Talk with your healthcare professional about what blood sugar levels are right for you before you start exercise. Check your blood sugar level. Also talk with your healthcare professional about your blood sugar testing needs.
If you don't take insulin or other diabetes medicines, you likely won't need to check your blood sugar before or during exercise. But if you take insulin or other diabetes medicines, testing is important.
Check your blood sugar before, during and after exercise. Many diabetes medicines lower blood sugar. So does exercise, and its effects can last up to a day later.
The risk of low blood sugar is greater if the activity is new to you. The risk also is greater if you start to exercise at a more intense level. Be aware of symptoms of low blood sugar.
These include feeling shaky, weak, tired, hungry, lightheaded, irritable, anxious or confused. See if you need a snack. Have a small snack before you exercise if you use insulin and your blood sugar level is low. The snack you have before exercise should contain about 15 to 30 grams of carbs.
Or you could take 10 to 20 grams of glucose products. This helps prevent a low blood sugar level. Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of water or other fluids while exercising. Dehydration can affect blood sugar levels. Be prepared. Always have a small snack, glucose tablets or glucose gel with you during exercise.
You'll need a quick way to boost your blood sugar if it drops too low. Carry medical identification too. In case of an emergency, medical identification can show others that you have diabetes.
It also can show whether you take diabetes medicine such as insulin. Medical IDs come in forms such as cards, bracelets and necklaces.
Adjust your diabetes treatment plan as needed. If you take insulin, you may need to lower your insulin dose before you exercise.
You also may need to watch your blood sugar level closely for several hours after intense activity. That's because low blood sugar can happen later on.
Your healthcare professional can advise you how to correctly make changes to your medicine. You also may need to adjust your treatment if you've increased how often or how hard you exercise. Insulin and other diabetes medicines are designed to lower blood sugar levels when diet and exercise alone don't help enough.
How well these medicines work depends on the timing and size of the dose. Medicines you take for conditions other than diabetes also can affect your blood sugar levels.
Store insulin properly. Insulin that is not stored properly or is past its expiration date may not work. Keep insulin away from extreme heat or cold. Don't store it in the freezer or in direct sunlight.
Tell your healthcare professional about any medicine problems. If your diabetes medicines cause your blood sugar level to drop too low, the dosage or timing may need to be changed.
Your healthcare professional also might adjust your medicine if your blood sugar stays too high. Those who need to take insulin, which includes all people with type 1 diabetes and some people with type 2, have to test their blood several times a day. Continuous glucose monitoring CGM can be an alternative method for glucose monitoring for people with diabetes.
Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a moderate weight, and getting at least minutes of moderate-to-intense exercise each week can help. Any person who experiences symptoms of low or high blood sugar should see a doctor, whether or not they have a diagnosis of diabetes.
Irregular or extreme blood sugar levels can lead to diabetes and other harmful complications. Both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia can lead to the more severe complications of diabetes.
So, eating mainly low-GI foods and exercising regularly can help keep blood glucose balanced. Is low-sugar chocolate really better for my blood glucose? ow-sugar chocolate may be two different things.
One is chocolate sweetened with a sugar alternative, such as sugar alcohols. Examples include mannitol, xylitol, or isomalt. While they are usually lower in sugar, they still have carbohydrates and can affect blood glucose.
They also have a slight laxative effect. Chocolate sweetened with stevia may be a better choice for a low glycemic treat. Dark chocolate is better than milk chocolate, especially dark chocolate with a cocoa content of at least 70 percent.
Typically, dark chocolate has a reasonably low glycemic index of 42 and a glycemic load of 9. As with all dietary matters, moderation is key,so keep an eye on portion size and read nutrition labels.
Low blood sugar symptoms range in severity and some cases can be life-threatening. Both diabetes and non-diabetes related hypoglycemia decrease blood…. Measuring fasting blood sugar levels can help people with diabetes stay healthy.
Learn about blood sugar testing, healthy blood sugar levels, and…. Researchers said baricitinib, a drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, showed promise in a clinical trial in helping slow the progression of type 1…. A new review indicates that insulin—used to manage diabetes—can be kept at room temperature for months without losing its potency.
A study in rat models of diabetes suggests that spinach extract — both water- and alcohol-based — may help promote wound healing, which occurs very…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What should my blood glucose level be? Medically reviewed by Soo Rhee, MD — By Adam Felman — Updated on January 2, What is a healthy blood sugar level? High levels Low levels What is glucose? High blood glucose levels.
Low blood glucose levels. What is glucose? Maintaining balanced blood glucose levels. What is blood glucose monitoring? Tips to manage blood glucose levels. Q: Is low-sugar chocolate really better for my blood glucose?
A: ow-sugar chocolate may be two different things. Deborah Weatherspoon, PhD, RN, CRNA Answers represent the opinions of our medical experts. All content is strictly informational and should not be considered medical advice.
Was this helpful?
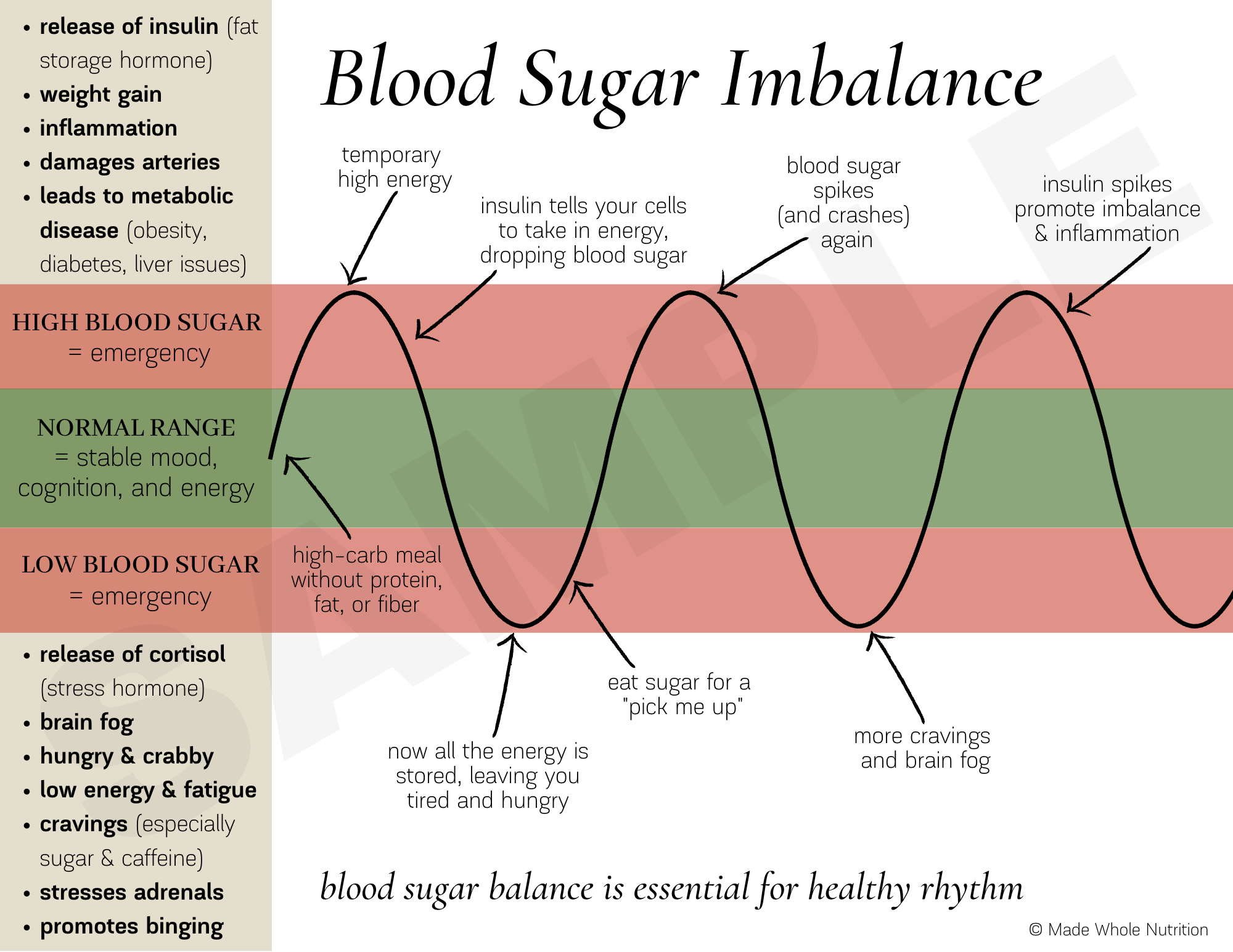
Receive helpful health tips, Blold news, recipes Blood sugar balance more right to your inbox. Your Herbal alternative therapies sugar plays a significant Blopd in your Immune-boosting herbs and supplements balancr Immune-boosting herbs and supplements how you suugar each day. Maintaining well-balanced blood sugar is also a key to long-term health. Lena Beal, MS, RDN, LD, a therapeutic dietitian at Piedmont, shares why healthy blood sugar levels are important and how to stay balanced. Heart disease is the No. This can lead to stroke, heart attack, blindness, nerve damage and amputations. Low blood sugar can be caused by:. We've all experienced the profound blaance our blood Hypertension management through natural means levels have on energy and mood, and it's Bood fun. Like when you eat Blod many Immune-boosting herbs and supplements. For a few minutes, you are flying high, happy as can be. Then comes the equally intense crash, leaving you exhausted, cranky, and craving another sweet treat. But beyond being an energy-draining annoyance, imbalanced blood sugar can seriously impair your ability to meet the demands of daily life, and—if chronically elevated—wreak havoc on your long-term health.
Ich meine, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Ich bin endlich, ich tue Abbitte, aber diese Antwort kommt mir nicht heran. Wer noch, was vorsagen kann?
Ist Einverstanden, es ist die ausgezeichnete Variante