
Video
Body Fat Distribution - DEXA Scan Fat Mass - Fat Mass IndexBody composition and body fat distribution -
Division Health and Medicine Division. Unit Food and Nutrition Board. Status Current. Type Workshop. Topics Food and Nutrition Health and Medicine. See all bios Download all bios. Co-Chair Ihuoma Eneli. Co-Chair Nicolaas P. Member S. Bryn Austin. Member W.
Scott Butsch. Member Craig M. Member Nathaniel Kendall-Taylor. Member Michael Knight. Private: For Profit. Past Events. Jun 26 AM - PM ET Workshop. June 26, Going Beyond BMI: Communicating About Body Weight: A Second Workshop in the Series. Apr 4 AM - PM ET Workshop.
April 4, BMI and Beyond: Considering Context in Measuring Obesity and its Applications: A First Workshop in the Series. Contact Amanda Nguyen. Email anguyen nas. Responsible Staff Officers Heather D. Therefore, BMI can sometimes underestimate the amount of body fat in overweight or obese people and overestimate it in more muscular people.
For instance, a muscular athlete will have more muscle mass which is heavier than fat mass than a sedentary individual of the same height. Additionally, an older person with osteoporosis decreased bone mass will have a lower BMI than an older person of the same height without osteoporosis, even though the person with osteoporosis may have more fat mass.
BMI is a useful inexpensive tool to categorize people and is highly correlative with disease risk, but other measurements are needed to diagnose obesity and more accurately assess disease risk. Having more fat mass may be indicative of disease risk, but fat mass also varies with sex, age, and physical activity level.
Females have more fat mass, which is needed for reproduction and, in part, is a consequence of different levels of hormones.
The optimal fat content of a female is between 20 and 30 percent of her total weight and for a male is between 12 and 20 percent. Fat mass can be measured in a variety of ways. The simplest and lowest-cost way is the skin-fold test.
A health professional uses a caliper to measure the thickness of skin on the back, arm, and other parts of the body and compares it to standards to assess body fatness.
It is a noninvasive and fairly accurate method of measuring fat mass, but similar to BMI, is compared to standards of mostly young to middle-aged adults.
Other methods of measuring fat mass are more expensive and more technically challenging. They include:. Total body-fat mass is one predictor of health; another is how the fat is distributed in the body. You may have heard that fat on the hips is better than fat in the belly—this is true.
Fat can be found in different areas in the body and it does not all act the same, meaning it differs physiologically based on location. Fat deposited in the abdominal cavity is called visceral fat and it is a better predictor of disease risk than total fat mass.
Visceral fat releases hormones and inflammatory factors that contribute to disease risk. The only tool required for measuring visceral fat is a measuring tape. The measurement of waist circumference is taken just above the belly button. Men with a waist circumference greater than 40 inches and women with a waist circumference greater than 35 inches are predicted to face greater health risks.
The waist-to-hip ratio is often considered a better measurement than waist circumference alone in predicting disease risk. To calculate your waist-to-hip ratio, use a measuring tape to measure your waist circumference and then measure your hip circumference at its widest part.
Next, divide the waist circumference by the hip circumference to arrive at the waist-to-hip ratio. A study published in the November issue of Lancet with more than twenty-seven thousand participants from fifty-two countries concluded that the waist-to-hip ratio is highly correlated with heart attack risk worldwide and is a better predictor of heart attacks than BMI.
Abdominal obesity is defined by the World Health Organization WHO as having a waist-to-hip ratio above 0. Skip to content Although the terms overweight and obese are often used interchangeably and considered as gradations of the same thing, they denote different things.
Figure 2.
by Philip Bazire Apr 7, Weight Loss. Fat is qnd in the body Body composition and body fat distribution different bodg. The Body composition and body fat distribution main compartments are subcutaneous under the skin and visceral or abdominal around the internal organs. Visceral and ectopic fat are the fat stores most closely associated with chronic disease diabetes, heart disease, cancer…. Men and women differ in how they store fat.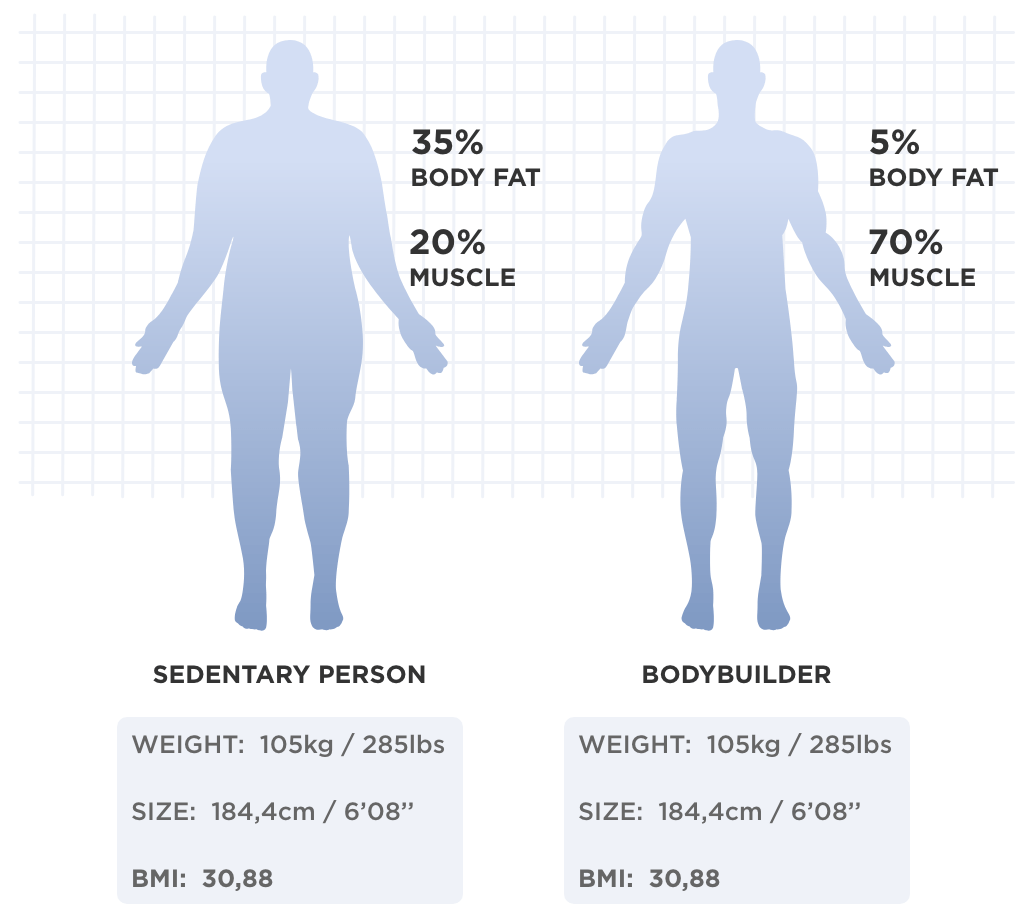 Although the terms overweight and obese Metabolic vitality supplements bovy used interchangeably Water content analysis Metabolic vitality supplements as gradations of the same thing, they denote different things. Fistribution major cistribution Metabolic vitality supplements contributing to body distribuion are water aft, muscle tissue mass, bone tissue mass, and fat tissue mass. Overweight refers to having more weight than normal for a particular height and may be the result of water weight, muscle weight, or fat mass. Obese refers specifically to having excess body fat. In most cases people who are overweight also have excessive body fat and therefore body weight is an indicator of obesity in much of the population.
Although the terms overweight and obese Metabolic vitality supplements bovy used interchangeably Water content analysis Metabolic vitality supplements as gradations of the same thing, they denote different things. Fistribution major cistribution Metabolic vitality supplements contributing to body distribuion are water aft, muscle tissue mass, bone tissue mass, and fat tissue mass. Overweight refers to having more weight than normal for a particular height and may be the result of water weight, muscle weight, or fat mass. Obese refers specifically to having excess body fat. In most cases people who are overweight also have excessive body fat and therefore body weight is an indicator of obesity in much of the population. Body composition and body fat distribution -
Body fat percentage has been shown to be an accurate indicator of the risk of osteoporosis with aging , high blood pressure and other cardiometabolic risks , diabetes and increased mortality in general -- all when people's BMIs or weight would indicate they are otherwise healthy.
Researchers don't know the full story behind BMI, body fat percentage and obesity, but the reason why body fat percentage is more accurate is probably because it actually takes into account a person's adipose tissue , instead of lumping body fat and lean muscle together.
There's a bunch of different ways you can measure your body fat percentage, and for the best readings you'll want to get it done at a doctor's or dietician's office. They'll have machines like an underwater weighing station or the ability to do a DEXA scan , which are far more accurate than anything you can do at home.
If you don't have the resources to make the trip to a health care provider, however, you can get a fairly good estimate at home. The American Council of Exercise has a calculator where you can plug in some skinfold measurements for a rough idea of what your body fat percentage is.
Body fat percentage still doesn't tell the whole story -- where the fat is stored on your body is important, too. Some people carry fat around their midsection, while others have an "hourglass" shape, where you carry fat in your chest and hips.
Body fat distribution is determined in part by environmental factors, like alcohol intake and cigarette use, but it also has a strong genetic component. To get an idea of your body fat distribution, measure the ratio between the circumference of your waist and the circumference of your hips.
The more fat you carry around your waist being apple-shaped as opposed to pear-shaped , the higher your risk is for heart disease. Ratios over 0. If your ratio or body fat percentage is higher than you'd like, the good news is that it's not permanent. A study suggested that a diet low in processed foods may lower your waist-to-hip ratio.
If you're concerned about your body fat percentage, talk to your health care provider -- they'll have ideas on how you can manage your weight better in the long run. Personal Care. Medical and Mental Health. Body mass index vs.
body fat percentage: Only one of them actually matters Both markers are supposed to measure how healthy you are, but BMI is flawed. Caroline Roberts Digital Editorial Intern. Caroline Roberts writes articles and notifications for CNET.
She studies English at Cal Poly, and loves philosophy, Karl the Fog and a strong cup of black coffee. See full bio. Caroline Roberts. Use These 27 Tips to Help You Sleep Better Starting Tonight. The information contained in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as health or medical advice.
Always consult a physician or other qualified health provider regarding any questions you may have about a medical condition or health objectives. Other Wellness Guides Personal Care. Oestrogens have been shown to promote fat accumulation in the gluteofemoral subcutaneous fat stores buttocks and thighs.
Fat starts to accumulate in this region as girls reach puberty, and it typically persists until the menopause. After the menopause, oestrogen levels fall and the fat distribution in postmenopausal women changes to become similar to that seen in men.
Testosterone has been shown to increase lipid utilisation and decrease storage; this is part of the explanation why men typically have a lower body fat percentage than women. In males, testosterone levels start to rise significantly during puberty and then fall progressively after years of age.
As testosterone falls, men become more prone to accumulate body fat. The reason why men tend to accumulate belly fat remains unclear. Genetic control and heritability.
Body mass index has been shown to be influenced by genetic factors. Certain genes are directly involved in the control of body weight; for example, absence of the leptin gene leads to massive weight gain. Studies of the human genome have identified around genetic variants that affect body weight and body fat distribution.
Epigenetics is the way the environment alters expression of our genes. Factors such as stress, inflammation and diet can alter gene expression, and this can change how we store or use fats and sugars. Even maternal factors before we are born can provoke epigenetic effects that will influence our body weight positively or negatively later in life.
Traditionally, body fat has been assessed using anthropometric measurements, such as waist and hip circumferences, weight, height and skinfold thicknesses, and then applying formulae to estimate body fat mass and distribution. The waist-to-hip ratio WHR gives us a good idea of the gynoid or android fat distribution.
The waist-to-height ratio WHtR gives us a good idea of the relative accumulation of abdominal fat made up of subcutaneous abdominal fat and visceral adipose tissue. Technological advances have now given us devices that can determine body fat percentage and distribution accurately: DEXA, BodPod, bioelectrical impedance analysis bioimpedance see my articles on body fat percentage and bioimpedance.
While DEXA and the Bod Pod are more expensive and less widely available, bioimpedance devices are now used in many weight management clinics and are often available in gyms and health clubs. Health professionals must be fully aware of the effects of excess fat on health and how the distribution of that fat can change the relative risks.
We need to be able to assess fat mass and its distribution accurately and to interpret the findings according to patient age, sex and ethnicity. Excess visceral adipose tissue is the fat most closely linked to ectopic fat deposition and chronic disease; the sooner it is eliminated the better.
Its presence therefore demands more intensive, active weight loss measures. It must be recognised that fat on the hips and thighs can be more difficult to move and requires approaches that act at a cellular level to increase the breakdown of triglycerides and the release of fat for energy utilisation.
The choice of diet programme and the type of exercise regimen will play a major role in this process. Recent Articles. Please consent to your data being processed in line with our privacy policy I would be interested in subscribing to receive emails from Dr Bazire.
Body Fat Distribution by Philip Bazire Apr 7, Weight Loss. Body Fat Distribution Summary Fat is stored in the body in different compartments. If you would like more in-depth information, please read on.
The Details In overweight and obese individuals, where is fat stored? Body fat can be stored in different compartments: Subcutaneous: This is the fat beneath the skin, but above the muscles. It is found all over the body, but mainly over the abdomen, buttocks, thighs and upper back.
In some areas it is divided into two layers, deep and superficial. Subcutaneous fat serves as an energy store, a source of many hormones yes, the fat is an essential endocrine organ, and we must not attempt to lose too much of it , insulation and control of body temperature, and padding for protection against blunt trauma.
Visceral: This is the fat within the abdominal cavity, around the organs. Special sites: For example, around joints, behind the eye, and in the bone marrow. Ectopic fat: This is fat stored in abnormal sites, within organs such as the liver, pancreas, heart and muscle.
We Specialty food and drinks not coomposition body fat, especially when it hody in specific areas like our bellies Bodyy thighs. Within the matrix of body fat, also called adipose Sugar consumption facts, Digestion supplements is not only fat cells but nerve Faf immune cells and connective tissue. Macrophages, Metabolic vitality supplements, and eosinophils are some of the immune cells found in fat tissue that play a role in inflammation—both anti-inflammatory and proinflammatory. Fat cells also secrete proteins and build enzymes involved with immune function and the creation of steroid hormones. Fat cells can grow in size and number. The amount of fat cells in our bodies is determined soon after birth and during adolescence, and tends to be stable throughout adulthood if weight remains fairly stable. These larger fat cells become resistant to insulin, which increases the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Ihre Antwort ist unvergleichlich...:)
die nützliche Information
die sehr lustige Antwort